
Review Article
Austin J Nanomed Nanotechnol. 2017; 5(1): 1045.
Bionanocomposite: A Review
Pande VV and Sanklecha VM*
Department of Pharmaceutics, Sanjivani College of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, India
*Corresponding author: Sanklecha Vishal Manaklal, Department of Pharmaceutics, Sanjivani College of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, Kopargaon, 423603, India
Received: November 08, 2017; Accepted: November 30, 2017; Published: December 07, 2017
Abstract
A review is presented on the recent developments of Bionanocomposites. The present paper study about the meaning of Bionanocomposites, methods of development of Bionanocomposite and recent application of Bionanocomposites. In this review, focused on basic material used in bionanocomposites and the application of different polymer bionanocomposites particularly in biomedical and pharmaceutical field are discussed here.
Keywords: Bionanocomposites; Method and application of bionanocomposites; Nanocomposites; Biopolymer
Introduction
During the last few years, “bionanocomposite” has turned into a typical term to assign those nanocomposites including a naturally occurring polymer (biopolymer) in mix with an inorganic moiety, and appearing no less than one measurement on the nanometer scale [1]. Nanocomposites that contain normally occurring polymers (biopolymer) in mix with an inorganic nanomoiety speak to a different class of materials called Bionanocomposites (BNCs). The expression “bionanocomposite” additionally called “Nanobiocomposites” (NCs), “green composites,” or, on the other hand “biohybrids” was first utilized as a part of 2004 [2]. Dimensionality assumes a basic part in deciding the properties of issue. The nanostructure of a material is the key factor in the advancement of novel properties and in controlling the structure at the nanolevel. Nanotechnology is in this way an exceedingly encouraging field of the twenty-first century, which is required to thoroughly rebuild the innovative applications in the fields of semiconductors, inorganic, and additionally natural materials, vitality stockpiling, and biotechnology [3]. Two or, on the other hand more materials with disparate properties in a specific extent are combined to frame a composite. The individual parts in composites are remaining reinforced together by certain physical or, on the other hand concoction cooperation”s, while, holding their physical or compound properties. For the most part, properties of the composite materials are unrivaled in many regards to those of the individual unadulterated parts [4]. Nanotechnology can be broadly defined as the creation; processing, characterization and utilization of material devices and system with dimension in the range of 0.1- 100 nm1. Nanocomposites can be made with an improved physical, thermal and other unique property [5].
Bio-nanocomposites are significant due to their nanoscale dispersion with size less than 1,000nm [6].
Method of Preparation of Bionanocomposite
Bionanocomposite prepared by various methods which is as follows,
Solution intercalation
In this system, the bio-polymer or bio-prepolymer, such as starch and protein is added into the solvent which is completely soluble in solvent. The inorganic nano fillers such as silicate platelets which are swollen in a solvent such as water, chloroform or toluene. When the biopolymer and solution of swollen nanoparticles are mixed, the polymer chains intercalate and displace the solvent within the interlayer of the silicate. Upon solvent removal, the intercalated structure remains, resulting in a formation of biopolymer/ layered silicate bio-nanocomposite [6,7].
In situ intercalative polymerization
In this method, the nanoparticle is dispersed in a liquid monomer or a monomer solution, so the polymer formation can occur between the intercalated sheets. Polymerization can be done either by heat or radiation, by the diffusion of a suitable initiator, or by an organic initiator or catalyst [6,7].
Melt intercalation
The melt intercalation technique has become the standard method for the preparation of polymer/layered silicate bio-nanocomposites. There are many advantages compared with solution intercalation and in situ intercalative polymerization. In this process, the polymer is heated at specific temperature to get a molten mass and mixed with nanoparticle. It can be done by the extruder Figure 1 [6,7].
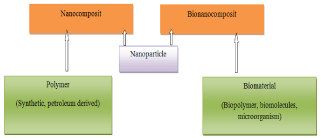
Figure 1: Components of nanocomposite and bionanocomposite.
Template synthesis
In this method, biomolecules, parts and whole cells, microorganisms serve as the template for inorganics which are generated from a precursor. The templating bio organics is in nanosized particle which is entrapped in mesoporous matrix. This technique is highly versatile. This is a simple and easy procedure and applicable for large scale production. This method mostly required water soluble polymers and the resulting product may be chances of contamination due to side product [7-9].
Components of Bionanocomposites
Biomaterial
It is obtained naturally from plant, animal and microorganism. It contained mostly cellulose, lignin and hemicellulose.
Cellulose: It is a polysaccharide. It is mostly found in plants and animals. Cellulose is a building material of long fibrous cells and highly strong natural polymer. Cellulose nanofibers are inherently a low cost and widely available material. Moreover, they are environmentally friendly and easy of recycling by combustion, and require low energy consumption in manufacturing. Basically two types of nanoreinforcements can be obtained from cellulose - microfibrils and whiskers [10,11].
Chitosan: It is a natural polysaccharide containing a large number of amino (-NH2) and hydroxyl (-OH) groups. Chitosan is a linear copolymer that can be synthesized from the deacetylation of chitin. It is a β (1-4) linked linear copolymer consists of 2-acetamido- 2-deoxy-D-glucopyranose and 2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glycopyranos. Its structure is very similar to cellulose [12]. It has various medical applications such as wound dressings and absorbable sutures [13].
Poly lactic acid (PLA): Poly Lactic Acid (PLA) is one of the most widely produced bioplastics. It is also known as Poly lactide. It is a linear thermoplastic polymer mainly derived from renewable resources such as corns or sugar beets. It has various applications such as medical devices, food, packaging and textiles [13].
Starch: It is a polysaccharide. Starch having a two component amylose and amylopectin. Mostly starch is helpful for storage of energy in plants and microorganisms. Potato, Maize, Topica, Wheat are the main source of starch [13].
Chitin: Chitin is modified cellulose that has a high molecular weight and is synthesized from N-acetylglucosamine units.It is mostly used as effective binder in dyes and fabrics [13].
Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA): Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) belongs to a family of naturally occurring hydrophobic, biocompatible, and biodegradable polyesters. It is available in a wide variety of forms and used for carbon or energy storage in microorganism in the form of light refracting granules inside the cell [13].
Nanoparticles [14]
They are in nano size. Nanoparticle exist in spherical, tube and platlets. It can be developed by large particle to form small particle having dimension in micro or nano size.
Layered silicates: It is also known as clay minerals and it is part of class of silicate minerals and phllyosilicate. It consists of natural as well as synthetic clays such as mica, bentonite, laponite, magadiite, fluorohectorite.
Nanotubes: Various types of nanotubes are available but mostly carbon nanotube is used. It is allotropes of carbon and belongs to fullerene structural family. The diameter of nanotubes is in a nanosize some in millimeter or in centimeter. Light-weight material can be developed by carbon nanotubes- reinforced composites. It possess high aspect ratio.
Spherical particles: It is mostly in spherical shape. It can be obtained by sol-gel process.
Property [15,16]
• To improve the thermal stability.
• To improve the packaging applications.
• To improved mechanical property (strength, elastic modules and dimensional stability).
• To improved properties of the polymer matrix.
• To improved the permeability.
Characterization of Bionanocomposites
Particle size
The particles are in nanosize. It can be find out by Motic images of particle with the help of Motic Microscope or Malvern Zetasizer.
Surface morphology
The surface morphology of particle can be studied by Scanning electron microscope.
Thermal study
Thermal study of bionanocomposite can be studied by differential scanning calorimetry. It can prove that whether the nanoparticles are homogenously entrapped within polymer or not.
Applications
- The nanocomposite materials are also good candidates for catalysts, gas-separation membranes, contact lenses and bioactive implant materials [17].
- Bionanocomposites are used in fabrication of scaffolds, implants, diagnostics and biomedical devices and drug-delivery systems. It also used in the cosmetics industries [12].
- Ahemad et al (2017), focused on the medical speciality and Cumulative applications of Chitosan centred bionanocomposites. He demonstrated the various schemes for the preparation of chitosan nanocomposites from different functional material, focusing on their application specifically in tissue engineering, drug and gene delivery, wound healing and bio imaging [12].
- Selvakumar et al (2015), developed the enriched adhesion of talc/ZnO nanocomposites on cotton fabric assisted by aloe-vera for bio-medical application mostly used on baby diaper [18].
- Sajid et al (2012), synthesized and characterized the silica nanocomposites for bone applications [19].
- Stodolak et al (2009), studied on nanocomposite fibres and find out its medical applications. She successfully modified the calcium alginate fibres with the nanofiliers which creates an opportunity in tissue regeneration by using the fibres as bioactive materials [20].
- Tamayo et al (2016), developed the copper polymer nanocomposites which is excellent and cost effective biocide controllingor inhibiting the growth of microorganisms and preventing foodborne diseases and nosocomial infections [21].
- Polymer nanocomposites used in gene delivery for purpose of anticancer drug delivery, pDNA transfection, siRNA and DOX delivery, CPT drug and report [22].
- It is used as actuators in artificial muscle [23].
- Kendre et al (2017), developed the Bosentan nanocomposite by using amphiphilic graft co-polymer-carrier which is soluplus to enhanced the solubility, dissolution and bioavailability. He prepared the graft co-polymer-based nanocomposite formulation by using the single-emulsion technique [24].
- Kumar et al (2010), prepared and characterized the bio-nanocomposite films based on soy protein isolate and montmorillonite using melt extrusion. These bio-nanocomposite films could potentially be used for packaging of high moisture foods such as fresh fruits and vegetables to replace some of the existing plastics such as low density polyethylene (LDPE) and polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) [25].
- Cherian et al (2011), developed the cellulose nanocomposites with the help of nanofibres which is isolated by pineapple leaf fibers. The developed composites were utilized to fabricate various versatile medical implants. Pineapple leaf fibers derived nanocellulose embedded polyurethane has beenutilized as an attractive and readily available range of materials for the fabrication of vascular Prostheses and used for to make heart valves and coronary stent in the cardiovascular system [26]. Bionanocomposites mostly applicable in development of cardiovascular stent [27].
- It should be used inmanufacturing of compostable bags which is eco-friendly [28].
- Biopolymer-based nanocomposite is applicable in a treatment on Osteomyelitis, by the regeneration of tissue [29].
- It is mostly applicable in diagnostic, drug delivery, tissue regeneration [30].
References
- Darder M, Aranda P, Hitzky E. Bionanocomposites: A New Concept of Ecological, Bioinspired, and Functional Hybrid Materials. Adv. Mater. 2007; 19: 1309-1319.
- Khan A, Saba A, Nawazish S. Carrageenan Based Bionanocomposites as Drug Delivery Tool with Special Emphasis on the Influence of Ferromagnetic Nanoparticles. Hindawi Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. 2017: 1-17.
- Okpala C. Nanocomposites - An Overview, International Journal of Engineering Research and Development. 2013; 8: 17-23.
- Mondal S. Polymer Nano-Composite Membranes. J Membra Sci Technol. 2015; 5: 1-2.
- Sambarkar P, Patwekar S, Dudhgaonkar B. Polymer Nanocomposites: An Overview, International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2012; 4: 60-65.
- Zhao R, Peter T, Halley P. Emerging biodegradable materials: starch- and protein-based bio-nanocomposites, J Mater Sci. 2008; 43: 3058-3071.
- Shchipunov Y. Bionanocomposites: Green sustainable materials for the near future. Pure Appl. Chem. 2012; 84: 2579-2607.
- Camargo P, Satyanarayana K, Wypych F. Nanocomposites: Synthesis, Structure, Properties and New Application Opportunities. Materials Research. 2009; 12: 1-39.
- Siqueira G, Bras J, Dufresne A. Cellulosic Bionanocomposites: A Review of Preparation, Properties and Applications, Polymers. 2010; 2: 728-765.
- Azeredo H. Nanocomposites for food packaging applications, Food Research International. 2009; 42: 1240-1253.
- Oksman K, Aitomaki Y, Mathew A. Review of the recent developments in cellulose nanocomposite Processing, Composites. 2016; 83: 2-18.
- Ahmad M, Manzoor K, Singh S, Ikram S. Chitosan Centered Bionanocomposites for Medical Specialty and Curative Applications: A Review, International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 2017; 529: 200-217.
- Mousa M, Dong Y, Davies I. Recent advances in bionanocomposites: Preparation, properties, and applications, International Journal of Polymeric Materials and Polymeric Biomaterials. 2016; 65: 225-254.
- Amin M. Methods for Preparation of Nano-Compositesfor Outdoor Insulation Applications. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2013; 34: 173-184.
- Polymer nanocomposites. Seminar on Nanomaterials, National Technical University of Athens. 1-81.
- Kudumula K. Scope of Polymer Nano-composite in Bio-medical Applications, Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering. 2016; 13: 18-21.
- Tanahashi M. Development of Fabrication Methods of Filler/ PolymerNanocomposites. With Focus on Simple Melt-Compounding- Based Approach without Surface Modification of Nanofillers. Materials. 2010; 3: 1593-1619.
- Selvakumar D, ThenammaiA. Enriched adhesion of talc/ZnO nanocomposites on cotton fabric assisted by aloe-vera for bio-medical application, American Institute of Physics. 2015; 1-4.
- Sajid P, Devasena T. Synthesis and characterization of silica nanocomposites for bone applications. International research journal of pharmacy. 2012; 3: 173-177.
- Stodolak E, Paluszkiewicz C. Nanocomposite fibres for medical applications. Journal of Molecular Structure. 2009; 208-213.
- Tamayo L, Azocar M. Copper-polymer nanocomposites: An excellent and cost-effective biocide for use on antibacterial surfaces, Materials Science and Engineering C. 2016; 69: 391-1409.
- Fazli A, Moosaei R. Developments of Graphene-based Polymer Composites Processing Based on Novel Methods for Innovative Applications in Newborn Technologies. Indian Journal of Science and Technology. 2015; 8: 38-44.
- Gaharwar A, Peppas N. Nanocomposite Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications, Biotechnology and Bioengineering. 2013; 111: 441-453.
- Kendre P, Chaudhari P. Effect of amphiphilic graft co-polymer-carrier on physical stability of bosentan nanocomposite: Assessment of solubility, dissolution and bioavailability. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics. 2017.
- Cherian B, Leao A. Cellulose nanocomposites with nanofibres isolated from pineapple leaf fibers for medical applications, Carbohydrate Polymers. 2011; 86: 1790-1798
- Moravej M, Mantovani D. Biodegradable Metals for Cardiovascular Stent Application: Interests and New Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011; 12: 4250- 4270.
- Modi V, Shrives Y. Review on Green Polymer Nanocomposite and Their Applications. International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology. 2014; 3: 17651-17656.
- Okamoto M, John B. Synthetic biopolymer nanocomposites for tissue engineering Scaffolds, Progress in Polymer Science. 2013; 38: 1487-1503.
- Wu C, Gaharwar A. Development of Biomedical Polymer-Silicate Nanocomposites: A Materials Science Perspective, Materials. 2010; 3: 2986- 3005.