
Case Report
Austin J Otolaryngol. 2023; 9(1): 1127.
Exophytic Papilloma
Tantry D¹, Tantry G² and Shriyan AJ³
1Associate Professor, Department of ENT, AJIMS, Mangalore
2Professor, Department of Anesthesia, AJIMS, Mangalore
3Postgraduate, Department of ENT, AJIMS, Mangalore
*Corresponding author: Abhinandan J Shriyan 3rd Year Postgraduate, Department of ENT, AJIMS, Kuntikana, Mangalore, Karnataka, India
Received: January 03, 2023; Accepted: February 09, 2023; Published: February 16, 2023
Abstract
Schneiderian papillomas are papillomas arising in the sinonasal tract, which is lined with Schneiderian epithelium, ectodermally derived respiratory mucosa [1,2]. This distinctive epithelium can give rise to three histologically unique types of papillomas: exophytic (fungiform, septal, and squamous), inverted (inverting), and oncocytic (cylindrical cell and columnar) papillomas. Exophytic papillomas almost exclusively arise from the nasal septum with rare cases arising from the vestibule or middle turbinate. In this paper a case of Exophytic papilloma in 52 year old male is presented.
Keywords: Sinonasal Papilloma; Exophytic Papilloma
Introduction
Sinonasal papillomas represent 0.5%-4% of all sinonasal tumors [1-5]. The first real distinction between papillomas and polyps was made by Kramer and Som [6] in 1935. To date, 3 types of sinonasal papillomas, also known as Schneiderian papillomas, have been described histologically: inverted, exophytic, and oncocytic. The exophytic papilloma is usually diagnosed after nasal obstruction or epistaxis. The macroscopic appearance is that of a whitish papillomatous tumor with a wide implantation base. The most common localization is the anterior wall of the septum, a transition zone between a cylindrical pseudostratified squamous epithelium and mucosal respiratory type. Microscopically, they are composed of papillary fronds with a fibrovascular core covered by epithelium of various aspects: squamous to transitional, ciliated, and pseudostratified columnar. The involvement of the Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) types 6 and 11 in the pathogenesis of exophytic papilloma is suggested by the presence of koilocytes on pathological examination, whereas Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) analysis of samples exhibit different HPV genotypes [3,7-9]. Although inverted papillomas have been codified and treatment approaches standardized, the treatment of pure exophytic papilloma is poorly described [1,4]. They are generally removed by endonasal surgery under endoscopic guidance with a recurrence rate of 22% [1,10]. The purpose of this retrospective study is to describe the clinical and pathological features of exophytic papillomas and to report our experience in their management.
Case Report
A 52 year old male patient came with complaints of left sided nasal obstruction and postnasal drip since 2 years and occasional headache. DNE showed greyish mass arising from left middle meatus extending into left nasal cavity.
HPE Report
Sections show multiple polypoidal tissue bits lined by hyperplastic respiratory epithelium with squamous metaplasia and transitional epithelium. The stroma is edematous with mixed inflammatory infiltrate composed of lymphocytes, plasma cells and eosinophils. At places papillary arrangement is noted with exophytic growth pattern and with focal areas displaying downward endophytic growth . Impression :- Features are of Schneiderian papilloma (exophytic papilloma)-left nasal polyp.
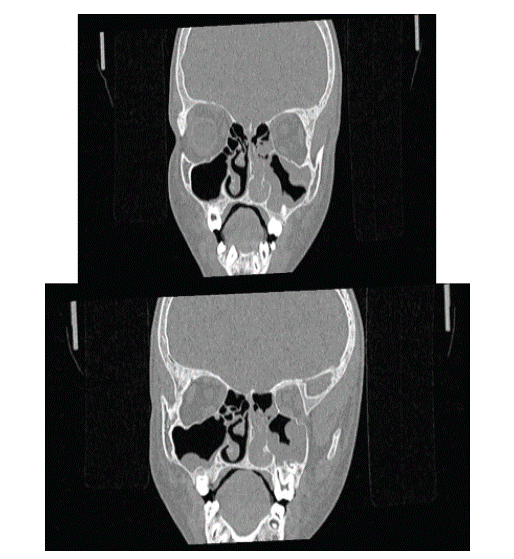
Treatment: FESS( left middle meatal antrostomy) + septoplasty was done.
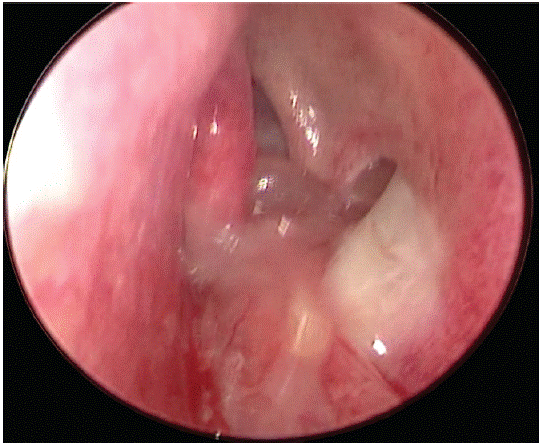
(Pre- Op image)
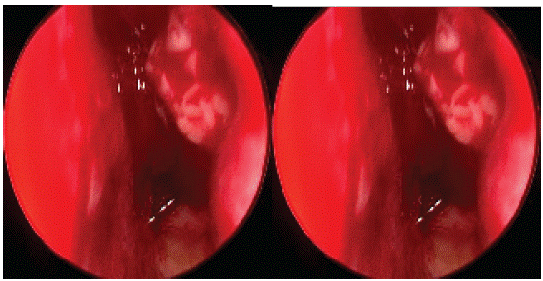
(Intra-Op images)
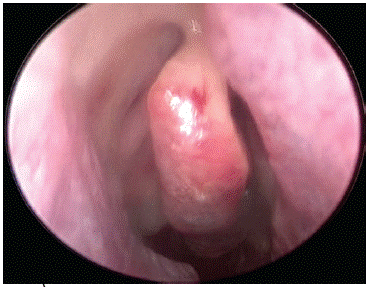
(Post-Op image)
Discussion
Sinonasal papillomas account for 0.5–4% of all nasal tumors [7]. IP and exophytic papillomas are the most commonly diagnosed subtypes, each accounting for almost one-half of all sinonasal papillomas, and oncocytic papillomas are the rarest type, found only in 3–5% of all papillomas [2,8]. Exophytic papillomas almost exclusively arise from the nasal septum with rare cases arising from the vestibule or middle turbinate. The Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) types 6, 11, 16, and 18 have been implicated as a leading factor in the development of IP and exophytic papillomas, although HPV does not seem to be related to the formation of OSP [1-11]. Exophytic papillomas grossly appear as gray–tan, exophytic, “mushroom-shaped” verrucous papillary proliferations classically arising from the anterior nasal septum attached to the underlying mucosa by a narrow stalk [7,10,19]. Histologically, exophytic papillomas have a cellular composition like IP with branching, exophytic proliferations with a fibrovascular core lined by well-differentiated stratified squamous epithelium .Unlike IP, keratin formation can be present in the surface epithelium, seen as hyper- and parakeratosis, and chronic inflammatory cells are uncommon. Koilocytosis may be seen in the superficial cells.
Conclusion
It is rare for an exophytic nasal papilloma to arise from maxillary sinus.
Patient Perspective
Satisfactory
Informed Consent
Separate informed consent was taken prior to CT scan and surgery.
References
- Vorasubin N, Vira D, Suh JD, Bhuta S, Wang MB. Schneiderian papillomas: comparative review of exophytic, oncocytic, and inverted types. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2013; 27: 287-292.
- Leoncini G, Zanetti L. The papillomas of the sinonasal tract. A comprehensive review. Pathologica. 2017; 109: 31-34.
- Meatchi T, Badoual C. Histopathologie des tumeurs benignes et malignes Rhino-sinusiennes. In: Traite d’ORL. Paris, France, Flammarion, 2008: 223-229. (Medecine-sciences).
- Serrano E, Vergez S, Percodani J. Tumeurs benignes rhinosinusiennes. In: Traite d’ORL. Paris, France, Flammarion, 2008: 230-240. (Medecine-sciences).
- Barnes L, Eveson J, Reichart P, et al. World Health Organization International Classification. Pathology and Genetics of Head and Neck Tumors. Lyon, France, IARC Press, 2005.
- Kramer R, Som ML. True papilloma of the nasal cavity. Arch Otolaryngol. 1935; 22: 22-43.
- Syrjänen KJ. HPV infections in benign and malignant sinonasal lesions. J Clin Pathol. 2003; 56: 174-181.
- Syrjänen K, Syrjänen S. Detection of human papillomavirus in sinonasal papillomas: systematic review and meta-analysis. Laryngoscope. 2013; 123: 181-192.
- Kashima HK, Kessis T, Hruban RH, Wu TC, Zinreich SJ, et al. Human papillomavirus in sinonasal papillomas and squamous cell carcinoma. Laryngoscope. 1992; 102: 973-976.
- Perez-Ordo~nez B. Hamartomas, papillomas and adenocarcinomas of the sinonasal tract and nasopharynx. J Clin Pathol. 2009; 62: 1085-1095.
- Batsakis JG, and Suarez P. Schneiderian papillomas and carcinomas: A review. Adv Anat Pathol. 2001; 8: 53–64.
- Cheng T-Y, Ueng S-H, Chen Y-L, et al. Oncocytic Schneiderian papilloma found in a recurrent chronic paranasal sinusitis. Chang Gung Med J. 2006; 29: 336–341.
- Ward N. A mirror of the practice of medicine and surgery in the hospitals of London. London Hosp Lancet. 1854; 2: 480–482.
- Ringertz N. Pathology of malignant tumors arising in the nasal and paranasal cavities and maxilla. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh). 1938; 27: 31–42.
- Shanmugaratnam K, Sobin LH. The World Health Organization histological classification of tumours of the upper respiratory tract and ear. A commentary on the second edition. Cancer. 1993; 71: 2689–2697.
- Rosenfeld RM, Andes D, Bhattacharyya N, et al. Clinical practice guideline: Adult sinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007; 137: S1–S31.
- Bawa R, Allen GC, and Ramadan HH. Cylindrical cell papilloma of the nasal septum. Ear Nose Throat J. 1995; 74: 179–181.
- Barnes L, Bedetti C. Oncocytic Schneiderian papilloma: A reappraisal of cylindrical cell papilloma of the sinonasal tract. Hum Pathol. 1984; 15: 344–351.
- Anari S, Carrie S. Sinonasal inverted papilloma: Narrative review. J Laryngol Otol. 2010; 124: 705–715.
- Perez-Ordon˜ ez B. Hamartomas, papillomas and adenocarcinomas of the sinonasal tract and nasopharynx. J Clin Pathol. 2009; 62: 1085–1095.
- Wood JW, Casiano RR. Inverted papillomas and benign nonneoplastic lesions of the nasal cavity. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2012; 26: 157–163.
- Orlandi RR, Rubin A, Terrell JE, et al. Sinus inflammation associated with contralateral inverted papilloma. Am J Rhinol. 2002; 16: 91–95.
- Bhalla RK, Wright ED. Predicting the site of attachment of sinonasal inverted papilloma. Rhinology. 2009; 47: 345-348.
- Okamoto T, Kodama S, Nomi N, Umemoto S, Suzuki M. Expression of bone morphogenic protein in sinonasal inverted papilloma with new bone formation. Allergy Rhinol (Providence). 2011; 2: 16–20.
- Melroy CT, Senior BA. Benign sinonasal neoplasms: A focus on inverting papilloma. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2006; 39: 601–617.
- Chrysovergis A, Paschalidis J, Michaels L, Bibas A. Nasopharyngeal cylindrical cell papilloma. J Laryngol Otol. 2011; 125: 86–88.
- Kaufman MR, Brandwein MS, Lawson W. Sinonasal papillomas: Clinicopathologic review of 40 patients with inverted and oncocytic Schneiderian papillomas. Laryngoscope. 2002; 112: 1372–1377.
- Kim S, Lee OY, Choi J, Park YH, Kim YM, et al. Pattern of expression of cell cycle-related proteins in malignant transformation of sinonasal inverted papilloma. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2011; 25: 75–81.
- Hyams VJ. Papillomas of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses: A clinicopathological study of 315 cases. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1971; 80: 192–206.
- Kapadia SB, Barnes L, Pelzman K, Mirani N, Heffner DK, et al. Carcinoma ex oncocytic Schneiderian (cylindrical cell) papilloma. Am J Otolaryngol. 1993; 14: 332–338.