
Research Article
Austin J Vaccines & Immunother. 2015; 2(1): 1007.
Association of Network Centralities to Uncover the Novel Protein Interactions in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Lakra VA1, Snijesh VP1, Singh S1, Vennila JJ2 and Wilson A3*
1Department of Bioinformatics, University of Karunya Health Sciences and School of Biotechnology, India
2Department of Biotechnology, University of Karunya Health Sciences and School of Biotechnology, India
3Division of Microbiology & Molecular Genetics, Loma Linda University, USA
*Corresponding author: Aruni Wilson, Department of Microbiology & Molecular Genetics, University of Loma Linda, USA
Received: June 04, 2015; Accepted: September 23, 2015; Published: October 01, 2015
Abstract
In current year’s network based approaches has emerged as powerful tools for studying complex diseases. The graph theory defines the biological network in a good manner with its already developed methods such as betweenness centrality and Q-modularity. It has become clear that many complex conditions such as cancer, autoimmune disease and heart diseases are characterized by specific gene network patterns. In recent times, research investigations on gene networks are much focused to identify significant reliable targets for any disease. The protein coding genes causing Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) were found from the Gene Cards database. Polar map per was used to explore the architecture of the protein interaction networks i.e. highly connected interact me. The potential targets identified as GFAP, SET, IGHG1, HNRNPA2B1, AFF2 and DECR1 were observed on the basis of high traffic value and Q modularity. Our result suggests that these target proteins will be helpful for future studies in RA pathogenesis and may outstandingly assist in the success of therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Rheumatoid arthritis; Polar map per; Gene cards; Fatigo
Introduction
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a common, chronic autoimmune disorder of unknown origin that results from aggressive synovial tissue inflammation [1]. The synovitis of RA is primarily confined to the small hand and foot joints, but inflammation can also be found in the larger peripheral joints dysfunction occurs via the destruction of particular cartilage, tendon and subchondral bone [2]. The vessels, skin, kidney and lung, among other organs, can also be affected as a function of RA severity [3]. Synovial macrophages, fibroblast and lymphocytes are critical to the pathogenesis of the RA [4].
Biological network analysis has become a central component of computational systems biology. Significant efforts have focused on analyzing and inferring the topology and structure of cellular networks and on relating them to cellular function and organization [5]. Graph theory portrays biological interactions as a huge network consisting of vertices, nodes as individual bio-entities, and edges, representing connection between vertices [6]. The networks are widely used to show interactions and the reliance among the entities [7].
The key objective of this paper is to find out the important RA target proteins apart from the seed proteins which play major role in RA. The network study was performed for the available RA proteins and its interacting proteins. Significant target proteins other than the reported proteins were identified by implying high traffic value. Biological Validation using molecular function, biological process and pathway studies equally conveys that these proteins are really influential in relation to autoimmune and inflammatory process of RA.
Materials and Methods
1435 RA related genes were obtained from Gene Cards which is an integrated database of human genes; it provides comprehensive and updated information on genomic, proteomic and transcriptomic data [8]. The genes were further filtered/screened by considering protein coding genes and score value which is based on Gene Cards Inferred Functionality Score (GIFTS) [9]. 1046 protein coding genes were found significant for the construction of biological network and these proteins coding genes are considered as the seed protein molecules in our research study.
Construction of the network and statistical analysis
The Polar Map per was used for the Protein Interaction Map (PIM) study. An interactome was generated which was further divided into 4 islands (Figure 1), 43 modules and 273sub modules. The architecture of the PIM in RA is exposed using the two prime theoretical network measures; they are betweenness centrality and Q-modularity. Traffic values, compute the betweenness centrality of each node [10,11]. Protein nodes are displayed as a circular graph depending upon two factors radial and angular coordinates, whose values are based on the calculation of between’s centrality measure [10]. The modules are generated via the Q-modularity algorithm [12]. The biological validation of the different modules was performed by using fatigo tool [13].

Figure 1: The PIM interactome with seed proteins (green) and their interacting
proteins (red) obtained from the biological network analysis.
Biological validation of hub networks
13647 protein interactions were obtained from string database which relies on fine resources such as HUGO (HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee), MINT(Molecular Interaction Database), PDB (Protein Data Bank), KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) [14]. 1046 protein coding genes were considered as the seed genes (mean value=13.046) and the interacting proteins obtained from STRING as significant molecules which may or may not play crucial role in the pathway of RA. Biological network analysis resulted in PIM interactome consisting of seed molecules and their interacting proteins as shown in the (Figure 1).
The interactome included 4988 nodes, 4 islands, 43 modules and 273 sub modules (Figure 2). The island 1(Q-score=0.657, 4971 nodes), island 2(Q-score=0.275, 11 nodes), island 3(Q-score=0.361, 6 nodes) included 39, 1, 2 modules and 263, 1, 2 sub modules respectively (Table 1). The Biological Processes (BP), Cellular Component (CC), Molecular Function (MF) and KEGG pathways are studied for each module which provides more elaborate information associated with interactome in PIM [13].
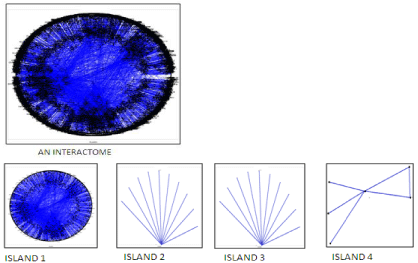
Figure 2: The interactome with its four Islands obtained from biological
network analysis using polar mapper.
Island
Module
SM
Gene Name
TV (Island)
TV (Module)
TV (SM)
1
21
140
KNG1
401456.1
13963.03
1686.32
1
10
61
POMC
304883
124.7667
124.7667
1
21
143
MAPK3
170128.5
10233.88
1461.91
1
31
207
GFAP
93693.93
2540.00
14.00
1
38
260
XRN1
71467.17
3308.67
78.67
1
2
16
DECR1
68882.11
4820.61
54.00
1
31
208
IGHG1
64386.02
2230.00
70.00
1
39
267
SET
50063.64
2146.00
10.00
1
28
187
OPRK1
49024.9
519.74
124.76
1
2
12
HNRNPA2B1
35753.90
4705.80
215.40
1
19
130
SHH
32904.59
7301.94
73.50
1
14
90
GOT2
31406.77
1186.00
16.00
1
11
73
RPL34
31225.80
4545.52
16.00
1
31
203
AFF2
27065.68
2322.00
10.00
1
13
85
GOT1
24605.84
4498.00
34.00
1
27
175
IDUA
24252.63
5878.00
32.00
1
12
76
RYR1
21854.52
2416.00
30.00
1
24
158
ERBB2IP
17156.21
12.00
12.00
1
25
165
ANK1
15484.42
4690.00
20.00
1
35
232
DEFB4A
15456.81
30.00
10.00
1
39
264
UGP2
14010.53
1294.00
22.00
1
1
4
SETD1A
13935.15
4222.00
14.00
1
32
212
LYL1
12843.63
1552.00
18.00
1
16
106
CBR1
12268.28
178.00
8.00
1
33
219
IGHA1
10990.95
1902.00
12.00
1
16
107
PTGDS
10968.48
138.00
8.00
1
20
133
VASP
10751.40
30.00
14.00
1
26
169
RARB
10475.06
20.00
10.00
Table 1: Significant RA proteins other than seed proteins identified on the basis of the traffic value.
1
35
231
KLK8
10289.30
30.00
12.00
1
35
231
SHISA7
10289.30
30.00
12.00
1
3
20
GLB1
9936.00
3072.00
30.00
1
4
24
XPC
9936.00
16.00
16.00
1
4
24
ERCC1
9936.00
16.00
16.00
1
4
24
ERCC2
9936.00
16.00
16.00
1
4
24
ERCC3
9936.00
16.00
16.00
1
6
41
MRPL30
9936.00
16.00
16.00
1
6
41
MRPL12
9936.00
16.00
16.00
1
6
41
MRPS24
9936.00
16.00
16.00
1
6
41
NDUFA8
9936.00
16.00
16.00
1
7
42
CHRNA4
9936.00
18.00
18.00
1
7
42
CHRNA5
9936.00
18.00
18.00
1
7
42
CHRNB2
9936.00
18.00
18.00
1
7
42
CHRNA2
9936.00
18.00
18.00
1
8
43
AKAP1
9936.00
18.00
18.00
1
8
43
ROPN1
9936.00
18.00
18.00
1
8
43
AKAP3
9936.00
18.00
18.00
1
8
43
ROPN1L
9936.00
18.00
18.00
1
16
106
PTGIS
9936
34
8
1
20
133
WASF1
9936.00
30.00
14.00
1
20
133
TMSB4Y
9936.00
30.00
14.00
1
22
146
ASCL3
9936.00
18.00
18.00
1
22
146
PCYOX1
9936.00
18.00
18.00
1
22
146
MEGF9
9936.00
18.00
18.00
1
22
146
FBXW2
9936.00
18.00
18.00
1
24
158
PKP4
9936.00
12.00
12.00
1
24
158
CTNND2
9936.00
12.00
12.00
1
24
158
PPCS
9936.00
12.00
12.00
1
26
169
RARG
9936.00
20.00
10.00
1
26
169
KARS
9936.00
20.00
10.00
1
30
201
LIMCH1
9936.00
6.00
6.00
1
30
201
LMO7
9936.00
6.00
6.00
1
30
201
PDLIM5
9936.00
6.00
6.00
2
40
270
OR4C45
20.00
20.00
20.00
2
40
270
OR2V1
20.00
20.00
20.00
2
40
270
OR1M1
20.00
20.00
20.00
2
40
270
OR5H14
20.00
20.00
20.00
3
41
41
DAPK3
20.00
20.00
20.00
3
41
41
LIPH
20.00
20.00
20.00
3
41
41
DMD
20.00
20.00
20.00
3
41
41
UTRN
20.00
20.00
20.00
4
42
272
LY6G6C
10.00
2.00
2.00
4
43
273
LY6G6F
10.00
6.00
6.00
4
43
273
LY6G6D
10.00
6.00
6.00
SM: Sub Module; TV: Traffic Value
Table 1(1of2):
Modular Network Characterization and Validation
In the PIM interactome, island 1 was observed with more number of modules and interconnectivity. It was found that the Module 25 contains 102 proteins and is statistically enriched with the Notch signaling pathway as given by BP (P=1. 52E-14) and KEGG (P=9. 49E- 15). Notch signaling pathway plays an important role in the regulation of pro-inflammatory mechanism in RA [15]. From recent research investigations, it is evident that the regulatory proteins present in the Notch pathway are also targeted in RA [16]. Module 2 as shown in the (Figure 2) contains 128 proteins out of which 2, 4-Dienoyl CoA Reductase 1 (DECR1) and Heterogeneous nuclear rib nucleoprotein A2/B1 (HNRNPA2B1) were found significant other than the seed proteins. DECR1 showed its involvement in the autoimmune diseases [17] and inflammatory diseases [18] as it damages tissue and the immune activity in Chagas disease [19]. The protein HNRNPA2B1 is connected with DECR1 and superoxide dismutase 3 (SOD3) (Figure 4) which is a seed protein targeted for antinuclear auto antibodies in the several autoimmune diseases such as RA, AIH (Autoimmune Hepatitis) and SLE (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus) [20,21].
Figure 3: Prominent Modules present in island 1.
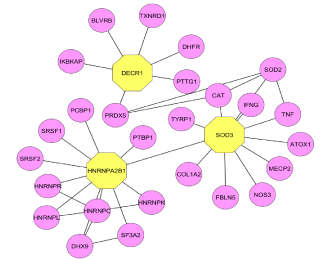
Figure 4: The proteins involved in the notch signaling pathway with their
interacting molecules.
The proteins present in Modules 2, 4 and 9 are found in nuclear part and they have significant function in DNA directed RNA polymerase activity (P=5.35E-08) and DNA binding (P=1.76E-05). They play an important role in Nucleotide excision repair (1.98E-16) and pyrimidine metabolism (P=2.92E-11) pathways. They are also involved in pyrimidine metabolism (P=2.92E-11), Nucleotide excision repair (P=1.98E-16), metabolism of amino acids (P=9.82E-06) and DNA repair (P=1.40E-09).These proteins, mainly involved in biological processes such as Cell redox homeostasis (P=5.32E-04), Nucleotide-excision repair, DNA incision (P=6.68E-09) and His tone modification (P=9.71E-09). The modules 6 and 11 contain 6 and 127 proteins respectively, which are present in ribosome (P=2.42E-33) and mitochondrion (P=7.08E-05) respectively, they are responsible for Structural constituent of ribosome (P=6.93E-33) and are involved in ribosome pathways (P=6.55E-30).The ribosomal proteins are found unregulated in the RA patients [22]. In module 20, Act in cytoskeleton organization is found statistically important given by CC (P=3.47E-06), BP (P=4.78E-07), and MF (P=4.51E-06). The Acting cytoskeleton organization reveals the pathogenic activation of synovial fibroblasts in the modeled TNF‐mediated arthritis [23]. Hence a protein in the above mentioned modules plays a critical role in the pathway of RA as their functional involvements are closely related to the pathogenesis of RA.
The module 27 contains 108 proteins present in Golgi apparatus (P=9.82E-05) they are major role players in Transferase activity (P=9.87E-10) and are important in the pathways such as the glycosylation of mammalian N-linked oligosaccharides (P=2.10E-03) and glcosaminoglycan degradation (P=9.47E-08). Glycosylation of mammalian oligosaccharides may be involved in an etiology of RA [24] Golgai apparatus takes part in terminal protein Glycosylation in RA [25]. The 119 proteins present in the module 28are related to Chemokines activity (P=5.463E-34) and GPCR binding (P=4.728E-32) and are also important in GPCR signaling (P=9.13E-39). Recent research reports show that targeting chemokines can be useful for the RA therapy [20-28]. The module 29 contains 11 proteins which are present in Aminocyl-tRNA synthetase multi enzyme complex (P=3.72E-02) that are involved in Aminoacyl-tRNA ligase activity (P=1.38E-09), Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis (P=4.28E-09) and Gene expression (P=2.75E-14) pathways. The specific AminocyltRNA synthetase is related to the Autoimmune disorders [29]. The module 16 contains 18 proteins which are present in Arachidonic acid metabolism (P=1.05E-05) and isomerase activity (P=1.04E-02).
Module 31 (Figure 5) contains 71 proteins out of which GFAP, IGHG1, and AFF2 were observed other than the seed proteins. These proteins are connected to each other and to other seed proteins such as HGFAC (HGF activator) and GJB6 (gap junction protein). The expression of Glial fibrillary acidic protein is found increased in the synovial fluid and thus it’s considered as the novel Auto antigen of RA [30]. The immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 1 (G1m marker) protein is important in the autoimmune response. AF4/FMR2 family, member 2 protein showed disturbance in the immune system as the immune activity in lymphocytic leukemia [31], it directly connects with the seed proteins such as Fragile Site-Associated Protein (KIAA1109) and ATP-binding cassette sub-family G, member 2 (ABCG2). SET nuclear oncogene protein is found in the module 39 (Figure 2) and which does not belong to the group of 65 seed genes, but it is directly connected with seed proteins such as DEK (DEK oncogene), TREX1 (three prime repair exonuclease 1) and HMGB2 (high mobility group box 2) (Supplementary File 1).
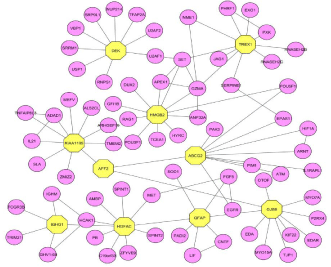
Figure 5: Proteins in the module 31 along with seed proteins which plays an
influential role in the pathway of RA.
Conclusion
RA etiology and target identification is very important as the cause of disease is unknown. Network based approach is one of the reliable methods to identify the target protein from the cluster of protein networks associated with the pathway of the disease. Biological network analysis provided a system level association of proteins in terms of functional interactions and biological pathways related to Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). 1435 RA associated genes obtained from Gene Cards were filtered to 1046 protein coding genes and which were used up for the construction of Protein Interaction Map (PIM). Biological and functional characterization of the clusters of protein networks in PIM resulted in the identification of significant proteins other than the seed proteins reported in Gene Card. The research investigations identified significant proteins like GFAP, SET, IGHG1, HNRNPA2B1, AFF2 and DECR1 in relation to the pathophysiology of RA. The significant proteins predicted using theoretical and statistical analysis can be further validated by in vivo and in vitro methods to identify their influential role in the pathophysiology of RA.
References
- Huber LC, Distler O, Tarner I, Gay RE, Gay S, Pap T. Synovial fibroblasts: key players in rheumatoid arthritis, Rheumatology. 2006; 45: 669–675.
- Cardiel MH. By the Latin American Rheumatology Associations of the Pan-American League of Associations for Rheumatology (PANLAR) and the Grupo Latinoamericano de Estudio de Artritis Reumatoide (GLADAR), First Latin American position paper on the pharmacological treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, Rheumatology. 2006; 45: ii7–ii22.
- Charles JM. Definingnval targets for intervention in rheumatoid arthritis: An overview, Current rheumatology reviews. 2008; 4: 214-218.
- Liu H, POPE RM. The role of apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis, Current opinion in pharmacology. 2003; 3: 317-322.
- Tanya Y. Berger-Wolf, Teresa M. Przytycka, Mona Singh, Donna Slonim. Dynamics of biological networks: session introduction, Pacific symposium on siocomputing. 2010; 15: 120-122.
- Georgios AP, Anna LW. Reinhard SA. Survey of visualization tools for biological network analysis, Bio data mining. 2008; 1: 12.
- Schreiber F, Dwyer T, Marriott K, Wybrow M. A generic algorithm for layout of biological networks. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009; 10: 375.Safran Marilyn, Chalifa-Caspi V, Orit Shmueli, Tsviya Olender, Michal Lapidot, Naomi Rosen, et al. Human Gene-Centric Databases at the Weizmann Institute of Science: Gene Cards, UDB, Crow 21 and HORDE, Nucl. 2003; 31: 142-146.
- Safran Marilyn, Chalifa-Caspi V, Orit Shmueli, Tsviya Olender, Michal Lapidot, Naomi Rosen, et al. Human Gene-Centric Databases at the Weizmann Institute of Science: Gene Cards, UDB, Crow 21 and HORDE, Nucl. 2003; 31: 142-146.
- Arye Harel, Aron Inger, Gil Stelzer, Strichman-Almashanu L, Irina Dalah,Marilyn Safran, et al. GIFtS: annotation landscape analysis with Gene Cards, BMC Bioinformatics. 2009; 10: 348.
- Freeman L. A set of measures of centrality based upon betweenness, Sociometry. 1977; 40: 35–41.
- Gonçalves JP, Mário Grãos, André XCN, Valente. POLAR Map per: a computational tool for integrated visualization of protein interaction networks and mRNA expression data, J R Soc Interface. 2009; 6: 881–896.
- Clauset A, Newman MEJ, Moore C. Finding community structure in very large Networks. Phys. Rev. 2004; E70: 066111.
- Al-Shahrour F, Diaz-Uriarte R, Joaquin Dopazo. FatiGO: a web tool for finding significant associations of Gene Ontology terms with groups of genes, Bioinformatics archive. 2004; 20: 578-580.
- Andrea Franceschini, Damian Szklarczyk, Sune Frankild, Michael Kuhn, Milan Simonovic, Alexander Roth, et al. STRING v9.1: protein-protein interaction networks, with increased coverage and integration, Nucleic Acids Res. 2014; 41: 808–815.
- Gao W, McCormick J, Connolly M, Balogh E, Veale DJ, Fearon U. Hypoxia and STAT3 signalling interactions regulate pro-inflammatory pathways in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014; 10: 1136.
- Zhijun Jiao, Wenhong Wang, Jie Ma, Shengjun Wang, Zhaoliang Su, Huaxi Xu. Notch Signaling Mediates TNF-α-Induced IL-6 Production in Cultured Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes from Rheumatoid Arthritis, Clinical and Developmental Immunology. 2011; 2012: 1-6.
- De Ravin SS, Naumann N, Cowen EW, Friend J, Hilligoss D, Marquesen M, et al. Chronic Granulomatous Disease as a Risk Factor for Autoimmune Disease, J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 122: 1097–1103.
- Eiji Matsuura, Fabiola Atzeni, Sarzi-Puttini P, Maurizio T, Lopez LR, Nurmohamed MT. Is atherosclerosis an autoimmune disease? BMC Medicine. 2014; 12: 47.
- Tarleton RL, Zhang L. Chagas disease etiology: autoimmunity or parasite persistence? Parasitol Today. 1999; 15: 94-99.
- Huguet S, Combet C, Ballot E, Johanet C, Deleage G, Samuel D, et al. 860 HNRNP A2/B1 as antinuclear antibodies target: epitope mapping and differential reactivity in autoimmune hepatitis and connective tissue diseases, Journal of hepatology. 2008; 48: 323.
- Beleoken E, Leh H, Arnoux A, Ducot B, Nogues C, De Martin E, et al. SPRI-Based strategy to identify specific biomarkers in systemic lupus erythematosus, Rheumatoid Arthritis and Autoimmune Hepatitis, PLOS ONE. 2013; 8: 84600.
- Meugnier E, Coury F, Tebib J, Ferraro-Peyret C, Rome S, Bienvenu J, et al. Gene expression profiling in peripheral blood cells of patients with rheumatoid arthritis in response to anti-TNF-alpha treatments, Physiol Genomics. 2011; 43: 365-371.
- Vasilopoulos Y, Gkretsi V, Armaka M, Aidinis V, Kollias G. Actin cytoskeleton dynamics linked to synovial fibroblast activation as a novel pathogenic principle in TNF‐driven arthritis, Ann Rheum Dis. 2008; 66: iii23–iii28.
- Elizabeth FH, Michael JD. Role of protein glycosylation in immune regulation, Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 1993; 52: S22-S29.
- Yang Y, Fujita J, Tokuda M, Bandoh S, Ishida T, Murota M, et al. Clinical features of several connective tissue diseases with anti-Golgi antibody, Ann Rheum Dis. 2001; 60: 986-987.
- Koch AE. Chemokines and their receptors in rheumatoid arthritis: future targets? Arthritis & Rheumatism. 2005; 52: 710–721.
- Catherine JH, Markus Koglin, Fiona HM. Therapeutic antibodies directed at G protein-coupled receptors Nat Rev Rheumatology, Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010; 10: 594-60.
- Neumann E, Khawaja K, Müller-Ladner U. G protein-coupled receptors in rheumatology, Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014; 10: 429-436.
- Sang GP, Paul Schimmel, Sunghoon Kim. Aminoacyl tRNA synthetases and their connections to disease, Sang Gyu Park. 2008; 105: 11043–11049.
- Biswas S, Sharma S, Saroha A, Bhakuni DS, Malhotra R, Zahur M, et al. Identification of novel autoantigen in the synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis patients using an immunoproteomics approach, PLOS ONE. 2013; 8: 0056246.
- Mireille Melko, Dominique Douguet, Mounia Bensaid, Samantha Zongaro, Céline Verheggen, Jozef Gecz, et al. Functional characterization of the AFF (AF4/FMR2) family of RNA-binding proteins: insights into the molecular pathology of FRAXE intellectual disability, Institute of Molecular and Cellular Pharmacology. 2011; 20: 1873-1885.