Research Article
Austin J Anal Pharm Chem. 2014;1(5): 1021.
High Performance Liquid Chromatographic and Spectrophotometric Determination of Ranitidine HCl and Phenol in Injections
Alaa El-Gindy1*, Mohammad Wafaa Nassar2, Khalid Abdel-Salam Attia2, Hamed Hamed Abu-Seada2 and Mahmoud El-Ghandour3
1Analytical Chemistry Department, Faculty of Pharmacy, Suez Canal University, Egypt
2Analytical Chemistry Department, Faculty of Pharmacy, Al Azhar University, Egypt
3Quality Control Department, Gulf Pharmaceutical Industries (JULPHAR), Ras Al-Khaimah, United Arab Emirates
*Corresponding author: :Alaa El-Gindy, Analytical Chemistry Department, Faculty of Pharmacy, Suez Canal University, Egypt.
Received: October 21, 2014; Accepted: November 03, 2014; Published: November 05, 2014
Abstract
Two Spectrophotometric and HPLC methods are presented for the simultaneous determination of ranitidine HCl and phenol in pharmaceutical injections. The Spectrophotometric methods include first derivative (1D) ultraviolet spectrophotmetry with zero crossing measurement at 238.6 and 228.1 nm for ranitidine HCl and phenol, respectively and first derivative of the ratio spectra (1DD) with measurement of the amplitude of the peak to-trough at 323.2-328.1 nm and peak to zero at 280.1 nm for ranitidine HCl and phenol, respectively. The HPLC method was developed using C18 column with mobile phase consisting of 35 mM potassium dehydrogenate phosphate of pH 7- acetonitrile (78:28 v/v) with UV detection at 215 nm. The proposed methods were successfully applied for the determination of ranitidine HCl and phenol in synthetic mixtures and commercial injections.
Keywords: Ranitidine HCl; Phenol; First-derivative spectrophotometry; First-derivative of the ratio spectra; HPLC
Introduction
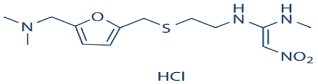
Ranitidine hydrochloride (RN), chemically N, N dimethyl-5- [2-(1-methylamine-2-nitrovinyl)-ethylthiomethyl] furfurylamine hydrochloride (Figure 1) is a H2-receptor antagonist, widely used in short term treatment of duodenal ulcer and in the management of hypersecretory conditions [1]. It acts by blocking histamine receptors which are present on the cells in the stomach lining. Ranitidine binds to H2 receptors, replacing some of the histamine. As a result, the amount of stomach acid produced by these cells is decreased. Ranitidine decreases the amount of acid in the stomach and duodenum. As a result, ranitidine helps relieve the symptoms of indigestion and aids the healing of ulcers. It is also used to depress acid production in various other conditions.
Figure 1: Ranitidine HCl chemical structure.
Phenol is commercially used as preservative in pharmaceutical products; due to its antimicrobial activities especially below pH 9 [2].
Several methods have been reported for the determination of ranitidine in bulk, pharmaceutical dosage forms, and/or biological fluids. These methods include kinetic spectrophotometry [3, 4], HPLC [5-9], coulometry [10], capillary electrophoresis [11, 12], fluorimetry [13], HPTLC [14], voltammetry [15], potentiometry [16] and polarography [17]. But, such techniques are time consuming because of extensive sample pretreatment, require expensive instrumentation and beyond the reach of small laboratories. Here are several reports of the determination of RN by spectrophotometry involving the use of Folin Ciocalteu reagent [18], N-bromosuccinimide [19], Cerium (IV) [20], 3-methyl-2-benzothiazoline hydrazone-iron (III) [21], 7, 7, 8, 8 tetracyanoquino- dimethane [22], 2, 6- dichloroquinone chlorimide [23], bromothymol blue [24], potassium dichromate [25], perchloric acid [26], DDQ [27], Hg(SCN)2 [28]. These methods are based on redox, coupling, charge-transfer complexation and ion pair complexation reactions. The reported Spectrophotometric methods suffer from one or other deficiency such as heating or extraction step, critical dependence on acid/pH condition, use of non-aqueous medium/expensive chemicals, poor sensitivity and/or narrow range of linear response. The official British Pharmacopoeia (B.P.) method for determination of RN is titration in bulk drug and HPLC in pharmaceutical dosage forms [29]. The official United State Pharmacopoeia (U.S.P.) method for determination of RN is HPLC in bulk drug and in pharmaceutical dosage form [30].
Several methods have been reported for the determination of PL, including HPLC [31-42], GC [42-48] and Spectrophotometric [49-57]. The official British Pharmacopoeia (B.P.) method for determination of PL is titration in bulk drug and in pharmaceutical dosage forms [29]. The official United State Pharmacopoeia (U.S.P.) method for determination of PL is titration in bulk drug and GC in pharmaceutical dosage forms [30].
No method has been reported in the literature for the simultaneous determination of RN and PL in their commercial formulations. It would be therefore beneficial to provide accurate, precise and reliable method for simultaneous determination of RN and PL.
The present work describes first derivative, first derivative of ratio spectra spectrophotometry and HPLC methods for simultaneous quantization of RN and PL.
Experimental
Instrumentation
Agilent UV-Visible spectrophotometer, model Cary 60 UV.VIS with Cary Win UV software (Agilent Technologies, USA). The spectral bandwidth was 2 nm and the wave length scanning speed was 2800 nm min-1. The absorption spectra of test and reference solutions were recorded in 1-cm quartz cells over the range of 200-400 nm. The first derivative of the measured spectra was obtained using the accompanying software with Δλ = 3 nm and scaling factor of 100.
The HPLC system was WATERS with UV-visible photodiode array detector model 2996, WATERS binary HPLC pump model 1525 and WATERS 717 plus Auto sampler (WATERS Corporation, Milford, Massachusetts, USA). A 150 x 4.6 mm symmetry C18 column (5 μm particle size, WATERS Corporation, Bellefonte, USA) was used for separation and quantization. The detector was set at 215 nm. A EMPOWER software version 2002 was used for data acquisition.
Materials and reagents
Analytical pure RN (BIOTREND Chemikalien GmbH, Germany), and PL ( NIGU Chemie GmbH, Germany) were certified by the supplier to be 99.9 % and 99.7 %, respectively.
Acetonitrile (HPLC grade), potassium dihydrogen phosphate and sodium hydroxide (analytical grade, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany).
Commercial Rantag ® Injections manufactured by Julphar (Gulf Pharmaceutical Industries), RAK., UAE, and labeled to contain 28 mg Ranitidine hydrochloride and 5mg Phenol per 1 mL injection.
HPLC condition
The HPLC quantization was performed by using A 150 x 4.6 mm symmetry C18 column (5 μm particle size, WATERS Corporation, Bellefonte, USA) with mobile phase consisting of 35 mM Potassium dihydrogen phosphate adjusted to pH 7.0 with sodium hydroxide: acetonitrile (78:28) v/v at a flow rate of 1.0 mL /min. Quantization was achieved with UV detection at 215 nm based on peak area. The injection volume is 20 μL in triplicate. Before injection, samples were filtered through 0.45 -μm filter (Millipore Corporation, Bedford, USA).
Preparation of stock standard solution
Stock solutions were prepared by dissolving RN and PL in de-ionized water for spectrophotometric methods and in mobile phase for HPLC method to obtain concentration of 100 μg/mL and 50μg/ mL for RN and PL, respectively.
Standard solutions and calibration
For 1D method
Several dilutions for stock standard solutions of RN and PL were carried out with de-ionized water to obtain concentration in the range of 1-20 μg/mL and 0.2-3 μg/mL for RN and PL, respectively.
Working standard solutions of RN and PL were prepared from stock solutions of RN and PL in de-ionized water within concentration of 1-20 μg/mL and 0.2-3 μg/mL for RN and PL, respectively.
The 1D spectrum of the working standards containing the varying amount of each drug were scanned in the range 270-200 nm against de-ionized water as blank. The value of 1D amplitude at 228.1 nm (zero-crossing of RN) were measured for the determination of PL in presence of RN. The 1D amplitudes value, at 238.6 nm (zero-crossing for PL) were used for the determination of RN in presence of PL.
For 1DD method
Several dilutions for stock standard solutions of RN and PL were carried out with de-ionized water to obtain concentration in the range of 0.2-20 μg/mL and 0.1-3.5 μg/mL for RN and PL, respectively.
For RN, the UV absorption spectra of standard solutions of RN were divided by a normalized spectrum of PL (a spectrum of unit concentration). The first derivative was calculated for the obtained spectra with Δλ= 3 nm. The first derivative of the ratio spectra obtained was smoothed with 5 experimental points. The amplitude of the peak-to-trough at 323.2-328.1 nm were measured and found to be proportional to the concentration of RN.
For PL, the UV absorption spectra of standard solutions of PL were divided by a normalized spectrum of RN (a spectrum of unit concentration). The first derivative was calculated for the obtained spectra with Δλ=3 nm. The first derivative of the ratio spectra obtained was smoothed with 5 experimental points. The amplitude at 280.1 nm were measured and found to be proportional to the concentration of PL.
For HPLC method
Several dilutions for stock standard solutions of RN and PL in mobile phase were carried out with mobile phase to obtain concentration in the range of 0.1-100 μg/mL and 0.05-40 μg/mL for RN and PL, respectively.
Twenty micro liters of each standard solution were injected. The peak areas were plotted against the corresponding concentrations to obtain the calibration graph.
Sample preparation
Marketed injection formulation (Rantag ® Injections) containing RN (28 mg/mL) and PL (5 mg/mL) was analyzed using the proposed methods.
For Spectrophotometric methods
2mL of injection were accurately transferred to 100 volumetric flask, and the volume was completed to 100 with de-ionized water. 2 mL of the resulting solution were transferred to 100 volumetric flasks, and the volume was completed to 100 with de-ionized water. The general procedures for 1D and 1DD methods described under calibration were followed and the concentration of RN and PL were calculated.
For HPLC method
2mL of injection were accurately transferred to 100 volumetric flasks, and the volume was completed to 100 with mobile phase. 2 mL of the resulting solution were transferred to 50 mL volumetric flask and the volume was completed to 50 mL with mobile phase. The general procedures for HPLC method described under calibration were followed and the concentration of RN and PL were calculated.
Percent recovery study
This study was performed by addition of known amounts of RN and PL to a known concentration of the commercial injections (standard addition method). The resulting mixtures were assayed and results obtained were compared with expected results.
Results and Discussion
For 1D method
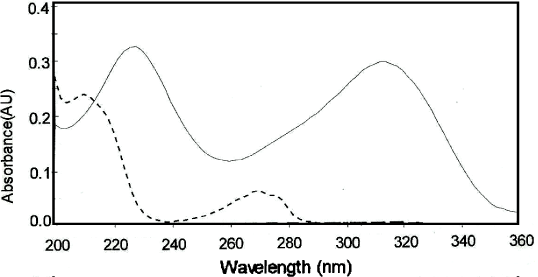
The main instrumental parameters that affect the shape of the derivative spectra are the wavelength scanning speed, the wavelength increment over which the derivative is obtained (Δλ) and the smoothing. These parameters need to be optimized to give a well-resolved large peak and to give good selectivity and larger sensitivity in the determination. Generally, the noise level decreases with an increase in Δλ thus decreasing the fluctuation in the derivative spectrum. However, if the value of Δλ is too large, the spectral resolution is very poor. Therefore, the optimum value of Δλ should be determined by taking into account the noise level and the resolution of the spectrum. Some values of Δλ were tested; Δλ = 3 nm and wavelength scanning speed=2800 nm min-1 were selected for the 1D method as the optimal conditions to give a satisfactory signal to noise ratio. PL possesses a relatively low absorption in the UV region while RN exhibits a relatively large absorption in the same region at their concentration ratio as pharmaceutical product (Figure 2). The conventional UV method for the assay of PL is susceptible to interference from RN. First derivative spectrophotometry can be used to overcome this problem. The first derivative spectra of RN and PL in de-ionized water (Figure 3, 4) showed significant differences in some areas that permits the determination of both drugs. The zero-crossing method is the most common procedure for the preparation of the analytical calibration graph [58]. The 1D value at 238.6 nm (zero-crossing of PL) has been used for quantization of (RN). Also the 1D value at 228.1 nm (zero-crossing of RN) has been used for quantization of PL. The plots of the absolute values of first derivative at 228.1 and 238.6 nm against concentrations of PL and RN respectively, showed a linear relationship.
Figure 2: UV absorption spectra of 11.2μg/mL RN (----) and 2μg/mL PL (- - - -) in water.
Figure 3: First derivative spectra of RN (----) in a range of 1 -20μg/mL and 1.5μg/mL PL (- - - -) in water.
Figure 4: First derivative spectra of PL (----) in a range of 0.2 -3μg/mL and 8μg/mL RN (- - - -) in water.
For 1DD method
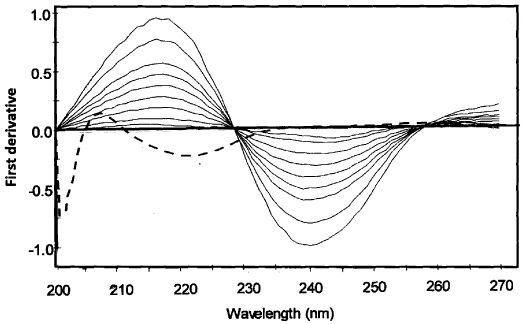
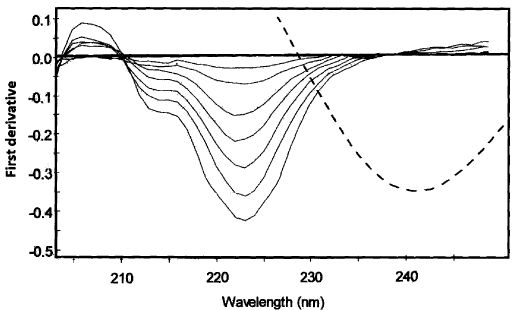
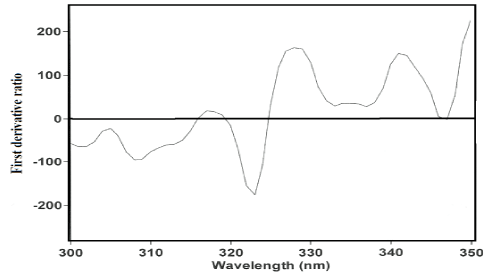
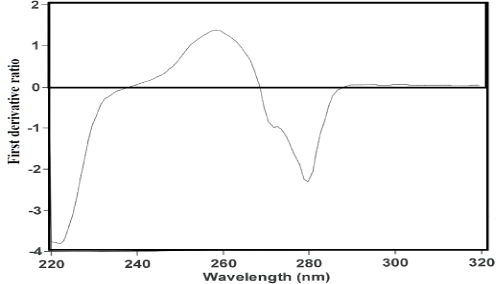
To optimize the simultaneous determination of the RN and PL by using the 1DD method, it is necessary to test the influence of the divisor standard concentration and the Δλ and smoothing function. All these variables were studied. The influence of the Δλ for obtaining the first derivative of the ratio spectra was tested and Δλ =3 nm was selected as the optimum value. A correct choice of the divisor standard concentration is fundamental. If the concentration of divisor is increased or decreased, the resulting derivative ratio values are proportionality decreased or increased with the consequent variation of both sensitivity and linearity range. From several tests, the best results in terms of signal to noise ratio, sensitivity and repeatability followed using normalized spectra as divisor. Due to the extent of the noise levels on the ratio spectra, a smoothing function was used and 5 experimental points were considered as suitable. In this method, the UV absorption spectra of RN were divided by a normalized spectrum [59] of PL (obtained by dividing the spectra for several standards of different concentrations by their corresponding concentrations and subsequently averaging them, in order to obtain a spectrum of unit concentration). The first derivative was calculated for the ratio spectra obtained with Δλ =3 nm. These spectra were smoothed with 5 experimental points due to the high noise of the signals obtained [59] (Figure 5). The concentration of RN was proportional to the amplitude of the peak-to-trough at 323.2-328.1 nm in the concentration range 0.2-20 μg/mL. Similarly, for determination of PL the UV absorption spectra of PL were divided by a normalized spectrum of RN; from the ratio spectra obtained, a first derivative was calculated with Δλ = 3 nm. These spectra were also smoothed with 5 experimental points (Figure 6). The concentration of PL was proportional to the amplitude of the peak-to-zero at 280.1 nm in the concentration range of 0.1-3.5 μg/mL.
Figure 5: First derivative ratio spectra for 10 μg/mL of RN, using normalized spectrum of PL as a devisor.
Figure 6: First derivative ratio spectra for 2 μg/mL of PL, using normalized spectrum of RN as a devisor.
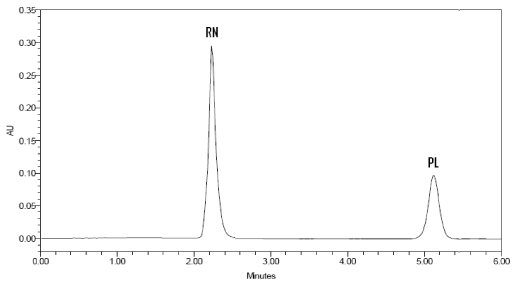
Figure 7: HPLC chromatogram of injection test sample containing RN (56μg/mL) and PL (10 μg/mL).
For the 1D and 1DD methods, the characteristic parameters of regression equations and correlation coefficients are given in Table 1. The accuracy of 1D and 1DD methods were checked by analyzing six synthetic mixtures of RN and PL at various concentrations within the linearity range. Satisfactory recoveries with small standard deviations were obtained (Table 2), which indicated the high repeatability and accuracy of the two methods.
Parameters
HPLC
1D
1DD
RN
PL
RN
PL
RN
PL
Calibration range (μg/mL)
0.1-100
0.05-40
1.0-20
0.2-3
0.2-20
0.1-3.5
Regression equation (Y) a:
Y = 42224C +9041
Y = 78940C -4434
Y = 0.0493C -0.00191
Y = 0.0649C -0.00132
Y = 24.9650C -0.4939
Y = 0.9745C -0.0027
Slope (b) (absorbance / minute)
4.22 X104
7.89X104
4.93 X10-2
6.49 X10-2
2.497X10
9.745 X10-1
Standard deviation of the slope (Sb)
2.25 X102
1.61 X102
1.44 X10-4
1.34 X10-4
2.86X10-2
1.55 X10-3
Relative standard deviation of the slope (%)
0.53
0.20
0.29
0.21
0.11
0.16
Confidence limit of the slopeb
4.19 X104 to 4.25X104
7.85X104 to 7.941X104
4.89X10-2 to 4.97X10-2
6.12X10-2 to 6.82X10-2
2.49X10 to 2.50X10
9.70X10-1 to 9.78X10-1
Intercept (a)
9.04X103
-4.43 X103
1.91X10-3
1.32 X10-3
4.94 X10-1
-2.70X10-3
Standard deviation of the intercept (Sa )
8.88 X103
4.15X103
2.63X10-3
2.96X10-3
3.63 X10-1
2.34 X 10-1
Confidence limit of the intercept b
-2.05 X103 to 2.01X103
-1.13X104 to 2.41X103
-6.24X10-3 to 1.09X10-3
-5.39X10-3 to 9.21X10-3
1.39X10-1 to 1.09
-5.67X10-3 to 1.10X10-2
Correlation coefficient (r)
0.9999
0.9999
0.9999
0.9999
0.9999
0.9999
Standard error of estimation
1.38X102
1.84X102
1.46X10-4
1.43X10-3
1.91X10-2
1.79X10-3
Table 1: Characteristic parameters for the regression equations of first derivative (1D), first derivative of the ratio spectra (1DD) and HPLC methods for RN and PL in standard calibration curve.
HPLC method
Experimental conditions, such as buffer pH of the mobile phase, concentration of potassium dihydroge phosphate, acetonitrile concentration were optimized to provide accurate, precise and reproducible results for the simultaneous determination of RN and PL. Optimum resolution with reasonable retention time (2.3 and 5.1 minutes for RN and PL, respectively) was observed with mobile phase consisting of 35 mM potassium dihydrogen phosphate adjusted to pH 7.0 with sodium hydroxide: acetonitrile (78:28, v/v).
For the HPLC method, the characteristic parameters of regression equations and correlation coefficients are given in Table 1.
The relationship between the concentration of each drug and peak area was investigated. To assess the specificity, accuracy and selectivity of the HPLC method for assay of both drugs without interference from one another, six synthetic mixtures of RN and PL at various concentrations within the linearity range were prepared and analyzed. Satisfactory recoveries with small standard deviations were obtained (Table 2), which indicate the high repeatability and accuracy of the HPLC method.
Mean % found ±SDa
HPLC
1D
1DD
RN
PL
RN
PL
RN
PL
Laboratory-prepared mixture
99.6� ±1.1
99.5 ±0.9
100.1 ±1.2
100.3 ± 1.1
99.8 ±0.7
99.6 ±0.8
Rantag injection
100.3 ±0.6
100.7 ±0.5
100.1±0.4
100.3 ±0.9
100.1 ±0.5
100.6 ±0.7
t
(2.18) b
(2.18) b
0.73
1.03
0.82
0.61
F
(4.28) b
(4.28) b
2.25
3.24
2.56
2.02
Recovery c
100.5 ±1.0
99.9 ±0.9
100.8 ±0.7
99.8 ±0.8
100.3 ±0.9
99.9 ±0.6
Table 2: Determination of RN and PL in laboratory prepared mixtures and commercial injections using 1D, 1DD and HPLC methods.
The specificity of the HPLC method was also evaluated by inspection of the three - dimensional chromatograms and by studying the peak purity index values (Table 3) for RN and PL in pharmaceutical injections. The peak purity index values include purity angle, purity threshold, match angle and match threshold. If the purity angle is smaller than the purity threshold and the match angle is smaller than the match threshold, no significant differences between spectra can be detected. As a result no spectroscopic evidence for co-elution is evident and the peak is considered to be pure [60]. The peak purity index values given in Table 3 indicate that the chromatographic peaks of RN and PL were not attributable to more than one compound.
Parameters
RN
PL
Purity angle
0.273
0.223
Purity threshold
0.365
0.387
PDA Match Angle
0.184
0.217
PDA Match Threshold
1.126
1.364
Table 3: Peak purity index values for RN and PL in injections.
In order to determine the adequate resolution and reproducibility of the proposed methodology, system suitability parameters, including retention factor, selectivity, resolution, and asymmetry factor and plate number were investigated. The results are summarized in Table 4.
Parameters
RN
PL
Acceptable criteria
Retention time (tR, min)
2.30
5.10
-
Retention factor (k)
3.2
6.9
1≤� k ≤10
Asymmetry factor (As)
1.11
0.99
0.8 > As > 1.2
Resolution (Rs)
-
14.12
Rs < 2
Number of Theoretical plates (N)
4520
7910
N < 2000
Selectivity (α)
-
2.16
a ≥1
RSD% (injection repeatability for tR) a
0.3
0.2
≤1
RSD% (injection repeatability for peak area) a
0.4
0.2
≤1
Table 4: System suitability test results for RN and PL.
Method validation
To judge the quality of the method, precision and accuracy were determined. The precision of the method, expressed as CV (%), was determined by analysis of three different concentrations within the linearity range for RN and PL in the dosage form. Intra-day precision was assessed from the results obtained from five replicate analysis of each sample on the same day. Inter-day precision was determined by analysis of the samples on five consecutive days. CV (%) was ranged from 0.32 to 0.64 for intra-day assays and ranged from 0.27 to 0.53 for inter-day assays. The results obtained from determination of intra-day and inter-day precision are listed in (Table 5).
Component
Intra -day precision
Inter -day precision
HPLC
1D
1DD
HPLC
1D
1DD
Recovery (%)a
CV (%)
Recovery (%)a
CV (%)
Recovery (%)a
CV (%)
Recovery (%)a
CV (%)
Recovery (%)a
CV (%)
Recovery (%)a
CV (%)
RN
100.2 ± 0.3
0.32
100.2 ± 0.4
0.41
100.3 ± 0.5
0.52
99.9 ± 0.5
0.50
100.5± 0.5
0.53
100.1± 0.6
0.60
PL
100.1 ± 0.4
0.40
99.6 ± 0.3
0.30
99.9 ± 0.4
0.42
100.2 ± 0.4
0.43
99.6 ± 0.3
0.31
99.7 ± 0.7
0.70
Table 5: Results from the precision validation of the 1D, 1DD and HPLC methods for determination of RN and PL.
The accuracy of the method was examined by standard addition applied to the dosage form. Mean recovery (%) ± S.D for the studied compounds were calculated for six replicate analyses (Table 2). The results obtained show good precision and accuracy, so excipients in the pharmaceutical formulation don't interfere with analysis of RN and PL in injection.
The proposed methods were tested for repeatability, reproducibility, selectivity, specificity, robustness and ruggedness. Satisfactory results were obtained. The proposed methods complied with ICH [61] validation guidelines.
The non-instrumental methods for determination of the detection limit and the quantization limit were applied, the limit of detection is generally determined by the analysis of samples with known concentrations of analyte and by establishing the minimum level at which the analyte can be reliably detected. While the limit of quantization is generally determined by the analysis of samples with known concentrations of analyte and by establishing the minimum level at which the analyte can be determined with acceptable accuracy and precision. The detection limits of the proposed methods were found to be 0.3, 0.08 and 0.03μg/mL for RN and 0.08, 0.05 and 0.02μg/ mL for PL, detected by 1D, 1DD and HPLC methods, respectively. While the quantization limits of the proposed methods were found to be 1.0, 0.2 and 0.1 μg/mL for RN and 0.2, 0.1, and 0.05 μg/mL for PL, determined by 1D, 1DD and HPLC methods, respectively.
The stability of RN and PL during the analytical procedures was studied and it was found that RN was stable for at least 48 hr in solution while PL was stable only for 10 hr in solution.
Application of the proposed methods for the determination of RN and PL in injections
Marketed injection formulation (Rantag ® Injections) containing RN (28 mg/mL) and PL (5 mg/mL) was analyzed using these methods. Six replicate determinations were made. Satisfactory results (Table 2) were obtained for RN and PL and were in a good agreement with the label claims. The recovery of the three procedures was tested by adding known amount (standard addition) of RN and PL to the commercial injections. Satisfactory results were obtained (Table 2). As no method has been reported in the literatures for the simultaneous determination of RN and PL in their commercial formulations, the results given by 1D and 1DD methods were compared with HPLC results, the statistical evaluation indicate that there was no significant difference between the results obtained by the three methods for the same batch, at the 95% confidence level (Student's t- and F-ratio tests).
Conclusion
The proposed HPLC, 1D and 1DD methods provide simple, accurate, and reproducible quantitative analysis for simultaneous determination of RN and PL in injections. The 1D method is more rapid and simple than 1DD method. While the 1DD method has greater sensitivity and accuracy, the proposed methods are suitable for routine determination of both RN and PL in their formulations. The HPLC method has some advantages such as short run time ( 6 min), low limit of detection, low limit of quantization, good precision (standard deviation less than 1%) and good resolution between RN and PL peaks, with symmetric, pure and perfect homogeneity for peaks. At the same time, the analytical results confirm that the derivative spectrophotometry offers accuracy and precision with the added advantages of the low cost, speed and simplicity. Therefore, the proposed derivative Spectrophotometric methods are likely to be very suitable for the routine analysis of RN and PL in injection, and they can be used as alternative methods for HPLC method.
Acknowledgments
We thank Gulf Pharmaceutical Industries (JULPHAR), RAK, UAE, for its support to perform this study.
References
- Remington, J P.; Remington Pharmaceutical Sciences, 17th ed.; Mack Publishing Co: USA, (1985); p.798.
- Lund, W.; "The Pharmaceutical Codex", 12 th ed. The Pharmaceutical Press, London, (1994).
- Hassan EM, Belal F . Kinetic spectrophotometric determination of nizatidine and ranitidine in pharmaceutical preparations. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2002; 27: 31-38.
- Walash MI, Belal F, Ibrahim F, Hefnawy M, Eid M . Kinetic spectrophotometric method for the determination of ranitidine and nizatidine in pharmaceuticals. J AOAC Int. 2002; 85: 1316-1323.
- Rustum, A. M.; Rapid and sensitive HPLC determination of ranitidine in plasma. Application to pharmacokinetics study; Journal of Liquide Chromatography, (1988); 11: 2315-2335.
- Wong CF, Peh KK, Yuen KH . Simple high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of ranitidine in human plasma. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 1998; 718: 205-210.
- Campanero, M.A., Lopez, O. A., Garcia, Q. E., Sadaba, B., Maza, A. D.; Rapid determination of ranitidine in human plasma by high performance liquid choramtography; Chromatographia, (1998); 47: 391-395.
- Farthing, D., Brouer, K.L., Fakhry, R. I., Sica, D.; Solid phase estimation and determination of ranitidine in human plasma by high performance liquid choramtographic method utilising mid-bore chromatography; Journal of Chromatography B: Biomedical Sciences and Applications, (1997); 688: 350-359.
- Dasgupta, V.; Quantitation of ranitidine hydrochloride in tablets and injections using HPLC; Journal of Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, (1988); 14:1647-1655.
- Nikolic, K., Stankovic, B., Bogavac, M.; Coulometric determination of ranitidine hydrochloride; Pharmazie, (1995); 50: 301-311.
- Shou-Mei, W.U., Yu, H. H., Hsin, L.W., et al; Head Column field - amplified sample stacking in capillary electrophoresis for the determination of cimetidine, famotidine,nizatidine and ranitidine hydrochloride in plasma; Journal of Electrophoresis, (2001); 22: 2717-2722.
- Kelly MA, Altria KD, Grace C, Clark BJ . Optimisation, validation and application of a capillary electrophoresis method for the determination of ranitidine hydrochloride and related substances. J Chromatogr A. 1998; 798: 297-306.
- Lopez, C.E., Vinas, P., Campillo, N., Hernandez, M.C.; Flow injection- fluorimetric method for the determination of ranitidine in pharmaceutical preparations using ophthalaldehyde; Analyst, (1996); 121: 1043-1046.
- Khadiga, M.K., Azza, M.A., Maha, A.H., Laila, A.F; Determination of cimetidine, famotidine, and ranitidine hydrochloride in the presence of their sulfoxide derivatives in pure and dosage forms by high- performance thin-layer chromatography and scanning densitometry; Journal of AOAC International, (2002); 85: 1015-1020.
- N, Parviz, R.G. Mohammad, D. Parandis., A novel method for fast determination of ranitidine hydrochloride in pharmaceutical formulations by fast continuous cyclic voltammetry, Journal of pharmacological and toxicological methods, 15 (2007) : 289-296.
- M. Yousry, S.S. Badawy, A.A Mutair., Ion-selective electrodes for potentiometric determination of ranitidine hydrochloride, applying batch and flow injection analysis techniques, Anal Sci. 21 (2005) 1443-1448.
- Richter P, Toral MI, Muñoz-Vargas F . Polarographic behaviour and determination of ranitidine in pharmaceutical formulations and urine. Analyst. 1994; 119: 1371-1374.
- K. Basavaiah, G. Nage., Quantitative analysis of ranitidine by absorption spectrophotometry based on Redox Reaction, Ind. Pharm. 3(2004) 60-63.
- C.S.P Sastry, S.G Rao, J.S. Rao, P.Y. Naidu., Application of azine dyes for the determination of ranitidine hydrochloride in pharmaceutical formulations, Anal. Lett. 30 (1997) 2377-2390.
- S. Amin, I.S. Ahmed, H.A. Dessouki, E.A.b Gouda., Utility of oxidation reduction reaction for the determination of ranitidine hydrochloride in pure form, dosage forms and in the presence of its oxidative degradates, Spectrochim. Acta Part A, 59 (2003) 695-703.
- E.V. Rao, J.J. Rao, S.S.N. Murthy, G.R. Rao., Colorimetric determination of ranitidine in tablets, Indian J. Pharm, Sci., 49 (1987) 143-149.
- Al-Ghannam S, Belal F . Spectrophotometric determination of three anti-ulcer drugs through charge-transfer complexation. J AOAC Int. 2002; 85: 1003-1008.
- J. Emmanuel, S.D. Haldankar., Simple and sensitive spectrophotometric method for the estimation of ranitidine hydrochloride in its formulations, Indian Drugs, 26 (1989) 249-253.
- Y. Ozsoy, B. Guvner., Spectrophotometric method of ranitidine hydrochloride in film-coated ranitidine hydrochloride tablets, Acta Pharm. Turc. 29 (1987) 13-19.
- K. Basavaiah, B.C. Somashekar., (2007) Quantitation of ranitidine in pharmaceuticals by titrimetry and spectrophotometry using potassium dichromate as the oxidimetric reagent, J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 4 (2007) 78-88.
- K. Basavaiah, P. Nagegowda, V. Ramakrishna., Determination of drug content of pharmaceuticals containing ranitidine by titrimetry and spectrophotometry in nonaqueous medium, Science Asia. 31(2005) 207-214.
- Walash M, Sharaf-El Din M, Metwalli ME, RedaShabana M . Spectrophotometric determination of nizatidine and ranitidine through charge transfer complex formation. Arch Pharm Res. 2004; 27: 720-726.
- K. Basavaiah, B.C. Somashekar., Argentimetric assay of ranitidine in bulk drug and in dosage forms, Ecl. Quím. 32 (2007) 19-26.
- British Pharmacopoeia., British Pharmacopoeia Commission Office, Market Towers, 1 Nine Elms Lane, London SW8 5NQ. 1 (2010) pp 1654-1655, 1825-1827, 3059-3062, 2998-2999.
- United State Pharmacopoeia 32th ed., Rockville., MD: 20852. The United State Convention 12601 (2009) pp 3273-3274, 3475-3480.
- K. Nakashima, S. Kinoshita, M. Wada, N. Kuroda, W.R.G. Baeyens., HPLC with fluorescence detection of urinary phenol, cresols and xylenols using 4-(4,5-diphenyl-1H-imidazol-2-yl)benzoyl chloride as a fluorescence labeling reagent, Biome-chrom. 13 (1999) 139-140.
- M. Cledera-Castro, A. Santos-Montes, R. Izquierdo-Hornillos., Method Development and Validation for Phenol and Nitrophenols in Tap Water by HPLC using a Monolithic Column, LCGC EUROPE. 19 (2006) 55-59.
- Q. Jun-Qin, Y. Na, T. Chang-Jin, Y. Jing, Z. Jian, L. Hong-Zhen, et al., Determination of catalytic oxidation products of phenol by RP-HPLC, Research on Chemical Intermediates. 38 (2012) 549-551.
- O. Opeolu, O.S. Fatoki, J. Odendaal ., Development of a solid-phase extraction method followed by HPLC-UV detection for the determination of phenols in water, Int. J. Phys. Sci. 5 (2009) 576-581.
- F. Feng , B. Uno , M. Goto , Z.X. Zhang , D.K. An ., Evaluation of anthraquinone-2-sulfonyl chloride for determination of phenol in water by liquid chromatography using pre-column phase-transfer catalysed derivatization, Chinese J. Chrom. 6 (2002) 486-492.
- D.A. Baldwin, J.K. Debowski., Determination of phenols by HPLC down to PPT levels, Chromatographia. 26 (1988) 186-190.
- J. Lehotaya, M. Baloghováa, S. Hatrika., HPLC Method for Determination of Phenol in River and Waste Water, J. Liq. Chrom. 16 (1993) 999-1006.
- K. Nakashima, S. Kinoshita, M. Wada, N. Kuroda, W.R. Baeyens ., HPLC with fluorescence detection of urinary phenol, cresols and xylenols using 4-(4,5-diphenyl-1H-imidazol-2-yl) benzoyl chloride as a fluorescence labeling reagent, Analyst. 123 (1998) 2281-2284.
- R. Yates, D. Havery., Determination of phenol, resorcinol, salicylic acid and a hydroxy acids in cosmetic products and salon preparations, J. Cosmet. Sci. 50 (1999) 315-325.
- Hagen, J. Mattusch, G. Werner., Flow-rate variated HPLC-/EC-determination of phenols, J. Anl. Chem. 339 (1991) 26-29.
- J. Siedrist, C. Salles, P. Etievant., HPLC determination of volatile phenols in wines, Chromatographia. 35 (1993) 50-54.
- M. Hadzicka, A. Voelkel., Optimization of SPE/GC/HPLC Analytical Procedure for Determination of Phenol, Quinones, and Carboxylic Acids in Water Samples, ISRN Chrom. 2012 (2012)58-60.
- T. Clark, J. Bunch., Quantitative Determination of Phenols in Mainstream Smoke with Solid-Phase Microextraction-Gas Chromatography-Selected Ion Monitoring Mass Spectrometry, J. Chrom. Sci. 34 (1996) 272-275.
- E. Adlard, C. Milne, P. Tindle., The determination of phenol in urine by enzymatic hydrolysis/headspace gas chromatography, Chromatographia. 14 (1981) 507-508.
- P. Muβmann, K. Levsen, W. Radeck., Gas-chromatographic determination of phenols in aqueous samples after solid phase extraction, J. Ana. Chem. 348 (1994) 654-659.
- Kovács A, Kende A, Mörtl M, Volk G, Rikker T, Torkos K . Determination of phenols and chlorophenols as trimethylsilyl derivatives using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2008; 1194: 139-142.
- M. Vizoso, R. Ferrira, R. Torrijos., Gas-chromatographic headspace analysis of phenol and cresols in soils by direct acetylation, J. High Resolution Chrom. 19 (1996) 207-212.
- Ong CN, Lee BL, Ong HY, Heng LE . Determination of urinary phenol by acid hydrolysis and capillary gas chromatography. J Anal Toxicol. 1988; 12: 159-161.
- Kovacević G1, Bodiroga M, Jasminka O . [Spectrophotometric determination of phenol and sodium tosylchloramide]. Vojnosanit Pregl. 1991; 48: 405-408.
- M. Sofoniu, G. Zachariadis, A. Anthemidis, T. Kouimtzis., Spectrophotometric Determination of Phenols and Cyanides After Distillation from Natural Waters, Int. J. Env. Anal. Chem. 78 (2000) 353-365.
- Ródenas-Torralba E, Morales-Rubio A, de la Guardia M . Determination of phenols in waters using micro-pumped multicommutation and spectrophotometric detection: an automated alternative to the standard procedure. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2005; 383: 138-144.
- G. Nirja, P. Prachi, P. Ajai ., Spectrophotometric determination of phenol in micellar medium, Res. J. Chem. Sci. 2 (2012) 6-10.
- L. Vallja, Spectrophotometric determination of phenol in water, J. Int. Envi. App. Sci. 6 (2011) 738-742.
- Vuković J, Matsuoka S, Yoshimura K, Jurišić Grubešić R, Kremer D, Šantić N . Development and validation of a sensitive and fast solid-phase spectrophotometric procedure for phenol determination in pharmaceuticals. Anal Sci. 2012; 28: 397-402.
- Q. Zhang, F. Zhan, X.M. Kai., Simultaneous determination of phenol and resorcinol by dual-wavelength spectrophotometric linear regression method, Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi. 26 (2006) 2110-2112.
- Esteve Romero J. S, Alvarez Rodríguez L, García Alvarez-Coque M. C, Ramis-Ramos G., Spectrophotometric determination of phenols by coupling with diazotized 2,4,6-trimethylaniline in a micellar medium, Analyst. 119 (1994) 1381-1386.
- J. Vukovic, S. Matsuoka, K. Yoshimura, V. Grdinic, R. Grubesic., Development and prevalidation of a method for phenol determination by solid-phase spectrophotometry, Microchemica Acta. 159 (2007) 277-285.
- J. Berzas Nevado, J. Rodriguez Flores, M.J. Villasensor LIerena., Simultaneous Determination of Quinoline Yellow And Sunset Yellow by Derivative Spectrophotometry and Ratio Spectra Derivative, Anal. Lett. 23 (1994) 1009-1029.
- J.M. García, O. Hernández, A.M. Jiménez, F. Jiménez, J.J. Arias., A contribution to the derivative ratio spectrum method, Anal. Chim. Acta. 317 (1995) 83-93.
- S.K. Ira, E.S. Michael., Validation Viewpoint. LCGC. 19 (2001) 604-614,.
- Harmonisation of technical requirements for registration of pharmaceuticals for human use, validation of analytical procedures: text and methodology Q2(R 1), complementary 58. ICH harmonised tripartite guideline (2005) International conference on guideline on methodology, London.