
Research Article
J Immun Res. 2014;1(3): 1013.
Lipofundin Affects Cytokine Release by Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells from Healthy Individuals
Bessler H1, Bergman M2, Sirota L3, Salman H2and Djaldetti M1*
1Laboratory for Immunology and Hematology Research, Rabin Medical Center, Hasharon Hospital, The Sackler School of Medicine, Tel-Aviv University, Israel
2Department of Internal Medicine C, Rabin Medical Center, Hasharon Hospital, The Sackler School of Medicine, Tel-Aviv University, Israel
3The Neonatal Intensive Care Unit, Schneider Children’s Medical Center of Israel, The Sackler School of Medicine, Tel-Aviv University, Israel
*Corresponding author: Meir Djaldetti, Laboratory for Immunology and Hematology Research, Rabin Medical Center, Hasharon Hospital, The Sackler School of Medicine, Tel-Aviv University, Israel
Received: November 26, 2014; Accepted: January 09, 2015; Published: January 09, 2015
Abstract
Background: Administration of intralipid to critically ill patients is a common therapeutic modality. Studies have shown that patients with life-threatening diseases expressed a marked improvement of their clinical and immunology features following feeding by parenteral intralipid regimens. Considering the important role of the peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) as immune system constituents, the question has been raised if intralipid added to the cells in vitro will affect their capacity for inflammatory cytokine generation.
Methods: Non-stimulated and LPS or PMA stimulated human PBMC were incubated with intralipid (Lipofundin) and the production of TNFα, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-1ra, IL-10, IL-2 and IFNγ was evaluated.
Results: Following 24 hrs of incubation a concentration dependent decreased production of IL-1β and IL-10 in LPS-stimulated and non-stimulated cells were observed, whereas that of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1ra was not affected. Intralipid suppressed the production of IFNγ and IL-2 following incubation with stimulated cells only.
Conclusions: The results indicate that intralipid modulates immune cells’ function, an observation that may explain the favorable effect of parenteral nutrition on patients with life-threatening diseases.
Keywords: Cytokines; Lipofundin; Immunity; Mononuclear cells; Parenteral nutrition
Graphical abstract: Incubation of PBMC from healthy individuals with
lipofundin (gray dots) reduced the production of inflammatory cytokines.
Abbreviations
IL – InterLeukin; PBMC - Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells; PBS – Phosphate Buffered Saline; CM – Complete Medium; LPS – LipoPolySaccharides; TNF – Tumor Necrosis Factor; IFN – InterFeron; PMA – Phorbol Myristate Acetate
Introduction
Parenteral nutrition is a widely accepted therapeutic modality in cases with intestinal failure. It is indicated in patients ranging from preterm infants up to adults suffering from disabling or incurable diseases requiring nutritional support for life maintenance [1, 2]. It is imperative to keep-in-mind that applying short- term, long-term or even cyclic parenteral nutrition necessitates the existence of a close collaboration between trained medical personnel, pharmacists and dietitians, as well as profound proficiency on the variety of nutritional lipid emulsions [2-4]. Inappropriate dosage, rapid intravenous administration, lack of carbohydrate addition may cause undesirable effects leading to fat overload syndrome [5, 6]. It is notable that intravenous administration of lipid emulsions has been used for purposes others than parenteral nutrition, such as reverse of life threatening drug toxicities, reducing heart’s ischemia-reperfusion injury and infarct-size, along with treatment for local anesthetic systemic toxicity [7-9]. Malnutrition in patients in need for parenteral nutrition is linked to conspicuous metabolic, hormonal and immune alterations, such as increased levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1, IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α [10]. Studies have proven that intralipid administration to critically ill patients with potentially impaired immune system may improve the outcome of the underlying disease. Muller et al. [11] have reported that patients with gastrointestinal carcinoma given preoperatively parenteral nutrition for 10 days showed lower postoperative complications than matched patients receiving regular hospital diet. Similar observations have been reported in other studies [12]. According to Ziegler [10] critically ill patients maintained on parenteral nutrition showed lower mortality compared to those given oral nutrition. On the other hand, in some cases the immune response may be impaired following parenteral nutrition. Cruccetti et al. [13] have found that LPS stimulated monocytes from parenteral fed infants confronted with microbial infections produced lower levels of TNF-α and IL-6 compared to enterally fed control infants and adults. Similar observations have been reported by others [14]. However, the impression from majority
of the studies on the subject is that intralipid administration activates immune cell functions. Accordingly, it has been shown that intralipid particles have been vividly ingested by human monocytes and remained within the cells up to three weeks. In addition, it has been observed that intralipid induces an increased phagocytosis of zymozan particles, without affecting other normal monocyte functions, such as superoxide production, glucose consumption and lyzozyme secretion [15]. A similar increase in monocyte lipid phagocytic ability has been reported in healthy subjects given intralipid [16]. Prolonged parenteral intralipid administration in pigs induced a lipid uptake by their lung macrophages, as well as an increase in both cell size and number [17]. In addition, increased lipid phagocytosis has been observed following 24 hrs incubation of their peripheral blood mononuclear cells with intralipid. According to Padeh et al. [18] cultured monocytes treated with intralipid showed an increased number of engulfed Candida albicans microorganisms, although their killing activity did not differ from that of control cells. Bearing in mind that mononuclear cells participate actively in the immune processes by functions other than phagocytosis, such as production of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, the aim of the present work was to examine the in vitro effect of lipid emulsion (lipofundin), on the capacity for cytokine production by human peripheral mononuclear blood cells (PBMC) from healthy individuals.
Materials and Methods
Lipofundin
A 20% solution of lipofundin MCT/LCT emulsion (B. Braun, Melsingen AG, Germany) containing 100gr/L soybean oil, 100gr/L medium chain triglycerides, 25gr/L glycerol, 12gr/L egg lecitin and 0.02% α-tocopherol, pH 6.5-8.5 was used. 1:3 dilutions of lipofundin were prepared in medium and added at a final volume of 5μl/ml of cell suspension. A concentration of 5μl/ml of 20% lipofundin MCT/ LCT emulsion was considered as 0.5% and designated as lipofundin solution
Cell preparation and culture conditions
PBMC were separated from healthy adult blood bank donors’ venous blood by gradient centrifugation using Lymphoprep-1077 (Axis-Shield PoC AS, Oslo, Norway). The cells were washed twice in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and suspended in RPMI-1640 medium (Biological Industries, Beith Haemek, Israel) containing 1% penicillin, streptomycin and nystatin and supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum (designated as complete medium CM).
Effect of lipofundin on cytokine production
2x106/ml of PBMC suspended in CM were incubated for 24 hrs without or with 20ng/ml lipopolysaccharide (LPS, E. coli, Sigma) to determine the secretion of TNFα, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-1ra and IL-10, or with 0.5μg/ml of phorbol myristate acetate (PMA-Sigma, Israel) and 0.25μg/ml of ionomycin (Sigma, Israel) to evaluate IL-2 and IFNγ production. Lipofundin (20% solution) was added at the onset of the cultures at final concentrations between 0.02% and 0.5%. Cultures without lipofundin served as control. The plates were incubated at 370C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2. At the end of the incubation period, the culture media were collected, the cells were removed by centrifugation and the supernatants were kept at -70oC until assayed for cytokine content.
Cytokine content in the supernatants
The concentration of cytokines in the supernatants was tested using ELISA kits specific for human cytokines (Biosource International, Camarillo, CA) as detailed in the guide-line provided by the manufacturer. Each kit is specific for one individual cytokine. The detection level of all cytokines was 30pg/ml. The percentage of the CV at the ELISA assay for the cytokines examined was 2% to the mean or less.
The possible effect of lipofundin on the ELISA assay was tested by comparing cytokine levels in the supernatants without and with lipofundin at final concentrations as described above.
Statistical analysis
Data was analyzed using one way ANOVA with repeated measures to evaluate the effect of lipofundin on each cytokine and two tailed paired Student’s t-test to compare the effect of various lipofundin concentrations on the controls (incubated without lipofundin). The results are expressed as mean ± SEM. P value of <0.05 was consideredas statistically significant.
Results
Effect of lipofundin on ELISA assay
The levels of all cytokines examined and tested in supernatants obtained from either LPS or PMA/ionomycin stimulated PBMC was not affected by addition of lipofundin at concentrations between 0.03% and 0.5% (data not shown).
Effect of lipofundin on IL-1β production (Figure 1)
Lipofundin caused a concentration dependent inhibition of IL- 1β secretion by both non-stimulated and LPS-stimulated PBMC (p=0.04). At lipofundin doses of 0.08%, 0.2% and 0.5%, the secretion of IL-1β by non-stimulated PBMC was lowered by 55%, 78% and 73%, respectively (p=0.05) and that by LPS-stimulated cells was reduced by 20%, 25% and 27%, respectively (p=0.04, p=0.014 and p=0.007, respectively).
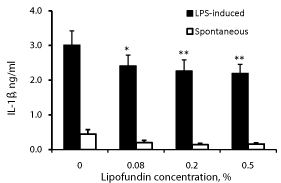
Figure 1: Effect of lipofundin on IL-1β production.
2x106 PBMC were incubated for 24 hrs without or with lipofundin in doses as
indicate in the absence (spontaneous) or presence of LPS. The level of IL-1β
in the supernatants was tested by ELISA. Each column represents the mean
of 12 experiments. Bars represent SEM. Asterisks represent statistically
significant difference from PBMC incubated without lipofundin (*p<0.05;
**p<0.01).
Effect of lipofundin on TNFα and IL-6 production
The results are shown in Table 1. Incubation of PBMC with various lipofundin doses did not cause any significant effect on either TNF-á or IL-6 production by non-stimulated PBMC (p=0.871, p=0.246, respectively) or LPS-stimulated PBMC (p=0.832, p=0.966, respectively).
Lipofundin concentration
0
0.08%
0.2%
0.5%
p
TNFα, pg/ml
Spontaneous
LPS-induced
322±86
595±59
197±52
614±66
176±37
634±69
217±64
559±63
NS
NS
IL-6, ng/ml
Spontaneous
LPS-induced
1.49±0.16
28.5±4.7
1.43±0.19
31.5±5.0
1.30±0.14
31.5±5.1
1.00±0.21
31.3±4.5
NS
NS
IL-1ra, pg/ml
Spontaneous
LPS-induced
336±59
567±62
374±71
563±57
376±89
608±56
372±86
691±75
NS
NS
The results are expressed as Mean ± SEM (n=12 for LPS-induced cytokine secretion and n=7 for spontaneous production). P calculated by ANOVA with repeated measures represents statistically significant difference between cells incubated without or with the various doses of lipofundin as indicated. NS- not significant.
Table 1: Effect of lipofundin on cytokine production by PBMC.
Effect of lipofundin on IFNγ secretion (Figure 2)
IFNγ could not be detected in supernatants obtained from non-stimulated PBMC incubated without or with lipofundin. A concentration dependent inhibition of IFNγ secretion was observed when lipofundin was added to PMA/ionomycin stimulated PBMC (p=0.001). At lipofundin doses of 0.02%, 0.08%, 0.2% and 0.5% the production of IFNγ was inhibited by 33% (p=0.01), 42% 74% and 90% (p<0.001), respectively.
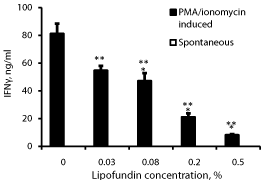
Figure 2: Effect of lipofundin on IFNγ production.
2x106 PBMC were incubated for 24 hrs without or with lipofundin in doses
as indicate in the absence (spontaneous) or presence of PMA/ionomycin.
The level of IFNγ in the supernatants was tested by ELISA. Each column
represents the mean of 12 experiments. Spontaneous secretion of IFNγ by
non-stimulated PBMC could not be detected. Bars represent SEM. Asterisks
represent statistically significant difference from PBMC incubated without
lipofundin (**p<0.01; ***p<0.001).
Effect of lipofundin on IL-2 production (Figure 3)
IL-2 could not be detected in supernatants obtained from non-stimulated PBMC incubated without or with lipofundin. A concentration dependent inhibition of IL-2 production was found when lipofundin was added to PMA/ionomycin stimulated PBMC (p=0.001). At lipofundin doses of 0.08%, 0.2% and 0.5% the production of IFNγ was inhibited by 32%, 60% and 84% (p<0.001), respectively.
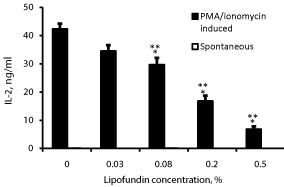
Figure 3: Effect of lipofundin on IL-2 production.
2x106 PBMC were incubated for 24 hrs without or with lipofundin in doses
as indicate in the absence (spontaneous) or presence of PMA/ionomycin.
The level of IL-2 in the supernatants was tested by ELISA. Each column
represents the mean of 12 experiments. Spontaneous secretion of IL-2 by
non-stimulated PBMC could not be detected. Bars represent SEM. Asterisks
represent statistically significant difference from PBMC incubated without
lipofundin (***p<0.001).
Effect of lipofundin on IL-10 production (Figure 4)
Lipofundin at the doses tested caused a concentration dependent reduced secretion of IL-10 by non-stimulated and LPS stimulated PBMC (p=0.007). At lipofundin doses of 0.08%, 0.2% and 0.5% the secretion of IL-10 by non-stimulated PBMC was reduced by 44%, 60% and 65% (p=0.076, p=0.04, p=0.0228), respectively and that by LPS-stimulated PBMC by 25%, 35% and 32% (p<0.005), respectively.
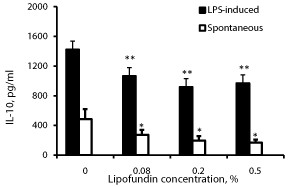
Figure 4: Effect of lipofundin on IL-10 production.
2x106 PBMC were incubated for 24 hrs without or with lipofundin in doses as
indicate in the absence (spontaneous) or presence of LPS. The level of IL-10
in the supernatants was tested by ELISA. Each column represents the mean
of 12 experiments. Bars represent SEM. Asterisks represent statistically
significant difference from PBMC incubated without lipofundin (*p<0.05;
**p<0.01).
Effect of lipofundin on IL-1ra production (Table 1)
At doses between 0.08% and 0.5%, lipofundin did not exert any significant effect on the production of IL-1ra by non-stimulated or LPS-stimulated PBMC, p=0.979, p=0.45, respectively.
Discussion
The results of this study demonstrate that incubation of PBMC from healthy individuals with lipofundin modulates their immune response expressed by modification of their capacity for cytokine production. This alteration was dose-dependent and related to the stimulant inducing their activation. Thus, lipofundin caused a decrease production of IL-1â and IL-10 in LPS-stimulated and nonstimulated cells. On the other hand, it did not affect the production of TNF-á, IL-6 and IL-1ra in both stimulated and non-stimulated PBMC. As for IFN and IL-2, their production was suppressed by lipofundin following incubation with stimulated cells only. The suppressive activity of lipofundin on the pro-inflammatory cytokines generation, i.e. IL-1â, IFN and IL-2, merits attention. Even though this effect was observed in vitro, it is conceivable that at least a part of the beneficial effect of intralipid given to patients with life-threatening diseases will proceed via inhibition of proinflammatory responses by PBMC. Inhibition of IL-2, TNF-áá and IL-1â release by stimulated peripheral white blood cells from healthy individuals following incubation with lipid emulsions with various fatty acid compositions has been reported by Granato et al. [19]. In patients with malignant diseases of the alimentary tract, parenteral nutrition post surgery induced a significant reduction in plasma concentration of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and IL-8 [20]. In a previous study from our laboratory we have found that intralipid caused a dose-dependent inhibition on IL-2 production by cord blood mononuclear cells, as well as a decreased capacity of IL-2 dependent CTLL-2 cell line to respond to IL-2 [21]. On the other hand, it has been reported that in patients receiving lipid emulsion during total parenteral nutrition, there was a significantly enhanced IL-2 production concurrently with increased peripheral blood T cell subsets and antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity [22]. It appears therefore, that the immunomodulatory properties of various lipid emulsions and the pattern of their efficacy on cytokine production depends on a few factors, such as emulsion’s ingredients, intralipid concentration and longevity of intralipid administration. Arias-Diaz et al. [23] have treated patients undergoing surgery because of gastrointestinal tract malignancies with three total parenteral nutrition regiments i.e. hypertonic glucose solution, 45% glucose and 20% long chain triglycerides and the third – as that in group two, but with addition of 20% emulsion of a mixture of medium- and long chain triglycerides The results showed a similar increase in TNF-á, IL-1, IL-6 and nitrate/nitrite plasma levels in all three regiments. A similar dependency of immunomodulatory responses on the type of intralipid composition has been observed by other investigators [19, 24-26]. It has been reported that feeding stressed rats with fat emulsions containing omega-3 and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids resulted in reducing IL-8 and IL-10 production by the first emulsion, where as the second one caused increased pro-inflammatory cytokines levels [27]. Administration of fish oil-enriched emulsion to patients during the postoperative period increased the production of the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-á, IFN and IL-2 by peripheral blood lymphocytes [28]. In disparity with these reports, lipofundin in the present work induced a decreased production of the proinflammatory cytokines by both non-stimulated and stimulated PBMC, while the production of TNF-á, IL-6, IFN and IL-2 by non-stimulated PBMC was not affected. Here again, the role of the brand of lipid emulsion on the capacity of immune cells to exert their activity for cytokine production is emphasized. However, stimulated PBMC did produce decreased levels of IFN and IL-2 following incubation with lipofundin. Ooi et al. [29] have reported that the levels of IL-1â, TNF-á, IL-6, IFN and IL-2 by phytohemagglutinin stimulated lymphocytes from parenterally fed healthy volunteers and patients with colorectal cancer did not differ before and after total parenteral nutrition. Considering the beneficial effects of lipofundin on immune responses, the decreased IL-10 production by PBMC following incubation with lipofundin observed in the present work is rather unexpected, since this is an anti-inflammatory cytokine. However, similar observation has been reported in other studies showing that IL-10 expression remained either unchanged after 14 days of parenteral nutrition in preterm infants [30], or its production by intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes in mouse models has been suppressed [31, 32]. Accumulating evidence has demonstrated that intralipid may affect immune mononuclear cells’ functions other than cytokine production. Experiments with rats given intralipid emulsion for five days showed an increased NK activity observed only with 10% and not with 5% concentration [33]. Following reports that impaired reproduction ability in women linked with increased NK activity may be improved by administration of intralipid infusions, Roussev et al. [34] have reported that intralipid given to fifty women with increased NK activity resulted in suppression and normalization of this cell function, indicating the possibility of applying intralipid as an alternative therapeutic modality in these cases.
In short, the present work demonstrates that lipofundin modifies the capacity for inflammatory cytokine production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells from healthy individuals emerging to be concentration dependent and related to the type of cell stimulation. These observations may clarify the favorable therapeutic effect of lipofundin administration to critically ill patients.
References
- Barclay AR, Beattie LM, Weaver LT, Wilson DC. Systematic review: medical and nutritional interventions for the management of intestinal failure and its resultant complications in children. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2011; 33: 175-184.
- Phillips GD, Odgers CL. Parenteral nutrition: current status and concepts. Drugs. 1982; 23: 276-323.
- Klek S, Chambrier C, Singer P, Rubin M, Bowling T, Staun M, et al. Four-week parenteral nutrition using a third generation lipid emulsion (SMOFlipid)--a double-blind, randomised, multicentre study in adults. Clin Nutr. 2013; 32: 224-231.
- Beau P, Meyran E, Chassin J, Matuchansky C. Cyclic parenteral nutrition in hospitalized adult patients: a 9-year experience. Clin Nutr. 1994; 13: 22-28.
- Förster H, Quadbeck R, Anschütz A. [The problem of dosage and importance of fats in parenteral feeding]. Infusionsther Klin Ernahr. 1979; 6: 362-368.
- Hojsak I, KolaÄek S. Fat overload syndrome after the rapid infusion of SMOFlipid emulsion. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2014; 38: 119-121.
- Presley JD, Chyka PA. Intravenous lipid emulsion to reverse acute drug toxicity in pediatric patients. Ann Pharmacother. 2013; 47: 735-743.
- Li J, Iorga A, Sharma S, Youn JY, Partow-Navid R, Umar S, et al. Intralipid, a clinically safe compound, protects the heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury more efficiently than cyclosporine-A. Anesthesiology. 2012; 117: 836-846.
- Hori K, Matsuura T, Mori T, Kuno M, Sawada M, Nishikawa K. The effect of lipid emulsion on intracellular bupivacaine as a mechanism of lipid resuscitation: an electrophysiological study using voltage-gated proton channels. Anesth Analg 2013; 117: 1293-130.
- Ziegler TR. Parenteral nutrition in the critically ill patient. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361: 1088-1097.
- Müller JM, Brenner U, Dienst C, Pichlmaier H. Preoperative parenteral feeding in patients with gastrointestinal carcinoma. Lancet. 1982; 1: 68-71.
- Dionigi P, Dionigi R, Prati U, Pavesi F, Jemos V, Nazari S. Effect of Intralipid on some immunological parameters and leukocyte functions in patients with esophageal and gastric cancer. Clin Nutr. 1985; 4: 229-234.
- Cruccetti A, Pierro A, Uronen H, Klein N. Surgical infants on total parenteral nutrition have impaired cytokine responses to microbial challenge. J Pediatr Surg. 2003; 38: 138-142.
- Okada Y, Papp E, Klein NJ, Pierro A. Total parenteral nutrition directly impairs cytokine production after bacterial challenge. J Pediatr Surg 1999; 34: 277-280.
- Szeinberg A, Messer G, Davidsohn J, Levanon M, Passwell JH. Studies on the effect of intralipid on human monocyte functions in vitro. Isr J Med Sci. 1986; 22: 791-796.
- Wiernik A, Jarstrand C, Julander I. The effect of intralipid on mononuclear and polymorphonuclear phagocytes. Am J Clin Nutr. 1983; 37: 256-261.
- Aksnes J, Børsum K, Rollag H, Hovig T. Intravascular lung macrophages play an essential role in lipid entrapment and the inflammatory tissue reaction seen after long-term lipid-based parenteral nutrition in pigs. An ultrastructural study. APMIS 1996; 104: 429-436.
- Padeh S, Shor R, Passwell JH. Effect of intralipid on the phagocytic and microbicidal capacity of human monocytes in culture. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1987; 6: 575-580.
- Granato D, Blum S, Rössle C, Le Boucher J, Malnoë A, Dutot G. Effects of parenteral lipid emulsions with different fatty acid composition on immune cell functions in vitro. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2000; 24: 113-118.
- Słotwiński R, Słodkowski M, Pertkiewicz M, Lech G, Zaleska M, Majewska K, et al. [Dynamic of IL-6 and IL-8 concentrations in patients after surgery treated with total parenteral nutrition]. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2002; 12: 45-48.
- Sirota L, Straussberg R, Notti I, Bessler H. Effect of lipid emulsion on IL-2 production by mononuclear cells of newborn infants and adults. Acta Paediatr. 1997; 86: 410-413.
- Monson JR, Ramsden CW, MacFie J, Brennan TG, Guillou PJ. Immunorestorative effect of lipid emulsions during total parenteral nutrition. Br J Surg. 1986; 73: 843-846.
- Arias-Díaz J, Rodríguez JM, Vara E, García C, Torres-Melero J, García-Carreras C, et al. NO2/NO3 and cytokine plasma profiles under different postoperative parenteral nutrition regimens. Nutrition. 1996; 12: 89-92.
- Krogh-Madsen R, Plomgaard P, Akerstrom T, Møller K, Schmitz O, Pedersen BK. Effect of short-term intralipid infusion on the immune response during low-dose endotoxemia in humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008; 294: E371-379.
- Furukawa K, Yamamori H, Takagi K, Hayashi N, Suzuki R, Nakajima N, et al. Influences of soybean oil emulsion on stress response and cell-mediated immune function in moderately or severely stressed patients. Nutrition. 2002; 18: 235-240.
- Reimund JM, Scheer O, Muller CD, Pinna G, Duclos B, Baumann R. In vitro modulation of inflammatory cytokine production by three lipid emulsions with different fatty acid compositions. Clin Nutr. 2004; 23: 1324-1332.
- Hayashi N, Tashiro T, Yamamori H, Takagi K, Morishima Y, Otsubo Y et al. Effects of intravenous omega-3 and omega-6 fat emulsion on cytokine production and delayed type hypersensitivity in burned rats receiving total parenteral nutrition. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 1998; 22: 363-367.
- Schauder P, Röhn U, Schäfer G, Korff G, Schenk HD. Impact of fish oil enriched total parenteral nutrition on DNA synthesis, cytokine release and receptor expression by lymphocytes in the postoperative period. Br J Nutr 2002; 87 Suppl 1: S103-110.
- Ooi SE, Chen GW, Chou CT. Adequate nourishment through total parenteral nutrition treatment may augment immune function in patients with colon cancer. Arch Med Res 2004; 35: 289-293.
- Gawecka A, Michalkiewicz J, Kornacka MK, Luckiewicz B, Kubiszewska I. Immunologic properties differ in preterm infants fed olive oil vs soy-based lipid emulsions during parenteral nutrition. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 2008; 32: 448-453.
- Sun X, Yang H, Nose K, Nose S, Haxhija EQ, Koga H et al. Decline in intestinal mucosal IL-10 expression and decreased intestinal barrier function in a mouse model of total parenteral nutrition. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2008; 294: G139-147
- Fukatsu K, Kudsk KA, Zarzaur BL, Wu Y, Hanna MK, DeWitt RC. TPN decreases IL-4 and IL-10 mRNA expression in lipopolysaccharide stimulated intestinal lamina propria cells but glutamine supplementation preserves the expression. Shock. 2001; 15: 318-322.
- Kurzer M, Tice D, Meguid MM, Reinitz ER. Natural killer cell activity in rats infused with Intralipid. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1989; 29: 33-35.
- Roussev RG, Acacio B, Ng SC, Coulam CB. Duration of intralipid's suppressive effect on NK cell's functional activity. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2008; 60: 258-263.