
Research Article
Austin Alzheimers J Parkinsons Dis. 2023; 6(2): 1039.
The Neuroprotective Effect of Clove Essential Oil Against 6-Ohda-Induced Cell Death in Sh-Sy5y and A Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease
Dhouha Hamdi1,2*; Omar Ouachikh¹; Lemlih Ouchchane¹; Hend Omara-Reda¹; Chokri Messaoud²; Aziz Hafidi¹*
¹INP, Institut Pascal, TGI, University of Clermont Auvergne, 63000 Clermont Ferrand France
²Laboratory of Nanobiotechnology and Valorization of Medicinal Phytoresources University of Carthage National Institute of Applied Science and Technology UR17ES22 Tunis Cedex Tunisia
*Corresponding author: Dhouha Hamdi & Aziz Hafidi, INP Institut Pascal, TGI, University of Clermont Auvergne, 63000 Clermont Ferrand France. Email: hamdihamdidhoha@yahoo.fr; aziz.hafidi@uca.fr
Received: June 05, 2023 Accepted: July 04, 2023 Published: July 11, 2023
Abstract
Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is the second most prevalent neurological disorder. Natural therapies are becoming more popular for preventing disease onset. Clove Essential Oil (CEO), a potent antioxidant derived from Syzygium aromaticum buds, was tested in vitro (SH-SY5Y) and in vivo (PD rat model) for its ability to protect against 6-OHDA-induced cell death. Twenty-four hours of SH-SY5Y cells’ exposure to 6-OHDA (100μM) drastically decreased cell viability. At doses lesser than 20μg/ml, CEO and its main component Eugenol (EG) had no cytotoxic effect on SH-SY5Y. CEO and EG at doses of 2.5-20μg/ml provided significant neuroprotection against 6-OHDA-induced cell death. A PD rat model was generated by injecting 6-OHDA (21μg/animal) unilaterally into the striatum. An assessment of motor performance can predict neuronal cell loss in the Substancia Nigra Compacta (SNc). Compared to 6-OHDA-lesioned, CEO-treated (10mg/Kg) rats’ locomotor performance (actimetry and cylinder tests) improved significantly one and two weeks after 6-OHDA-lesion. Tyrosine Hydroxylase (TH) cell count showed a significant decrease in cell death in ipsilateral SNc in both CEO-treated and 6-OHDA-lesioned rats when compared to contralateral. In contrast to the 6-OHDA-lesioned group, the ipsilateral SNc of the CEO-treated group showed a significant high TH cell number. In the present study, the neuroprotective effect of CEO was demonstrated both in vitro and in vivo against 6-OHDA cytotoxicity. Therefore, CEO could be used as a food supplement for PD prevention.
Keywords: Parkinson; Syzygium aromaticum buds; Eugenol; 6-OHDA; Dopaminergic neurons; Hemiparkinsonian rat; SNc
Introduction
Parkinson's Disease (PD) is the most common neurological disease, affecting over 10 million individuals throughout the world [29]. Age, male gender, and environmental circumstances are all risk factors [5]. PD is characterized by a progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons of the Substantia Nigra Compacta (SNc). As a result, signs of PD such as tremors, myotonia, and dyskinesia appear [2]. Oxidative stress, which produces SNc cell death [42], is responsible for the onset and progression of the pathology [10]. The neurotoxin 6-Hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) preferentially causes cell death in catecholaminergic neurons by an auto-oxidation process that generates an excessive amount of reactive oxygen species [14,22]. This neurotoxin is widely used to induce dopaminergic cell death in vitro or in vivo animal PD model [8,14,31].
Natural substances with potential antioxidant properties have been investigated in preclinical studies of neuropathological diseases. Due to their therapeutic effectiveness, low cost, and lack of adverse effects medicinal aromatic plants have attracted a lot of interest in recent decades [29,38]. Based on their antioxidant activities, bioactive substances such as essential oils, which are byproducts of plant secondary metabolism, are employed in a variety of medicinal sectors [41]. A variety of pharmacological applications has been reported to Clove Essential Oil (CEO) (Syzygium aromaticum). CEO is a very used herb in traditional medicine and has a wide range of biological properties, including antibacterial, antioxidant, and insecticidal activity as well as, anesthetic, antinociceptive, and anticancer effects [15]. The CEO contains antioxidant chemicals such as Eugenol (EG), eugenyl acetate, β-caryophyllene, and α-humulene. Eugenol (EG, 85.61%) constitutes the major compound of CEO [1,26]. In the brain, EG plays different roles such as analgesic, anti-inflammation, anti-nociceptive, anti-depression, anti-stress [15,30] and neuroprotective effect on dopaminergic cells [20,28,34,44].
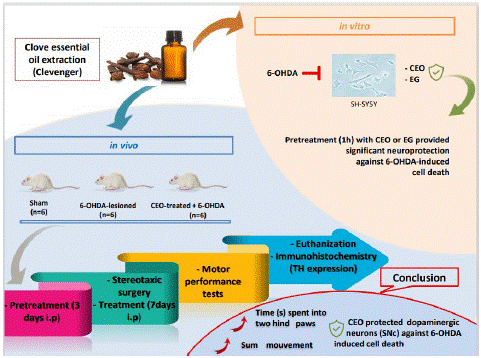
Graphical Abstract:
In the present study, the neuroprotective activity of CEO was examined, for the first time, in vitro against 6-OHDA-induced cytotoxicity in the SH-SY5Y cell line. This cell line has many dopaminergic neuron characteristics and is commonly used to study neurodegenerative pathologies [17]. Furthermore, the in vitro neuroprotective effect of the CEO’s main constituent (EG) has been explored. In addition, CEO has been studied in vivo using a rat PD model. This model is generated by injecting the 6-OHDA neurotoxin into the striatum, which causes dopaminergic neurons in the SNc to degenerate retrogradely [11]. Motor performance is a useful measure for predicting the extent of neuronal cell loss in the SNc [27]. As a result, locomotor performance in CEO-treated and control 6-OHDA-lesioned rats was assessed as a marker of 6-OHDA's effect on neuronal death in the SNc.
Results
Dose-Response Cytotoxicity of 6-OHDA, CEO, and EG in SH-SY5Y Cells
The 6-OHDA-induced cell death was determined using the MMT approach. At all concentrations tested (20, 40, 60, 80, and 100μM), 6-OHDA causes a significant (p<0.05) dose-related decrease in cell viability in the dopaminergic neuroblastoma cells, SH-SY5Y (Figure 2 A-B). Over half of the SH-SY5Y cells (58.58±3.4%) were affected by the 6-OHDA 100μM dose as compared to the untreated control. Therefore, this concentration was considered appropriate for producing neurotoxicity in later trials.
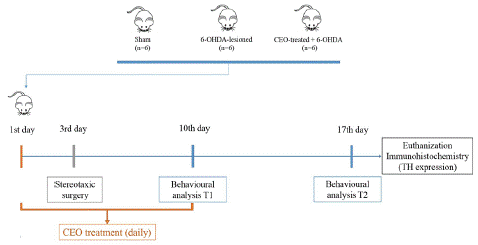
Figure 1: The figure depicts the experiment’s temporal progression.
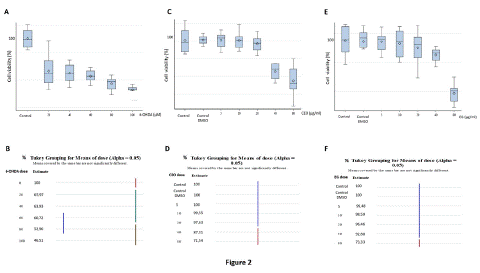
Figure 2: Effects of 24 hours exposure of various concentrations of 6-OHDA (A-B), CEO (C-D), and EG (E-F) on SH-SY5Y cell viability. Data are expressed in percentage of cell viability and are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was done using one-way ANOVA followed by THSD tests. At all employed concentrations, 6-OHDA caused significant (p<0.05) SH-SY5Y cell death, with the largest effect obtained with the 100μM (A). DMSO did not exert any toxic effects. At concentrations below 20μg/ml, CEO and EG have no significant effect (D, F) on SH-SY5Y cell mortality. At 40 and 80μg/ml both CEO and EG respectively decrease significantly (p<0.05) the viability of the cells.
CEO (Figure 2 C-D) and EG (Figure 2 E-F) cytotoxicity was studied by incubating SH-SY5Y cell cultures for 24 hours at various concentrations (5, 10, 20, 40, and 80μg/mL). When compared to controls (untreated cell group or culture treated with 0.1% DMSO), CEO and EG treatments at concentrations lower than 20μg/ml demonstrated no cytotoxic effects on SH-SY5Y cells. Cell cytotoxicity was only statistically significant (p<0.05) at the highest doses of 40μg/ml for CEO (Figure 2 C-D) and 80μg/ml for EG (Figure 2 E-F).
CEO And EG Protective Effects against 6-OHDA-Induced Cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells
Pretreatment of SH-S5Y5 for one hour with CEO (Figure 3A-B) or EG (Figure 3 C-D) at doses of 2.5, 5, 10, and 20μg/ml reduced significantly (p<0.05) the cytotoxicity induced by 6-OHDA exposure. When compared to control cells (6-OHDA treatment alone), the percentage of cell viability was 134.23; 149.58; 139.74 and 132.06% for CEO and 129.40; 142.34; 135.58 and 132.96% for EG at respective doses of 2.5, 5, 10, and 20μg/ml. The neuroprotective effect of CEO and EG could be illustrated morphologically in the cultures (Figure 3E). Pictures were taken 24 hours following treatment, as shown in Figure 3E, 6-OHDA lead to SH-SY5Y cell death (decreased cell density in the culture when compared to control untreated). Conversely, CEO and EG treatments at 5μg/ml protected the neuroblastoma cells (presence of a relatively similar cell density as the one observed in the control culture) from 6-OHDA cell toxicity. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey Honestly Significant Difference (THSD) test revealed no significant difference in the neuroprotective effect between CEO and its major compound EG (Figure 3F).
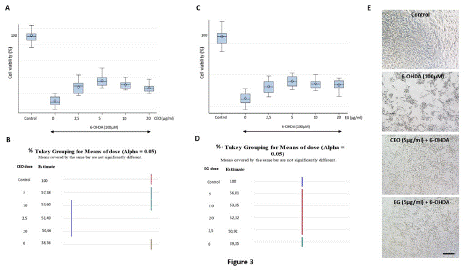
Figure 3: Neuroprotective effects of CEO (A-B) and EG (C-D) (1h pretreatment exposure) against 24 hours 6-OHDA exposure (100μM) induced SH-SY5Ycell death. At all employed concentrations, pretreatment with CEO or EG significantly (p<0.05) reduced cell death induced by 6-OHDA (B, D). Both the CEO and EG at 5μg/ml provided the most important SH-SY5Y neuroprotection. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was done using one-way ANOVA followed by THSD tests. (E) SH-SY5Y microscopic images of the different cell culture groups: control, 6-OHDA, CEO, and EG at 5μg/ml. The bar represents 60μm. (F) Two-way ANOVA followed by THSD, displayed no significant differences in the interaction plot of cell viability between CEO and EG.
CEO's Effect on Motor Performance
Motor ability was used as a predictor for the degree of neuronal cell loss in the SNc [27]. The actimetry test [32] was used to assess total rat locomotor performance in the three animal groups: sham, 6-OHDA-lesioned, and CEO-treated (Figure 4). The test captures each of the rat's 15-minute total movements at one and two weeks following surgery. 6-OHDA injection resulted in a significant reduction in motor activity (Figure 4A) at both one (p=0.0026) and two weeks (p=0.0004) following injury when compared to sham. CEO-treated animals showed a significant improvement in motor ability at one (p=0.032) and two weeks (p=0.04) post-injury when compared to 6-OHDA-lesioned rats. There was no discernible change in motor performance between the CEO-treated and sham groups at one (p=0.9174) or two (p=0.3176) weeks following injury. Additionally, there was no significant difference in motor performance between week 1 and week 2 post-injury for all groups (p=0.9343 for 6-OHDA, p=0.7576 for CEO-treated, and p=0.999 for sham). Rats were also measured for their ability to stand on their two hind paws for five minutes using a cylinder test (Figure 4B). One and two weeks after injury, a significant (p<0.0001) difference in motor activity was seen between 6-OHDA-lesioned and sham. At both one (p<0.0001) and two (p=0.0002) weeks after the lesion, there was a significant difference in motor activity between the groups that had received CEO treatment and those that had had 6-OHDA lesion only. The CEO-treated group had noticeably the longest stand duration when compared to the 6-OHDA group. There was no discernible difference between the CEO-treated group and the sham group in the amount of time spent using two hind paws at one (p=0.9996) and two (p=0.9936) weeks following injury. Between weeks one and two following the injury, there was no significant difference in motor function between the 6-OHDA-lesioned (p=0.6570), CEO-treated (p=0.1369), and sham (p=0.2135) groups.
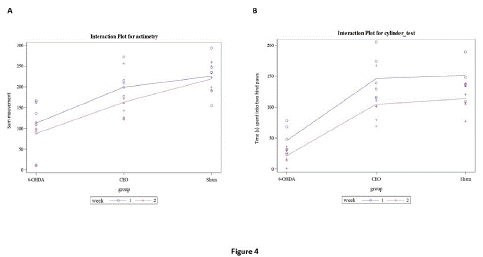
Figure 4: The figure represents motor performance [actimetry: total movement (A-B); Cylinder: time rats stand on their two hind paws during 5 minutes session (C-D)] in sham, 6-OHDA-lesioned, and CEO-treated rats. The animals were subjected to motor behavioral tests at one (blue) and two (red) weeks post-lesion. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 6/group). To test for both effects of CEO treatment and time (week 1 and 2) (including their interaction), two-way ANOVA was performed followed by THSD tests to handle post-hoc multiple comparisons. At both one and two weeks post-lesion, there was no significant difference in total movement between CEO-treated and sham rats (A). A significant (p=0.032) difference in total movement is observed between 6-OHDA-lesioned and CEO-treated rats at both one and two weeks post-lesion. Similarly, there is a significant difference in total movement at both one (p=0.0026) and two (p=0.0004) weeks between 6-OHDA-lesioned and sham rats. At one week after the lesion a significant (p<0.0001) difference was observed between 6-OHDA- lesioned and CEO-treated or sham rats. No significant difference was observed at one and two weeks post-lesion between CEO-treated and sham rats.
Dopaminergic cell Count in the SNc
The chemical marker Tyrosine Hydroxylase (TH) is extensively employed in the brain to identify dopaminergic cells and allow cell counting. The TH expression (Figure 5A-C) was evaluated in contralateral (non-lesioned side) and ipsilateral (lesioned side) SNc of sham, 6-OHDA-lesion and CEO-treated rats. The SNc's neurons exhibit TH labeling, which did not show any variation in intensity between the ipsilateral and contralateral sides in the sham (Figure 5A). The ipsilateral and contralateral SNc in both the 6-OHDA-lesioned (Figure 5B) and CEO-treated (Figure 5C) groups, however, showed a difference in TH labeling intensity. An intense TH labeling was visible on the contralateral SNc. TH positive cell count in the SNc contralateral side, revealed no significant difference between the three groups (p=0.9999) (Figure 5D). Additionally, there was no significant difference in the TH cell count between the two sides of the sham rat. However, in both the 6-OHDA-lesioned and CEO-treated groups, there was a significant difference (p<0.0001) in the number of TH cells in the ipsilateral SNc compared to the contralateral. The ipsilateral SNc showed a significant (p<0.0001) difference between the three groups (6-OHDA-lesioned, CEO-treated, and sham). TH positive cell number within SNc ipsilateral side was significantly higher in the sham followed by CEO-treated and 6-OHDA-lesioned.
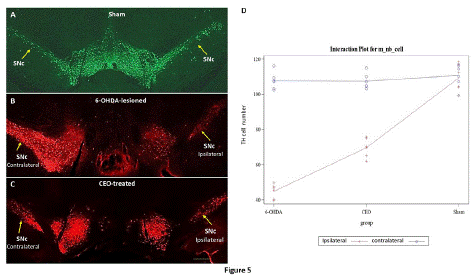
Figure 5: The figure represents the TH immunostaining in sham (A), 6-OHDA-lesioned (B), and CEO-treated (C) animals. For cell count, data are displayed as mean ± SEM and statistical analysis was done using two-way ANOVA with additional THSD tests to handle post-hoc multiple comparisons. In the sham, TH immunostaining was localized in numerous neuronal cell bodies within bilateral SNc (arrows). A differential TH labeling was observed between the ipsilateral and the contralateral of the SNc in both 6-OHDA-lesioned rat (B) and CEO-treated (C). A very intense TH immunolabeling was present within the contralateral when compared to the ipsilateral SNc. The number of TH positive cell was counted in ipsilateral (red) and contralateral (blue) SNc (D). Between the three groups, there was no significant TH cell count difference in the contralateral SNc. Comparing ipsilateral and contralateral SNc in the 6-OHDA-lesioned and CEO-treated groups revealed a significant (p<0.0001) difference in TH cell count. When compared to the 6-OHDA-lesioned SNc, the CEO-treated ipsilateral SNc exhibit a greater number of TH-positive cells (p<0.0001). The bar represents 200μm.
Discussion
The potential neuroprotective efficacy of CEO was evaluated against cell toxicity caused by 6-OHDA both in vitro in SH-SY5Y and in vivo in a rat PD model. The current study is the first to demonstrate that CEO, as well as its most abundant component EG, protects SH-SY5Y cells from 6-OHDA-induced cell death in vitro. In addition, CEO treatment improves motor performance in 6-OHDA-lesioned rats, which could be linked to the neuroprotective effect of CEO on dopaminergic neurons of the SNc. This is corroborated by a higher number of TH cells present in CEO-treated compared to 6-OHDA-lesioned rats.
All used 6-OHDA concentrations (20, 40, 60, 80, and 100μM) showed a significant SH-SY5Y cell viability reduction compared to the control cell culture. The highest dose of 100μM caused the most cell damage (around 58.58±3.4% cell death). This result is in accord with previous reports demonstrating the use of 6-OHDA as a successful tool for inducing neurodegeneration in cell culture [12,13]. Therefore, the neuroprotective effects of CEO and EG against the 6-OHDA cytotoxicity were investigated using the dose of 100 μM.
SH-SY5Y were also treated with each of CEO or EG to determine their potent cytotoxic doses. At concentrations below 20 μg/ml, neither EG nor CEO had cytotoxic effects on SH-SY5Y cells. There was no significant difference in viable cell number between CEO or EG-treated and the control cultures at these concentrations. Only at the highest doses, 40μg/ml for the CEO and 80μg/ml for EG, a significant cytotoxic effect was observed. There are several inconsistencies in the literature when it comes to EG's cytotoxic (apoptosis) and anti-proliferative actions [45]. These disparities could be caused by differences in concentrations, EG purity, and cell line types. The CEO's toxicity has been linked to the compounds EG and phenolic terpene. The cytotoxic doses of EG range from 100 to 300μM, depending on the cell line culture [3,4,16]. CEO and EG toxicity have been linked to their effects on ion fluxes [6,23,36] or the intracellular synthesis of metabolic change of EG to a quinone methide [19,43].
In the present study, the neuroprotective effects of CEO and EG against 6-OHDA have been investigated in vitro at concentrations lesser than 20μg/ml. Both CEO and EG showed a significant neuroprotective effect on 6-OHDA-treated SH-SY5Y cells at doses ranging from 2.5 to 20μg/ml, with the highest effect obtained at 5μg/ml. To our knowledge, this is the first study demonstrating a protective effect of CEO and EG against 6-OHDA-induced cell death on SH-SY5Y cells. Comparative analysis between CEO and EG revealed no significant difference in cell viability. This suggests that the CEO neuroprotective effect is probably due to its major compound EG. The current study's in vitro findings on CEO and EG effects matched those of a previous study on different cell lines [37]. EG has been shown to protect PC12 cells against amyloid-induced cytotoxicity through its ability to prevent calcium intake induced by amyloid [18]. EG also protects cortical cell culture from NMDA-induced cytotoxicity through the modulation of NMDA-receptors [44].
Further research into the protective impact of CEO in rat models of PD was examined in light of the promising in vitro neuroprotectivity evidence. CEO's neuroprotective effect was tested in vivo against 6-OHDA-induced neuronal degeneration in the SNc. To investigate the impact of 6-OHDA on SNc neuronal death, a locomotor function was first assessed in 6-OHDA-lesioned and CEO-treated rats and compared to the sham group. Motor performance constitutes an important tool that could predict the degree of neuronal cell loss [27]. CEO treatment significantly enhanced rat motor performance, as indicated by both cylinder and actimetry tests one and two weeks after the 6-OHDA lesion. This is most likely due to CEO treatment's impact against 6-OHDA-induced cell death in the SNc. In addition, this is the first study demonstrating a neuroprotective effect of CEO on a rat model of PD. The findings backed up a prior study that used EG, which represents the major CEO compound in a rat model of PD [28,34]. EG has been demonstrated to improve motor performance using different motor tests [7,28,34,35]. The motor effect of EG was attributed to its ability to reduce oxidative stress and the modulation of genes related to antioxidant activity caused by 6-OHDA [28,34]. One study, however, reported that ingestion of EG after brain injury or after the onset of Parkinson's disease may increase oxidative stress and exacerbate the injury [21]. This discrepancy may be due to the EG doses, the way of administration, and the animal model used.
The CEO effect on motor performance is also supported by the presence of a high number of TH-labeled cells in the ipsilateral SNc of CEO-treated rats when compared to 6-OHDA-lesioned. TH cell count demonstrated the impact of the neurotoxin 6-OHDA on the SNc dopaminergic neurons. It is well established that 6-OHDA neurotoxic injection within the striatum causes dopaminergic neurons in the SNc to degenerate retrogradely [20]. Ipsilateral SNc in both CEO-treated and 6-OHDA-lesion rats had a significantly high TH cell number when compared to the contralateral. Indeed, within the ipsilateral SNc of the CEO-treated, the TH staining demonstrated a higher cell number than that of the 6-OHDA-lesion rats. The number of cells in the contralateral SNc side (non-lesioned side) did not differ significantly across groups, indicating that CEO had no cytotoxic effect on neurons in the non-lesioned SNc side. Overall, the findings showed that the CEO had neuroprotective effects on SNc neurons damaged by 6-OHDA.
In conclusion, the current study demonstrated that CEO protects against 6-OHDA cytotoxicity both in vitro and in vivo. Clove buds may constitute a potent compound that could be used as a food supplement to aid those at risk of Parkinson's disease.
Materials and Methods
Chemicals and Reagents
Dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) (D8418, Sigma-Aldrich, France)
Tween 20 (P1379, Sigma-Aldrich, France)
SH-SY5Y cells (Sigma-Aldrich, France)
DMEM1X medium (31885-023, Gibco, France)
Vitamin 100X (11120-037, Gibco, France)
Non-essential amino acid 100X (11140-035, Gibco, France)
Heat inactivated FBS (F9665, Sigma-Aldrich, France)
Penicillin-streptomycin solution (P0781, Sigma-Aldrich, France)
Trypsin-EDTA (0.05%) (59417C, Sigma-Aldrich, France)
Trypan blue (0.4%) (T8154, Sigma-Aldrich, France)
Cell counting slide (C10283, Invitrogen, France)
MTT (tetrazolium salt) (M5655, Sigma-Aldrich, France)
Eugenol (E51791, Sigma-Aldrich, France)
Xylazine (ROMPUN 2%, Bayer Pharma)
Ketamine (Imalgene 1000, Merial)
Pentobarbital (Ceva Santé Animale, France)
Primary antibody (mouse anti-TH, sigma-Aldrich, France)
Secondary antibodies (anti-mouseDylight549, Vector, France)
Slides (Superfrost® plus, Thermo scientific)
Fluorescence microscope (Nikon Eclipse Ni)
Coverslip in mounting medium (Dako Fluorescence Mounting Medium, Dako)
Extraction and Preparation of Clove Essential Oil (CEO)
CEO was hydrodistilled using Clevenger type equipment as described previously [25]. The condensed vapor transforms into an organic phase (essential oil). The CEO was extracted from the hydrolate, stripped of any leftover water, and kept in dark glass pill containers at 4°C until analysis. For the in vitro pretreatment, the CEO was dissolved in 0.1% DMSO. Intraperitoneal injectable solutions of 10mg/kg CEO [28] were made in 0.9 % saline solution diluted in 3% Tween 20 (Sigma, France) for the rats' treatment.
SH-SY5Y Cell Line Culture
SH-SY5Y cell line was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, France. The cells were cultured in DMEM medium (31885-023, Gibco) supplemented with 1% vitamin 100X (11120-037, Gibco), 1% non-essential amino acid 100X (11140-035, Gibco), 10% heat-inactivated FBS (F9665, Sigma) and 100X penicillin-streptomycin solution (P0781, Sigma). The cells were incubated at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2.
Cell Viability Test
For this analysis, 3.104 cells were seeded in 96-well plates in a complete medium and incubated at 37°C and 5% CO2. For 6-OHDA toxicity, SH-SY5Y cells were treated with 20, 40, 60, 80, and 100μM of 6-OHDA for 24 hours. Potent cytotoxicity of CEO and its major component eugenol (Sigma-Aldrich, France) was determined by treating SH-SY5Y for 24 hours with different concentrations (5, 10, 20, 40, 80μg/ml) of each drug diluted in complete media containing 0.1% DMSO (D8418, Sigma). In addition, a 0.1% DMSO-containing vehicle group was used [9,39]. To test the neuroprotective effects of CEO and EG, against 6-OHDA-induced cell death, SH-SY5Y were pretreated for one hour with each aromatic compound at varying concentrations (2.5, 5, 10, and 20μg/mL), and subsequently, cells were cultured in the presence of 6-OHDA (100μM) for an additional 24 hours. The 3-[4,5-dimethylthiazole-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) (M5655, Sigma) test was employed at a dose of 0.5mg/mL to assess cell viability. At the end of treatment, the medium was replaced by 110μL of fresh complete medium containing 10μL of MTT solution (tetrazolium salt) and then incubated at 37°C. Two hours later, the medium was removed and 100μL of DMSO was added. The optical density was measured at 540 and 630nm using Biotech Epoch spectrophotometer. Viable cells were counted (percentage) by the formula [(Optic Density treated cells/Optic density control cells) x100] [33].
Animals
Charles River (L'Arbresle, France) Sprague-Dawley male rats (n=18: 176-200g) were used. The animals were kept in a controlled environment with standard feed and water accessible at all times (lighting from 7a.m. to 7p.m., 22°C). The testing followed the ethical guidelines of the International Association for the Study of Pain, as well as directions from the European Community Council and the Animal Ethics Committee at the University of Clermont Auvergne. A variety of measures was taken to minimize the number of animals and their suffering.
Stereotaxic Surgery and Treatment
The animals were random divided into three groups (n=6 per group) (Figure 1). Group 1 (Sham) the animals received aunilateral intrastriatal injection of 0.9% saline solution containing 0.02% of L-ascorbic acid into the rat striatum. In group 2 (6-OHDA-lesioned) and 3 (CEO-treated), the lesion was carried out by unilateral injection of 21μg of 6-OHDA solution dissolved in a 0.9% saline solution containing 0.02% of L-ascorbic acid into the rat striatum. The treatments were performed 3 days as pretreatment and 7 days after 6-OHDA-lesion by intraperitoneal injection (i.p). The group 2 were i.p injected with a saline solution containing Tween 20 (3%). Rats in group 3 received 10mg/kg of CEO diluted in a saline solution containing Tween 20 (3%) [24,28]. Stereotaxic surgery Moreira Vasconcelos et al., 2020 is performed 3-day after a daily i.p injection of CEO (10mg/Kg) or saline solution containing Tween 20 (3%). One hour after the third i.p injection, the rats were anesthetized with 10mg/Kg of Xylazine (ROMPUN 2%, Bayer Pharma) and 60mg/ kg of Ketamine (Imalgene 1000, Merial) administered intraperitoneally. The stereotaxic coordinates were determined according to the Paxinos and Watson, 2004 atlas at the following coordinates: + 0.8mm Anteroposterior (AP) from the bregma, ± 2.7mm laterally from the Midline (ML), -4.5mm in dorso ventral (DV), tooth bar at + 3.4mm and + 0.8mm (AP), ± 2.7mm (ML), -5.2mm (DV), tooth bar at + 3.4mm [46]. The injections were carried out at a speed of 0.5μl / min with a 10μL Hamilton syringe connected to a microinjector. At the end of the injection, the needle remains in place for 5 min then was raised by 1 mm/min [32].
Motor Performance
Actimetry test: Locomotor activity was performed in rats in weeks one and two after a stereotaxic surgery. A 15-minute test, using an infrared probe, records the rat's total movements in the CPP apparatus. The data were analyzed with the IMétronic software (Bordeaux, France). The sum of all movements was made to obtain the overall data on the locomotor activity of the rat [32].
Cylinder test: The cylinder test [40] was used to assess the movement behavior of the lesioned rat after CEO treatment and in control. A beaker (30cm high and 20cm in diameter) was used to conduct the cylinder test. At one and two weeks following the 6-OHDA lesion, the rat was video recorded for 5 minutes. Videotapes were evaluated to measure the time the animal spends on its two hind paws throughout the course of a five-minute session. The ability of the rat to stand and retain balance on its hind paws was determined by this test.
Immunohistochemistry
At the end of the behavioral tests, the animals were anesthetized with a lethal dose of pentobarbital (80mg/kg), then infused with 0.5% heparinized saline via the cardiac route, followed by a 4% paraformaldehyde solution made in a Tris Phosphate-buffered Saline (TPS) solution (0.2M). The brains were extracted and put in Phosphate-Buffered Saline (PBS) solution (0.1M). Thirty μm vibratome sections were collected in PBS. The sections were saturated in a TBS, 0.3% X100 triton, and 1% Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) for 1 hour before being incubated overnight in a solution of primary antibody (1: 5000 mouse anti-TH, Sigma-Aldrich) at room temperature. The sections were then washed several times in PBS before being treated with secondary antibody (1: 500 anti-mouse Dylight 549, Vector) for 2 hours at room temperature. TBS containing 1% BSA and 0.3% Triton X-100 was used to dilute all antibodies. The sections were then rinsed several times in PBS before being placed on slides (Thermo Scientific's Superfrost® plus), dried, and then mounted between slides and coverslipped in mounting medium (Dako Fluorescence Mounting Medium, Dako). Slides were examined using a fluorescent microscope (Nikon Eclipse Ni) and the TH-positive cells were counted using ImageJ software. The number of brain sections (each SNc side) used for TH count was n=29 for for sham, n=35 for 6-OHDA-lesioned, and n=39 for the CEO-treated group.
Figure 1 presents the experiment's time course.
Statistical Snalysis
Cell viability was subjected to One-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey Honestly Significant Difference (THSD) tests. The interaction plot of cell viability between CEO and EG was done using two-way ANOVA followed by THSD (results are shown in figures 1 to 3). For behavioral characteristics (actimetry and cylinder test) and immunohistochemistry (cell count), which were all considered quantitative criteria and displayed as mean ± SE (standard error mean), to test for both effects of CEO treatment and time (week 1 and 2) (including their interaction), two-way ANOVA was performed with additional THSD test to handle post-hoc multiple comparisons. These results are shown in figures 4 and 5. All statistical analysis were performed using SAS v9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA) with a type I error set at 0.05.
Author Statements
Author Contributions
All authors contributed substantially to this study: conception and design of the study (DH, AH, OO, CM); acquisition and interpretation of data (DH, AH, OO); drafting of the article (DH, AH), revising the article critically for important intellectual content (DH, AH, CM); and final approval of the version to be submitted (DH, AH, OO, CM, HOR).
Competing Interests
The present study was funded by University Clermont Auvergne. The testing followed the ethical guidelines of the International Association for the Study of Pain, as well as directions from the European Community Council and the Animal Ethics Committee at the University of Clermont Auvergne (D6311316). A variety of measures was taken to minimize the number of animals and their suffering. The authors have no conflict of interest to declare in this work.
References
- Adefegha A, Oboh G, Odubanjo O, Ogunsuyi O. Comparative study on the antioxidative activities, anticholinesterase properties and essential oil composition of Clove (Syzygium aromaticum) bud and Ethiopian pepper (Xylopia aethiopica). Riv Ital Sostanze Grasse. 2016; 92: 257-68.
- Armstrong MJ, Okun MS. Diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson disease: a review. JAMA. 2020; 323: 548-60.
- Atsumi T, Fujisawa S, Satoh K, Sakagami H, Iwakura I, et al. Cytotoxicity and radical intensity of eugenol, isoeugenol or related dimers. Anticancer Res. 2000; 20: 2519-24.
- Babich H, Stern A, Borenfreund E. Eugenol cytotoxicity evaluated with continuous cell lines. Toxicol In Vitro. 1993; 7: 105-9.
- Balestrino R, Schapira AHV. Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Neurol. 2020; 27: 27-42.
- Bard M, Albrecht MR, Gupta N, Guynn CJ, Stillwell W. Geraniol interferes with membrane functions in strains of Candida and Saccharomyces. Lipids. 1988; 23: 534-8.
- Barot J, Saxena B. Therapeutic effects of eugenol in a rat model of traumatic brain injury: A behavioral, biochemical, and histological study. J Trad Complement Med. 2021; 11: 318-27.
- Bové J, Perier C. Neurotoxin-based models of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience. 2012; 211: 51-76.
- Caputo L, Nazzaro F, Souza LF, Aliberti L, De Martino L, et al. Laurus nobilis: composition of Essential Oil and Its Biological Activities. Molecules. 2017; 22: 930.
- Dionísio PA, Amaral JD, Rodrigues CMP. Oxidative stress and regulated cell death in Parkinson’s disease. Ageing Res Rev. 2021; 67: 101263.
- El-Gamal M, Salama M, Collins-Praino LE, Baetu I, Fathalla AM, Soliman AM et al. Neurotoxin-induced rodent models of Parkinson’s disease: benefits and drawbacks. Neurotox Res. 2021; 39: 897-923.
- Elyasi L, Eftekhar-Vaghefi SH, Esmaeili-Mahani S. Morphine protects SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced cell damage: involvement of antioxidant, calcium blocking, and anti-apoptotic properties. Rejuvenation Res. 2014; 17: 255-63.
- Elyasi L, Jahanshahi M, Jameie SB, Hamid Abadi HG, Nikmahzar E, et al. 6-OHDA mediated neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cellular model of Parkinson disease suppressed by pretreatment with hesperidin through activating L-type calcium channels. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2020; 32: 11-7.
- Glinka Y, Gassen M, Youdim MBH. Mechanism of 6- hydroxydopamine neurotoxicity. Adv Res Neurodegener. 1997; 50: 55-66.
- Haro-González JN, Castillo-Herrera GA, Martínez-Velázquez M, Espinosa-Andrews H. Clove essential oil (Syzygium aromaticum L. Myrtaceae): extraction, chemical composition, food applications, and essential bioactivity for human health. Molecules. 2021; 26: 6387.
- Hume WR. Effect of eugenol on respiration and division in human pulp, mouse fibroblasts, and liver cells in vitro. J Dent Res. 1984; 63: 1262-5.
- Iglesias-González J, Sánchez-Iglesias S, Méndez-Álvarez E, Rose S, Hikima A, et al. Differential toxicity of 6-hydroxydopamine in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells and rat brain mitochondria: protective role of catalase and superoxide dismutase. Neurochem Res. 2012; 37: 2150-60.
- Irie Y, Keung WM. Rhizoma acori graminei and its active principles protect PC-12 cells from the toxic effect of amyloid-beta peptide. Brain Res. 2003; 963: 282-9.
- Jeng JH, Hahn LJ, Lu FJ, Wang YJ, Kuo MYP. Eugenol triggers different pathobiological effects on human oral mucosal fibroblasts. J Dent Res. 1994; 73: 1050-5.
- Kabuto H, Tada M, Eugenol KM. 2-methoxy-4-(2-propenyl)phenol prevents 6-hydroxydopamine-induced dopamine depression and lipid peroxidation inductivity in mouse striatum. Biol Pharm Bull. 2007; 30: 423-7.
- Kabuto H, Yamanushi TT. Effects of zingerone [4-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-butanone] and eugenol [2-methoxy-4-(2-propenyl) phenol] on the pathological progress in the 6-hydroxydopamine-induced Parkinson’s disease mouse model. Neurochem Res. 2011; 36: 2244-9.
- Kondo T. Parkinson’s disease and free radicals. Mechanism of neurodegeneration and neuroprotection. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1996; 786: 206-16.
- Kreydiyyeh SI, Usta J, Copti R. Effect of cinnamon, clove and some of their constituents on the Na+-K+-ATPase activity and alanine absorption in the rat jejunum. Food Chem Toxicol. 2000; 38: 755-62.
- Lahmar A, Dhaouefi Z, Khlifi R, Sioud F, Ghedira LC. Pituranthos Chloranthus oil as an antioxidant-based adjuvant therapy against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. J Toxicol. 2020; 2020: 7054534.
- Messaoud C, Boussaid M. Myrtus communis Berry color morphs: A comparative analysis of essential oils, fatty acids, phenolic compounds, and antioxidant activities. Chem Biodivers. 2011; 8: 300-10.
- Mittal M, Gupta N, Parashar P, Mehra V, Khatri M. Phytochemical evaluation and pharmacological activity of Syzygium aromaticum: A comprehensive review. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2014; 6: 67-72.
- Miyanishi K, Choudhury ME, Watanabe M, Kubo M, Nomoto M, et al. Behavioral tests predicting striatal dopamine level in a rat hemi-Parkinson’s disease model. Neurochem Int. 2019; 122: 38-46.
- Moreira Vasconcelos CF, da Cunha Ferreira NM, Hardy Lima Pontes N, de Sousa dos Reis TD, Basto Souza R, et al. Eugenol and its Association with levodopa in 6‐hydroxydopamine‐induced hemiparkinsonian Rats: behavioural and Neurochemical Alterations. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2020; 127: 287-302.
- Nagrik SU, Patil PA, Nagrik DM, Zagare V, Avchar P, et al. Herbal drugs Used on Parkinson Disease. J Drug Deliv Ther. 2020; 10: 235-9.
- Nisar MF, Khadim M, Rafiq M, Chen J, Yang Y, et al. Pharmacological properties and health benefits of eugenol: A comprehensive review. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021; 2021: 2497354.
- Ouachikh O, Dieb W, Durif F, Hafidi A. Anterior ventral tegmental area dopaminergic neurons are not involved in the motivational effects of bromocriptine, pramipexole, and cocaine in drug-free rats. Behav Brain Res. 2014; 262: 1-7.
- Ouachikh O, Dieb W, Durif F, Hafidi A. Differential behavioral reinforcement effects of dopamine receptor agonists in the rat with bilateral lesion of the posterior ventral tegmental area. Behav Brain Res. 2013; 252: 24-31.
- Picerno P, Autore G, Marzocco S, Meloni M, Sanogo R, et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of verminoside from Kigelia africana and evaluation of cutaneous irritation in cell cultures and reconstituted human epidermis. J Nat Prod. 2005; 68: 1610-4.
- Pontes NHL, Reis TDDSD, Vasconcelos CFM, Aragão PDTTDD, Souza RB, et al. Impact of eugenol on in vivo model of 6-hydroxydopamine-induced oxidative stress. Free Radical Research. 2021; 55: 556-568.
- Prasad SN, Muralidhara. Neuroprotective efficacy of eugenol and isoeugenol in acrylamide-induced neuropathy in rats: behavioral and biochemical evidence. Neurochem Res. 2013; 38: 330-45.
- Prashar A, Hili P, Veness RG, Evans CS. Antimicrobial action of Palmarosa oil (Cymbopogon martinii) on Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Phytochemistry. 2003; 63: 569-75.
- Prashar A, Locke IC, Evans CS. Cytotoxicity of clove (Syzyqgium aromaticum) oil and its major components to human skin cells. Cell Prolif. 2006; 39: 241-8.
- Proestos C, Sereli D, Komaitis M. Determination of phenolic compounds in aromatic plants by RP-HPLC and GC-MS. Food Chem. 2006; 95: 44-52.
- Romero A, Ramos E, Castellano V, Martínez MA, Ares I, et al. Cytotoxicity induced by deltamethrin and its metabolites in SH-SY5Y cells can be differentially prevented by selected antioxidants. Toxicol In Vitro. 2012; 26: 823-30.
- Schallert T, Tillerson JL. Intervention strategies for degeneration of dopamine neurons in parkinsonism. In: Central nervous system diseases. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press. 2000; 131-51.
- Sen T, Samanta SK. Medicinal plants, human health and biodiversity: A broad review. In: Biotechnological applications of biodiversity. 2015; 59-110.
- Tamtaji OR, Reiter RJ, Alipoor R, Dadgostar E, Kouchaki E, et al. Melatonin and Parkinson disease: current status and future perspectives for molecular mechanisms. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2020; 40: 15-23.
- Thompson DC, Barhoumi R, Burghardt RC. Comparative toxicity of eugenol and its quinone methide metabolite in cultured liver cells using kinetic fluorescence bioassays. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1998; 149: 55-63.
- Wie MB, Won MH, Lee KH, Shin JH, Lee JC, et al. Eugenol protects neuronal cells from excitotoxic and oxidative injury in primary cortical cultures. Neurosci Lett. 1997; 225: 93-6.
- Zari AT, Zari TA, Hakeem KR. Anticancer properties of eugenol: a review. Molecules. 2021; 26: 7407.
- Zhang JN, Huang YL, Yang HM, Wang Y, Gu L, et al. Blockade of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 attenuates axonal degeneration in 6-hydroxydopamine-induced model of Parkinson’s disease. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2021; 110: 103572.