
Special Article - Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Austin J Pulm Respir Med 2017; 4(2): 1055.
Anti-TNF Treatment and Tuberculosis
Kaya FO*
Assistant Professor, Department Internal Medicine, Medical School of University of Maltepe, Istanbul, Turkey
*Corresponding author: Fatih Öner Kaya, Assistant Professor, Department Internal Medicine, Medical School of University of Maltepe, Istanbul, Turkey
Received: August 04, 2017; Accepted: September 06, 2017; Published: September 13, 2017
Abstract
Bacteria, lipopolysaccharide are largely by stimulating macrophages such as IL-2, to a lesser extent B and T lymphocytes, NK cells, mast cells and intestinal epithelial cells by production of TNF- α ; Induces acute phase reactions. Endotoxic shock, inflammation, regeneration, immunity, provides destruction apoptotic cell cytotoxicity. The development of tumours and inhibits viral replication [1-4].
TNF-α is secreted as a precursor. TNF-α converting enzyme is activated with. Three TNF-α jointly trimetric TNF-α becomes or Trimetric TNF-α TNFR-1 or by connecting to one of the TNFR-2 receptor IL-1β/6/8 increments. MCP-1/1α/2, RANTES, ICAM-1, VCAM-1 increases the cytokines. These molecules provides start and continuation of inflammation [2,3,5,6].
Creating TNF- α in the immune system against Mycobacterium granuloma tuberculosis allows the isolation of bacteria. Of activated macrophages in granulomas of epithelioid cells with TNF- α effect is transformed into cells combine and become giant cells. Suppression of the TNF- α enable the activation of tuberculosis by preventing the granulomatous inflammation [7,8,9].
Rheumatologic illnesses commonly used these drugs for the disease in countries deemed more active TBC biggest problem form [10,11].
Mycobacterium TBC infections of immune response that occurs TNF-α and p55 receptor signal is increased by raising the burden of Mycobacterium and Granuloma formation and demonstrates how to accelerate death [12]. Granuloma formation for chronic as TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-12, IL-15 secretion and TNFR-1 and have the presence of TNFR-2 receptor. TNF-α makes the macrophages activated, dendrite cells, increasing migration of lymphocytes and bringing to maturity, inflammation causes the proliferation [13,9,14].
Infliksimab
Adalimumab
Etanersept
Sertolizumab
Golimumab
Class
Monoklonal Ac
Monoklonal Ac
Fc fuzyonprot
Monoklonal Ac fragman
Monoklonal Ac
Structure
Mouse / human chimeric IgG1?
Human IgG1?
Human sTNFR2-Fc
PEG-Human IgG1? Fab
Human IgG1?
Specificity
TNF
TNF
TNF/LTa
TNF
TNF
TNF liganti
sTNF, tmTNF
sTNF, tmTNF
sTNF, tmTNF
sTNF, tmTNF
sTNF, tmTNF
LT liganti
LTa2β1, LTa3
sTNF
medium
medium
strong
no data
no data
tmTNF
strong
strong
medium
no data
no data
Table 1: Anti TNF-α drugs.
*Anergy panel testing is not recommended.
†Interferon-γ–release assay (IGRA) is preferred if the patient has a history of BCG vaccination.
‡Risk factors for TB exposure are defined based on a publication from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention as: close contacts of persons known or suspected to have active TB; foreign-born persons from areas that have a high incidence of active TB (e.g., Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, Latin America, and Russia); persons who visit areas with a high prevalence of active TB, especially if visits are frequent or prolonged; residents and employees of congregate settings whose clients are at an increased risk for active TB (e.g., correctional facilities, long-term care facilities, and homeless shelters); health care workers who serve clients who are at an increased risk for active TB; populations defined locally as having an increased incidence of latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection or active TB, possibly including medically underserved, low-income populations, or persons who abuse drugs or alcohol; and infants, children, and adolescents exposed to adults who are at an increased risk for latent M tuberculosis infection or active TB
- If the patient is immunosuppressed and false-negative results are more likely, consider repeating screening test(s) with Tuberculin Skin Test (TST) or IGRA.
¶Chest radiograph may also be considered when clinically indicated in patients with risk factors, even with a negative repeat TST or IGRA.
#Obtain respiratory (e.g., sputum, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid) or other samples as clinically appropriate for Acid-Fast Bacilli (AFB) smear and culture and consider referral to a TB specialist for further evaluation and treatment.
**In a patient diagnosed with latent or active TB, consider referral to a specialist for the recommended treatment.
††Patients who test positive for TST or IGRA at baseline often remain positive for these tests even after successful treatment of TB. These patients need monitoring for clinical signs and symptoms of recurrent TB disease, since repeating tests will not allow help in diagnosis of recurrent TB.
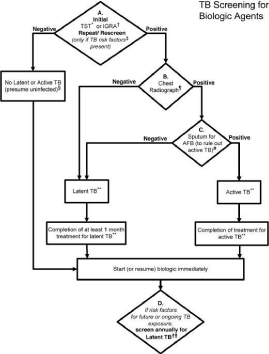
Figure 1: 2012 American College of Rheumatology recommendations update for Tuberculosis (TB) screening with biologic agent use. Depending on a patient's current therapy, the management may begin at an appropriate rectangle in the figure, rather than only at the top of the figure. The level of evidence supporting each recommendation for TB reactivation was “C” except for initiation of biologic agents in patients being treated for latent TB infection, where the level of evidence was “B.”
*Anergy panel testing is not recommended.
†Interferon-γ–release assay (IGRA) is preferred if the patient has a history of BCG vaccination.
‡Risk factors for TB exposure are defined based on a publication from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention as: close contacts of persons known or suspected to have active TB; foreign-born persons from areas that have a high incidence of active TB (e.g., Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, Latin America, and Russia); persons who visit areas with a high prevalence of active TB, especially if visits are frequent or prolonged; residents and employees of congregate settings whose clients are at an increased risk for active TB (e.g., correctional facilities, long-term care facilities, and homeless shelters); health care workers who serve clients who are at an increased risk for active TB; populations defined locally as having an increased incidence of latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection or active TB, possibly including medically underserved, low-income populations, or persons who abuse drugs or alcohol; and infants, children, and adolescents exposed to adults who are at an increased risk for latent M tuberculosis infection or active TB
- If the patient is immunosuppressed and false-negative results are more likely, consider repeating screening test(s) with Tuberculin Skin Test (TST) or IGRA.
¶Chest radiograph may also be considered when clinically indicated in patients with risk factors, even with a negative repeat TST or IGRA.
#Obtain respiratory (e.g., sputum, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid) or other samples as clinically appropriate for Acid-Fast Bacilli (AFB) smear and culture and consider referral to a TB specialist for further evaluation and treatment.
**In a patient diagnosed with latent or active TB, consider referral to a specialist for the recommended treatment.
††Patients who test positive for TST or IGRA at baseline often remain positive for these tests even after successful treatment of TB. These patients need monitoring for clinical signs and symptoms of recurrent TB disease, since repeating tests will not allow help in diagnosis of recurrent TB.
Anti- TNF- α drugs is 5 pcs. 3 of them infliximab, adalimumab, etanercept are older drugs and that's why we have more experience with developing TB cases .However new drugs such as Sertolizunab and Golimumab we haven't gotany experience and new experiences related to these drugs will be finalized in a few years Table 1.
In Spain around 2000 in the study increased 20 times the frequency, Infliximab and Etanercept TBC treated patients with Infliximab and Adalimumab were found to be lower than that. In 2000 and 2001, 100,000 100,000/1893/1113, 2003 de 17/100,000 cases were identified [15].
In a study published in 2004 in the USA between 1998 and 2002 was reported 25 cases and 100,000 connected to etarnecept/10 has been identified as. In this study, the doses of the drug for the first time between the detection of an active with TBC were determined as an average 11.5 months [16].
Askling and colleagues in 2005 Anti TNF-α in patients with rheumatoid arthritis drug to be kept according to 4 fold increase in Anti-TNF-α have enforced and implemented according to the generalized increase risk of patients identified TBC [17].
In Turkey the Association of Anti TNF-α drugs in Tuberculosis in patients; in 2005, in 2007, 100,000 100,000/26/25.2 has identified [18].
Hanta and colleagues in 2008, in their study of 192 patients diagnosed 3 active monitoring of TBC 3 years [19].
In 2009, James and his colleagues have shown that the patient was diagnosed with active 6 pieces TBC 702. [20].
In the UK in 2008 10.712 RA patients all Anti TNF-αlar for 100,000/95 (Adalimumab 144, infliksamib 136, etarnecept 39) has been identified as [21].
RATIO (French Research Axed onTolerance of Biotherapies) in 2003 for all Anti TNF-α s 100.000/116,7 (Adalimumab 215, infliksamib 187,5, etarnecept 9.3) identified as [22].
The reason of these differences; Adalimumab and liksamibpatogenematurasyonfagosom in the inf inhibit the TBC, CD4 T-cell complement-dependent sitotoksiste and INF-γ inhibits the release [23].
All patients should be screened for latent infection is TBC. In The Scan; the medical history, physical examination, the Tuberculin Skin Test (TDT), chest radiography, socio-economic level, living environment and should be treated in the country where the frequency of TBC. The scans found as new TBC Delayed Gamma Interferon, which measures the response against INF-γ Release Assay (IGRA) is available. Quentiferon TB-Gold test Myocabacterium TBC UN ESA-6, CFT-10 against antigens such as developing INF-γ level gauge. Quentiferon TB-Gold test, Non TBC does not cross react with Mycobacteria and BCG, booster effect is not visible, repeatable, as soon as there are advantages to be the answer [24].
Gardam and his friends if you have migrated in FROM AC chart in patients with active or if you have contact with TBC infected with TDT's 0-4 mm, latent TBC have proposed to start in terms of prophylactic therapy. Epidemiological risk factors in patients with 5-9 mm TDT agreed as positive. The rest of the Group of 10 mm and above are considered to be positive [7].
USA Breast Association guidelines in patients with positive 5 mm or above immunosuppressive agreed [25].
In Turkey, Rheumatologic research and Education Association, Turkish Thoracic Society has developed a guide with you. Accordingly, the TDT 0-4 mm resulting in 1-3 weeks after the booster dose in the question be repeated, with the repetition of 5 mm and above if there are Anti TNF-α drugs 1 months ago start and at least 9 months of INH 300 mg/day to proceed, it is suggested to use. Occurrences of 0-4 mm turns out to do the treatment but the physician's patient, according to the State risk set for deciding on an individual basis, provided that they can give the decision of prophylaxis. Active TBC is detected Anti TNF-α therapy should be immediately cut to begin treating TBC. Clinician Anti TNF therapy should consider also the possibility of extra pulmonary during TBC (Figure 1)
References
- Danase S. Mechanisms of action of infliximab in inflammatory bowel disease: an anti-inflammatory multitasker. Dig Liv Dis. 2008; 40: S225-228.
- Beutler B, Cerami A. The biology of cachectin/TNF-α primary mediator of the host response. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989; 7: 625-655.
- Feldmann M, Maini RN. Anti-TNF alpha therapy of rheumatoid arthritis: what have we learned? Annu Rev Immunol. 2001; 19: 163-196.
- Camussi G, Albano E, Tetta C, Bussolino F. The moleculer action of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Eur J Biochem. 1991; 202: 3-14.
- Flynn JL, Goldstein MM, Chan J, Pfeffer K, Mak TW, Bloom BR, et al. Tumor necrosis factoralpha is required in the protective immune response against Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mice. Immunity. 1995; 2: 561-572.
- Roach DR, Bean AG, Demangel, France MP, Briscoe H, Britton WJ. TNF regulates chemokine induction essential for cell recruitment, granuloma formation, and clearance of mycobacterial infection. J Immunol. 2002; 168: 4620-4627.
- Gardam MA, Keystone EC, Menzies R, Manners S, Long R, Vinh DC, et al. Anti-tumour necrosis factor agents and tuberculosis risk: mechanisms of action and clinical management. Lancet Infect Dis. 2003; 3: 148-155.
- Keane J, Gershon S, Wise RP, Braun MM, Siegel JN, Kasznica J, et al. Tuberculosis associated with infliximab, a tumor necrosis factor alpha-neutralizing agent. N Engl J Med. 2001; 345: 1098-1104.
- Stenger S, Modlin RL. Control of Mycobacterium tuberculosis through mammalian Toll-like receptors. Curr Opin Immunol. 2002; 14: 452-457.
- Hochberg MC, Lebwohl MG, Plevy SE, Hobbs KF, Yocum DE. The benefit/risk profile of TNF-blocking agents: findings of a consensus panel. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 34: 819-836.
- Mutlu GM, Mutlu EA, Bellmeyer A, Rubinstein I. Pulmonary adverse events of anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha antibody therapy. Am J Med. 2006; 119: 639-646.
- Ehlers S. Why does tumor necrosis factor targeted therapy reactivate tuberculosis? J Rheumatol Suppl. 2005; 74: 35-39.
- Jacobs M, Brown N, Allie N, Chetty K, Ryfell B. Tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 plays a minor role for mycobacterial immunity. Pathobiology. 2000; 68: 68-75.
- Mohan VP, Scanga CA, Yu K, Scott HM, Tanaka KE, Tsang E, et al. Effects of tumor necrosis factor alpha on host immune response in chronic persistent tuberculosis: possible role for limiting pathology. Infect Immun 2001; 69: 1847-1855.
- Gomez-Reino JJ, Carmona L, Valverde VR, Mola EM, Montero MD, Biobadaser Group. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors may predispose to significant increase in tuberculosis risk: a multicenter active-surveillance report. Arthritis Rheum. 2003; 48: 2122-2127.
- Mohan AK, Coté TR, Block JA, Manadan AM, Siegel JN, Braun MM. Tuberculosis following the use of etanercept, a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor. Infect Dis. 2004; 39: 295-299.
- Askling J, Fored CM, Brandt L, Bertillson L, Coster L, Geoborek P, et al. Risk and case characteristics of tuberculosis in rheumatoid arthritis associated with tumor necrosis factor antagonists in Sweden. Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 52: 1986-1992.
- Gümüslü F, Özkara S, Özkan S, ve ark. TürkiyedeveremSavasi 2007 raporu. VeremSavasDaireBaskanligi Ankara. 2007.
- Hanta I, Ozbek S, Kuleci S, Kocabas A. The evaluation of latent tuberculosis in rheumatologic diseases for anti TNFTherapy: Experience with 192 patients. Clin Rheumatol. 2008; 27: 1083-1086.
- Cagatay T, Aydin M, Sunmez S, Cagatay P, Gul A, Artim B, et al. Follow-up results of 702 patients receiving tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonists and evaluation of risk of tuberculosis. RheumatolInt. 2010; 30: 1459-1463.
- Dixon WG, Hyrich KL, Watson KD, Lunt M, Galloway J, Symmons DP, et al. Drug-specific risk of tuberculosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with anti-TNF therapy: results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register (BSRBR). Ann Rheum Dis. 2010; 69: 522-528.
- Mariette X, Salmon D. French guidelines for diagnosis and treating latent and active tuberculosis in patients with RA treated with TNF blockers. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003; 62: 791.
- Harris J, Keane J. How tumour necrosis factor blockers interfere with tuberculosis immunity. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010; 161: 1-9.
- Barnes PF. Diagnosing latent tuberculosis infection: turning glitter to gold. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004; 170: 5-6.
- Crum NF, Lederman ER, Wallace MR. Infections associated with tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonists. Medicine (Baltimore). 2005; 84: 291-302.