Abstract
Objective: To investigate research patterns of international author collaboration in pharmacology and pharmaceutics by collecting data from Medline and to visualize data using Google maps and Social Network Analysis (SNA).
Methods: Selecting 14,403 abstracts, author names and countries, keywords, and Medical Subject Headings (MESH) on November 23, 2017 from the Medline based on the title involving pharmacology or pharmaceutics, we reported following features of pharmacology and pharmaceutics: (1) nation and journal distribution; (2) main keywords frequently presented in papers; (3) the prominent author and the research domain defined by the MESH terms. We programmed Microsoft Excel VBA routines to extract data from Medline. Google Maps and SNA Pajek software were used for displaying visual representations on features of pharmacology and pharmaceutics.
Results: We found that (1) the most number of nations are from US.(3272, 40.27%) and UK.(721, 8.87%); (2) the most number of journals in production of pharmacology and pharmaceutics are J Pharmacol Exp Ther (351, 2.44%) and Arzneimittel-forschung (315, 2.19%); (3) the most linked keywords are pharmacology and experimental lab study; (4) the research domain defined by MESH terms are pharmacology and molecular targeted therapy for the prominent Author Joanna L Sharman.
Conclusion: Social network analysis provides wide and deep insight into the relationships among entities or subjects. The results drawn by Google maps can be provided to readers for future paper submission in academics.
Keywords: Authorship collaboration; Google Maps; Social network analysis; Medline
Introduction
Google Maps offers a global view of geospatial visualization for our interesting objects dispersed on a map [1,2]. However, only four papers were collected in Medline library using keyword Google map to search on November 22, 2017. Many papers [3-5] have conducted studies on co-author collaboration in academics, but failed to display results using graphical representation on Google maps.
The co-author relation is similar to the comorbid co-occurred with one another in medicine. Many studies have made efforts to explore the association of two or more entities (or objects) such as obesity and altered aspirin pharmacology [6] and pharmacology and perioperative considerations of pain medications [7]. The pattern of international co-author collaboration in pharmacology and pharmaceutics is still unclear. It is hard using traditional statistics to observe the association of two or more symptoms co-occurred at one moment. Even if Social Network Analysis (SNA) [8] has been launched to explore the pattern of elements in a system, none were found incorporating SNA with Google maps to report their results.
An apocryphal story often told to illustrate the concept of co- occurrence is about beer and diaper sales. It usually goes along with both beer and diaper sales which were strongly correlated [9-11] in a market place. All possible pairs our observed in a system can be counted using advanced computer techniques. However, we have not seen any computer algorithms that can teach us how to select the most possible pairs co-occurred in a system.
Social network analysis (SNA)
Social Network Analysis (SNA) [12] has been applied to authorship collaboration in bibliometrics. Co-authorship among researchers can form a type of social network, called co-author network [13]. We are thus interested in applying SNA to investigate the most number of authors and keywords in relation for the topic of pharmacology and pharmaceutics in which we are interested.
Author collaborations and international relations
Many papers have been saved in Medline library. However, few extracted data from Medline to investigate valuable information regarding author relations and keyword frequency in an academic domain. Whether the field of pharmacology and pharmaceutics is similar to the finding [14,15] that the dominant nations come from U.S. and Europe. International collaboration in science has increased rapidly in recent decades [16]. Mass data storage electronic communications [17] and less expensive travel might be ones of the drivers and facilitators [18] to facilitate international co-author collaboration in paper publication. Some governments of notably smaller nations [19] also invest purposefully in the stimulation of internationalization. We are thus interested in investigating the pattern of author collaboration in pharmacology and pharmaceutics using Google maps.
Aims of the study
Our aims are to investigate patterns of international collaborations in pharmacology and pharmaceutics by collecting data from Medline and to visualize results in following representations: (1) nation and journal distribution; (2) main keywords frequently presented in papers; (3) the prominent author and the research domain defined by the Medical Subject Headings (MESH).
Methods
Data sources
We programmed Microsoft Excel VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) modules for extracting abstracts and their corresponding coauthor names as well as keywords on November 23, 2017 from Medline library. Only those abstracts entitled with pharmacology (or pharmaceutics) and labeled with Journal Article were included. Others like those labeled with Published Erratum, Editorial or those without author nation were excluded from this study. A total of 14,403 eligible abstracts were obtained from Medline since 1992. Only 8,129 papers are labeled with 1st author nation in Medline database.
Data arrangement to fit SNA requirement
We analyzed all eligible papers with complete data including author countries, MESH terms. Prior to visualize representations using SNA, we organized data in compliance with the SNA format and guidelines using Pajek software [20]. Microsoft Excel VBA was used to deal with data fitting to the SNA requirement.
Graphical representations to report
Author nations and their relations: Two cross tables (i.e., columns for publication years and rows for the 1st author nations as well as journals) were made for presenting the distribution of nations and the most number of journals publishing papers of pharmacology and pharmaceutics. The bigger bubble means the more number of the nodes (i.e., nations, authors, or MESH terms in this study). The wider line indicates the stronger relations between two nodes. Community clusters are filled with different colors in bubbles.
Keywords, authors and MESH terms to present the research domain: Keywords are defined by authors. Research domain can be highlighted by the relation between any pair of two keywords using SNA. The presentation for the bubble and line is interpreted similar to the previous section.
Statistical tools and data analyses: Google Maps [21] and SNA Pajek software [22] were used to display visualized representations for papers published in the field of pharmacology and pharmaceutics. Author-made Excel VBA modules were applied to organize data.
Results
Author nations and their relations
A total of 8,129 eligible papers with complete author nations based on journal article since 1992 are shown in Table1. We can see that the most number of nations are from US. (3272, 40.27%) and UK. (721, 8.87%). The trend in the number of publications with authorship from countries is present in the column of correlation (denoted by corr.) in Table 1. The diagram (shown by SNA and Google maps) in Figure 1 displays author collaboration among nations. The highest productive nations are from US. and Europe. China (corr. =0.98) and Australia (corr. =0.74) also placed a distinct portion and an increasing trend. Any nation collaborated with other nations are shown with a blue line. Interested authors are recommending clicking the bubble of interest to see details on a website at reference [23].
Nation
1992-2007
2008
2009
2010
2011
2012
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
Total
corr.
%
U.S
2012
107
100
117
137
129
129
130
127
147
136
3272
0.8
40.3
U.K
376
21
33
33
40
33
42
28
34
34
47
721
0.55
8.87
France
326
14
12
9
13
9
16
15
12
14
15
455
0.39
5.6
Germany
268
11
17
18
17
16
19
17
6
18
11
418
-0.2
5.14
Italy
213
14
11
11
14
15
20
19
23
15
16
371
0.6
4.57
China
26
8
8
7
16
24
35
42
50
51
66
335
0.98
4.12
Canada
161
7
11
13
10
11
12
15
12
13
7
273
0.18
3.36
Japan
200
10
7
8
12
6
6
5
3
5
7
269
-0.6
3.31
Australia
111
8
6
5
8
7
10
9
15
9
21
209
0.74
2.57
Netherlands
116
12
7
4
5
5
2
5
19
7
13
195
0.29
2.4
New Zealand
148
1
1
3
5
3
5
5
2
173
0.55
2.13
Switzerland
116
3
5
6
2
5
4
5
6
8
6
166
0.6
2.04
India
27
2
5
15
14
13
12
17
13
31
10
159
0.6
1.96
Sweden
91
4
3
6
3
2
4
4
5
4
2
128
-0.2
1.58
Spain
68
7
4
3
5
6
9
4
6
6
6
124
0.21
1.53
Denmark
75
5
6
2
5
2
3
6
7
2
113
-0.1
1.39
Belgium
43
3
2
1
11
3
2
5
6
1
77
0.04
0.95
Poland
20
1
2
2
3
3
5
4
4
5
3
52
0.75
0.64
Mexico
18
2
4
1
4
2
3
7
41
0.52
0.5
Hungary
19
1
3
1
3
2
1
5
2
37
0.35
0.46
Brazil
15
4
1
4
3
1
5
33
0.15
0.41
Israel
20
3
3
2
1
2
1
1
33
-0.8
0.41
Austria
16
1
2
2
1
2
1
3
1
3
32
0.37
0.39
Iran
3
1
3
4
3
6
6
26
0.92
0.32
Finland
15
2
2
1
2
2
24
-0.2
0.3
Ireland
18
2
1
1
1
1
24
-0.6
0.3
Russia
12
1
1
1
2
1
3
2
23
0.67
0.28
Hong Kong
8
2
2
1
2
1
2
3
21
0.17
0.26
Malaysia
3
1
1
2
1
3
6
2
19
0.55
0.23
Norway
10
3
2
2
1
1
19
-1
0.23
Others
107
9
12
15
19
10
21
15
30
23
22
284
0.74
3.49
Total
4661
259
264
292
344
321
361
364
406
431
418
8126
0.97
100
Table 1: Nation distribution based on the 1st author for papers regarding pharmacology and pharmaceutics.
Journals and the trend
A total of 14,403 eligible abstracts were analyzed regarding journals in pharmacology and pharmaceutics. The most number of journals in production of pharmacology and pharmaceutics are J Pharmacol Exp Ther (351, 2.44%) and Arzneimittel-forschung (315, 2.19%). The trend in the number of publications for a journal is shown in the column of correlation in Table 2. We can see some journals are increasing and some are decreasing in papers regarding pharmacology and pharmaceutics.
Journal
1992-2007
2008
2009
2010
2011
2012
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
Total
corr.
%
J Pharmacol Exp Ther
300
4
6
4
6
6
7
5
5
5
3
351
-0.2
2.44
Arzneimittelforschung
314
1
315
-0.3
2.19
Br J Pharmacol
162
9
12
12
8
14
17
7
21
3
24
289
0.33
2.01
Drugs
203
2
1
2
2
1
1
212
-0
1.47
J Med Chem
168
4
3
1
2
4
3
8
1
5
199
0.45
1.38
Pharmacol Rev
115
4
3
7
6
6
6
5
12
3
7
174
0.35
1.21
Clin Pharmacol Ther
99
10
6
8
7
8
8
4
5
6
10
171
-0.2
1.19
Farmakol Toksikol
156
156
-
1.08
J Clin Pharmacol
116
2
1
2
3
4
3
3
9
3
8
154
0.72
1.07
Eur J Pharmacol
113
8
1
5
3
2
1
4
7
4
5
153
0.05
1.06
Br J Clin Pharmacol
98
8
5
3
12
3
7
4
6
3
149
-0
1.03
Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther
144
144
-
1
J Ethnopharmacol
27
5
1
1
6
3
13
15
20
14
15
122
0.84
0.85
Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi
97
3
1
3
2
1
1
3
2
4
117
-0.1
0.81
Trends Pharmacol Sci
81
2
2
1
7
3
4
2
5
3
110
0.01
0.76
Biochem Pharmacol
78
4
8
1
4
1
6
4
1
1
108
-0.3
0.75
Pharmacol Ther
72
5
1
7
1
4
1
4
2
4
5
106
0.02
0.74
Ann N Y Acad Sci
89
1
1
1
1
93
0.14
0.65
Therapie
85
1
2
1
2
1
92
-0.2
0.64
Mol Pharmacol
59
3
2
3
2
5
3
4
7
88
0.22
0.61
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol
76
2
2
1
2
1
2
86
0.43
0.6
Cancer Res
82
1
2
1
86
-0.5
0.6
J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods
20
8
5
5
9
4
4
7
4
11
9
86
0.29
0.6
J Cardiovasc Pharmacol
75
2
1
1
1
1
81
-0.5
0.56
Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol
56
3
2
2
2
3
3
3
4
78
0.5
0.54
Pharmacotherapy
72
1
1
1
1
76
-0.4
0.53
Eur J Clin Pharmacol
47
5
1
2
1
6
1
3
3
69
-0.2
0.48
Antimicrob Agents Chemother
61
1
1
1
1
1
1
67
-0.1
0.47
Pharmacol Res
28
1
6
4
2
8
13
5
67
0.66
0.47
Neuropharmacology
38
2
3
2
1
2
2
7
3
1
5
66
0.35
0.46
Others
7383
207
222
244
299
268
309
345
341
370
345
10338
0.95
71.8
Total
10514
294
286
326
377
357
404
438
473
466
461
14403
0.96
100
Table 2: Journal distribution for papers regarding pharmacology and pharmaceutics.
Keywords to present the feature of research domain
The most linked keywords are pharmacology and experimental lab study, see Figure 2 or click it on the reference [24]. We can see that the two bigger bubbles are of pharmacology and experimental lab study in pink cluster at the right-top part in Figure 2.
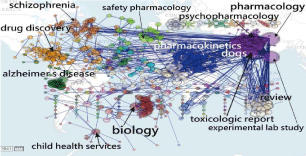
Figure 2: Keywords in papers regarding pharmacology and pharmaceutics.
Prominent authors selected by SNA
The most prominent authors are shown in Figure 3 or click it on the reference [25]. We can see that the two bigger bubbles are of Joanna L Sharman and Adam J Pawson in the green cluster.
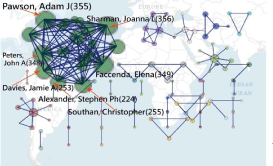
Figure 3: Prominent authors in papers regarding pharmacology and
pharmaceutics (frequency number is shown in parentheses).
MESH terms to present the feature of research domain
After extracting 38 papers in a search by a keyword Sharman, Joanna L [Author - Full] on Medline, we analyzed data by SNA and present the most linked MESH terms (pharmacology and molecular targeted therapy), see Figure 4 or click it on the reference [26] to see the research domain of Joanna L Sharman. We can see that several bigger clusters that can represent the research domain of an author.
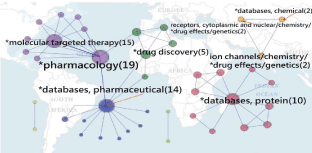
Figure 4: Research domain for an author (Joanna L Sharman) in pharmacology
and pharmaceutics (frequency number are shown in parentheses).
Discussion
This study used SNA techniques to report that (1) the most number of nations are from US and UK; (2) the most number of journals in production of pharmacology and pharmaceutics are J Pharmacol Exp Ther and Arzneimittel-forschung; (3) the most linked keywords are pharmacology and experimental lab study; (4) the research domain defined by MESH terms are pharmacology and molecular targeted therapy for the prominent Author Joanna L Sharman.
What this adds to what was known
An apocryphal story is often told to discover the co-occurrence about beer and diaper sales [9-11]. It is hard display all possible pairs of our observed phenomena at a short moment. In literature, no such examples but studies [3-6] were illustrated to investigate coauthor collaboration using SNA. We further incorporated SNA with Google maps to present informative messages to readership, which is never seen in previous published papers in academics.
Journal authorship collaboration can be compared with each other using Google Maps. We can see that many links connecting nations, indicating a collaboration pattern to the previous study [3]. Hence the researchers present a huge international author collaborations in the field of pharmacology and pharmaceutics which is inconsistent with the previous studies that investigated scientific collaboration of Iranian Psychology and Psychiatry Researchers [27,28].
There are two papers [29,30] incorporated MeSH into social network analysis to explore interesting informative knowledge. However, no any that can be found incorporating SNA with Google maps to show more value information like the current study. The way we illustrated is novel and promising in future, especially in the field of pharmacology and pharmaceutics.
What it implies and what should be changed?
Scientific publication is one of the objective measurements to evaluate the achievements of a medical specialty [31]. It is worth using SNA and Google Maps to report journal features or author research domains in future.
Several algorithms have been developed and applied to SNA. If we study whether any author domains or paper keywords most are fitting the features of a journal, the centrality measures using SNA can be applied [3]. It means that the core subject can be analyzed using the centrality measure [27] yielded in SNA.
Strengths of this study
The way we incorporated SNA with Google Maps is unique, which is never demonstrated in previous published papers. Another strength and feature in the current study is that we applied Google Maps provided to interested readers who can practice it on their own ways by clicking the links in references [23-27]. The nation distribution in Figure 1 is easy to understand the feature on the topic of pharmacology and pharmaceutics one picture is worth ten thousand words. We hope following studies can report more such kinds of information using SNA and Google Maps to readers.

Figure 1: International coauthor collaboration in the topic of pharmacology
and pharmaceutics.
Limitations and Future Study
The interpretation and generalization of the conclusions of this study should be cautious. First, the data of this study were collected from Medline for a single journal. It is worth noting that any attempt to generalize the findings of this study should be made in the similar journal domain with similar topic and scope contexts.
Second, although the data were extracted from Medline and carefully dealt with every linkage as correct as possible, the original downloaded text file including some errors in symbols such as period and comma in author address that might lead to some bias in the resulting nation distribution.
Third, there are many algorithms used for SNA. We merely applied separation components showing in Figures. Any changes made along with algorithm used will present different pattern and judgment.
Fourth, the social network analysis is not subject to the Pajeck software we used in this study, others such as Ucinet [32] and Gephi are suggested to readers for use in future.
Conclusion
Social network analysis provides wide and deep insight into the relationships among nations, coauthor collaborations, and abstract keywords or MESH terms. The results drawn by Google maps can be provided to readers for future paper submission in academics.
References
- Dasgupta S, Vaughan AS, Kramer MR, Sanchez TH, Sullivan PS. Use of a Google Map Tool Embedded in an Internet Survey Instrument: Is it a Valid and Reliable Alternative to Geocoded Address Data? JMIR Res Protoc. 2014; 3: e24.
- Kobayashi S, Fujioka T, Tanaka Y, Inoue M, Niho Y, Miyoshi A. A geographical information system using the Google Map API for guidance to referral hospitals. J Med Syst. 2010; 34: 1157-1160.
- Sadoughi F, Valinejadi A, Shirazi MS, Khademi R. Social Network Analysis of Iranian Researchers on Medical Parasitology: A 41 Year Co-Authorship Survey.Iran J Parasitol. 2016; 11: 204-212.
- Osareh F, Khademi R, Rostami MK, Shirazi MS. Co-authorship Network Structure Analysis of Iranian Researchers’ scientific outputs from 1991 to 2013 based on the Social Science Citation Index (SSCI). Collnet J Scientometr Info Manag. 2014; 8: 263-271.
- Liu X, Bollen J, Nelson ML, Sompel VDH. Co-authorship networks in the digital library research community. Info Process Manag. 2005; 41: 1462-1480.
- Norgard NB. Obesity and Altered Aspirin Pharmacology. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2017.
- Chadha RM, Aniskevich S, Egan BJ. Pharmacology and Perioperative Considerations of Pain Medications. Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2017.
- Bright CF, Haynes EE, Patterson D, Pisu M. The Value of Social Network Analysis for Evaluating Academic-Community Partnerships and Collaborations for Social Determinants of Health Research. Ethn Dis. 2017; 27: 337-346.
- Domingos p. A few useful things to know about machine learning. Communications of the ACM. 2012; 55: 78-87.
- Verhoef PC, Kooge E, Walk N. Creating Value with Big Data Analytics: Making Smarter Marketing Decisions. London: Routledge. 2016.
- Power DJ. What is the “true story” about data mining, beer and diapers? DSS News. 2017.
- International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. Uniform Requirements for Manuscripts Submitted to Biomedical Journals. N Engl J Med. 1997; 336: 309-316.
- https://www.scribd.com/document/56056686/255-How-to-Write-a-Scientific-Article-Dr
- Leydesdorff L, Wagner C, Park HW, Adams J. International collaboration in science: the global map and the network. 2013.
- Glänzel W, Schlemmer B. National research profiles in a changing Europe (1983–2003) an exploratory study of sectoral characteristics in the Triple Helix. Scientometrics. 2007; 70: 267-275.
- National Science Board. Science and Engineering Indicators. Washington DC: National Science Foundation. 2017.
- Barjak F, Eccles K, Meyer ET, Robinson S, Schroeder R. The Emerging Governance of E-Infrastructure. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication. 2013; 18: 1-24.
- Adam J. Collaborations: the rise of research networks. Nature. 2012; 490: 335-336.
- Kwon KS, Park HW, So M, Leydesdorff L. Has globalization strengthened South Korea’s national research system? National and International Dynamics of the Triple Helix of Scientific Co-authorship Relationships in South Korea. Scientometrics. 2012; 90: 163-175.
- Nooy DW, Mrvar A, Batagelj V. Exploratory Social Network Analysis with Pajek: Revised and Expanded, 2nd edn. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press. 2011.
- Phan TG, Beare R, Chen J, Clissold B, Ly J, Singhal S, et al. Googling Service Boundaries for Endovascular Clot Retrieval Hub Hospitals in a Metropolitan Setting: Proof-of-Concept Study. Stroke. 2017; 48: 1353-1361.
- Chien TW. Google Maps on author collaboration for pharmacology and pharmaceutics. 2017.
- Chien TW. Google Maps on author-defined keywords for pharmacology and pharmaceutics. 2017.
- Chien TW. Google Maps on prominent authors for pharmacology and pharmaceutics. 2017.
- Chien TW. Google Maps on research domain for one author. 2017.
- Erfanmanesh MA, Rohani VA, Jahromi BR, Gholamhosseinzadeh Z. Investigating Scientific Collaboration of Iranian Psychology and Psychiatry Researchers. J Info Process Manag. 2013; 29: 137-163.
- Osareh F, Chakoli NA, Keshvari M. Co-authorship of Iranian researchers in science, social science, art and humanities citation indexes in the web of science between 2000 and 2006. J Info Sci Technol. 2010; 25: 573-595.
- Hu SK, Huang J, Hong WD, Du XJ, Jin R, Lin TS. The 50 Most-cited Articles in Gastroenterology and Hepatology from Mainland China. Pak J Med Sci. 2017; 33: 215-220.
- Coelho DH, Edelmayer LW, Fenton JE. A century of citation classics in otolaryngology-head and neck surgery journals revisited. Laryngoscope. 2014; 124: 1358-1362.
- Chang HT, Lin MH, Hwang IH, Chen TJ, Lin HC, Hou MC, et al. Scientific publications in gastroenterology and hepatology in Taiwan: An analysis of Web of Science from 1993 to 2013. J Chin Med Assoc. 2017; 80: 80-85.
- Borgatti SP, Everett MG, Freeman LC. Ucinet for Windows: Software for Social Network Analysis. Harvard, MA: Analytic Technologies. 2002.
- Bastian M, Heymann S, Jacomy M. Gephi: open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. International AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media. 2009.
