
Research Article
Ann Nurs Res Pract. 2023; 8(1): 1053.
A Multicentre, Fully Nurse-Coordinated, Intensive, Cardiovascular Prevention Intervention Programme after an Acute Coronary Syndrome
La Sala R¹*, De Stefano G², Paoli G², Sinno F³, Mattioli M², Ricci M², Gurgoglione FL², Barocelli F², Tuttolomondo D², Leporati S², Cazzato S², Ardissino D²
1Bachelor of Science in Nursing, Department of Health Professions - Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria di Parma - Department of Medicine and Surgery, University of Parma, Italy
2Division of Cardiology, Department of Cardio Toracic and Vascular - Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria di Parma, Parma, Italy
3Division of General Pediatrics-Urgency, Department of Pediatrics, Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria di Parma - Parma, Italy
*Corresponding author: La Sala RBachelor of Science in Nursing, Department of Health Professions - Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria di Parma - Department of Medicine and Surgery, University of Parma, Via Gramsci 14, 43100 Parma, Italy
Received: January 02, 2023; Accepted: February 09, 2023; Published: February 16, 2023
Abstract
The main objective of cardiovascular disease prevention is to reduce morbidity and mortality by promoting a healthy lifestyle, reducing risk factors, and improving adherence to medications. Secondary prevention after an acute coronary syndrome has proved to be effective in reducing new cardiovascular events, but its limited use in everyday clinical practice suggests there is considerable room for improvement. The short-term results of evidence-based studies of nurse-coordinated secondary prevention programmes have been positive, but there is a lack of long-term outcome data. The Aliance for Secondary Prevention after an acute coronary syndrome in the Emilia-Romagna region (ALLEPRE) is a multicentre, randomised, controlled trial designed to compare the effects of a structured, intensive nursing intervention on long-term outcomes and risk profiles after an acute coronary syndrome with those of the standard of care. Nurses fully coordinate secondary prevention in the intervention arm using a multi- dimensional nursing form after attending ad hoc teaching sessions. All of the patients randomised to the intervention group take part in nine 1-to-1 sessions with an experienced nurse from the participating centres that have the aim of promoting healthy lifestyles, reducing risk factors, and increasing adherence to medication over a mean period of five years. The primary clinical end point is the reduction in the risk of the 5-year occurrence of major adverse events.
Keywords: Multi-dimensional nursing form; Narrative; Acute coronary syndrome; Secondary prevention; Coronary heart disease
Abbreviations: ACS: acute coronary syndrome; ALLEPRE: ALLiance for sEcondary PREvention after an acute coronary syndrome; MNF: Multi-dimensional Nursing Form; NANDA: North American Nursing Diagnosis Association.
Introduction
Coronary heart disease is a chronic degenerative disease, and patients who recover from an Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) are at high risk of developing recurrent events [1].
Although secondary prevention measures have proved to be effective and are strongly recommended by all of the international guidelines [2,3], the EUROASPIRE IV surveys [4,5] have shown that there is still a high prevalence of conventional risk factors, that secondary prevention measures are inadequately implemented, and that their main goals were often not reached. In addition, there are considerable discrepancies in secondary prevention practices between centres and countries, and cardiac prevention and rehabilitation programmes are widely under-used despite their demonstrated effectiveness in reducing cardiovascular risk over time [6,7]. Over the last 10 years, nurses have been increasingly involved in successful cardiovascular risk management [8-10] but, although this has improved the levels of cardiovascular risk, it has not led to a clearly demonstrated reduction in hard endpoints such as major cardiovascular adverse events or mortality [7].
The aim of the ALLEPRE trial is to evaluate the benefit of a homogeneous, structured, secondary prevention intervention programme that is fully coordinated by nurses from in- and outpatient clinics in terms of major clinical events and the cardiovascular risk profiles of ACS patients living in the large Emilia-Romagna region of Italy. This paper describes the trial protocol with particular focus on the leadership role of nurses and the use of a specially developed Multi-dimensional Nursing Form (MNF).
Materials and Methods
Study Design
The ALLEPRE trial (NCT02522182) is a prospective, randomised, multicentre, interventional study designed to assess the efficacy of a fully nurse-coordinated prevention programme for patients hospitalised because of an ACS (Figure 1). Patient enrolment started in October 2012 and was completed in April 2022; the follow-up is still ongoing. The study was approved by the Ethics Committees of all of the participating centres, and written consent was obtained from all of the patients enrolled.
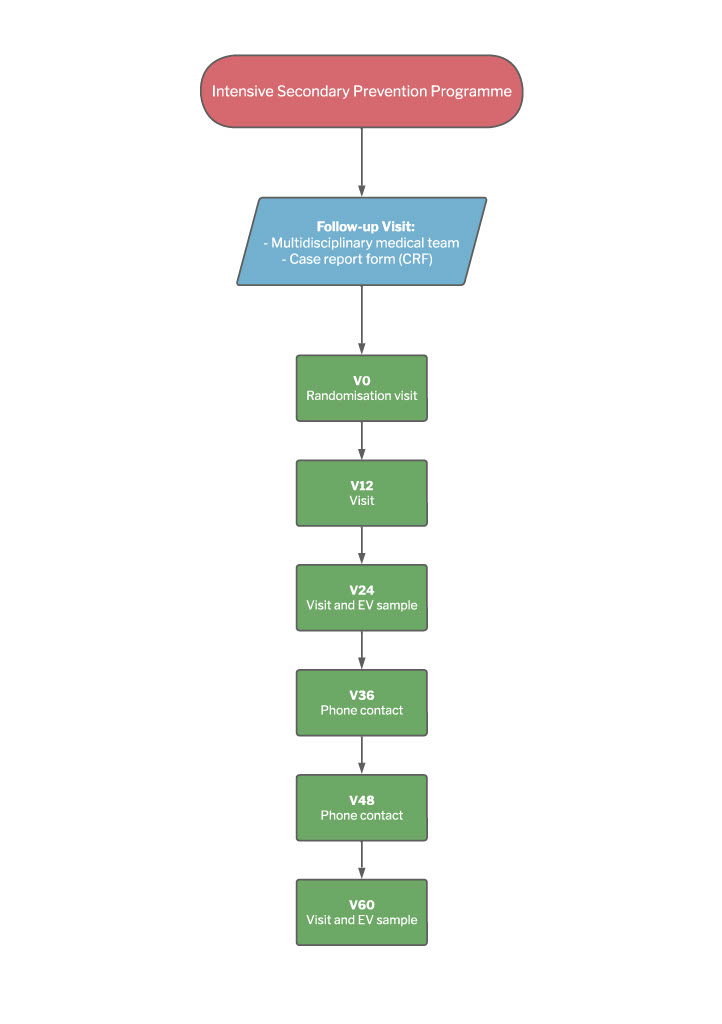
Figure 1 S1
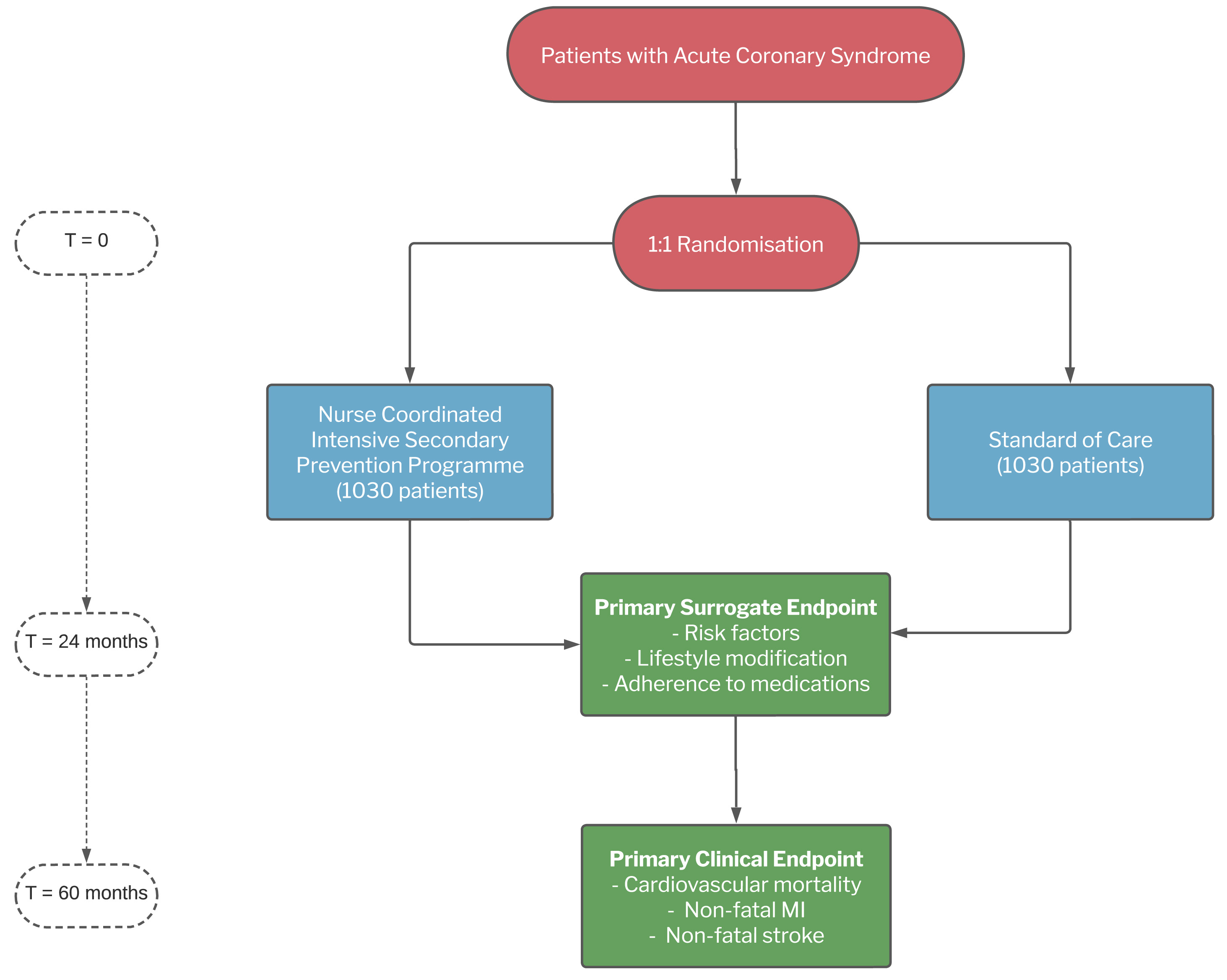
Figure 1 S2
Study Population
Eligible patients aged >18 years with an ACS (unstable angina, non–ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction [MI], or ST-segment elevation MI) admitted to the Cardiological Divisions of six participating centres in Emilia- Romagna (Italy) were considered for enrolment for up to 20 days after the index event and before being discharged. Once it had been verified that the patients were capable of participating in a prospective study, the only exclusion criterion was a life expectancy of <12 months because of severe non-cardiac disease.
Study Organisation
A preliminary training phase involved 100 professional nurses working at the participating hospitals and community service centres (about 50% of each): about 80% of the nurses were female, the average age of the participants was 35 years, and they had an average professional experience of 5-10 years. The training was centralised, coordinated by the Training and Continuous Education Centre of Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria di Parma), and involved a multidisciplinary team of medical, nursing, and psychological experts who used specially prepared paper-based teaching materials. The course consisted of three full-day sessions designed to train nurses in the secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease using appropriate communication strategies aimed at reducing risk factors, modifying lifestyles, and improving adherence to prescribed pharmacological therapy. The knowledge and skills acquired by the nurses was assessed and certified, with the recognition of credits for continuing education in medicine.
In order to standardise secondary prevention activities in the participating centres, the nurses were also trained in protocol procedures using an innovative paper clinical file called the Multi- dimensional Nursing Form (MNF) [11], which has been validated and described elsewhere [12] and is included in the Supplementary material [13].
Given the high turnover of nurses in Italian hospitals, the course is repeated when necessary to ensure a steady number of participating nurses over time.
Multi-dimensional Nursing form: During the training sessions, the nurses were trained how to use our innovative MNF, an interactive guide to patient assessment and education aimed at promoting all three of the study objectives. Based on the latest scientific evidence and the Cardiovascular Secondary Prevention Guidelines [6,14] it was prepared by a multi-disciplinary team of nurses, cardiologists and psychologists from the University Teaching Hospital of Parma, and will be used for all of the nine interviews planned for the patients in the study’s experimental arm: a pre-discharge interview, followed by others after one, three, six, 12, 18, 24, 36 and 48 months. It is based on a “cure” and “care” nursing paradigm that affectively integrates the bio-clinical and psycho-socio-relational dimensions of nursing using NANDA language [15] and a cardiovascular narrative approach (Table 1). The model considers CVD in the three senses of “illness”, “disease” and “sickness”, and uses quantitative and qualitative data collected by means of narrative-based interviews in order to make a multi-dimensional assessment of each patient with the aim of arriving at a more profound understanding of themr and their caregivers (the phase of nursing ascertainment). The model of care is based on a nurse/patient/caregiver co-construction of the therapeutic plan and personalised education in order to favour behaviours oriented towards reaching the ALLEPRE study end ponts. In addition to a socio-demographic part that includes the patient’s personal details and CV medical history (the number of CV events at the time of admission), the MNF is divided into five areas, each of which is covered during all of the nine interviews:
A) The assessment of classic risk factors (diabetes, smoking, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and obesity);
B) The assessment of additive risk factors (physical activity, diet, and alcohol consumption);
C) The assessment of psycho-social risk factors (anxiety, depression, anger/hostility, type A and D personality patterns, self-efficacy, and social support);
D) The assessment of adherence to CV drugs (aspirin, anti-aggregant, ACE inibitor/sartan, statin, beta- blocker) and other drugs (e.g. antidepressants and anxiolytics), as well as the intentional (insufficient information, incredulity and irrationality) and non-intentional factors (forgetting) underlying therapeutic non-compliance;
E) A narrative nursing assessment.
Areas A-D have fields for the ascertainment of CV risk factors, the definition of selected nursing diagnoses and related objectives, and the definition of the required educational interventions. Area E consists of a grid with stimulus questions that guide the narrative interview, which is essential for completing the assessment of aspects relating to disease perception, strategies for coping with the critical event, and the difficulties perceived by the patient in relation to the prescribed treatment (e.g. What are the difficulties you may encounter once you return home? What strategies will help you to confront the disease and its treatment?). (Table 1) shows some sample extracts of the MNF.
The nurses autonomously activate a multi-disciplinary medical network for the specific purposes of treating diabetes and/or hypertension, encouraging patients to stop smoking, promoting physical activity, and providing psychological support in accordance with the MNF recommendations (Supplementary Materials S2, S3, and S4).
Given the nurse-coordinated management of the prevention programme, the nurses undergo quality assessments made by a dedicated psychologist at each centre to evaluate the validity of their recommendations, the effectiveness of their communications, their adherence to protocol procedures, and their overall empathy.
Re-training sessions take place in the case of a nurse with a suboptimal score. In this sense, the completed MNF cards (n = 100/300) were randomly analyzed in order to evaluate the effectiveness of the MNF in terms of the completeness and appropriateness of the “closed” fields, and the completeness and accuracy of the “open” fields. In general, the MNF has proved to be an effective means of assessing and planning the process of care. The appropriateness, accuracy and completeness of the closed and open fields were above the pre-established standard (80%).
The patients randomized to standard care follow the standard secondary prevention practices of the hospital they attend.
End points: The ALLEPRE study has two co-primary endpoints: a clinical and a surrogate endpoint. The primary clinical end point is a composite of cardiovascular death, the first occurrence of a non-fatal re-infarction, and non- fatal stroke after 5 years (minimum 24 months, maximum 86 months; median treatment duration 60 months). The secondary clinical endpoints are: 1) a composite of cardiovascular mortality, non-fatal re-infarction, non-fatal stroke, and myocardial ischemia-driven revascularisation; 2) non-fatal reinfarction; 3) non-fatal stroke; 4) cardiovascular mortality; and 5) all-cause mortality.
The primary surrogate endpoint is the improvement in achieving the goals relating to risk factors and lifestyle and pharmacological adherence suggested by all of the international guidelines [2,16,17] between baseline and month 24. The secondary endpoint is the improvement in achieving the goals of the co-primary surrogate end point between baseline and month 60.
Follow-up is stil ongoing at the time of writing: outcomes in both arms are recorded arms by cardiologists during three programmed follow-up visits (12, 24, and 60 months after randomisation) using a web-based electronic case report form. At the end of the study, the outcomes will be verified on the basis of the clinical records and/or death certificate of the individual patients, and all of the events will be adjudicated by an independent Clinical Event Committee of three cardiologists who are unaware of the patients’ treatment allocation.
On the basis of the results of the GRACE UK-Belgian Study [1], it is conservatively expected that the cumulative rate of the co-primary composite clinical endpoint of cardiovascular mortality, non-fatal re-infarction, and non-fatal stroke in the standard care arm during the 5 years of follow-up will be 28%. Using the formula of Lakatos and Lan [20], at least 1,030 patients are required in each group to detect a 25% risk reduction in the experimental arm with 90% power and a 2-sided significance level of 0.25. The estimated sample size is also more than sufficient for the 24-month analysis of the co-primary surrogate endpoint.
Expected Results and Discussion
Over the last 50 years, the importance of treating the acute phase of ACS has been clearly demonstrated [2,3] but, despite the newly available drugs and the evolving technologies of cardiovascular procedures, post-ACS mortality and morbidity rates remain high [1]. Secondary prevention, which consists of controlling established risk factors, modifying life styles, and ensuring adherence to appropriate treatment regimens, has proved to be effective in patients with coronary heart disease and is strongly recommended by all of the international cardiovascular societies [2,4,18].
The involvement of nurses is a key element in the primary and secondary prevention of CVDs [19-21]. Nurse-led health education programmes increase the patients’ awareness and understanding of a disease and its treatment, and improve their expectations concerning their health [22], thus favouring treatment compliance [7,9,10,22,23]. Even relatively brief, individualised interventions [24-26] based on multiple methods (e.g. direct con tact, printed booklets, and the use of audio-visual aids) can lead to self-care behaviours [24], and may improve outcomes [25,26] even in the long term [27].
One major challenge when trying to improve health results in ACS patients is to implement multi-dimensional, structured nursing care pathways oriented towards therapeutic continuity [28,29] because the limitations of many programmes include the partial nature of their goals (e.g. concentrating on only one or just a few classic risk factors) and the lack of structured healthcare instruments whose efficacy has been demonstrated in terms of outcomes. For example, the Global Secondary Prevention Strategies to Limit Event Recurrence after Myocardial Infarction study does not propose a nursing care model for managing patients during follow-up or describe the changes in nursing care activities generated by the training, and the RESPONSE study [31] did not specify whether or not the healthcare professionals had participated in a special training programme, and therefore does not describe what the content of such a programme might have been or what method was used. Finally, the paper describing the principal results of the EUROACTION study [10] does not mention the training of nurses, the nursing model and instruments used, or any collaboration with other professionals such as psychologists or dieticians.
The GOSPEL study (the only trial measuring the clinical effects) failed to demonstrate any beneficial effect on its primary composite endpoint of cardiovascular mortality, non-fatal MI, non-fatal stroke, and hospitalisation due to angina pectoris, heart failure, or urgent revascularisation [7] mainly because of recruitment bias (a relatively young and low-risk population with recent MI within three months of routine referral to a cardiac rehabilitation centre) and a loss of power due to the fact that a large proportion of the patients were lost to follow-up and/or dropped out.
Our study is the first to evaluate the use of an innovative nursing instrument aimed at maximising the potentially great contribution that nurses can make to CV secondary prevention. Based on a multi-disciplinary approach, it allows a multi-dimensional assessment that takes into account bio-clinical and psycho-socio-relational factors, and thus responds to four major healthcare needs: 1) to assess risk factors and treatment compliance in ACS patients by means of standardised parameters based on scientific evidence; 2) to identify disease-related problems and factors predicting noncompliance by means of narrative interviews that allow the personalisation of subsequent interventions; 3) to maintain continuity of care between hospital and home with the aim of improving health outcomes by increasing treatment compliance and reducing the incidence of re-infarctions and re-hospitalizations as a result of multiple follow-up visits; and 4) to overcome the known limitations of concentrating exclusively on bio-clinical findings and ignoring psycho-socio-relational factors by evaluating the efficacy of an instrument in terms of its effects on nursing practices in various operational contexts.
The inclusion of the MNF in a 5-year clinical trial will make it possible to assess whether the patients treated using the form’s underlying model of integrated care leads to better health outcomes than those obtained using traditional standards of care. The trial incorporates all of the elements that heve been shown to be most effective in meta- analyses, [5,32-37] and can be expected to provide a clinical benefit in terms of a lasting improvement in risk profiles.
Conclusions
The ALLEPRE trial is the first to test a structured, fully nurse-led, intensive secondary prevention programme based on a broad multi-disciplinary network of primary care and hospital nurses in a large population of high-risk ACS patients in Emilia-Romagna (which is sufficiently representative of Italy as a whole) by evaluating its clinical efficacy on major endpoints and its feasibility and impact on the regional healthcare system. Its two main limitations are that it is an open-label trial that may lead to a risk of ascertainment bias (although this should be mitigated by the activities of the Clinical Event Committee), and the fact that the patients in the control group follow heterogeneous prevention programms that depend on the policies of their individual hospitals, but this simply reflects real world heterogeneity.
Funding
The first phase of this trial was supported by a grant from Emilia Romagna’s Regional government; the second phase has benefited from a financial contribution made by AstraZeneca. The authors are solely responsible for the design and conduct of the study, all of the analyses, and the contents of this paper. Supplementary data relating to this article can be found online at https://doi. org/10.1016/j.ahj.2018.06.001.
References
- Fox KA, Carruthers KF, Dunbar DR, Graham C, Manning JR, Raedt D, et al. Underestimated and under- recognized: the late consequences of acute coronary syndrome (GRACE UK-Belgian Study). Eur Heart J. 2010; 31: 2755-64.
- Steg PG, James SK, Atar D, Badano LP, Lundqvist CB, et al. ESC guidelines for the management of acute myocar-dial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation: the Task Force on the Management of ST-Segment Elevation Acute Myocardial Infarction of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2012; 33: 2569–629.
- Roffi M, Patrono C, Collet JP, Mueller C, Valgimigli M, et al. Authors/Task Force Members. 2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation: Task Force for the Management of Acute Coronary Syndromes in Patients Presenting Without Persistent ST-Segment Elevation of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J. 2016; 37: 267-315.
- Piepoli MF, Hoes AW, Agewall S, Albus C, Brotons C, et al. European guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical prac- tice: the Sixth Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and Other Societies on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice. Eur Heart J. 2016; 37: 2315–81.
- Kotseva K, Wood D, Bacquer DD, Backer GD, Ryden L, et al. EUROASPIRE IV: a European Society of Cardiology survey on the lifestyle, risk factor and therapeutic management of coronary patients from 24 European countries. EUROASPIRE Investigators. 2016; 23: 636–684.
- Clark AM, Hartling L, Vandermeer B, McAlister FA. Meta-analysis: secondary prevention programs for patients with coronary artery disease. Ann Intern Med. 2005; 143: 659–72.
- Giannuzzi P, Temporelli PL, Marchioli R. Global secondary prevention strategies to limit event recurrence after myocardial infarction: results of the GOSPEL study, a multicenter, randomized controlled trial from the Italian Cardiac Rehabilitation Network. Arch Intern Med. 2008; 168: 2194–204.
- Allen JK, Blumenthal RS, Simenon M. Nurse case management of hypercholesterolemia in patients with coronary heart disease: results of a randomized clinical trial. Am Heart J. 2002; 144: 678–86.
- Jorstad HT, Birgelen CV, Alings AM, Liem A, Dantzig JM, et al. Effect of a nurse-coordinated prevention programme on cardiovascular risk after an acute coronary syndrome: main results of the RESPONSE randomized trial. Heart. 2013; 99: 1421–1451.
- Wood DA, Kotseva K, Connolly S. Nurse-coordinated multidisciplinary, family-based cardiovascular disease prevention programme (EUROACTION) for patients with coronary heart disease and asymptomatic individuals at high risk of cardiovascular disease: a paired, cluster-randomized controlled trial. Lancet. 2008; 371: 1999–2012.
- La Sala R, Foà R, Paoli G, Mattioli G, Solinas M, Artioli E, et al. Multi-dimensional nursing form: a novel means of approaching nurse-led secondary cardiology prevention. Acta Biomed. 2015; 86: 26828335– 26828335.
- La Sala R, Foà R, Paoli G. Multi-dimensional nursing form: a novel means of approaching nurse-led sec- ondary cardiology prevention. Acta Biomed. 2016; 86: 174–82.
- Paoli G, Notarangelo MF, Mattioli M, La Sala R, Foà R, Solinas C, et al. ALLiance for sEcondary PREvention after an acute coronary syndrome. The ALLEPRE trial: A multicenter fully nurse-coordinated intensive intervention program. Am Heart J. 2018; 203: 12-16.
- Members WC, Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, Butler J, De C, et al. American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation. 2013; 128: e147-239.
- La Sala R. Traditional and integrated models of care compared: bio-clinical and psycho-socio-relational outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndromes [dissertation]. La Sala Theses, 2013.
- Ibanez B, James S, Agewall S. ESC Guidelines for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation: the Task Force for the Management of Acute Myocardial Infarction in Patients Presenting with ST-Segment Elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2017; 39: 119–77.
- American Diabetes Association standards of medical care in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2017; 40: 1–142.
- O’gara PT, Kushner FG, Ascheim DD. ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of ST-elevation myocar- dial infarction. A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013; 61: 78–140.
- Chummun H, Gopaul K, Lutchman A. Current guidance on the management of acute coronary syndrome. Br J Nurs. 2009; 18: 1292–1300.
- Delaney EK, Murchie P, Lee AJ, Ritchie LD, Campbell NC. Secondary prevention clinics for coronary heart disease: a 10-year follow-up of a randomised controlled trial in primary care. Heart. 2008; 94: 1419-23.
- Chummun H, Gopaul K, Lutchman A. Current guidance on the management of acute coronary syndrome. Br J Nurs. 2009; 18: 1292–8.
- Briggs J. Nurse-led interventions to reduce cardiac risk factors in adults. Nurs Health Sci. 2010; 12: 288– 91.
- Holst M, Willenheimer R, Martensson J, Lindholm M. Telephone follow-up of self-care behaviour after a single session education of patients with heart failure in primary health care. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2007; 6: 153–162.
- Amodeo R, Ponti D, Sorbara A, Avanzini L, F, Giulio D, et al. How to increase patient knowledge of their coronary heart disease: impact of an educational meeting led by nurses. G Ital Cardiol. 2009; 10: 249–55.
- Buckley T, Mckinley S, Gallagher R, Dracupck, Moserd DK, Aitkene LM. The effect of education and counselling on knowledge, attitudes and beliefs about responses to acute myocardial infarction symptoms. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2007; 6: 105–111.
- Kirchberger I, Meisinger C, Seidl H, Wende R, Kuch B, Holle R. Nurse-based case management for aged patients with myocardial infarction: study protocol of a randomized controlled trial. BMC Geriatr. 2010; 27: 10–29.
- Tokunaga-Nakawatase Y, Taru C, Miyawaki I. Development of an evaluation scale for self-management behavior related to physical activity of patients with coronary heart disease. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2012; 11: 168-74.
- Fredericks S, Beanlands H, Spalding K, Silva DM. Effects of the characteristics of teaching on the outcomes of heart failure patient education interventions: a systematic review. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2009; 9: 30-7.
- Mckinley S, Dracup K, Moser DK, Riegel B, Doering LV, Meischke H, et al. The effect of a short one-on- one nursing intervention on knowledge, attitudes and beliefs related to response to acute coronary syndrome in people with coronary heart disease: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Nurs Stud. 2009; 46: 1037-1046.
- Sreedharan J, Muttappallymyalil J, Venkatramana M. Nurses’ attitude and practice in providing tobacco cessation care to patients. J Prev Med Hyg. 2010; 51: 57-61.
- Longo F, Salvatore D, Tasselli S. Are Public Health Authorities Able to “Steer” rather than “Row”? An Empirical Analysis in the Italian NHS. International Journal of Health Planning and Management. 2011; 26: 319–333.
- Leventhal H, Marcia JE, Carlsonc B, Geest DS. Negotiating compliance in heart failure: Remaining issues and questions. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2005; 4: 298–307.
- Giannuzzi P, Temporelli PL, Marchioli R, Maggioni AP, Balestroni G, Ceci V, et al. Global secondary prevention strategies to limit event recurrence after myocardial infarction: results of the GOSPEL study, a multicenter, randomized controlled trial from the Italian Cardiac Rehabilitation Network. Arch Intern Med. 1920; 168: 2194–204.
- Jorstad HT, Alings AM, Liem AH, Birgelen CV, Tijssen JG, Vries CJD, et al. RESPONSE study: Randomised Evaluation of Secondary Prevention by Outpatient Nurse SpEcialists: Study design, objectives and expected results. Neth Heart J. 2009; 17: 2758346–2758346.
- Lorgeril MD, Salen P, Martin JL, Monjaud I, Mamelle N. Mediterranean diet, traditional risk factors, and the rate of cardiovascular complications after myocardial infarction: final report of the Lyon Diet Heart Study. Diffusione. 1999; 99: 779–85.
- Kotseva K, Wood D, Backer DG, Bacquer DD, Pyorala K, et al. EUROASPIRE III: a survey on the lifestyle, risk factors and use of cardioprotective drug therapies in coronary patients from 22 European countries. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2009; 16: 121–37.
- Kotseva K, Wood D, Backer DG, Bacquer DD, Pyorala K, et al. EUROASPIRE Study Group. Cardiovascular prevention guidelines in daily practice: a comparison of EUROASPIRE I, II, and III surveys in eight European countries. Lancet. 2009; 373: 929–40.