
Research Article
Austin J Forensic Sci Criminol. 2015; 2(4): 1038.
Multi-residue Determination of Seven Methyl-Carbamate Pesticides by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Diode Array Detection: Investigation of Suspected Animal Poisoning in the Period 2010-2014 in North- Eastern Italy
Gallocchio F*, Basilicata L, Benetti C, Angeletti R and Binato G
Department of Chemistry, Istituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale delle Venezie, Italy
*Corresponding author: Gallocchio F, Department of Chemistry, Istituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale delle Venezie, Viale dell’Università 10, 35010 Legnaro, Padova, Italy
Received: August 24, 2015; Accepted: October 17, 2015; Published: October 20, 2015
Abstract
Misuse or deliberate abuse of Methyl-Carbamate pesticides (MC) may often result in incidental or malicious non-target animal poisoning. This study presents preliminary results of the analysis of 1674 real suspected samples, ranging from baits and stomach contents, collected at the Istituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale delle Venezie (official reference laboratory for the regions of north-eastern Italy), in the period 2010-2014.
Samples were analyzed by liquid chromatography with Diode Array Detection (HPLC-DAD) able to identify 7 different MC (aldicarb, carbaryl, carbofuran, methiocarb, methomyl, pirimicarb, propoxur).
Keywords: Methyl-Carbamate pesticides; Animal poisoning; HPLC-DAD
Abbreviation
MC: Methyl-Carbamate; AChE: Acetyl Cholin Esterase; Ach: Acetyl Choline; CNS: Central Nervous System; WHO: World Health Organization; HPLC-DAD: Liquid Chromatography With Diode Array Detection
Introduction
Animal poisoning is a worldwide issue which has been widely described and reported in several studies [1-3].
Pesticides result to be one of the most common cause of animal poisoning [4,5] and their misuse or deliberate abuse might represent an actual and current hazard for animals.
Among all pesticides, Methyl-Carbamate (MC) compounds represent one of the most common causes of animal intoxication and several poisoning cases have been reported with increasing frequency [6-11].
Chemically MC derive from Methyl-Carbamic Acid (HOOCNHCH3), a toxic compound recognized as accountable for the toxicity of physostigmine, an alkaloid occurring in Calabar bean (Physostigmina venenosum) which has been exploited as ordeal poison since antiquity in West Africa witchcraft [12].
More in detail, physostigmine was highlighted to be the methylcarbamate derivative of a substituted indole compound (Figure 1) [12] and, since this particular discovery, different studies of structure-activity relationship were carried out.
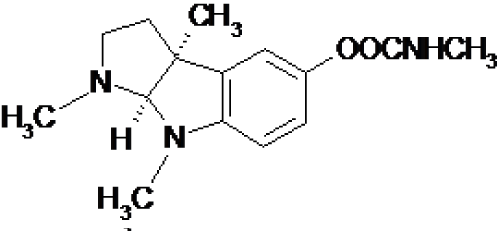
Figure 1: Physostigmine chemical structure.
The introduction of a naphtyl group to carbamic acid ester produced a very effective insecticide known as carbaryl (Figure 2) which started industrial laboratories synthesis and production of a lot of carbamates pesticides for a widespread multitude use [13].
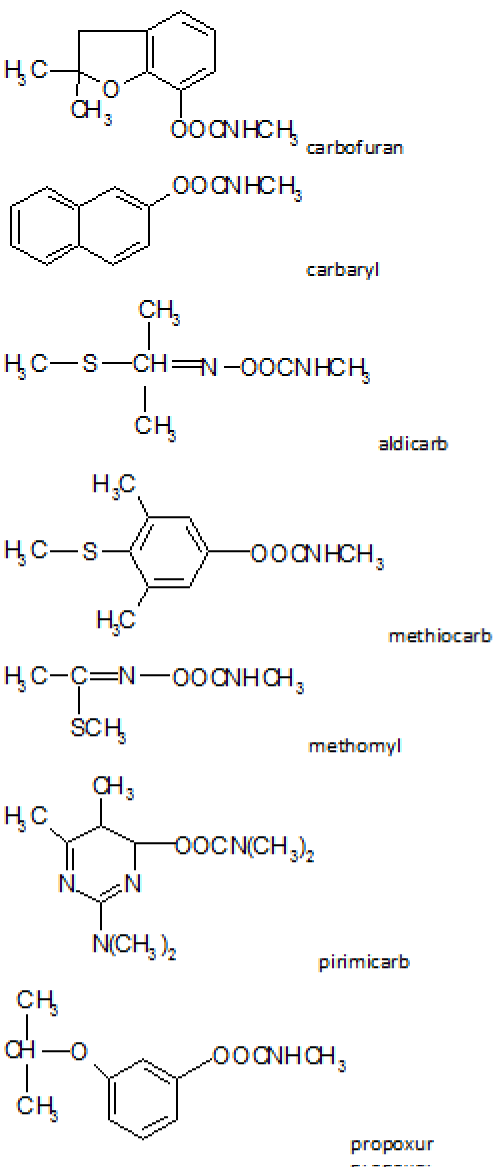
Figure 2: Carbamates chemical structure.
Due to their broad spectrum of activity, MC have been worldwide used since 1970s as Insecticides, Herbicides, Nematocides, Acaricides, Fungicides, Avicides and Bird Repellant in different and heterogeneous habitats such as agricultural lands, forests, rangelands, wetlands, and urban settlements as well.
MC are commercially easily available in the market in different formulations such as granules, pellets, wettable powders, and liquid formulation (emulsion, suspension) [4].
The toxicity of MC to animals is due to their property to inhibit Acetyl Cholin Esterase (AChE) which is the enzyme that catalyzes the idrolysis of the neurotrasmitting agent Acetyl Choline (Ach) in order to prevent further impulse transmission. In particular MC act by reversible acylation (carbamoylation) of the serine hydroxyl group in the enzyme active site [14] and as consequence, a massive accumulation of Ach in the gap junction occurs causing hyperstimulation of cholinergic receptor. In fact clinical signs of MC poisoning may be muscarinic, nicotinic, or generalized Central Nervous System signs (CNS) [15]. Muscarinic signs include dyspnea (caused by bronchorrhea and bronchocostricton), excessive lacrimation, salivation, miosis, micturition (urination), and defecation. Bradycardia is often seen, but tachycardia resulting from catecholamine release may also be seen. Nicotinic signals include twitching of facial muscles, tremors, generalized muscle fasciculations, and then weakness and eventually paralysis. Sign referable to the CNS include convulsions, seizure, ataxia, and anxiety; centrally mediated respiratory depression may lead to respiratory failure and death. Depression or aggression may be seen [15].
Some MC have such an acute and excessive toxicity that have be assigned a toxic class of World Health Organization (WHO) in extremely hazardous (e.g. Aldicarb) and a toxic class of WHO highly hazardous (e.g. Cabofuran, Methiocarb, Methomyl) [16]. These kinds of pesticides are those frequently implicated in animal poisoning cases [17-19].
In Italy, a Decree of the Ministry of Labour, Health and Social Policies (Italian Ministerial Regulation of December 18, 2008 – Italian Official Journal n°13, January 17, 2009) has been in force since January 2009, banning the improper or malicious use of poisoned baits. Whenever poisonings and intoxications are suspected or clinically diagnosed by a health official or veterinary practitioner, they must be reported to the appropriate authorities, who will take the necessary legal action and prosecution. At the same time, relevant sample materials involved in the case (meat and grain baits, stomach and gut contents, unknown suspicious samples) are collected and referred to official laboratories for detailed chemical analyses. The Istituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale delle Venezie (IZSVe) is the official reference laboratory for the regions of north-eastern Italy (Veneto, Friuli Venezia Giulia, Trentino Alto Adige). Such mandatory procedures have contributed to a marked increase in the number of samples being sent for toxicological assay, prompting the need for fast, effective and easily applicable analytical methods.
For this reason, a qualitative method to identify 7 MC (aldicarb, carbaryl, carbofuran, methiocarb, methomyl, pirimicarb, propoxur) (Figure 2), by liquid chromatography with diode array detection (HPLC-DAD) has been developed for and applied to the analysis of real samples.
Data analysis of samples from suspected cases of poisoning collected at the Istituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale delle Venezie in the period 2010-2014 are presented and discussed here below.
Materials and Methods
Reagents: HPLC-grade HiPersolv®CHROMANORM®acetonitrile was purchased from Prolabo (VWR international, Leuven, B). Dichloromethane was supplied by VWR International (Radnor, PA, USA). Distilled water was deionized by means of a Milli-Q system from Millipore™ (Bedford, MA, USA). Capped 15-ml polypropylene centrifuge tubes were purchased from Vakutest Kima s.r.l. (Padova, Italy).
Certified analytical mix of aldicarb, carbaryl, carbofuran, methiocarb, methomyl, pirimicarb, propoxur standards of 500 μg/ml each was purchased from Restek (Bellefonte, PA, USA). Composite intermediate standard solution of 5 μg/ml was prepared by mixing the appropriate amounts of the mix standard solutions and diluting with Acetonitrile.
Apparatus: Chromatographic analysis was performed on Waters Alliance 2695 HPLC separation module equipped with a Waters 2996 diode-array (DAD) detector. (Waters, Milford, MA, USA).
Sample collection: In the period 2010-2014 (January 2010- August 2014), 1674 different suspect samples, mainly ranging from baits and stomach contents, were collected at IZSVe for MC analysis. Some samples were suspected to contain MC poisoning mainly due to observed clinical symptoms or to post mortem findings in animals; others belonged to dead animals found in areas where MC treatments had been conducted; others still were analysed for MC simply because other causes of poison had been ruled out in previous analyses.
Fortified samples: For the verification of method performances twenty independent blank samples of stomach content belonging to different animal species (such as dog, cat, fox) and twenty negative bait were fortified at 2 and 1 mg/kg respectively, chosen as Decision Point Concentration. These samples were considered as positive controls.
Samples preparation: All samples collected, including positive and negative controls, were processed according to the following procedure.
Extraction: Samples were prepared by weighing about 1 g of homogenized matrix (baits, stomach contents) in a capped 15-ml polypropylene centrifuge tube. Each sample was extracted with 5 ml of dichloromethane for 15 minutes in an ultrasonic bath and then centrifuged for 5 minutes at 2000 rpm. The supernatant was then transferred in a 15 ml capped 15-ml polypropylene centrifuge tube, evaporated to dryness under gently stream of nitrogen (50oC) and finally reconstituted with 1 ml of deionized water and acetonitrile (80/20) mixture.
Calibration: To avoid possible variability of retention time or instrumental response due to matrix effects, a matrix calibration point for the identification of the analytes was prepared daily processing a blank sample of bait and stomach content and spiking the two final evaporated extract with 100 and 200 μl of intermediate standard solution of MC (5 μg/ml) respectively. After stirring, this solution was evaporated to dryness under gentle nitrogen steam (40oC) and finally reconstituted with 1 ml of deionized water and acetonitrile (80/20) mixture. The final concentration of this working solutions corresponded to 1 mg/kg and 2 mg/kg of MC on samples.
HPLC analysis: Chromatographic separation was achieved using a Phenomenex®(Torrance, CA, USA) Luna HPLC column 5μ C18 (2) 100A (250 mm x 4.6 mm). The mobile phase consisted of deionized water (A) and HPLC-grade acetonitrile (B). The flow rate was 0.75 ml/min, the injection volume was 20μl and the auto sampler temperature was 4oC.
Gradient conditions are reported in Table 1.
Time (min)
% Phase A
% Phase B
0
80
20
30
10
90
35
10
90
38
80
20
48
80
20
Table 1: Gradient Conditions.
UV-DAD detection was performed for all the analytes at the absorption wavelengths 220 nm. For each analyte the absorption spectrum of a certified reference standard was recorded and stored in the software library for further confirmation purposes.
Results and Discussion
Verification of method performance: The proposed method was intended for qualitative identification of MC in toxicological samples, which is why it was in house developed and validated. The following qualitative parameters were selected to assess whether the proposed method was fit for purpose: interference studies (specificity), Limit of Detection (LOD), carryover and sample extracts stability [20].
Interference study (specificity): Analytical methods used in toxicological assays must demonstrate good power of discrimination between analytes and closely related substances [20]. The following analyses were performed to verify this aspect:
(a) Analysis of representative blank samples to detect the presence of any interference, as endogenous substances and matrix constituents; for this purpose twenty independent blank samples of liver and stomach content belonging to different animal species (dog, cat etc.) and twenty negative baits were analysed. No interference peaks were noticed around the retention time of analytes in the matrices under investigation (Figure 3).
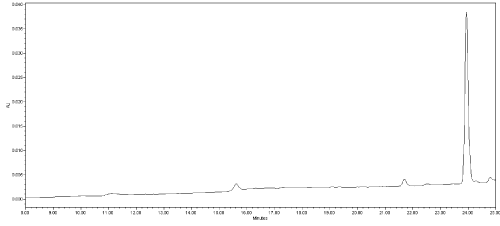
Figure 3: Chromatogram of a negative dog liver; x-axis: time (minute); y-axis:
instrument response (mAU); (220 nm UV absorption wavelength).
(b) Analysis of blank samples containing other toxicological substances likely to be encountered with or alternatively to MC in incurred samples. The responses of three previously negative stomach content samples spiked with anticoagulant rodenticides pesticides (5 mg/kg) were tested for this latter purpose. No interfering peaks near the retention time of MC compounds were detected (Figure 4).
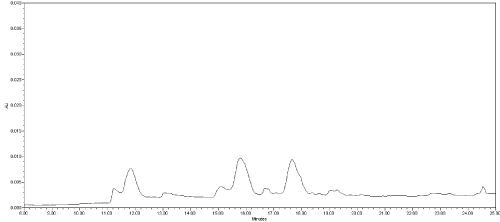
Figure 4: Chromatogram of a stomach content spiked with anticoagulant
rodenticides pesticides (5 mg/kg); x-axis: time (minute); y-axis: instrument
response (mAU); (220 nm UV absorption wavelength).
Limit of detection: This parameter was verified by analysing 20 previously negative bait and stomach content samples spiked at 1 and 2 mg/kg chosen as Decision Point Concentration for the two matrices respectively (Figure 6). In fact, due to higher matrix interference occurring in stomach content samples it was no possible to keep/ perform the same concentration for both matrices.
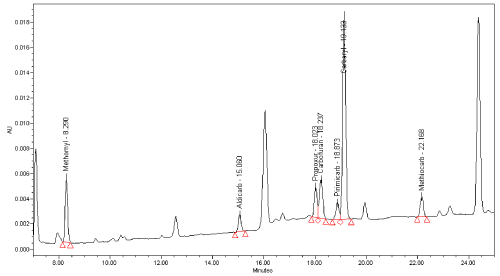
Figure 5: Chromatogram of negative bait sample spiked at 1 mg/kg x-axis:
time (minute); y-axis: instrument response (mAU); (220 nm UV absorption
wavelength).
Since analyte carryover into a subsequent sample may lead to an inaccurate qualitative or quantitative result when using instrumental methods, blank samples (stomach content, bait) were extracted and then analyzed immediately after a corresponding sample spiked with 50 mg/kg of MC. No carryover effects were observed throughout the analyses performed. None of blank samples analyzed after corresponding fortified samples at 50 mg/kg presented unintended analyte signal.
The concentration limit chosen for carryover study has proved to be a cautionary one, since during routine sample analyses no positive samples gave a response exceeding the signal of fortified samples used in the carryover experiments.
Sample stability: Sometimes samples prepared for instrumental analysis might not be immediately analyzed, hence stability study is important to evaluate how long a sample can be stored before analyses [20]. For stability assessment two fortified samples at 1 mg/kg and 2 mg/kg for bait and stomach content respectively, were analyzed in triplicate in three different moments: immediately (time zero), 24, 48 and 72 hours after their preparation. Samples analyzed after 24, 48 and 72 hours were kept at room temperature (assumed in order to simulate autosampler condition). For each MC, stability was calculated in percentage comparing the averages response (area) at each time interval to the time zero responses.
Setting a reasonable bias limit of ±15% no significant response change was observed for each MC in baits matrix in the considered storage condition (Figure 6), whereas in stomach content matrix a significant signal decrease where observed after 72 hours (all the average signals of all MC were lower than 85%) (Figure 7).
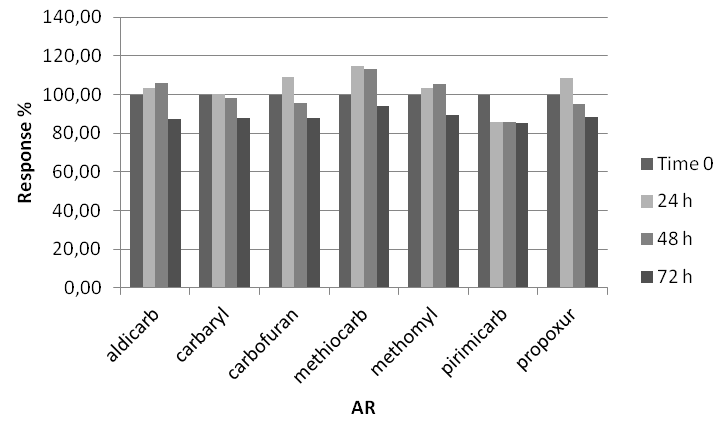
Figure 6: MC stability in bait matrix.
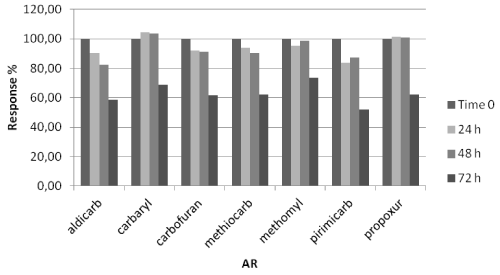
Figure 7: MC stability in stomach content.
Analysis of real samples: This paper consider 1674 different suspected samples ranging from baits to stomach contents brought to the IZSVe during the period 2010-2014 (January 2010- August 2014) and analyzed for MC.
Among the 1674 analyzed samples, stomach content matrices were the most representative (66%, 1117 samples), followed by baits (30%, 505 samples) (Figure 8), a small percentage was represented by liver (2%), carcass (1%) and few samples were defined as “others” (1%) simply because there were neither a specific identification/ description in the accompanying sample dedicated sampling form nor it was possible to define them after a visual inspection.
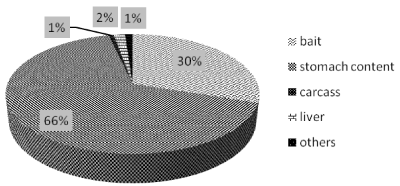
Figure 8: Type of samples analyzed in the period 2010-2014.
Positive samples: 308 out of 1647 samples were found positive (18,5%), of which 81% were stomach contents (251 samples), 18% baits (57 samples), and 1% (3 samples) were represented by liver ad carcass (Figure 9).
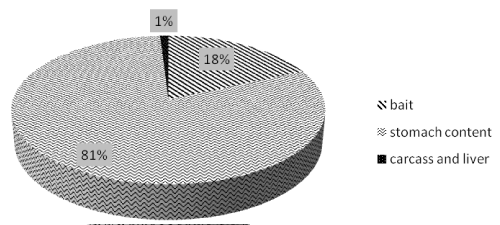
Figure 9: Type of positive samples analyzed in the period 2010-2014.
Aldicarb and carbofuran were the most frequently found compounds as has also been previously observed elsewhere [5,9,10] with a percentage of 40% (124 samples) and 37% (113 samples) respectively, followed by methiocarb 9% (27 samples), methomyl 6% (20 samples), propoxur 5% (16 samples), carbaryl 2% (7 samples) and pirimicarb 1% (2 samples) (Figure 10).
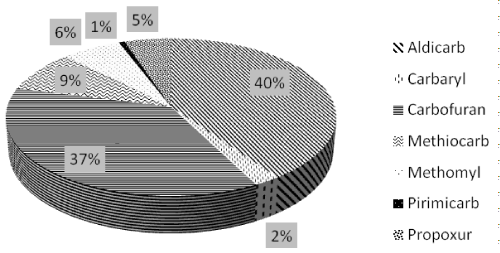
Figure 10: MC distribuition in positive samples.
Furthermore, considering animal species involved in poisoning incidents caused by MC compounds the mostly affected are cats (61%) followed by dogs (Figure 11), differently from other studies where different pesticides were involved and where dogs seemed to be the most susceptible animal to pesticides poisoning [21,22].
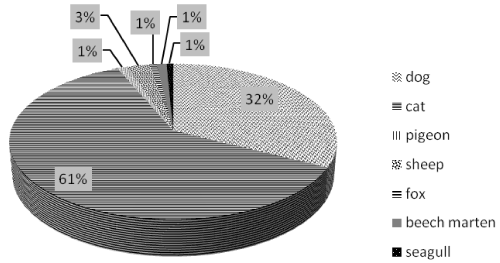
Figure 11: Animal species in positive samples.
Conclusion
The proposed HPLC method to qualitatively identify and determine seven MC compounds has proven to be effective and fitfor- purpose in the investigation of animal poisoning incidents where MC are suspected to be the toxic agent. A total of 1674 suspected samples were analyzed with this method in the period 2010-2014 (January 2010- August 2014), ranging mainly from stomach content (66%) to suspected poisoned baits (30%).
The percentage of positive samples was found to be 18.5 % of the total analyzed samples, and the most frequently found MC in positive samples were aldicarb and carbofuran, followed by methiocarb, methomyl, propoxur, carbaryl and pirimicarb.
The main qualitative parameters such as limit of detection, specificity, carryover and sample stability, were studied and verified for stomach content and bait matrices, showing that the method was suitable for the simultaneous detection of the seven MC in these matrices. The assay is fast, requires small samples and simple extraction procedures, and can be easily applied in routine analyses, ensuring high daily sample throughput. Hence it can be successfully applied in the characterization of MC in suspected cases of poisoning.
References
- Guitart R, Croubels S, Caloni F, Sachana M, Davanzo F, Vandenbroucke V, et al. Animal poisoning in Europe. Part 1: Farm livestock and poultry. The Veterinary Journal. 2010; 183: 249-254.
- Guitart R, Sachana M, Caloni F, Croubels S, Vandenbroucke V, Berny P. Animal poisoning in Europe. Part 3: Wildlife. The Veterinary Journal. 2010; 183: 260-265.
- Buchweitz JP, Bokhart M, Johnson M, Lehner A. Determination of methomyl in the stomach contents of baited wildlife by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2013; 25: 744-749.
- BERNY P. Pesticides and the intoxication of wild animals. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2007; 30: 93-100.
- Wang Y, Kruzik P, Helsberg A, Helsberg I, Rausch W. Pesticide poisoning in domestic animals and livestock in Austria: A 6 years retrospective study. Forensic Sci Int. 2007; 169: 157-160.
- Wobeser G, Bollinger T, Leighton F, Blakley B, Mineau P. Secondary poisoning of eagles following intentional poisoning of coyotes with anticholinesterase pesticides in western Canada. J Wildl Dis. 2004; 40: 163-172.
- Tsatsakis A, Tsakalof A, Siatitsas Y, Michalodimitrakis E. Acute poisoning with carbamate pesticides: the Cretan experience. Science & Justice. 1996; 36: 35-39.
- Risher JF, Mink FL, Stara JF. The toxicologic effects of the carbamate insecticide aldicarb in mammals: a review. Environ Health Perspect. 1987; 72: 267-281.
- Novotný L, Misík J, Honzlová A, Ondráček P, Kuča K, Vávra O, et al. Incidental poisoning of animals by carbamates in the Czech Republic. Journal of Applied Biomedicine. 2011; 9: 157-161.
- Mineau P, Fletcher MR, Glaser L, Thomas N, Brassard C, Wilson L, et al. Poisoning of raptors with organophosphorus and carbamate pesticides with emphasis on Canada, US and UK. J Raptor Rese. 1999; 33: 1-37.
- Kaye B, Elliott C, Jalim S. Methiocarb poisoning of a horse in Australia. Aust Vet J. 2012; 90: 221-224.
- Metcalf RL. Structure-activity relationships for insecticidal carbamates. Bull World Health Organ. 1971; 44: 43-78.
- Hummel HE. Insecticides and their design. J Nematol. 1983; 15: 615-639.
- Fukuto TR. Mechanism of action of organophosphorus and carbamate insecticides. Environ Health Perspect. 1990; 87: 245-254.
- Gfeller RW, Messonnier SP. Handbook of small animal toxicology and poisonings. : Mosby St. Louis; 2004.
- World Health Organization. The WHO recommended classification of pesticides by hazard and guidelines to classification 2009. 2010.
- Anastasio JD, Sharp CR. Acute aldicarb toxicity in dogs: 15 cases (2001-2009). J Vet Emerg Crit Care (San Antonio). 2011; 21: 253-260.
- Kaye BM, Elliott CR, Jalim SL. Methiocarb poisoning of a horse in Australia. Aust Vet J. 2012; 90: 221-224.
- Tennakoon S, Perera B, Haturusinghe L. Intentional poisoning cases of animals with anticholinesterase pesticide-carbofuran in Sri Lanka. Leg Med (Tokyo). 2009; 11: S500-502.
- Scientific Working Group for Forensic Toxicology (SWGTOX). Practices for Method Validation in Forensic Toxicology Rev. 01. Electronic source 2013.
- Gallocchio F, Basilicata L, Benetti C, Angeletti R, Binato G. Multi-residue determination of eleven anticoagulant rodenticides by high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array/fluorimetric detection: Investigation of suspected animal poisoning in the period 2012–2013 in north-eastern Italy. Forensic Sci Int. 2014; 244: 63-69.
- Berny P, Caloni F, Croubels S, Sachana M, Vandenbroucke V, Davanzo F, et al. Animal poisoning in Europe. Part 2: Companion animals. The Veterinary Journal. 2010; 183: 255-259.
Citation: Gallocchio F, Basilicata L, Benetti C, Angeletti R and Binato G. Multi-residue Determination of Seven Methyl-Carbamate Pesticides by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Diode Array Detection: Investigation of Suspected Animal Poisoning in the Period 2010-2014 in North-Eastern Italy. Austin J Forensic Sci Criminol. 2015; 2(4): 1038. ISSN : 2380-0801