
Review Article
Austin J Vet Sci & Anim Husb. 2023; 10(1): 1111.
A Review of Swine Brucellosis in Ethiopia: Epidemiology, World Distribution, Risk Factors of Infection, Public Health and Economic Importance
Demena GK¹* and Sorsa M²
¹Animal Health Institute, Sebeta, Oromia, Ethiopia
²Ambo University, Ambo, Oromia, Ethiopia
*Corresponding author: Getachew Kinfe Demena Animal Health Institute, Sebeta, Oromia, Ethiopia
Received: December 13, 2022; Accepted: January 31, 2023; Published: February 07, 2023
Abstract
Brucellosis is an emerging disease causing devastates loss in the livestock industry and considered as contagious bug producing chronic infections however it is one of the world’s neglected zoonosis. Though epidemiological data are limited, swine brucellosis occurs with different rate of incidence in sub Saharan African countries. There are several reports on the prevalence rate of the disease in most parts of Ethiopia in different animal species except in pigs. This review denotes the epidemiology of the bacteria, an overview of its distribution, and Risk factors of infection and Public Health importance.
Keywords: Brucellosis; pig; Epidemiology; Risk factors; Ethiopia
Introduction
Brucellosis is world zoonosis caused by intracellular bacteria belonging to the genus Brucella gram-negative bacilli [56]. Is a contagious disease causing chronic infections with intermittent bacteremia manifested typically by abortion and cross-species transmission of certain species of the bacteria can occur [49]. In most of the underdeveloped world causes upsetting losses to the livestock industry. It is a widespread disease in Central and South America in most of the Southern European countries, Central and Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and in Sub-Saharan Africa countries though epidemiologic data are limited [15,16]. Swine production in Ethiopia is in its childhood and this work aims to review prevalence and the different characteristics of brucellosis in pigs.
Epidemiology of Swine Brucellosis
Epidemiology in this contacts’ is to indicate the host range of the Bacteria. Resistance to the environment, wide host range and the intracellular nature of Brucellae makes the epidemiology of the disease complex [57,66].
B. suis, the biotype 1, 2, or 3 infect commonly other host animal species such as cattle, sheep, goats, horses, dogs, and rodents. B. suis infection in cattle causes mastitis, and the bacteria are excreted in the milk leading to a potentially serious human infection [8,35,46]. B. suis biovar 1 has been recovered from European hares and sheep in Argentina. B. suis biovar 2 from roe deer in Germany and biovar 3 from horses in Croatia [29,58].
Swine brucellosis is maintained in wild boar and feral pigs’ populations that can serve as reservoirs if there is contact with domestic pigs reared outdoors [18]. Rabbits were infected experimentally with a biovar 1 isolate from wild hares in South America. Peoples those who have contact with B. suis infected cat has acquired infection by the bacteria had been recorded. Dogs, and rodents, such as rats and mice, acquire the agent by cohabitation with infected hosts. B. suis biotype 1was repeatedly isolated from the semen of a dog with a clinical history of hind limb lameness [45]. In swine rearing areas there have been abundant instances of B. suis infection in rodents and carnivorous species [47].
Global Distribution of Swine Brucellosis
B. suis infection in wild boar populations has increased in Germany and Japan and has attained a very high level in southern Spain façade a serious hazard both to local domestic pigs, hunters, and animal care professionals [2]. Epidemiological data imply that an extensive distribution of B. suis in domestic swine in Central and South America (Argentina, Brazil, Columbia, Cuba, Chile, Honduras, Paraguay, and Peru) with infections predominantly caused by biovar1 [54]. This disease is not common but occurs sporadically in Europe Asia and Oceania. The north European countries and Canada are free also Israel and Many Muslim countries show free from Swine brucellosis because of religious and culture that restrict swine production and impact populations of the preferred host species (Meirelles et al., 2012). Generally, swine brucellosis occurs worldwide with low prevalence but is enzootic and highly prevalent in South-East Asia and South America.
In Latin America, it is thought to have the highest prevalence in the world [45,47]. In parts of Central and Southeast Asia, swine brucellosis appears to be prevalent with the greatest economic impact and human infection in the People’s Republic of China due to high levels of swine production [30]. Although epidemiological data are limited, there were reports of the occurrence of swine brucellosis in many Southeast Asian countries such as French Polynesia, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Taiwan, Tonga, and other islands in the Pacific [53,60]. (Figure 3) depicts the worldwide distribution of livestock outbreaks of B.abortus, B.melitenis, and B.sui
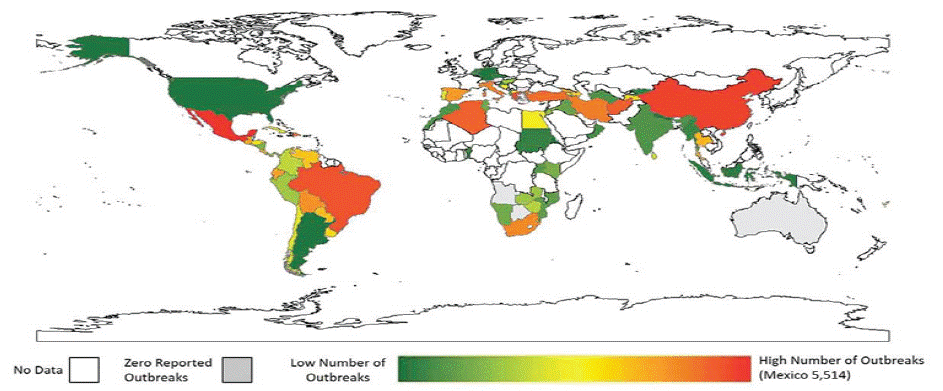
Figure 1: Global distributions of livestock outbreaks of B.abortus, B.melitenis & B.suis Source: Noah and Brant (2018).
Distribution of Swine Brucellosis in Africa
Although because of lack of surveillance lots of cases of Brucella infections are not detected, Brucellosis is endemic and prevalent in sub-Saharan countries causing abortion, premature birth and decreased productivity in animals, and long debilitating illness in humans (Mazeri et al., 2013; Havelaar et al., 2015; Ladbury et al., 2017). Africa has relatively small swine populations and although porcine brucellosis is believed to be extensive across sub-Saharan Africa, epidemiologic data are limited (Olsen et al., 2012; Godfroid et al., 2013; Ducrotoy et al., 2015). B. suis biovar 1 has been isolated from bovine in Zimbabwe and Egypt (Ledwaba et al., 2014; Ahmed et al., 2014). Few serological investigations in Uganda, Nigeria, and Zambia indicate low prevalence of swine brucellosis (Joseph et al., 2016) and lately reports 0.57% sero prevalence of swine Brucellosis in Kenya (James et al., 2020). On the other hand, there were reports of higher prevalence in Nigeria 30.6% (Ngbede EO et al., 2013) and recently 10.8% in Egypt (Khan et al., 2019).
Outlook of Swine Brucellosis in Ethiopia
Although the management practice remains traditional, small scale swine production sometimes integrated with mixed farming has practiced particularly in the central part of the country [1]. Few studies on management and production system conclude that lack of veterinary care and awareness about swine diseases, and extensive husbandry system makes pig as potential reservoir hosts of diseases causing economic sufferers to the piggery sector [61]. In Ethiopia there are only very few surveillance study and therefore epidemiological data that shows status of the disease are limited (Table 1).
Locations
Prevalence rate
References
RBT
CFT
IELISA
Central Ethiopia
4.5%
--
--
Kebeta et al.( 2015)
East Shoa
5.1%
3.57%
Girmay et al (2018)
Central Ethiopia
3.85%
--
3.48%
Kinfe et al. (2022)
Table 1: Sero prevalence of brucellosis in pigs in Ethiopia from 2015-2022.
Risk Factors of Brucella Infection
Risk Factors Associated with the Agent and its Mode of Transmission
Brucellosis in animals can be transmitted both by vertical and horizontal transmission causing abortion and infertility in their primary natural hosts. [14,17]. Horizontal transmission occurs through Copulation and ingestion of feed or water contaminated by birth products or vaginal discharges from an infected Sow. Fetal membranes and aborted fetuses contain large amounts of bacteria so is an important means of transmission when contact with mucosa in livestock [52]. Pigs also shed this organism in milk, urine, and semen. B.suis can become established in the mammary gland of ruminants and are subsequently found in the milk. B. suis has also had been found in canine testes, salivary gland, and kidneys [47]. Sexual partners of infected patients may be at risk for exposure to brucellosis though is a rear cause in human [40]. Vertical transmission could occur during a maternal bacteremia phase through trans-placental transmission, through breastfeeding or from urine and vaginal secretions during delivery. While neonatal brucellosis cases are rare B. melitensis, and also B. abortus has been documented [65].
Risk Factors Associated with the Host
Although the Brucella species are bound to a specific host, their pathogen host relationship is not restricted therefore cross-transmission to other animal species and human infection is commonly observed [16]. Brucellosis sero-prevalence increased with age and sexual maturity. Sexually mature and pregnant animals are more susceptible to brucellosis than sexually immature animals of either sex [23,50]. This may in the young animal after entry, the organism localizes itself in the regional lymph nodes without provoking detectable antibody production until their first parturition/abortion or until the animal is conceived and start secreting erythritol sugar. Erythritol is related to sex hormones in both sexes that stimulate the growth and multiplication of the organisms and tend to increase in concentration with age and sexual maturity [4,38]. However, variations in the age of sexual maturity among breeds could present differences between age and brucellosis positivity [36]. When the boars and sows encounter vaginal or uterine discharges during courting before mating they can also be infected by the bacteria via the mouth. Rodents and carnivorous are a potential risk in the diffusion of the disease, acting as mechanical disseminators by feeding on contaminated biological materials, dragging them along, and spreading the bacteria [47,64].
Occupational Risk Factors of Brucella Infection
Veterinarians, laboratory workers, butchers, breeders, hunters, and pig rearing Farmers are at high risk of acquiring infection through close direct contact with contaminated biological materials or infected animals and accidental exposure to culture and inactivated brucella cells [6,67]. Swine brucellosis in man is most often a disease of occupation [59].
Risk Factors Associated with Food Born Infections
Hunting Dogs can contract brucellosis from feral swine through direct contact with infected swine or by consumption of uncooked pork or scraps [54]. Foodstuffs of animal origin stand for the major source of infection to humans. High risks for food-borne B. suis infection occur to feral swine hunters who consume raw or undercooked pork. Homemade cheese and Ice cream spread the disease well among human as they are prepared in a way which does not eliminate viable Brucella organisms [34,62]. Infection with individuals who come in contact with marine mammals, consuming raw fish or shellfish has been documented in the Gulf countries like Mexico, Atlantic, and Pacific coasts [9].
Management Risk Factors
Introduction of infected purchased pigs and insemination with semen from infected boars are the main risks associated with pig brucellosis. Poor husbandry methods and lack of effective disposal of biological materials and carcasses into the environment cause significant environmental contamination and scavengers and rodents play a considerable role in the prevalence of the disease [3,24].
Public Health Importance of Swine Brucellosis
Brucellosis is considered a re‑emerging zoonotic disease worldwide causing considerable human morbidity in endemic areas [15,56]. It is a serious and long-lasting disease in human which does not act in response well to antibiotics [5,10,13]. B. suis is the second most pathogenic and invasive species with severe disease in humans [11,19]. In various parts of the world, brucellosis becomes a significant human disease especially in the Middle East, Mediterranean countries of Europe, south and central Asia, central and South America, and north and east Africa, however, it is frequently neglected and often goes unreported [7,55]. Due to its highly infectious nature, the bacteria have been used as potential bio-weapons as they can be readily aerosolized for mass destruction [56]. Moreover, an outbreak of brucellosis is possibly complicated to notice because the initial symptoms are easily confused with those of malaria, typhoid and influenza [42,63]. Lack of hygienic erasures in animal husbandry and food handling, expansion of livestock industries, and urbanization partly account for the disease leftover as public health hazard. Penetration via breaks in skin wounds, mucous membranes, and direct contact with materials associated with abortion, or with infected animals can lead to human infection through aerosols into respiratory tissues [12,13].
Economic Importance
The Brucella organisms infect large varieties of animals, and their prevalence is variable worldwide. The disease can cause high economic burdens associated with the application of prevention, surveillances and diagnosis [33,51,68]. Brucellosis makes difficult trade of animals and animal products, blocks free animal movement. Abortions, losses of young born, and still birth, culling of infected or unproductive animals are heavy economic losses in the community caused by the disease [28]. Genital infections are more frequent in boars than in bulls. Infection in pigs is characterized by abortion, decreased litter size, weak piglets, infertility, irregular oestrus and lameness/paralysis causing significant loss in the sector [39,47].
Conclusion and Recommendations
Swine brucellosis is prevalent across pig rearing worlds exerting considerable burdens on the economic growth of communities in developing countries but it is not well recognized. Wide host range, resistance to environment and treatment, and host immune system facilitate its survival in the populations and make the epidemiology of the bacteria complex. Subsequently, it remains a significant risk for human zoonotic infection. While swine brucellosis is believed to be extensive across sub-Saharan Africa, epidemiological data are limited. More importantly in Ethiopia, there is no study conducted related to its public health significance. Based on the above conclusion the following points are suggested.
Extensive survey or epidemiological study should be conducted.
There is a need to carry out survey to see the zoonotic implication.
References
- Abdu S, Gashaw A. Production system dynamism and parasitic interaction of swine in and around Holetta, Ethiopia. Ethiopian Veterinary Journal. 2010; 14: 71-81.
- Alfred S Evans, Philip S Brach man. Bacterial Infections of Humans: Epidemiology and Control. Second edition. M 04 2013; 1: 17- 865.
- Althouse, Rossow. The Potential Risk of Infectious Disease Dissemination via Artificial Insemination in Swine. Reproduction in Domestic Animals. 2011; 46: 64-7.
- Asgedom H, Damena D, Duguma R. Sero prevalence of Bovine Brucellosis and Associated Risk Factors in and around Alage District, Ethiopia. Springer plus. 2016; 5: 851.
- Aypak C, Altunsoy A, Kutta Çelik A. Epidemiological and clinical aspects of human brucellosis in eastern anatolia. J Nippon Med Sch. 2012; 79: 343-48.
- Brough HA, Solomon AW, Wall RA, Isaza F, Pasvol G. Brucellosis acquired by eating imported cheese. Journal of paediatrics and child health. 2011; 47: 840-41.
- Calvet F, Heaulme M, Michel R, Demoncheaux JP, Boue S, Girardet C. Brucellose et contexte opérationnel. Médecine et armée. 2010; 38: 429-34.
- Cao X, Li Z, Liu Z, Fu B, Liu Y, et al. Molecular epidemiological characterization of Brucella isolates from sheep and yaks in northwest China. Transbound Emerge Dis. 2018; 65: 425-33.
- (CDC, 2012): Human exposures to marine Brucella isolated from a harbor porpoise - Maine, 2012. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2012; 61: 461-63.
- (CDC, 2017): Brucellosis reference guide: exposures, testing, and prevention. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2017.
- Compés Dea C, Guimbao Bescós J, Alonso Pérez, de Ágreda JP, Muñoz Álvaro PM, et al. Epidemiological investigation of the first human brucellosis case in Spain due to Brucella suisbiovar 1 strain 1330. Enfermedades infecciosas y microbiologia clinica. 2017; 35: 179-81.
- Dean AS, Crump L, Greter H, Schelling E, Zinsstag J. Global burden of human brucellosis: a systematic review of disease frequency. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012; 6: e1865.
- Decretory M, Ammary K, Lbacha H, Zouagui Z, Mick V, et al. Narrative overview of animal and human brucellosis in Morocco: intensification of livestock production as a driver for emergence. Infect Dis Poverty. 2015; 4: 57.
- Diaz Aparicio E. Epidemiology of brucellosis in domestic animals caused by B. melitensis, B. suis and B. abortus. Rev Sci Tech. 2013; 32: 43-51, 53-60.
- Donev D, Karadzovski Z, Kasapinov B, Lazarevik V. Epidemiological and Public Health aspects of Brucellosis in the Republic of Macedonia. Prilozi. 2010; 1: 33-54.
- Ducrotoy M, Bertu WJ, Matope G, Cadmus S, Conde Álvarez R, et al. Brucellosis in Sub Saharan Africa: Current challenges for management, diagnosis and control. Acta Tropica. 2015; 165: 179-193.
- Ducrotoy M, Bertu WJ, Matope G, Cadmus S, Conde-Alvarez R, et al. Brucellosis in sub-Saharan Africa: current challenges for management, diagnosis and control. Acta Trop. 2017; 165: 179-93.
- Franco-Paredes C, Chastain D, Taylor P, Stocking S, Sellers B. Boar hunting and brucellosis caused by Brucella suis. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2017; 16: 18-22.
- Galińska E, Zagórski J. Brucellosis in humans Etiology, diagnostics, clinical forms. Annals of agricultural and environmental medicine. 2013; 20: 233-38.
- Girmay A. Epidemiology of canine and swine brucellosis in selected areas of east shoa zone, Oromia Regiononal state, Ethiopia: A Thesis submitted to Addis Ababa University College of veterinary medicine and agriculture in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in veterinary epidemiology. 2018.
- Godfroid J, Garin Bastuji B, Saegerman C, Blasco Martínez JM. Brucellosis in terrestrial wildlife. Revue Scientifique et Technique. 2013; 32: 27-42.
- Havelaar AH, Kirk MD, Torgerson PR, Gibb HJ, Hald T, et al. World Health Organization global estimates and regional comparisons of the burden of food‐borne disease in 2010. Plos Medicine. 2015; 12: e1001923.
- Ifa N, Shimelis S, Beyene D. Sero-prevalence of small ruminant brucellosis and its public health awareness in selected sites of Dire Dawa. Journal of Veterinary Medicine and Animal Health. 2012; 4: 61-66.
- Jean BN, Lucas EM, Sharadhuli IK, John B Muma, Esron DK. Association of Brucellosis with Abortion Prevalence in Humans and Animals in Africa: A Review. African Journal of Reproductive Health. 2018; 22: 120-36.
- Joseph E, Kristina R, Michel M, Dione A, Francis E, et al. Serological and molecular investigation for brucellosis in swine in selected districts of Uganda. J Infect Public Health. 2016; 48: 1147-55.
- Kebeta M, Gezahegn M, Tesfu K, Mebratu A, Hagos A, et al. Seroprevalence of Brucellosis from Pigs: The First Report in Central Ethiopia. Veterinary Science & Technology. 2015; 8: 338-44.
- Khan AU, Melzer F, El-Soally SAGE, Elschner MC, et al. Serological and molecular identification of brucella spp. in pigs from Cairo and Giza governorates, Egypt. Pathogens. 2019; 8: 1-7.
- Khurana SK, Sehrawat A, Tiwari R, Prasad M, Gulati B, et al. Bovine brucellosis - a comprehensive review. Vet quarterly. 2021; 41: 61-88.
- Kin MS, Fort M, de Echaide ST, Casanave EB. Brucella suis in armadillos (Chaetophractus villosus) from La Pampa Argentina. Vet Microbiol. 2014; 170: 442-45.
- Kutlu M, Cevahir N, Erdenlig-Gurbilek S, Akalin S, Ucar M, et al. The first report of Brucella suis isolation in human in Turkey. J Infect Public Health. 2016; 12: 345-55.
- Ladbury G, Allan KJ, Cleaveland S, Davis A, De Glanville WA, et al. One health research in Northern Tanzania, challenges and progress. East African Health Research Journal. 2017; 1: 8-18.
- Ledwaba B, Mafofo J, van Heerden H. Genome Sequences of Brucella abortus and Brucella suis Strains Isolated from Bovine in Zimbabwe. Genome announcements. 2014; 2: eo1063-14.
- Liu Q, Cao L, Zhu XQ. Major emerging and re-emerging zoonoses in China: a matter of global health and socioeconomic development for 1.3 billion. Inter J Infect Dis. 2014; 25: 65-72.
- Lucero N, Tenenbaum M, Jacob N, Escobar G, Groussaud P, et al. Application of variable number of tandem repeats typing to describe familial outbreaks of brucellosis in Argentina. J Med Microb. 2010; 59: 648-52.
- Mailles A, Ogielska M, Kemiche F, Garin –Bastuji B, Brieu N, et al. Brucella suis biovar 2 infection in humans in France: emerging infection or better recognition. Epidemiol Infect. 2017; 145: 2711-16.
- Matope DG, Bhehe E, Muma JB, Land A, Skjerve E. Risk factors for Brucella spp. infection in smallholder household herds. Epidemiol Infect. 2010; 39: 157-64.
- Mazeri S, Scolamacchia F, Handel IG, Morgan KL, Tanya VN, et al. Risk factor analysis for antibodies to Brucella, Leptospira and C. burnetii among cattle in the Adamawa Region of Cameroon: A cross sectional study. Tropical Animal Health and Production. 2013; 45: 617-23.
- Megersa B, Biffa D, Abunna F, Regassa A, Godfroid J, et al. Sero epidemiological study of livestock brucellosis in a pastoral region. Epidemiol Infect. 2012; 140: 887-96.
- Megid J, Mathias LA, Robles CA. Clinical Manifestations of Brucellosis in Domestic Animals and Humans. The Open Veterinary Science Journal. 2010; 4: 119-26.
- Meltzer E, Sidi Y, Smolen G, Banai M, Bardenstein S, et al. Sexually transmitted brucellosis in humans. Clin Infect Dis. 2010; 51: e12-e15.
- Ahmed MSM, Marta PS, Teresa GS, Hosein IH, Nerea IG, et al. Assessment of Genetic Diversity of Zoonotic Brucella spp. Recovered from Livestock in Egypt Using Multiple Locus VNTR Analysis. Biomed Res Int. 2014; 2014: 353876.
- Neubauer H. Brucellosis: New demands in a changing world. Prilozi. 2010; 31: 209-17.
- Ngbede EO, Momoh AH, Bala RS, Madaki BD, Maurice NA. An Abattoir based study on sero diagnosis of swine brucellosis in Makurdi, Benue State, and North Central Nigeria. Journal of Advanced Veterinary Research. 2013; 3: 57-59.
- Noah CH, Brant AS. Comparisons of brucellosis between human and veterinary medicine. Infection ecology and Epigimeology. 2018; 8: 1500846.
- OIE. Porcine brucellosis. Version adopted by the World Assembly of Delegates of the OIE. Terrestrial Manual. 2009; 1106-12.
- OIE. Bovine brucellosis.Office International des Epizooties (OIE).Terrestrial Manual. 2012; 616-50.
- OIE. World Organisation for Animal Health. Brucellosis (B. abortus, B.melitensis and B.suis) (Infection with B. abortus, B. melitensis and B. suis). Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals. 2018.
- Olsen SC, Garin Bastuji B, Blasco JM, Nicola AM, Samartino L, et al. Diseases of Swine. 10th ed. Hokoben: Wiley-Blackwell. 2012; 697-708.
- Olsen SC, Palmer MV. Advancement of knowledge of Brucella over the past 50 years. Vet Pathol. 2014; 51: 1076-89.
- Olsen SC, Tatum FM. Swine brucellosis: current perspectives. Vet Med(Auckland, N.Z.). 2016; 8: 1-12.
- Pal M, Gizaw F, Fekadu F, Alemayehu G, Kandi V. Public health and economic importance of bovine Brucellosis: an overview. Amer J Epidemiol Infect Dis. 2017; 5: 27-34.
- Poester FP, Samartino LE, Santos RL. Pathogenesis and patho-biology of brucellosis in livestock. Rev Sci tech. 2013; 32: 105-15.
- Quance C, Robbe-Austerman S, Stuber T, Brignole T, DeBess EE, et al. Identification of source of B. suis infection in human by using whole-genome sequencing, United States and Tonga. Emerging Infect Dis. 2016; 22: 79-82.
- Ramamoorthy S, Woldemeskel M, Ligett A, Snider R, Cobb R, et al. Brucella suis infection in dogs, Georgia, USA. Emerging Infect Dis. 2011; 7: 2386-87.
- Rubach MP, Halliday JEB, Cleaveland S, Crump JA. Brucellosis in low-income and middle-income countries. Current Opin Infect Dis. 2013; 26: 404-12.
- Seleem MN, Boyle SM, Sriranganathan N. Brucellosis: A Re-Emerging Zoonosis. Veterinary Microbiology. 2010; 140: 392-98.
- Skendros P, Pappas G, Boura P. Cell mediated immunity in human brucellosis. Microbes Infect. 2011; 13: 134-42.
- Sting R, Schwabe I, Oehme R, Elschner MC, Melzer F. First report of a Brucella suis infection in rose deer (Capreolus capreolus). Berl Munch Tierarzti Wochenschr. 2014; 127: 120-22.
- Swai ES, Schoonman L. A survey of zoonotic diseases in trade cattle slaughtered at Tanga city abattoir: a cause of public health concern. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine. 2012; 2: 55-60.
- Tay BY, Norazah A, Rohaidah H, Jama’ayah M, Zahidi K, et al. Multiple-locus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis (MLVA) genotyping of human Brucella isolates in Malaysia. BMC infect Dis. 2015; 15: 220.
- Tomass Z, Imam E, Kifleyohannes T, Tekle Y, Weldu K. Prevalence of gastrointestinal parasites and Cryptosporidium spp. in extensively managed pigs in Mekelle and urban areas of southern zone of Tigray region, Northern Ethiopia. Vet World. 2013; 6: 433-39.
- Tuon FF, Gondolfo RB, Cerchiari N. Human to human transmission of Brucellaa systematic review. Trop Med Int Health. 2017; 22: 539-46.
- (WHO, 2013): Seven Neglected endemic zoonoses some basic fact. zoonoses /Diseases/brucellosis/en/.World Health Organization (WHO), http://www.who.int/
- Xiang F, Xia Z, Wu Q, Chen Y, Yu J, Wan J. Sero epidemiology of canine brucellosis in Beijing, China. Turkish Journal of Veterinary and Animal Sciences. 2013; 37: 38-42
- Yagupsky P. Neonatal brucellosis: rare and preventable. Annals of Tropical Paediatrics. 2010; 30: 177-79.
- Yasmin B, Lone SA. Brucellosis: An Economically Important Infection. Med Microb Diagn. 2015; 4: 208.
- Zakaria AM, Ahmed SF, Motawae MS. Sero-positivity in animals and risk of occupational brucellosis among abattoirs personnel associated with poor work practices and absence of safety policy in Egypt. Int J Occup Environ Health. 2018; 24: 55-60.
- Zinsstag J, Schelling E, Solera X, Blasco J, Moriyon I. Brucellosis: textbook of zoonoses. Oxford: Blackwell Science. 2011; 54-6.