
Research Article
Ann Agric Crop Sci. 2021; 6(4): 1082.
Pesticides Analysis in Beans by Gas Chromatography Couplet with Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Mizutani G* and Bustillos O
Centro de Química e Meio Ambiente, Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares, São Paulo, Brazil
*Corresponding author: Mizutani G, Centro de Química e Meio Ambiente, Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares, São Paulo, Brazil
Received: May 11, 2021; Accepted: June 07, 2021; Published: June 14, 2021
Abstract
Beans are part of the basic diet alimentation for Brazilian population, as they gather proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, mineral salts, fibers, amino acids and essential nutrients such as iron and calcium, being a complete food that can be compared with the amount of protein that the meat has. Considering the beans world production, in development countries represent almost 50%, being that Myanmar, India and Brazil the top three position. The use of pesticides is widely spread in these countries to reduce agricultural losses due to pests that interfere with grain production. Therefore the risk that could be generated from foods pesticides residues makes their analyses of quantification mandatory. The purpose of this work was to develop an analytical method to quantitatively characterize fungicides pesticides residues, flutriafol, procymidone and tebuconazole that were used to angular spot control, anthracnose, rust and alternaria spot, white mold fungi, present in beans, by means of gas chromatography coupled with a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer. Samples of beans, Phaseolus vulgaris L, types white, black, string and Vigna angularis, type adzuki, had been bought in grains store and supermarkets at metropolitan São Paulo city. The validation of analytical method was explored for sensitivity, selectivity, precision. The extraction procedure was performed in two different forms, QuEChERS, and solid-liquid extraction with low temperature. Through this methodology, reached below the maximum limit allowed by Brazilian law 0.5mgkg-1 for procymidone and 0.1mgkg-1 for flutriafol and tebuconazole. Several samples of four types of beans were tested and all of them had procymidone identified and 7% of samples higher than the law limit.
Keywords: Beans; GCMSMS; Pesticides
Introduction
In Brazil, beans are the most popular food for general population, they have nutrients and energy that work in health prevention. In their composition there are proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, mineral salts, fibers and amino acids [1].
Grains producers have been using several pesticides in this vegetable culture to preserve and improve the crop. The fungicides utilization has a function of preventing plant tissues infection by phytopathogenic fungi, currently we can find other concepts such as chemical compounds that are used to control diseases that are caused by fungi, bacteria and algae, in some cases they do not eliminate fungi, but temporarily inhibit spore germination [2].
The procymidone is using in mold-white fungi in a concentration of 500gkg-1 and acts to inhibit the growth of micelles, in the protection, cure [3,4].
The flutriafol and tebuconazole are fungicides that doing inhibit the synthesis of sterols that act in the formation and selectivity of the plasma membrane are used to control angular stain, anthracnose, rust and alternaria stain [3,4].
Fruits, vegetables, cereals are the most matrices that could find some pesticides residues in different classes and method development for this compounds are very important [5].
For these pesticides analyses several extraction are being used to aim these analytes. Acetonitrile is the best solvent to extract the samples because it has the best interaction with the analytes [6].
Therefore sample preparation using the QuEChERS multiresidues method, starts with the sample grind to get the most surface area to be in solvent contact, add magnesium sulfate, sodium chloride or sodium acetate, drying agents and clean up processes [7,8].
Other extraction technique used was solid-liquid with low temperature, in this extraction the sample, liquid or solid, in contact with solvent less dense than water and the less melting point less than 20°C negative, after shaking, rest in freezer about 16 hours, the water phase will be freeze and the organic phase will be liquid, this part has to be transfer to a vial and chromatography analyses [9,10].
This paper developed a method to characterize and quantify the fungicides that is present in vegetable with high protein content, beans specifically, that used a gas chromatography with mass spectrometry triple quadrupole TANDEM.
Methods and Materials
Materials and equipment
The following materials were used in this work:
• Falcon tube 10mL and 50mL;
• Analytical standards, flutriafol, procymidone, tebuconazole;
• Acetronitrile HPLC grade, isopropyl alcohol HPLC grade and ultrapure water;
• Vortex;
• Low temperature freezer -20°C;
• Blender;
• Gas chromatography coupled with Tandem mass spectrometry Bruker-EVOQ.
Method
Extraction: For extraction it was used a two different methods: QuEChERS, the most analytical extraction for pesticides, was used sample crushed, 3g, extraction salt, magnesium sulfate, 4g, and sodium acetate, 1g, with organic solvent, 4mL acetonitrile and 1mL isopropyl alcohol, shake 1 minute, centrifuge transfer 1mL to and clean up vial 150mg magnesium sulfate and 50mg PSA, transfer to 2mL vial and chromatography analyses, the second method solidliquid with low temperature, was used a sample crushed, 3g, in contact with organic solvent less dense than water, 4mL acetonitrile and 1mL isopropyl alcohol, and fusion point less than 20°C negative, the organic phase was liquid, transfer to 2mL vial and chromatography analyses, flowchart should be observe in Figure 1.
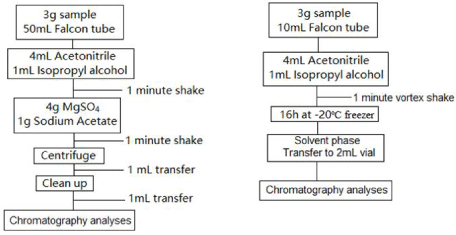
Figure 1: Extraction flowchart.
Analytical method: For analytical method it was used an instrumental analytical, gas chromatograph coupled with Tandem mass spectrometry equipment. It was developed method to separate the analytes. This method had a good sensitivity, accuracy and precision to fungicides compounds. All parameters of this analytical method can be found in Table 1 and 2.
Auto sampler
1μL
Injector
250°C
Flow
1mLmin-1 splitless 0.80min
Carrier Gas
Helium
Column
5MS - 30m x 0.25mm x 0.25μm
Oven
Rate
Temperature
Hold
Initial
100°C
0min
20°C min-1
220°C
3min
40°C min-1
280°C
4min
Table 1: Chromatography method.
Source
250°C
Transfer line
230°C
MS mode
MRM - Multiple Reaction Monitoring
Diuron
161 > 90 (10eV)
Flutriafol
219 > 164.70 (10eV)
Procymidone
96 > 67 (10eV)
Tebuconazole
250 > 125 (10eV)
Table 2: Mass spectrometry method.
Validation
The analytical method validation has been processed with efficiency; the following parameters were evaluated to suitability guarantee.
These are selectivity, linearity, work range, detection limit, quantitation limit, recovery and accuracy. All validation steps add compound in matrix and follow the INMETRO DOQ-CGCRE-008, Brazilian validation document [11].
Selectivity
An analytical method to quantify the aim analyte in presence with other analytes or interference material was established. To identify the selectivity, standard injection had been done, to evaluate, retention time, fragmentation and column analytes separation. Full scan mode with extraction ions and four multiple reaction monitoring, MRM were done, these are shown in Figure 2.
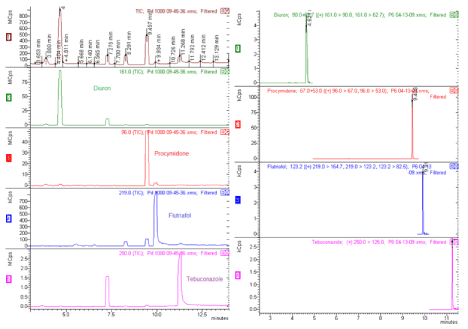
Figure 2: Full scan, left and MRM, right, analyses.
Linearity and work range
Linearity is an analytical procedure that can produce results proportionality to a sample analyte concentration. Work range is the range between the highest and lowest sample concentration, (10ugkg-1, 25ugkg-1, 50ugkg-1, 75ugkg-1, 100ugkg-1, 250ugkg-1, 500ugkg-1) that it has the method with an acceptable precision, accuracy and linearity. In Figure 3 it can see the linearity for four analytical compounds.
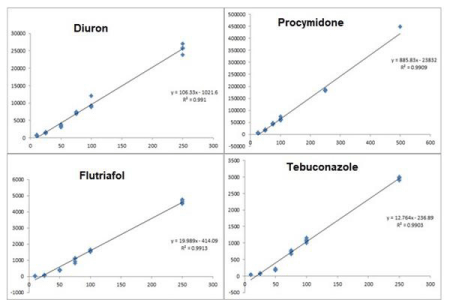
Figure 3: Calibration curve.
Detection and quantitation limit
Detection limit is the lowest concentration that can be found but not necessarily quantified. For this test all spectra compound has a lowest concentration 10ugkg-1 detectable.
Quantitation limit is the less sample quantity that can be quantified with precision and accuracy. For quantitation limit, four compounds used 25ugkg-1. Figure 4 shows a spectrum for detection limit, in the left hand and quantitation limit, in the right hand.
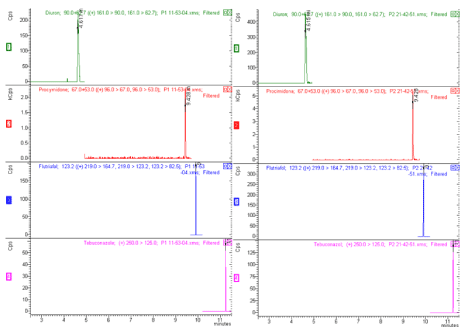
Figure 4: Detection limit, left and Quantitation limit, right.
Recovery
Recovery is estimated by fortified sample analysis with known compound and three different concentrations, low, 25ugkg-1, medium, 75ugkg-1 and high, 250ugkg-1, the recovery range is between 80-110. It was used two different compounds to evaluated recovery, Diuron and Tebuconazole standard in solvent, observe the recovery in Table 3 and Table 4.
Sample
Amount
Reference
Recovery
Sample
Amount
Reference
Recovery
Sample
Amount
Reference
Recovery
1
24.915
25
99.66
1
79.865
75
106.486
1
251.538
250
100.615
2
24.117
25
96.468
2
73.68
75
98.24
2
241.158
250
96.463
3
22.005
25
88.02
3
75.573
75
100.764
3
247.505
250
99.002
4
23.789
25
95.156
4
73.003
75
97.337
4
244.964
250
97.985
5
22.809
25
91.236
5
72.969
75
97.292
5
243.366
250
97.346
6
22.933
25
91.732
6
78.727
75
104.969
6
241.52
250
96.608
7
22.242
25
88.968
7
72.842
75
97.123
7
233.069
250
93.227
8
20.983
25
83.932
8
70.818
75
94.424
8
245.562
250
98.224
9
21.965
25
87.86
9
67.38
75
89.84
9
244.704
250
97.881
10
22.064
25
88.256
10
73.77
75
98.36
10
246.558
250
98.623
Average
22.782
Average
73.862
Average
243.994
SD
1.19
SD
3.6
SD
4.87
RSD(%)
5.21
RSD(%)
4.87
RSD(%)
2
Table 3: Diuron recovery.
Sample
Amount
Reference
Recovery
Sample
Amount
Reference
Recovery
Sample
Amount
Reference
Recovery
1
27.017
25
108.068
1
73.47
75
97.96
1
236.964
250
94.785
2
22.18
25
88.72
2
69.259
75
92.345
2
252.761
250
101.104
3
22.711
25
90.844
3
78.465
75
104.62
3
252.986
250
101.194
4
22.265
25
89.06
4
74.692
75
99.589
4
238.172
250
95.268
5
27.209
25
108.836
5
82.358
75
109.81
5
248.208
250
99.283
6
27.036
25
108.144
6
75.666
75
100.888
6
252.419
250
100.967
7
26.548
25
106.192
7
75.92
75
101.226
7
252.308
250
100.923
8
26.634
25
106.536
8
71.885
75
958.466
8
254.679
250
101.871
9
24.045
25
96.18
9
83.509
75
111.345
9
240.578
250
96.231
10
21.121
25
84.484
10
78.16
75
104.213
10
240.134
250
96.053
Average
24.676
Average
76.338
Average
246.92
SD
2.44
SD
4.43
SD
7.1
RSD(%)
9.9
RSD(%)
5.81
RSD(%)
2.88
Table 4: Tebuconazole recovery.
Accuracy
In the accuracy was not more than 20% and the standard deviation relative was not more than 5%. There are three most common evaluations: repeatability, intermediate precision and reproducibility, usually expressed by standard deviation and coefficient of variation. For this validation it was used repeatability which means that this procedure needs the same requirements, such as operator, preparation conditions, systems, and place. The compounds were added the compounds in the matrix and used different range concentration, low, 25ugkg-1, medium, 50ugkg-1 and high 250ugkg-1 (Table 5-7).
Sample
Concentration
Referencie Concentration
Accuracy (%)
Flutriafol
White beans
1
23.671
25
-5.316
2
23.614
25
-5.544
3
23.764
25
-4.944
4
26.196
25
4.784
5
24.202
25
-3.192
Average
24.289
SD
1.09
RSD(%)
4.49
Sample
Concentration
Referencie Concentration
Accuracy (%)
Flutriafol
Adzuki beans
1
23.753
25,000
-4,988
2
24.216
25,000
-3,136
3
23.171
25,000
-7,316
4
23.528
25,000
-5,888
5
23.103
25,000
-7,588
Average
23.554
SD
0.46
RSD(%)
1.93
Table 5: Flutriafol low precision.
Sample
Concentration
Referencie Concentration
Accuracy (%)
Diuron
String beans
1
58.517
50
17.034
2
58.606
50
17.212
3
57.982
50
15.964
4
54.312
50
8.624
5
56.627
50
13.254
Average
57.209
SD
1.8
RSD(%)
3.15
Sample
Concentration
Referencie Concentration
Accuracy (%)
Diuron
White beans
1
49.924
50
-0.152
2
56.291
50
12.582
3
54.79
50
9.58
4
55.175
50
10.35
5
54.15
50
8.3
Average
54.066
SD
2.44
RSD(%)
4.52
Table 6: Diuron medium precision.
Sample
Concentration
Referencie Concentration
Accuracy (%)
Tebuconazole
White beans
1
228.017
250
-8.793
2
244.589
250
-2.164
3
229.1
250
-8.36
4
247.478
250
-1.009
5
234.857
250
-6.057
Average
236.808
SD
8.87
RSD(%)
3.75
Sample
Concentration
Referencie Concentration
Accuracy (%)
Tebuconazole
Adzuki beans
1
248.837
250
-0.4652
2
259.327
250
3.731
3
239.374
250
-4.25
4
231.291
250
-7.484
5
255.876
250
2.35
Average
246.941
SD
11.61
RSD(%)
4.7
Table 7: Tebuconazole high precision.
Results and Discussion
The analytical method validations were satisfactory for selectivity, sensitivity, linearity and accuracy. Two different extractions were done, for QuEChERS extraction we made a comparative between clean-up and without clean-up. The results showed that cleanup was very effective to matrix effect and reduced the signal to noise chromatogram protein and showed better results than without cleanup, Table 8. The solid- liquid extraction at low temperature had different results for all types of beans, these results may have occurred due to bad interaction of the contact surface or bad organic solvent interaction (Table 9). Therefore, in this comparative extraction method low temperature was not efficient to these fungicides’ compounds.
Beans
Black
White
String
Adzuki
Unit
QuEChERS
Without cleanup
0
0
0
0
μgkg-1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
With cleanup
24.171
24.162
23.268
24.546
μgkg-1
24.423
24.072
25.268
24.233
24.28
23.561
24.83
25.963
23.422
23.932
23.814
26.6
23.823
25.142
22.896
24.627
Table 8: QuEChERS comparations results.
Beans
Black
White
String
Adzuki
Unit
Low temperature
145.117
77.314
203.524
103.577
μgkg-1
143.115
77.61
199.542
102.983
43.567
31.932
25.024
0.000
40.059
45.41
70.903
30.968
35.888
49.25
59.902
0.000
Table 9: Low temperature extraction results.
All samples had showed procymidone as identified and their quantitative results are shown at Table 10. Nevertheless the most procymidone samples results are below the Brazilian law regulation limit 0.5mgkg-1 and that means that it is good for consumption but in 7% in all sample showed a lit bit higher than law regulation limit. Flutriafol and tebucanozole don’t appear in spectrum results or above the detection limit (Figure 5).
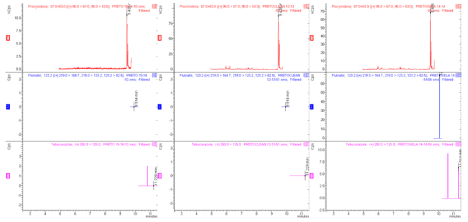
Figure 5: Sample spectrum, left without cleanup, middle with cleanup, right low temperature.
Sample
Feijão
Unit
Black
White
String
Adzuki
1
188.562
376.87
39.799
28.038
μg kg-1
2
81.485
47.794
37.58
46.64
3
76.05
53.36
41.263
48.008
4
80.736
47.213
36.133
46.229
5
80.422
37.362
37.039
49.239
6
77.025
29.606
37.458
50.501
7
72.305
28.769
35.849
47.078
8
295.22
40.293
259.189
31.537
9
228.267
39.446
264.227
35.264
10
143.115
40.36
265.558
35.286
11
43.567
39.164
261.514
35.319
12
128.507
39.388
274.735
31.957
13
85.193
39.66
43.386
32.938
14
83.439
216.96
35.667
31.284
15
76.419
235.209
35.978
269.502
16
67.355
252.365
33.286
273.641
17
64.969
214.37
33.251
264.055
18
318.243
198.962
31.454
258.239
19
229.906
203.131
30.278
263.66
20
230.778
183.936
28.689
427.029
21
237.54
296.371
34.841
411.554
22
492.752
286.666
36.896
625.149
23
515.174
267.477
33.919
283.468
24
256.627
267.268
34.278
353.411
25
276.036
260.405
33.076
513.987
26
467.731
286.363
31.281
311.317
27
632.52
378.321
584.215
550.785
28
287.996
670.378
484.459
188.446
29
126.227
188.18
505.939
174.998
30
137.286
618.594
295.423
265.352
31
224.257
415.396
98.444
52.011
Table 10: Sample Results.
Conclusion
The methodology developed in this work shows a good agreement due to validation method for linearity, sensibility, accuracy, detection and quantitation limit.
Two different extractions were tested and it was observed that low temperature extraction has a disadvantage, a long time inside low temperature freezer, about 15 hours, to freeze the aqueous phase but was not efficient for these fungicides compounds, but it is not necessarily useless for other pesticides compounds.
In QuEChERS extraction showed that the clean-up extraction was efficient to prevent matrix effect, the signal to noise chromatogram protein is reduced and better results were achieved, but in disadvantage some difficult to buy a extraction salt and a abruptly agitation about 1 minute.
We were analyzed about 30 samples and the fungicides results in the beans stood below the regulation limit, which means that they are good for consumption except for 2 sample in 30, that a lit bit higher than regulation limit, that maybe bought when the store recently receive, this proves that we have a fungicides degradation by time of exposure.
References
- Lemes VRR, Kussumi TA, Nakano VE, Rocha SB, de Oliveira MCC, Rodrigues MP, et al. Avaliação de Resíduos de Agrotóxicos em Arroz e Feijão e sua Contribuição para Prevenção de Riscos à Saúde da População Consumidora. Revista do Instituto Adolfo Lutz. 2011.
- Araújo EJDR. Controle Químico de doenças do feijão. Linkedin SlideShare. 2017.
- Garcia A. Fungicidas I: utilização no controle químico de doenças e sua ação contra os fitopatógenos. EMBRAPA - Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária. 1999.
- Fidélis MR. MÉTODO VOLTAMÉTRICO PARA A DETERMINAçãO SIMULTÂNEA DE PROCIMIDONA E TEBUTIURON EM ÁGUA. Universidade Federal de Viçosa. 2015.
- de Kok e Ionara R. Pizzutti Mhcwodpmbarza. Validação de métodos multirresíduos para determinação de resíduos de 52 pes-ticidas em soja utilizando GC-MS (SIM) e GC-MS/MS (EI+ E CI-). Sociedade Brasileira de Química (SBQ). 2006.
- Pinho GPD. Extração de Pesticidas em Amostras de Tomate pelas Técnicas: Extração Sóli-do- Líquido e Purificação em Baixa Temperatura (ESL-PBT) e Dispersão da Matriz em Fase Sólida (DMFS) para Análise por Cromatografia Gasosa. Universidade Federal de Viçosa. 2007.
- Grave G. Vida e Química - Dicas da vida, uteis p dia a dia. E um pouco mais de Química, que tb faz parte do meu dia-dia. Extração Sólido-Líquido. 2011.
- Prestes OD, Friggi CA, Adaime MB, Zanella R. Um método moderno de preparo de amostra para determinação multirresíduo de pesticidas em alimentos por métodos cromatográficos acoplados à espectrome-tria de massas. Química Nova. 2009.
- Vieira HP. Otimização e validação da extração simultânea de piretróides em água e solo e análise por cromatografia gasosa. Universidade Federal de Viçosa. 2005.
- Vieira HP, Neves AA and de Queiroz MELR. Otimização e validação da técnica de extração líquido-líquido com partição em baixa temperatura (ELLPBT) para piretróides em água e análise por CG. Química Nova. 2007.
- Inmetro-Instituto Nacional de Metrologia, Qualidade e Tecnologia. ORIENTAÇÃO SOBRE VALIDAÇÃO DE MÉTODOS ANALÍTICOS - DOQCGCRE- 008. INMETRO. 2016.