
Review Article
Austin J Pharmacol Ther. 2015; 3(3).1076.
Potential Benefits of Methylcobalamin: A Review
Gupta JK* and Qureshi Shaiba Sana
Department of Pharmacology, GLA University Mathura, India
*Corresponding author: : Jeetendra Kumar Gupta, Department of Pharmacology, Institute of Pharmaceutical Research, GLA University Mathura, India
Received: August 17, 2015; Accepted: September 30, 2015; Published: October 08, 2015
Abstract
Methylcobalamin is an active form of vitamin B12 that helps in synthesis of methionine and S-adenosylmethionine. It is required for integrity of myelin, neuronal function, proper red blood cell formation and DNA synthesis. The largest group of vitamin B12 deficiency is found in typical vegetarians all over the world, which can be alleviated with its analogue Methylcobalamin. It is a beneficial drug to most of the common disorders like cardiovascular disorders, diabetes, anemia, hyperhomocysteinemia and degenerative disorders. Methylcobalamin helps in the synthesis of neuronal lipids, regeneration of axonal nerves and has neuroprotective activity, which promote neurons to function in proper way and thus improves Alzheimer disease, Parkinsonism, Dementia and neuropathic syndromes. It is an approved treatment for peripheral neuropathy.
Keywords: Mecobalamin; Neuropathy; Anemia; Nootropic; Dietary supplement
Abbreviations
SAMe: S-Adenosyl Methionine; ERK: Extracellular Signal- Regulated Kinases; PKB: Protein Kinase B; B-globulin: Beta Globulin; ENFD: Epidermal Nerve Fiber Density; DPN: Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy; NSAIDs: Non Steroidal Anti Inflammatory Drugs; THF: Tetrahydrofolate; BHMT: Betaine Homocysteine Methyltransferase.
Introduction
Methylcobalamin is a potent and active form of vitamin cyanocobalamin. It plays a key role in maintaining good health. Dietary cobalamin deficiency causes many serious health problems. The commonest are blood deficiency, depression, irritability and psychosis. The long term deficiency of vitamin B12 substance can lead to hyperhomocysteinemia and finally cardiovascular disorder. In today’s world, healthcare plays an important role in our personal lives. This merges a huge responsibility for improving and saving thousand lives on earth. Despite having incredible improvements in health since 1950, there are number of challenges which have to be solved. Each year 36 million deaths are caused by non communicable diseases such as hyperhomocysteinemia, cancer, chronic lung disease, anemia, diabetes and almost 17.5 millions died from cardiovascular disease in 2005 [1].
Folate and vitamin B12 are essential nutrients which are not synthesized in humans and whose deficiency is considered as heath problem worldwide such as anemia and neuronal dysfunction. Vitamin B12 deficiency is observed more in elderly and pregnant women. Methylcobalamin (commonly known as mecobalamin or methyl B12) is an analog of vitamin B12 which treats or prevents the pathology arising from the deficiency of vitamin B12. It contains methyl alkyl bonds and is different from cyanocobalamin because it contains cynide [2]. It has an octahedral cobalt (III) center and is produced in laboratory by reducing cyanocobalamin with sodium borohydride in alkaline solution which is followed by the addition of methyl iodide. Methylcobalamin (5 mg, 60 mg vegetarian lozenges) is active in the central nervous system outside the mitochondrion and is essential for cell growth and replication. Sometimes the liver cannot convert cyanocobalamin into adequate amount of methylcobalamin needed for proper neuronal functioning. Through enhanced methylation, it exerts its nerve cell protective effect and accelerates its growth. A lot of energy is required for cyanocobalamin to remove its cyanide and replaces it with methyl group [3]. Methylcobalamin is the only form of vitamin B12 that can cross the blood brain barrier without biotransformation. Its methyl group stimulates serotonin creation, a neurotransmitter which is responsible for mood enhancement and protects the brain from damage against excitotoxins. High homocysteine level is the main culprit for brain, vascular diseases, stokes risk and causes sclerosis in the arteries. Methlcobalamine converts homocysteine to methionine and reduces the potential to damage. It also forms adenosylcobalamine, the other form of vitamin B12 for mitochondrial energy production. Along with methylcobalamin, 5 methyltetrahydrofolate is also an important element to eliminate homocysteine. Vitamin supplements reduce the chances of building homocysteine associated with stress. Sublingual absorption of methylcobalamin has become very popular because it can be easily absorbed with better bioavailability. It also increases the available amount of SAMe (S- adenosylmethionine), which acts as a mood enhancer and works as an effective alternative to tricyclic antidepressant [4].
Therapeutic use of Methylcobalamine
Methylcobalamin is used in the treatment of diabetic neuropathy, degenerative disorders and in the preliminary treatment of amyotropic lateral sclerosis. It has been used to treat some nutrition based disease such as dementia, rheumatoid arthritis and exerts neuronal protection by promoting regeneration to injured nerves. It antagonizes the glutamate induced neurotoxicity and also manifests analgesic effects. It alleviates pain behavior in diabetic neuropathy, low back pain, neuralgia and promotes nerve conduction. It helps the body to use fats and carbohydrates for energy.
Oral administration of 500 mcg three times daily for four weeks results in improvement of peripheral neuropathy and it produces very significant effect after 12 weeks of treatment [5]. An improvement in vibration sense, lower motor neuron weakness and sensitivity to pain is also observed. It also improves visual function in Bell’s palsy, sleep wake rhythm disorder [6].
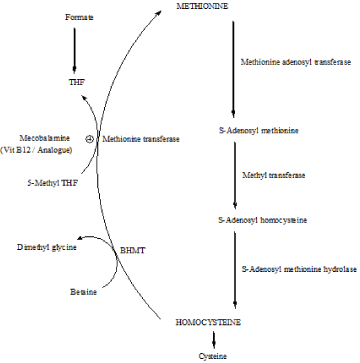
Figure 1: Mobilization of Homocysteine to Methionine by vitamin B12.
Human urinary excretion of methylcobalamin is about one third that of a similar dose of cyanocobalamin that indicate greater tissue retention. It improves sperm count by 37.5% at a dose of 6mg per day for 16 weeks. When given at a dose of 1,500 microgram per day for 4-28 weeks results in 38% sperm concentration, sperm motility increases in 50% of cases [7-11]. Glutamate neurotoxicity was prevented by chronic exposure to methylcobalamin and SAMe. Its chronic exposure with SAMe also inhibits the neurotoxicity induced by sodium nitroprusside which is mediated by nitrous oxide. Its chronic dose also up regulate gene transcription and therefore protein synthesis. Methylcobalamin at concentration above 100nm promote neuronal survival and neurite growth, increases ERK ½ and AKT activities through methylation cycle. Continous administration of high dose of methylcobalamin results in nerve regeneration and functional recovery in rat sciatic nerve injury. Methylcobalamin (1 mg/kg intramuscular) inhibits ototoxic action of gentamycin and promote visual field defects in normal tension glaucoma. Combination of methylcobalamin, alpha lipoic acid and pregabalin improves sleep interference, nerve function and pain relief [12].
Mechanism of Action
It works by functioning in the production of a compound called myelin, which covers and protect nerve fibers [13]. Methylcobalamin rejuvenates the damaged neuron. Without enough methylcobalamin, myelin sheath does not form properly due to which nerve fibers suffers and people experience irreversible nerve damage. An intrinsic factor made in the stomach, must be present in the intestinal tract to allow its proper absorption. People lacking this factor show vitamin B12 deficiencies such as pernicious anemia (a slow and insidious process that can end in death. Pernicious anemia in fact means ‘leading to death’). Methylcobalamin is used as a cofactor in methionine transferase enzyme, an enzyme which converts aminoacid homocysteine to methionine via folate cycle [14-16].
Pharmacokinetics
Methylcobalamin can be administered orally, parenterally and intranasal. Methylcobalamin binds with an intrinsic factor and form a complex which is absorbed in distal ileum. Its half life is 6 days. The absorption is mediated by very specific receptor mediated transport system. It is distributed to every cell of the body upon binding to Transcobalamine II, a B-globulin carrier protein and is stored in the liver in an amount of 300- 500 microgram. It is eliminated through bile. Methylcobalamin nasal sprays bioavailability is 9% [17-19].
Dose
For daily stress relief, methylcobalamin should be taken in the dose of 500 mcg per day. In the acute cases of neuropathy, dose of 1500 mcg per day can be safely taken. Dose of 1 mg per day is required to be taken for age related brain decay. Methylcobalamin can be combined with similar dose of folic acid and pyridoxine [20]. Deficiency of vitamin B12 is strictly seen in pure vegetarian, dose of 100 mg day can rebalance its requirement in the intestine. All human being need at least 3 mg per day of this drug for the basic nerve support. The medicine is stored in the refrigerator below 41°F (5°C) to avoid moisture. Methylcobalamin is also injected deep in to the muscles [21].
Combinations / Interactions
Fixed dose combination of sustained release pregabalin and methylcobalamin reduces neuropathic pain. Treatment with lipoic acid – methylcobalamin for 2-4 weeks is associated with better outcome in nerve conduction velocity and neuropathic symptoms. Oral combinations of methylcobalamin, L-methylfolate and Pyridoxal-5 phosphate improves Epidermal Nerve Fiber Density (ENFD) with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy (DPN). Medicines such as Antibiotics (penicillin, cefalexin, ciprofloxacin), metformin, nitrous oxide, colchicines, NSAIDs (Ibuprofen, Para aminosalicyclic acid, sulphasalazine) decrease the absorption and induce reversible mal-absorption of methylcobalamin by altering the function of ilea mucosa. Some drugs like nitrates (nitroglycerin), fluorouracil interacts with methylcobalamin and their side effects are increased [22]. Chloramphenicol antagonizes the hematopoietic action of this drug. Administration of methylcobalamin during pregnancy and breast feeding is dangerous because it can cross maternal-fetal barriers and also gets excreted in milk. Barbiturates (phenobarbitol), primidone, pyrimethamine, valproic acid, hydantoins should not be taken along with methylcobalamin because their effectiveness is inhibited. Aminoglycosides, proton pump inhibitors, anti hyperglycemic medications (metformin), anticonvulsants interfere with methylcobalamin absorption and function. Consumption of ethanol along with methylcobalamin therapy counteracts its action [13,23-25].
Adverse Effects
At a very high dose, methylcobalamin causes blood clots, diarrhea, paresthesia, rhinitis, ataxia, pruritis and allergic reactions. People with polycythemia should consult with a physician before taking this therapy [26-29]. This drug can be applied as a topical paste on the skin without any adverse reaction. Sometimes intravenous injection of this drug leads to hypersensitivity reactions and end up to anaphylactic shock. In some cases, hypokalamia and thrombocytosis has occurred in the patient while treating megaloblastic anemia with methylcobalamin [30-37].
Conclusion
Methylcobalamin aids in growth of healthy blood cells, nerve cells in the body. It is a best treatment as well as dietary supplement for the people who cannot absorb vitamin B12 and / or suffers from its deficiencies. Monotherapy of methylcobalamin improves plasma / serum homocysteine level and improve the neuropathic symptoms also [28-37]. Combination therapy with other vitamin B complexes seems to be more effective. Hence methylcobalamin may be considered as one of the promising dietary supplement and medicine having a number of potential benefits [5,38-41].
References
- Rusu T, Ekoume I, Malaurie E, Poullain S. Patient safety and risk management. European journal of hospital pharmacy. 2015; 22: 1-6.
- Banerjee R, Ragsdale SW. The many faces of vitamin B12: catalysis by cobalamin-dependent enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 2003; 72: 209-247.
- Yamashiki M, Nishimura A, Kosaka Y. Effects of methylcobalamin (vitamin B12) on in vitro cytokine production of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1992; 37: 173-182.
- Metz J, Kelly A, Swett VC, Waxman S, Herbert V. Deranged DNA synthesis by bone marrow from vitamin B-12-deficient humans. Br J Haematol. 1968; 14: 575-592.
- Maladkar M, Saggu NJS, Moralwar P, Mhate AA, Zemse D, Bhoraskar A. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of epalrestat and epalrestal in combination with methylcobalamin in patients with diabetic neuropathy in a randomized, comparative trial. Journal of Diabetes mellitus. 2013; 3: 20-26.
- Zhang M, Han W, Hu S, Xu H. Methylcobalamin: a potential vitamin of pain killer. Neural Plast. 2013; 2013: 424651.
- Kira J, Tobimatsu S, Goto. Vitamin B12 metabolism and massive dose methyl vitamin B12 therapy in Japanese patients with multiple sclerosis. Intern Med journal. 1994; 33: 82-86.
- Gröber U, Kisters K, Schmidt J. Neuroenhancement with vitamin B12-underestimated neurological significance. Nutrients. 2013; 5: 5031-5045.
- Gueant JL. Malabsorbtion of cobalamins in cobalamin and related binding proteins in clinical nutrition. Ann Intern Med journal. 1994; 120: 211-215.
- Lane LA, Rojas-Fernandez C. Treatment of vitamin b(12)-deficiency anemia: oral versus parenteral therapy. Ann Pharmacother. 2002; 36: 1268-1272.
- van der Dijs FP, Fokkema MR, Dijck-Brouwer DA, Niessink B, van der Wal TI, Schnog JJ, et al. Optimization of folic acid, vitamin B(12), and vitamin B(6) supplements in pediatric patients with sickle cell disease. Am J Hematol. 2002; 69: 239-246.
- Poongothal S, Ilavarasan R, Karrunakaran CM. Simultaneous and accurate determination of vitamin B12, B6, B12 and alpha lipoic acid in multivitamin capsules by reverse phase high performance liquid chromatographic method. International journal of pharmacy and pharmaceutical sciences. 2010; 2: 133-139.
- Brouwer M, Chamulitrat W, Ferruzzi G, Sauls DL, Weinberg JB. Nitric oxide interactions with cobalamins: biochemical and functional consequences. Blood. 1996; 88: 1857-1864.
- Randaccio L, Furlan M, Geremia S, Slouf M, Srnova I, Toffoli D. Similarities and differences between cobalamins and cobaloximes, Accurate structural determination of Methylcobalamin and LiCl and KCL containing cynocobalamins by Synchrotron Radiation. Inorganic chemistry journal. 2000; 39: 3403-3413.
- Lodowski P, Jaworska M, Garabato BD, Kozlowski PM. Mechanism of Co-C bond photolysis in methylcobalamin: influence of axial base. J Phys Chem A. 2015; 119: 3913-3928.
- Ghosh SK, Rawal N, Syed SK, Paik WK, Kim SD. Enzymic methylation of myelin basic protein in myelin. Biochem J. 1991; 275: 381-387.
- Koyama K, Ito A, Yamamoto J, Nishio T, Kajikuri J, Dohi Y, et al. Randomized controlled trail of the effect of short term co-administration of methylcobalamin and folate on serum ADMA concentration in patients receiving long term hemodialysis. American journal of kidney diseases. 2010; 55: 1069-1078.
- Mostafa Youssef, Mamdouh Ghorab, Mostafa Khater, Shadeed Gad. Effect of additives on intranasal preparation of cynocobalamine. International journal of pharmacy and pharmaceutical sciences. 2015; 7: 210-217.
- Ganesan M, Solairaj P, Rajesh SC, Senthikumar T, Thangathirupathi A. A simple spectrophotometric method for the estimation of mecobalamin in injections. International journal of pharmacy and pharmaceutical science. 2012; 4: 559-562.
- Kaji R, Kodama M, Imamura A, Hashida T, Kohara N, Ishizu M, et al. Effect of ultra high dose of methylcobalamin on compound muscle action potentials in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Wiley journal. 1998; 21: 1775-1778.
- Nava-Ocampo AA, Pastrak A, Cruz T, Koren G. Pharmacokinetics of high doses of cyanocobalamin administered by intravenous injection for 26 weeks in rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2005; 32: 13-18.
- Qi Lin, Guo-Sheng Wang, Guangye Ma, Qiaofang Shen. The role of pharmaceutical care in oncology department. European journal of hospital pharmacy. 2015; 22: 128-131.
- Jacqueline C Dominguez, Arlene R Ng, Ludwig F Damian. A prospective, open label, 24 week trail of methylcobalamin in the treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy. Journal of diabetes mellitus. 2012; 2: 4 408-412.
- Kuwabara S, Nakazawa R, Azuma N, Suzuki M, Miyajima K, Fukutake T, et al. Intravenous methylcobalamin treatment for uremic and diabetic neuropathy in chronic hemodialysis patients. Internal medicine journal. 1999; 38: 472-475.
- Yaqub BA, Siddique A, Sulimani R. Effects of methylcobalamin on diabetic neuropathy. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1992; 94: 105-111.
- Maron BA, Loscalzo J. The treatment of hyperhomocysteinemia. Annu Rev Med. 2009; 60: 39-54.
- Vinik AI, Ziegler D. Diabetic cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy. Circulation. 2007; 115: 387-397.
- Watanabe T, Kaji R, Oka N, Bara W, Kimura J. Ulta high dose methylcobalamin promotes nerve regeneration in experimental acrylamide neuropathy. Journal of neurological sciences. 1994; 12: 140-143.
- Partanen J, Niskanen L, Lehtinen J, Mervaala E, Siitonen O, Uusitupa M. Natural history of peripheral neuropathy in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1995; 333: 89-94.
- England JD, Gronseth GS, Franklin G, Miller RG, Asbury AK, Carter GT, et al. Distal symmetric polyneuropathy: a definition for clinical research: report of the American Academy of Neurology, the American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine, and the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Neurology. 2005; 64: 199-207.
- Ziegler D, Nowak H, Kempler P, Vargha P, Low PA. Treatment of symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy with the antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid: a meta-analysis. Diabet Med. 2004; 21: 114-121.
- Yamada N. Treatment of recurrent hypersomnia with methylcobalamin (vitamin B12): a case report. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1995; 49: 305-307.
- Hashimoto S, Kohsaka M, Morita N, Fukuda N, Honma S, Honma K. Vitamin B12 enhances the phase-response of circadian melatonin rhythm to a single bright light exposure in humans. Neurosci Lett. 1996; 220: 129-132.
- Takahashi K, Okawa M, Matsumoto M, Mishima K, Yamadera H, Sasaki M, et al. Double-blind test on the efficacy of methylcobalamin on sleep-wake rhythm disorders. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1999; 53: 211-213.
- Devathasan G, Teo WL, Mylvaganam A, Thai AC, Chin JH. Methylcobalamin in chronic neuropathy, a double blind clinical and electrophysiological study. Clinical trials journal. 1986; 23: 130-140.
- He Q, Madsen M, Kilkenney A, Gregory B, Christensen EI, Vorum H, et al. Amnionless function is required for cubilin brush-border expression and intrinsic factor-cobalamin (vitamin B12) absorption in vivo. Blood. 2005; 106: 1447-1453.
- Alonso S Castellanos, Gonzalez Paniagua, Briones Cuesta, Pedros Naudin, Lopez Insua A Hermida Perez. The use of glutamine supplementation in the parenteral nutrition support in a third level hospital. European journal of hospital pharmacy. 2013; 19: 217-218.
- Surajit Bhattacharjee, Chaitali Sarkar, Sudipta Pal. Additive benefial effects of folic acid and vitamin b12 co-administration on Arsenic – Induced Oxidive Damage In Cardiac Tissue in vitro. Asian journal of pharmaceutical and clinical research. 2013; 6: 64-69.
- Tiemeier H1, van Tuijl HR, Hofman A, Meijer J, Kiliaan AJ, Breteler MM . Vitamin B12, folate, and homocysteine in depression: the Rotterdam Study. Am J Psychiatry. 2002; 159: 2099-2101.
- Akramshueb. Pharmacist intervention in the management of Parkinson›s disease. European journal of hospital pharmacy. 2012; 19: 355-359.
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz A, Keith G, Dirheimer G. Effect of cobalamin derivatives on in vitro enzymatic DNA methylation: methylcobalamin can act as a methyl donor. Biochemistry journal. 1991; 30: 8045-8051.