
Research Article
Ann Agric Crop Sci. 2024; 9(4): 1162.
Evaluation of Improved Exotic Head Cabbage Varieties at Bale high Lands, South Eastern Ethiopia
Gemechu Ejigu*
Oromia Agricultural Research Institute, Sinana Agricultural Research, Robe Bale, Ethiopia
*Corresponding author: Gemechu Ejigu, Oromia Agricultural Research Institute, Sinana Agricultural Research, Robe Bale, Ethiopia. Email: gemechuejigu55@gmail.com
Received: July 29, 2024 Accepted: August 22, 2024 Published: August 29, 2024
Abstract
Evaluation of exotic head cabbage varieties was conducted to select the most adaptable variety which was/were high yielder, disease and insect tolerant and best fit for the study area. The field experiment was conducted during the 2021 and 2022 rainy season at three locations. Randomized complete block design with three replications were used; each plot consisted of six rows and seven plants per row having spacing of 40cm x 50cm (intra and inter row) respectively, on a plot size of 2.8m x 3m (Width and length respectively). Cabbage varieties those were commercially available on the market Rossen, Royal, Monarch, Green and Delta was used in the study. Widely cultivated variety Bakker brother was included as check. From this experiment the combined analysis over locations and years indicated that almost all phenological, growth, yield and yield components of cabbage are significantly influenced due to varieties. From the ANOVA analysis the longest days to head initiation [70.93] was recorded for Delta seed variety, while the minimum [63.13] was attained by Monarch seed variety. In terms of days to 90 % head maturity the highest record [110] was recorded from Delta seed variety, while the lowest [105.5] was from royal seed varieties. The maximum gross head yield [118.11 ton/ha] was recorded from the variety green seed followed by Monarch seed variety [111.21 ton/ha], while the smallest number [88.72 ton/ha] was from Bakker brothers’ variety. Similarly, the highest marketable yield [94.15 ton/ha] was green seed variety, the next also from monarch seed variety [85.42 ton/ha] and the minimum record [61.57 ton/ha] was from Bakker brothers’ variety. Finally, from this experiment we get the result that green seed and Monarch seed variety showed best performance in almost all tested agronomic parameters over the tested varieties, therefore these two exotic head cabbage varieties were recommended for the study area and similar agro-ecologies.
Keywords: Exotic head cabbage varieties; Gross head yield; Marketable yield; Parameters
Abbreviations: RCBD: Randomized Complete Block Design; ANOVA: Analysis of Variance.
Introduction
Vegetables are substantial sources of vitamins, fiber, minerals, anti-oxidant and plant proteins in human diet which are useful for ordinary functioning of body systems and avoidance of cancer. Vegetable farming is becoming expensive due to the rising use of purchased inputs such as pesticides, herbicides and fertilizers to withstand production levels [13]. It was first originated in Northern Europe, the Baltic Sea coast and the Mediterranean region, where it has been produced for more than three thousand years and is well adapted to cool moist conditions [14].
Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.) is a critical Cole crops which is a member of the family Cruciferae or Brassicaceae with 2n=2x=18 chromosome number. This family includes broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower, kale, mustard (greens), and collards. Communally, these crops are mentioned to as cole crops or crucifers Cabbage is assumed to have originated in Western Europe and it was the first cole crop to be grown [5]. Prior to growing and use as for consumptions, cabbage was principally used for medicinal purposes. In addition to the marketed fresh, cabbage is also processed into Kraut, egg rolls, and there is the option for other specialty markets for the numerous types comprising of red, savoy and mini cabbage [8].
Cabbage is an admirable source of Vitamin C. In addition to having some B vitamins, cabbage provides some potassium and calcium to the nutrition. Two hundred fifty millilitres of raw cabbage contain twenty one kilocalories [12]. Cabbage (containing several varieties of Brassica oleracea) is a leafy green, red (purple), or white (pale green) biennial plant produced as an annual vegetable crop for its condensed-leaved heads. Plants are 40–60 cm tall at the matured vegetative stage [10]. According to [4], cabbage (Brassica oleracea L.) ranks second in terms of production among the vegetables in Ethiopia behind red pepper (Capsicum spp.). A latest estimate shows that Africa has about one million hectares planted with head cabbage [7]. Commercial seed sales indicate that at least 40,000 ha of white-headed cabbage are grown in Kenya, Uganda and Tanzania; 10,000 ha in Malawi, Zambia, and Zimbabwe; 4,000 ha in Ethiopia; and 3000 ha in Cameroon. Ethiopia has substantial agro-ecological variability that shapes crop production areas across the country [2].
In Ethiopia, a total of 38 thousand hectares of land are used for its cultivation, yielding almost three hundred ninety-five thousand tons per hectare under irrigation and rain-fed conditions. As a compared to the world average, Ethiopia's cabbage production is very low [10.4 t ha-1] [6]. In terms of cabbage productivity, Japan and the Republic of Korea are the top two producers of cabbage in the world with 71.2 and 67.6 t ha-1, respectively [9].
In recent decades, head cabbage has become increasingly important in tropical and subtropical regions. Africa has been estimated to have 1 00,000 hectares planted with head cabbage [1]. At least 40,000 ha of white-headed cabbage is grown in Kenya, Uganda and Tanzania; 10,000 ha in Malawi, Zambia and Zimbabwe; 4000 ha in Ethiopia; and 3000 ha in Cameroon [3]. Several reports have shown that vegetables can be planted throughout the year as long as there is enough moisture in the soil. Smallholder farmers in Kenya grow cabbage for food, income, and it is one of the most important vegetables.
The average cabbage head weighs between 0.5 and 4 kilograms, and it can be green, purple, or white. There are many types of green cabbage, but the most common are those with smooth and firm leaves. Savoy cabbages with smooth leaves and those with crinkle leaves are both uncommon. During the summer, high northern latitudes can experience extended sunny days that encourage cabbages to grow large. Cabbages can be consumed in many ways; they can be soured, fermented, steamed, parboiled, deep-fried, braised, or eaten raw [11].
Conducting cabbage adaptation will be helpful for breeders, seed companies, and farmers to evaluate varieties for adaptation to environment and yield, so they can select varieties that are best suited to the local environment and market. The high lands of Bale area have high potential for cabbage production. Improved cabbage cultivars are not yet adequately put under production and majority of the areas in the Bale zone are using unknown variety from unknown source; as a result, the production is resulted in low yield due to the lack of high yielding and disease/insect pest resistant variety/ies and scarcity of improved varieties and low access. Therefore, conducting evaluation of exotic head cabbage varieties is very important to solve these problems and increase income of the farmer.
Material and Methods
Description of the Study Area
The field experiment was conducted during 2021 and 2022 main cropping season at Sinana, Agarfa, and Gobba (Alloshe) locations of Bale zone. Sinana is located 463 Km southeast of Finfinne (Addis Ababa) and it has an altitude of 2400 m above sea level. It is located at 07007'N latitude and 40010'E longitude respectively. The periodic rainfall varies from 346 to 861 mm during the first rainy season (March to July) and 353 to 894 mm during the main season (August to December). The mean temperatures are 9.5 and 21°C (annual min and max respectively). Agarfa is situated at 7° 16' 12.32"N and 39° 49' 28.09"E latitude and longitude respectively and it has 362 km distance from Addis Ababa. Agarfa has Average minimum and maximum temperatures of 80C-230C and 86.34 millimetres average rainfall. Gobba is located about 446 km southeast of Addis Ababa; it has a latitude and longitude of 7°0'N 39°59'E respectively and an elevation of 2,743 meters above sea level. Gobba has average temperature of 8.60C-22.60C, and average rainfall of 1272mm per year. The majority of these woredas population livelihood relies on crop production and livestock production.
Treatments and Experimental Design
For the experiment RCBD with three replications were used. The spacing between plants and rows were 40cm x 50cm respectively, having plot size of 2.8m x 3m (Length and width respectively), each plot was consisted of six rows and seven plants per row. Cabbage varieties those were commercially available on the market Rossen, Royal, Monarch, Green and Delta was used in the study. A widely grown variety Bakker brother was included as check. Cabbage seedlings was raised on bed for one month and then transplanted. The trial was conducted during rainy season and all agronomic practices were applied to all varieties according to recommendations.
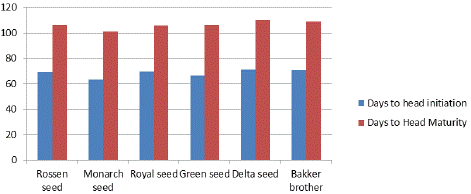
Figure 1: Response of cabbage varieties to days to head initiation and maturity.
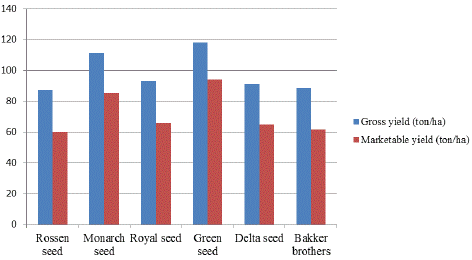
Figure 2: Response of exotic head cabbage varieties to Gross and marketable head yield.
Data Management
Data was collected for phenological parameters (Days to head initiation, head maturity), Growth parameters (Plant height, number of expanded leaves per plant), and yield and yield components (Height of head, Diameter of head, Fresh weight of untrimmed and trimmed head, Gross head yield and Marketable yield).
Statistical Data Analysis
All the measured parameters were subjected to analysis of variance (ANOVA) appropriate to factorial experiment in RCBD according to the General Linear Model (GLM) of Gen Stat 15thedition [GenStat, 2012], then the data was subjected to Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) using SAS 9.3 and the interpretations were made following the procedure described by Gomez and Gomez (1984). Least Significance Difference (LSD) test at 5% probability level was used for treatment mean comparison when the ANOVA showed significant differences (Statistical Analytical System, [2003].
Results and Discussions
Phenological and Growth Parameters of Head Cabbage
The Combined over location analysis from two consecutive years indicated that Days to 50 % head initiation, Days to 90 % maturity, diameter of head and height of head were high significantly [P<0.01] influenced by variety.
From the ANOVA analysis the result indicated that the highest number of days to head initiation [70.93] was recorded for Delta seed variety, while the minimum (63.13) was attained by Monarch seed variety [Table 1]. In terms of days to 90 % head maturity the longest days to head maturity [110] and [109] was recorded from Delta seed and Bakker brothers variety, while the shortest [105.5 and 106.1] was from royal seed and Green seed varieties respectively. In case of number of leaves per plant the highest record [16.53] was from Green seed variety followed by monarch seed variety [16.29], and the lowest [14.20, 14.23, 14.47 and 14.82] was from Bakker brother, Delta seed, Royal seed and Rossen seed varieties respectively. In case of plant height there was no significant difference [P<0.05] among varieties.
S. No
Varieties
DHI
DHM
PH
NL
1
Rossen Seed Variety
69.07ab
106.1b
33.27
14.82b
2
Monarch Seed Variety
63.13a
100.9a
31.79
16.29a
3
Royal Seed Variety
69.93ab
105.5b
33.25
14.47b
4
Green Seed Variety
66.40b
106.1b
32.53
16.53a
5
Delta Seed Variety
70.93c
110c
34.57
14.23b
6
Bakker Brothers Variety
70.40c
109c
33.31
14.20b
Mean
68.31
106.09
33.12
15.091
Lsd
2.719
2.34
NS
0.63
CV
4.4
7
5.7
Means within the same column followed by the same letter (s) are not significantly different at 5% level of significance; LSD: Least Significant Difference; NS: Not Significant; CV: Coefficient of Variation; DHI: Days to Head Initiation; DHM: Days to Maturity, NL: Number of Leaves; PH: Plant Height.
Table 1: Mean value of Days to head initiation and maturity, Plant height and number of leaves.
Yield and Yield Components of Head Cabbage
The combined over location and year ANOVA result also showed that different varieties of cabbage had significant [P<0.05] effect on Diameter of head, height of head, fresh weight of trimmed and untrimmed head [Table 2].
S. No
Varieties
HH
DH
FWUH (gm)
FWTH (gm)
GHY (ton/ha)
MY (ton/ha)
1
Rossen Seed Variety
20.72b
20.25a
2677c
2013c
87.44d
60.03d
2
Monarch Seed Variety
21.67a
21.38ab
3227b
2648b
111.21b
85.42b
3
Royal Seed Variety
20.26bc
18.81c
2700c
2066c
93.28c
65.96cd
4
Green Seed Variety
22.26a
22.08a
3512a
2880a
118.11a
94.15a
5
Delta Seed Variety
19.49c
18.95c
2653c
2093c
91.07cd
64.81c
6
Bakker Brothers Variety
20.19bc
19.63c
2749c
2230c
88.72cd
61.57cd
Mean
20.76
20.18
2920
2322
98.31
71.99
Lsd
0.929
1.571
156.8
224.2
5.01
4.88
CV
6.1
10.7
7.3
13.2
7
9.3
Means within the same column followed by the same letter (s) are not significantly different at 5% level of significance; LSD: Least Significant Difference; CV: Coefficient of Variation; HH: Height of Head; DH: Diameter of Head; FWUH: Fresh Weight of Untrimmed Head; FWTH: Fresh Weight of Trimmed Head; GHY: Gross Head Yield; MY: Marketable Yield
Table 2: Mean value of head height and diameter, trimmed and untrimmed head weight, Gross and Marketable yield.
The longest head height [22.26] was recorded by green seed variety followed by monarch variety [21.67], while the lowest [19.49] from Delta seed variety. Similarly, the largest diameter of head [22.08] was from green seed variety and the smallest [18.81] from royal seed variety. This result showed that genetic variation among the varieties can influence the growth characteristics of the crop that can have direct positive or negative influence on yield per hectare and its acceptance on the market [Table 2].
On the other hand, ANOVA result showed that these varieties of cabbage had high significantly affect [P<0.01] gross head yield and marketable head yield. The maximum gross head yield [118.11 t/ha] was recorded from the green seed variety and the next from monarch variety [111.21 t/ha] while the lowest [61.57 t/ha] gross head yield per hectare was recorded from Bakker bothers variety [Table 2].
Summary and Recommendation
Head Cabbage is increasingly becoming important vegetable produced for domestic markets. Farmers in the study area were practicing production of cabbage. However, they were not using well adapted and improved seed from known source. In the local market the seed of cabbage sold with small packed materials which have no direction for sowing which means unknown variety from unknown source. Due to these and other agronomic practices production and productivity per hectare was very low. In order to solve problems related to Lack of improved varieties and proper management practice’s introduction and adaptation of high yielding varieties with proper agronomic practices are very important. Therefore, this experiment was initiated with the objective to select varieties those are high yielding, resistant/tolerant to major diseases and insects. To minimize cabbage production constraints, we conduct this experiment using one widely cultivated variety with five improved exotic cabbage varieties at Agarfa, Sinana and Gobba locations of Bale zone, south eastern Ethiopia for two consecutive years by using Randomized complete block design with three replications having plot size of 2.8m x 3m for one experimental unit (plot).
From this study the combined analysis over locations and years indicated that almost all phenological, growth, yield and yield components of cabbage are significantly influenced due to varieties. The maximum gross head yield [118.11 ton/ha] was recorded from the variety green seed followed by Monarch seed variety [111.21 ton/ha], while the smallest number [88.72 ton/ha] was from Bakker brother’s variety. Similarly, the highest marketable yield [94.15 ton/ha] was green seed variety, the next also from monarch seed variety [85.42 ton/ha] and the minimum record [61.57 ton/ha] was from Bakker brother’s variety.
Generally, from this experiment we get the result that green seed and Monarch seed variety showed best performance in almost all tested agronomic parameters over the tested varieties. Therefore, as the Recommendation, Head cabbage growers at study area and similar agro ecologies should grow green seed and Monarch seed varieties for their short maturity period, good head height and diameter, and best marketable yield that distinguish them from other tested varieties.
Author Statements
Acknowledgement
We thank Oromia Agricultural Research Institute (OARI) for financing this experiment. We also thank the staff of Sinana Agricultural Research Center (SARC) for supplying all logistics during the conducting of the trial. We also acknowledge all Horticulture team of Sinana Agricultural Research Center for data collection and management of the trial.
References
- Adeniji OT, Swai I, Oluoch MO, Tanyongana R, Aloyce A. Evaluation of head yield and participatory selection of horticultural characters in cabbage (Brassica oleraceae var. capitata). Journal of Plant Breeding and Crop Science. 2010; 2: 243-250.
- Ahmed MH, Lemma Z, Endrias G. Technical efficiency of maize producing farmers in Arsi Negelle, Central Rift valley of Ethiopia: Stochastic frontier approach. Poljoprivreda i Sumarstvo. 2014; 60: 157.
- Aktas Z, Bakkalbasi E. Effect of Widely Used Thermal Processes on Surface Color, Total Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Activity of White Cabbage. Yuzuncu Yil University Journal of Agricultural Sciences. 2016; 26: 505-511.
- Alamerie K, Ketema M, Gelaw F. Risks in vegetables production from the perspective of smallholder farmers: The case of Kombolcha Woreda, Oromia region, Ethiopia. Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries. 2014; 3: 1-5.
- Bekele A, Kassa B, Legesse B, Lemma T. Effects of crop commercial orientation on productivity of smallholder farmers in drought-prone areas of the Central Rift Valley of Ethiopia. Ethiopian Journal of Agricultural Sciences. 2011; 21: 16-34.
- Daniel KAM, Muindi EMD, Muti SMD. Cabbage (Brassica oleracea) Production in Kenya: A Review of its Economic Importance, Ecological Requirement and Production Constraints. International Journal of Plant & Soil Science. 2023; 35: 245-254.
- Gary TL, Baptiste-Roberts K, Gregg EW, Williams DE, Beckles GL, Miller 3rd EJ, et al. Fruit, vegetable and fat intake in a population-based sample of African Americans. Journal of the National Medical Association. 2004; 96: 1599-1605.
- Hussain J, Rehman N, Al-Harrasi A, Ali L, Ullah R, Mabood F, et al. Nutritional prospects and mineral compositions of selected vegetables from Dhoda Sharif-Kohat. J Med Plants Res. 2011; 5: 6509-6514.
- Jaskani MJ, Khan IA. Horticulture: An Overview. University of Agriculture Faisalabad. 2021.
- Lundberg JO, Feelisch M, Björne H, Jansson EÅ, Weitzberg E. Cardioprotective effects of vegetables: is nitrate the answer?. Nitric Oxide. 2006; 15: 359-362.
- Mason AS, Nelson MN, Takahira J, Cowling WA, Alves GM, Chaudhuri A, et al. The fate of chromosomes and alleles in an allohexaploid Brassica population. Genetics. 2014; 197: 273-283.
- Monteiro A, Lunn T. Trends and perspectives of vegetable Brassica breeding world-wide. In WCHR-World Conference on Horticultural Research. 1998; 495: 273-280.
- Shah MM, Hassan A, Mahmood Q, Akbar K, Khan MS. Assessment of pesticide residues on selected vegetables of Pakistan. Journal of the Chemical Society of Pakistan. 2011; 33: 816.
- Thompson MD, Thompson HJ. Botanical diversity in vegetable and fruit intake: Potential health benefits. In Bioactive Foods in Promoting Health. Academic Press. 2010: 1-17.