
Special Article: Crop Improvement
Ann Agric Crop Sci. 2023; 8(2): 1132.
‘FT’, A Spontaneous Doubled Haploid Recipient of Transient Transformation in Chinese Cabbage
Han Wu²; Kuangye Zhang²; Jiaxu Wang²; Jia Li²; Youhou Duan²; Zhiqiang Liu²; Ying Zhao¹; Yun Zhang¹
¹College of Horticulture, Shenyang Agricultural University, Shenyang 110866, China
²Sorghum Research Institute, Liaoning Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Shenyang 110161, China
*Corresponding author: Yun Zhang College of Horticulture, Shenyang Agricultural University, Shenyang 110866, China. Email: zhangyun511@syau.edu.cn
Received: April 05, 2023 Accepted: May 03, 2023 Published: May 10, 2023
Abstract
Chinese cabbage is relatively recalcitrant to genetic transformation. Microspore is an ideal haploid single cell recipient for genetic m anipulation, whereby homozygous Doubled Haploid (DH) transformants can be obtained to accelerate the breeding process. In this study, Microspore Derived Embryo (MDE) productive material DH ‘FT’ is screened out from 10 candidates; microspore culture parameters were optimized: bud size ranged from 2.4mm to 2.7mm and microspore density 20000~40000/mL shows highest MDE yield. Antibiotic (chemical) sensitivity assay indicates that 100mg/L Carbenicillin or 300mg/L Timentin can be applied to inhibit the overgrowth of Agrobacterium after transformation; microspores are sensitive to cellulase and lysozyme treatments when liquid cultured, kanamycin slight below 5mg/L can be used as selection marker. ‘FT’ microspore and MDE were successfully transfected by Agrobacterium. Transient expression of embryogenic transcription factor LEC1-GFP in nucleus, rather than cytoplasm, was clearly detected by confocal microscopy. ‘FT’ microspores, 14/28d MDEs can be used as transient transfection recipients in Chinese cabbage. This study provides an efficient and spontaneous doubled haploid recipient system in Brassica rapa.
Keyword: Chinese cabbage; DH line; Microspore culture; Transformation; Recipient
Abbreviations: DH: Doubled Haploid; MDE: Microspore Derived Embryo; PPT: Phosphinothricin
Introduction
Immature pollen of plants, which is known as microspore, has haploid genome and simple cell structure. Under stress or exogenous hormone induction, haploid plantlets can regenerate through embryoid pathway from microspores that is called isolated microspore embryogenesis [2-4]. After colchicin treatment or spontaneous genome doubling, homozygous DH (doubled haploid) lines can be obtained to sharply shorten the breeding cycles [5], which also provides a technical platform for single cell genetic operation. Chinese cabbage is recalcitrant to regenerate after Agrobacterium transfection [6]. Some relative successful attempts have been made in Brassica rapa transformation [7-12]. However, the results showed strong genotype dependency, and the transformation efficiency is hardly stable and repeatable, which is the bottleneck to study gene function in Brassica rapa. An efficient recipient system is urgently needed, especially single cell recipient.
Efficient recipient system is the first step of transformation protocol. In the past two decades, the molecular mechanism [13] of totipotency has been well studied [14]. Morphogenic transcription factors play important roles in embryogenesis [15] and can induce somatic embryogenesis when over-expressed [16]. Some discovered morphogenic transcription factors can be applied to enhance regeneration after transformation, such as BBM [17], WUS [18], GRF–GIF [19,20]. The LEC transcription factors [22] were firstly discovered [21] to improve somatic embryogenesis when ectopically expressed [22]. The LEC-GFP fusion protein can be found in the nucleus of embryogenic cells rather than cytoplasm [4], which marks the initiation of microspore embryogenesis. A microspore-based transient transformation system is suitable to understand gene function, especially in embryogenesis phase.
In this study, a Microspore Derived Embryo (MDE) productive variety DH 'FT' were screened out from 10 candidates, the microspore culture parameters were optimized, and antibiotic sensitivity assay was performed. Microspore and MDE of 'FT' were used as recipient of Agrobacterium mediated transformation. Transient expression of LEC1-GFP, an embryo-expressed transcription factor, were successfully detected in nucleus, rather than cytoplasm, by confocal as expected. We offered an efficient spontaneous doubled haploid recipient system of transformation in Brassica rapa.
Materials and Methods
Plant Materials
The following 10 materials: 'Golden Crow', 'Yangchun' 'Chundajiang’,'Leader', 'Hongkang 1’, 'Rich Spring', 'Beijing New 3', 'Multi-resistant3', 'FT', 'Golden Spring' were used as candidates in microspore culture experiment. They were cultured in a greenhouse. 'FT' is Double Haploid line (DH) from hybrid 'Futian 50' in Brassica rapa.
Isolated Microspore Culture
The microspore culture protocol in this study is modified from Sato et al., (1989). Buds were selected from healthy inflorescence, 30 buds as a group. 70% ethanol and 2% bleach solution were used for surface disinfection. Vibrate from time to time to drive away the bubbles on surface. Rinse with sterile water 3 times for 1 min, 4 min and 10 min, respectively. Add 5mL NLN liquid medium, crush the buds with sterile grinding rod to press out the microspores. The debris was removed by nylon mesh. The yellow precipitates (microspores) were rinsed 3 times with 5mL B5 medium, centrifuged at 100rpm. 20μL microspore culture was used for DAPI staining to investigate the developmental stages. The microspore concentration was determined by blood cell counting plate to meet the gradient 20000, 40000 and 80000 cells/mL in NLN-13 medium. 1.0mL microspore suspension was transferred into a 3cm sterile culture dish, sealed, and heat shock in precis 32°C for 24h. Then the dishes were transferred to 25°C in dark for 20 days. The microspore derived embryos can be found at the edge of dishes by then.
Antibiotic Sensitivity Assay
Concentration gradient of Carbenicillin (0, 50, 100 and 500mg. L-1 ); Timentin (0, 60, 150, and 300mg. L-1 ); Kanamycin (0, 0.5, 5, 25, 50 and 100mg. L-1 ); Phosphinothricin (PPT) (0, 7.5, 15, 30 and 90mg. L-1 ); Cellulase (0, 10, 20, 25, 30, 40, and 50mg. L-1) and lysozyme (0, 10, 20, 25, 30, 40, and 50mg. L-1) were added to the liquid NLN13 medium respectively for microspore antibiotic sensitivity assay. Each concentration in line with 3 replicates (dishes) for statistics. Suitable concentrations were screened out for downstream experiments.
Ploidy Identification of Regenerated Plants
Ploidy of microspore regenerated plants was identified by FACS calibur flow cytometry in this study. 1mL chopping buffer was added into a culture dish, and 1.5cm of regenerated plant leaves were selected and chopped with blade. The supernatant was filtered with nylon mesh and collected into a tube. Centrifugation was performed at 1000rpm for 10 min at room temperature. Discard the supernatant and add 1mL propidium iodide in dark for 15 minutes, filtered. The cell ploidy was detected on FACS calibur flow cytometry with 3 replicates.
Transformation of Microspore and MDE
The microspore density was kept at 40×103 cells·mL-1. 1μL Agrobacterium stock with OD value 1.0 was added into 10mL microspore suspension containing 0.007% cellulase. 1.0mL microspore suspension was pipetted into a sterile 30mm culture dish, 33°C heat shock for 24h. The Agrobacterium was controlled by washing with 0.01% lysozyme solution, and then rinse twice with NLN13 containing timentin 300mg/L. Finally, the cells were cultured in NLN13 medium containing 100mg/L Timentin and corresponding antibiotics at 25°C. Fresh media were changed weekly to keep the embryo developing. The transient expression of fluorescent markers was traced by confocal. 1 or 3 weeks after heat shock, typical globular MDE, or torpedo embryo were used as transfection recipient. After 24h co-culture, the Agrobacterium were washed with 0.01% lysozyme in order to digest the cell wall of bacterium. Then wash twice with NLN13 medium containing Timentin 300mg/L. Finally, the cells were kept in NLN13 medium containing 150mg/L Timentin and corresponding antibiotics at 25°C. Fresh media were changed weekly. The expression of fluorescent markers was continuously tracked by confocal.
Statistics
Statistics analysis was conducted by SPSS 16.0 software. Statistically significant differences among the number of microspore embryo per dish were calculated using Ducan's t-test (*P<0.05). ANOVA analysis of variance was applied in antibiotic sensitivity experiment.
Results
Genotype Dependency of Microspore Embryogenesis in Brassica rapa
Ten Chinese cabbage varieties 'Golden Crow' 'Yangchun' 'Chundajiang' 'Leader' 'Hongkang 1' 'Rich Spring' 'Beijing New 3' 'Multi-resistant3' 'FT' 'Golden Spring' were used as candidates to induce microspore derived embryos. 14d after microspore isolation, the embryos can be found at the edge of dishes, embryogenesis rate was calculated. 'FT' showed the highest microspore embryogenesis rate, which reached 144 embryos per 10000 microspores. On the contrary, the embryogenesis rate of 'chundajiang' and 'duokangxin 3' had only 1 or 2 embryos per 10000 microspores (Table 1). Microspore embryogenesis shows strong genotype dependency in Brassica rapa.
Materials
#MDE from 10000 microspores
Yangchun
14.67±1.86cd
Chundajiang
1.67±0.33d
Leader
45.67±4.37b
Hongkang 1
21.67±4.26c
Rich Spring
27.33±3.84c
Beijing New 3
13.33±3.38cd
Multi-resistant 3
1.33±0.67cd
FT
143.67±12.24a
Golden Spring
53.33±5.04b
Note: Ducan's test, different lowercase letters indicated significant difference at a=0.05.
Table 1: Microspore embryogenesis rate from 10 materials in B.rapa.
Ploidy Identification
FACS calibur flow cytometry was used to identify the ploidy of microspore regenerated plants in this study. Compared to wild type 'FT' leaf samples, most regenerated plants were spontaneous diploid, reached 83.1%, 7.1% tetraploids appeared, and only 9.8% of microspore plants were still haploid (Figure 1 & Table 1). The results indicate that, spontaneous diploid process happened frequently after 'FT' microspore regeneration; where by homozygous DH line can be obtained without colchicine treatment.
#microspore plantlets 'FT'
Haploid
Doubled haploid
Tetraploid
#plantlet
#plantlet
ratio%
#plantlet
ratio%
71
7
9.8
59
83.1
5
7.1
Table 2: Ploidy identification result of microspore derived plantlet in 'FT'.
Developmental Stages and Microspore Culture Density
In order to reach higher MDE yield, the relationship among bud length, microspore developmental stage and microspore embryogenesis rate was investigated. When buds ranged from 2.4mm to 2.7mm, the percentage of microspores in late mononuclear and early binucleate stage was about 90% (Figure 2). When the microspore culture density was 20000~40000/mL, the highest embryogenesis rate 1.6% was found. Although there was some difference depending on the sample batches, bud size from 2.4mm to 2.7mm and culture density 40000/mL were used in subsequent 'FT' transformation experiment (Figure 2).
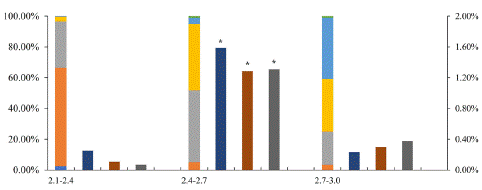
Figure 2: The relationship among ‘FT’ bud size, developmental stage, and microspore embryogenesis rate. Left Y axis: ratio of developmental stages, right Y axis: microspore embryogenesis rate: X axis: bud size (mm) and microspore density. eu: early uninuclei, mu: mid-uninuclei, lu: late uninuclei, eb: early binuclei, lb: late binuclei, tri: tri-nuclei pollen. The density is 20000, 40000, 80000 microspores /ml, respectively. Asterisk indicates significant difference, p<0.05.
Antibiotic Sensitivity Pattern of ‘FT’MDEs
After co-cultivation, it is necessary to inhibit the overgrowth of Agrobacterium and select out the transformants in liquid NLN13 medium. To screen out the available antibiotics and concentration, we performed an antibiotic tolerance test (Figure 3). Carbenicillin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic. There is no significant difference among the gradient treatment from 0 to 100mg/L, but the MDE number decreased significantly when treated with 500mg/L (Figure 3A). Timentin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic either, which is often used to inhibit the overgrowth of Agrobacterium in transformation experiment, especially in embryonic callus recipient system. There is no significant difference among the gradient treatment of timentin (Figure 3B). Thus, 100mg/L Carbenicillin and 300mg/L Timentin were chosen to inhibit the overgrowth of Agrobacterium without serious toxicity to the recipients.
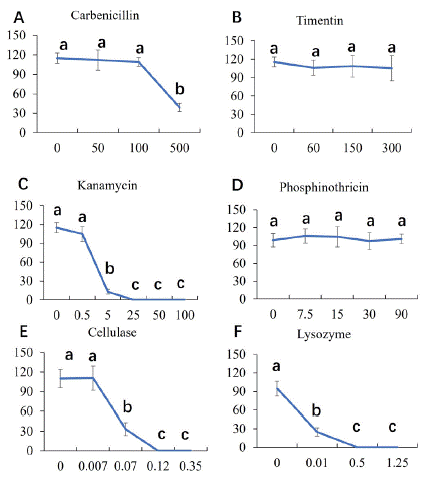
Figure 3: Antibiotic sensitivity pattern of ‘FT’ MDEs. A: The number of MDE decreased significantly when carbenicillin 500mg/L; B: There is no significant difference among the gradient treatment of timentin; C: Kanamycin over 5mg/L significantly inhibits microspore embryogenesis; D: Phosphinothricin (PPT) cannot inhibit microspore embryogenesis even in 90mg/L; E: the number of MDE significantly dropped from 0.07% Cellulase. F: Lysozyme decrease the number of MDE significantly from 0.01%.
Kanamycin is an inhibitor of protein biosynthesis used as an efficient selection marker in plant transformation. Kanamycin over 5mg/L significantly inhibits microspore embryogenesis (Figure 3C). Phosphinothricin (PPT) is a broad-spectrum herbicide which also used as an efficient selection marker. There is no significant difference among the gradient treatment of PPT (Figure 3D). Cellulase and lysozyme can digest the thick exine of microspore and cell wall of Agrobacterium respectively, whereby improve transformation efficiency and enhance the antibiotics inhibitory against naked Agrobacterium cells. The number of MDE significantly dropped from 0.07%, and there was no MDE above 0.12%. Lysozyme decrease the number of MDE significantly from 0.01%, MDE became smaller, and development was deformed. Microspore derived embryos are sensitive to cellulase and lysozyme (Figure 3E, F). Therefore, microspores can be rinsed with 0.07% cellulase and 0.01% lysozyme after cocultivation; kanamycin slight below 5mg/L, rather than Phosphinothricin (PPT), can be used as selection marker.
LEC1-GFP Transient Expression in Microspores
LEC1:LEC1-GFP frame was built in pBi121 backbone sequence (Figure 4). The LEC-GFP fusion protein would only be found in the nucleus of embryogenesis cells rather than cytoplasm [4]. After Agrobacterium mediated transformation, the fluorescence signal was tracked by confocal (Figure 5). GFP signal cannot be observed in negative control, which was transfected with activated Agrobacterium competent cells without Ti plasmid. But LEC1-GFP was expressed in two diffusely DAPI stained microspore nuclei, which is the generative and vegetative nuclei. 1090 transformed microspores were observed, of which 17 were GFP positive. Transformation efficiency is about 1.56% (Table 3). The results suggest that 'FT' microspore can be transformed by Agrobacterium, and the transient expression could be detected within 72h.
Treatments
Transformation efficiency (%)
Agrobacterium mediated transformation
1.56 ± 0.70*
Negative control
0
Note: Student’s t test (*indicate difference p<0.05.
Table 3: Transformation efficiency in Chinese cabbage 'FT' microspores.

Figure 4: LEC1:LEC1-GFP frame was built in pBi121 backbone for transformation.
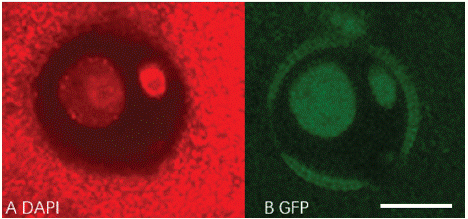
Figure 5: Expression of LEC1-GFP in transformed ‘FT’ microspore. A: DAPI staining, B: GFP signal in nucleus. Scale bar, 10μm.
LEC1-GFP Transient Expression in MDE
Later, we tried to transform LEC1:LEC1-GFP vector into 'FT' Microspore Derived Embryos (MDEs). The transient expression was continuously tracked by confocal. LEC1-GFP fluorescence can only be found in the nuclei rather than cytoplasm [4]. Arrows indicate that there is no GFP signal in the negative control as expected (Figure 6E). Interestingly, in both 14 and 28d MDEs, LEC1-GFP expression was observed 48h after transfection (Figure 6 B, G). The 28d MDEs are too thick for laser went though, positive GFP signal can be found on the epidermal cells by fluorescent microscopy (Figure 6G). In total, 68 GFP positive MDE transformants were found from 403 transfected MDEs. Transformation efficiency is about 16.87% (Table 4). The results suggest that 'FT' MDE can be used as recipient, and the transient expression could be detected within 72h.
Treatments
Transformation efficiency (%)
Agrobacterium mediated transformation
16.87±3.43**
Negative control
0.00
Note: Student’s t test (** indicate significant difference p<0.01)
Table 4: Transformation efficiency in Chinese cabbage 'FT' microspore derived embryos.
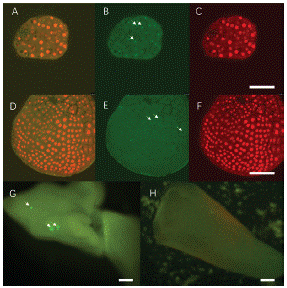
Figure 6: LEC1-GFP expression in transformed ‘FT’ MDEs. A, B, C 14d MDE positive transformants. A: Merge; B: Positive GFP signal in nuclei; C DAPI staining shows the nuclei, Scale bar, 50μm. D, E, F: Negative control, D: Merge, E: Negative GFP signal in nuclei. F: DAPI staining. Scale bar, 50μm. G: 28d MDE positive transformant, H: Negative control. Scale bar, 500μm.
Discussion
Among Cruciferae Plants, Chinese cabbage is more difficult to regenerate after transfection [7-12]. Genotype dependencies restrict the genetic transformation, and the recipient is recalcitrant to regenerate after transfection [6]. Researchers tried to screen out a generic transformation system [12,23,24] nevertheless, a generic and repeatable protocol is still needed to be presented in Chinese cabbage. Microspore shows strong embryogenesis potential in Brassica rapa., which can shorten the breeding cycle by homozygous DH lines [5]. Microspore embryogenesis in Brassicas can be divided into four stages: multicellular structure, spherical embryo, heart-shaped embryo, and torpedo shaped embryo [3,4]. And there are four types of multicellular structure when microspore culture in Brassica napus: classic embryo forming structure, compact callus like structure, extruded sporophytic structure and loose callus like structure. Except for the embryo forming structure, the rest three types stopped growing and died eventually [4]. Microspore can be used as transformation recipient [23,26,27]. The material developmental stages and culture density are important to MDE yield. In this study, the microspore culture system of 'FT' was optimized (Figure 1). Bud size ranged from 2.4mm to 2.7mm and microspore density 20000~40000/mL show highest MDE yield, which is in line with previous reports [2].
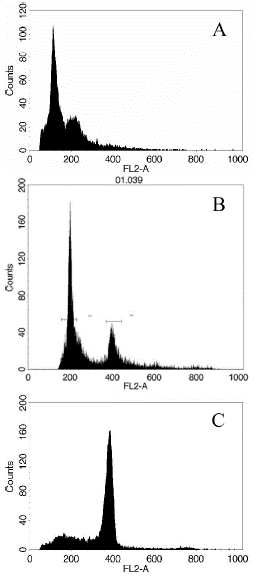
Figure 1: Ploidy determination of regenerated plantlets. A: Haploid; B: Doubled haploid; C: Polyploid.
Antibiotics are commonly used to inhibit Agrobacterium overgrowth in transformation experiments [6,9]. The MDEs were cultured in liquid medium, which was disadvantageous to control the overgrowth of Agrobacterium. According to previous reports [6,9], lysozyme can effectively digest the cell wall of bacterium, that is more conducive for antibiotics to kill the naked bacterium. Although FT microspore was sensitive to cellulase and lysozyme (Figure 3E, F), Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58 could be inhibited by three times 0.01% lysozyme rinse and kept culture in 150mg/L Timentin contained NLN-13 medium.
LEAFYCOTYLEDON1(LEC1) is the first identified embryo-expressed transcription factor, which encodes B9 subunit of NF-YB9, a nuclear factor Y protein [21], and involve in a larger transcription factor network called “LAFL” [28]. LEC1 activate the expression of a key auxin biosynthesis enzyme YUC10. Over-expression of LEC1 induces embryogenesis and development [29]. LEC1 transcription factors are only expressed during embryogenesis process, and technically, can be detected in the nucleus, rather than cytoplasm, in embryogenic tissue [4]. Microspore embryogenesis and transformation were well-studied in B. napus [4,23,26,27], but hardly reported in B. rapa. In this study, 'FT' microspores were transformed by Agrobacterium right after isolation, and strong transient LEC1-GFP signal was detected (Figure 5), which is in line with previous study [27]. The wild type 'FT' MDE shows green fluorescence background in the cytoplasm but very weak in the nucleus (Figure 6 E), which benefits identification transcription factors in the nucleus. The LEC1-GFP fluorescent signal can be found in the nucleus (Figure 6B), rather than cytoplasm, which is in line with previous results [4]. In general, we show that 'FT' is a MDE productive material that can be used as transient transformation recipient in Chinese cabbage.
Conclusion
'FT' can effectively produce spontaneous DH plantlets in Chinese cabbage. Microspores and MDEs of' 'FT' can be used as transient transformation recipients.
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by the Fellowship of China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2021M693846); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31972404).
References
- Azam P, Ahmad M, Hamid D, Sajad RM. Field-grown donor plants and arabinogalactan proteins improve microspore embryogenesis in sweet pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Plant. 2021; 57: 1-9.
- Sato T, Nishio T, Hirai M. Plant regeneration from isolated microspore cultures of Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris spp. pekinensis). Plant Cell Rep. 1989; 8: 486–8.
- Joosen R, Cordewener J, Supena EDJ, Vorst O, Lammers M, et al. Combined transcriptome and proteome analysis identifies pathways and markers associated with the establishment of rapeseed microspore-derived embryo development. Plant Physiol. 2007; 144: 155–72.
- Li H, Soriano M, Cordewener J, Muiño JM, Riksen T, et al. The histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin a promotes totipotency in the male gametophyte. Plant Cell. 2014; 26: 195–209.
- Huang S, Liu Z, Li D, Yao R, Feng H. A new method for generation and screening of Chinese cabbage mutants using isolated microspore culturing and EMS mutagenesis. Euphytica. 2016; 207: 23–33.
- Guoliang LI, Lixin YUE, Fei LI, Shifan Z, Hui Z, et al. Research Progress on Agrobacterium tumefaciens -based Transgenic Technology in Brassica rapa. Hortic Plant J. 2018; 4: 126–32.
- Zhang L, Xu B. Medium and genotype factors influencing shoot regeneration from cotyledonary explants of Chinese cabbage ( Brassica campestris L. ssp. pekinensis ). 1998; 780–6.
- Zhang FL, Takahata Y, Watanabe M, Xu JB. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of cotyledonary explants of Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris L. ssp. pekinensis). Plant Cell Rep. 2000; 19: 569–75.
- Dormann M, Wang H-M, Oelck M. Transformed Embryogenic Microspores for the Generation of Fertile Homozygous Plants. 2001; 1: 1–13.
- Tang GX, Zhou WJ, Li HZ, Mao BZ, He ZH, Yoneyama K. Medium, Explant and Genotype Factors Influencing Shoot Regeneration in Oilseed Brassica spp. J Agron Crop Sci. 2003; 189: 351–8.
- Yang ZH, Jiang Guo Bin, Woong BT, Woo JG, Yun HD, et al. An Improved Plant Regeneration Protocol using Cotyledonary Explants from Inbred Lines of Chinese Cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis). 2004.
- Baskar V, Gangadhar BH, Park SW, Nile SH. A simple and efficient agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated plant transformation of brassica rapa ssp. Pekinensis. 3 Biotech. 2016; 6: 1–6.
- Ikeuchi M, Rymen B, Sugimoto K. How do plants transduce wound signals to induce tissue repair and organ regeneration? Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2020; 57: 72–7.
- Iwase A, Kondo Y, Laohavisit A, Takebayashi A, Ikeuchi M, et al. WIND transcription factors orchestrate wound-induced callus formation, vascular reconnection and defense response in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2021; 232: 734–52.
- Horstman A, Willemsen V, Boutilier K, Heidstra R. AINTEGUMENTA-LIKE proteins : hubs in a plethora of networks. Trends Plant Sci. 2014; 19: 146–57.
- Mu J, Tan H, Hong S, Liang Y, Zuo J. Arabidopsis transcription factor genes NF-YA1, 5, 6, and 9 play redundant roles in male gametogenesis, embryogenesis, and seed development. Mol Plant. 2013; 6: 188–201.
- Boutilier K, Offringa R, Sharma VK, Kieft H, Ouellet T, et al. Ectopic expression of BABY BOOM triggers a conversion from vegetative to embryonic growth. Plant Cell. 2002; 14: 1737–49.
- Lowe K, Wu E, Wang N, Hoerster G, Hastings C, et al. Morphogenic Regulators Baby boom and Wuschel Improve Monocot Transformation. 2016; 28: 1998–2015.
- Debernardi JM, Tricoli DM, Ercoli MF, Hayta S, Ronald P, et al. A GRF–GIF chimeric protein improves the regeneration efficiency of transgenic plants. Nat Biotechnol. 2020; 38: 1274–9.
- Kim JH. Biological roles and an evolutionary sketch of the GRF-GIF transcriptional complex in plants. BMB Rep. 2019; 52: 227–38.
- Lotan T, Ohto M, Yee KM, West MAL, Lo R, Kwong RW, et al. Arabidopsis LEAFY COTYLEDON1 Is Sufficient to Induce Embryo Development in Vegetative Cells. 1998; 93: 1195–205.
- Stone SL, Kwong LW, Yee KM, Pelletier J, Fischer RL, et al. LEAFY COTYLEDON2 encodes a B3 domain transcription factor that induces embryo development. 2001; 98: 11806-11.
- Abdollahi MR, Corral-Martínez P, Mousavi A, Salmanian AH, Moieni A, et al. An efficient method for transformation of pre-androgenic, isolated Brassica napus microspores involving microprojectile bombardment and Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Acta Physiol Plant. 2009; 31: 1313–7.
- Abdollahi MR, Moieni A, Mousavi A, Salmanian AH. High frequency production of rapeseed transgenic plants via combination of microprojectile bombardment and secondary embryogenesis of microspore-derived embryos. Mol Biol Rep. 2011; 38: 711–9.
- Tsuwamoto R, Yokoi S, Takahata Y. Arabidopsis EMBRYOMAKER encoding an AP2 domain transcription factor plays a key role in developmental change from vegetative to embryonic phase. Plant Mol Biol. 2010; 73: 481–92.
- Fukuoka H, Ogawa T, Matsuoka M, Ohkawa Y, Yano H. Direct gene delivery into isolated microspores of rapeseed ( Brassica napus L .) and the production of fertile transgenic plants. Plant Cell Rep. 1998; 323–8.
- Nehlin L, Möllers C, Bergman P, Glimelius K. Transient β-gus and gfp gene expression and viability analysis of microprojectile bombarded microspores of Brassica napus L. J Plant Physiol. 2000; 156: 175–83.
- Tedeschi F, Rizzo P, Rutten T, Altschmied L, Helmut B. RWP - RK domain - containing transcription factors control cell differ- entiation during female gametophyte development in Arabidopsis. 2016.
- Horstman A, Bemer M, Boutilier K. A transcriptional view on somatic embryogenesis. Regeneration. 2017; 4: 201–16.