
Special Issue: Pesticides
Ann Agric Crop Sci. 2024; 9(5): 1165.
Investigation on the Efficacy of Hydrophobic Nano Silica on German Cockroach (Blattela Germanica)
Mohammad Hassan Amini Esfanjani1; Basseri Hamid Reza1*; Baniardalan Mozhgan1; Abai Mohammad Reza1; Vatandoot Hassan1,2*
¹Department of Medical Entomology and Vector Control, School of Public Health, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
²Department of Environmental Chemical Pollutants and Pesticides, Institute for Environmental Research, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
*Corresponding author: Vatandoot Hassan, Department of Medical Entomology and Vector Control, School of Public Health, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, & Department of Environmental Chemical Pollutants and Pesticides, Institute for Environmental Research, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. Email: basserih@tums.ac.ir; hvatandoost1@yahoo.com; vatando@tums.ac.ir
Received: September 23, 2024 Accepted: October 11, 2024 Published: October 18, 2024
Abstract
Background: The German cockroach (Blattella Germanica (L)) is one of the synanthrope insects that is an important health pest, especially in kitchens, restaurants, and hospitals due to the use of human food scraps and the potential for mechanical transfer of pathogenic microorganisms. On the other hand, repeated reports of German cockroach resistance to insecticides indicate the high potential of this insect in relation to insecticides, so the control options of this pest have gradually decreased and the costs risk of controlling it due to increasing the dose of insecticides, also toxicity for the human is constantly enhancing. Therefore, finding new low-risk solutions with appropriate efficacy to control this insect seems necessary. According to recent successful studies, using the Nano silica insecticide effect in pest control of agricultural products
Methods: In this study, the effects of hydrophobic Nano silica powder on different instars of German cockroaches were investigated.
Results: The results showed high mortality of this insect, especially first and second instar nymphs in contact with hydrophobic Nano silica. Also, studies with the SEM (Scanning electron microscope) have shown that Nano silica particles adhere to the insect’s body in large numbers, and cause serious damages such as cuts and cracks in the cuticle of contacted cockroaches. Also, the tiny hair loss on the antennae was accompanied by hydrophobic Nano silica whereas the cockroaches that were killed by CO2 did not have these injuries.
Conclusion: Due to insecticide resistance of German cockroach, this novel approach for control of insect is appropriate
Keywords: German cockroach; insecticide; Hydrophilic Nano silica
Background
Isolation of a variety of human pathogenic microorganisms, including funguses, parasites, bacteria and viruses from German cockroaches indicates the importance of this insect in health [1-4]. On the other hand, this cockroach has been able to adapt to human living conditions [5] and Existence of suitable conditions in terms of temperature, humidity, food, water and shelter, especially in Hospital and homes kitchens, restaurants and food preparation places and hotels, and the reproductive ability of this insect causes its rapid spread in the mentioned places. On the other hand, pollutant potential of this insect and Unpleasant presence of this insect in front of customers, causes annoyance to business owners, and stimulates them to use insecticide toxins to quickly remove this pest, which itself causes other problems such as human environmental contamination and global population impact. Also, the continued use of insecticide toxins has led to the expression of resistant genes in this insect and the selectivity of resistant generations [6]. This is because the German cockroaches have a high resistance potential for insecticides, and numerous articles have reported the presence of several genes that cause resistance to the main groups of insecticides in this insect. Also, many articles from the 1950s have confirmed the insect's resistance to many of the insecticides used by the organo-phosphorus and organelle-chlorine groups, as well as carbamates and pyrethroids [4,7-13]. Also there have been reports of extremely high resistance to some insecticides [14,15]. These future reports show that controlling this insect with synthetic insecticides is risky and unjustifiable. Therefore, it would be desirable to find new ecofriendly materials and methods for controlling this cockroach. In this regard, researchers have tried to use nanotechnology to make pesticides that are both less environmentally ecofriendly and more efficient than other pesticides, in recent decades, researches have often been done to find nanomaterials that are used in insecticide polymers, or they themselves have pesticidal effects [16]. One of these materials is Nano silica, whose main ingredient of that is silica, which is an ecofriendly substance; surveillance organizations consider amorphous silica to be a harmless to humans. Nano silica has a variety of applications, and is used in industry, pharmaceuticals and medicine, so It is known to be effective in eliminating some agricultural pests [17]. In this study, we investigated the effects of Nano silica hydrophilic and hydrophobic on a German cockroach due to its biodegradability and lack environmental pollution as well as considering the findings of previous researches. These cockroaches were collected from various restaurants and student dormitories in Tehran, capital of Iran, and were raised in the insectarium of the Faculty of Health, University of Tehran. Then the male and female, and nymphs of the first and second instars of this insect were placed in direct contact with the hydrophilic and hydrophobic Nano silica powder. Also, mortality rate was assessed at specific times and the LC50 was determined for hydrophobic Nano silica. The later killed insects were examined to determine the type of damage caused by the SEM electron microscope.
Materials and Methods
Cockroaches’ Collection and Rearing
The cockroaches were collected during the night from the kitchens in dormitories of the Tehran University of Medical Sciences, as well as several specific restaurants in Tehran. In the insectarium, in the health Faculty of Tehran University Medical Sciences was maintained and bred in conditions with a temperature of 27°C ± 2°C and 45%±5% humidity with 12/12 h reversed light/dark cycle. The cockroaches were fed by bread and dates and rodent food. Also, a two-layer piece of cardboard about 50 cm square were putted as a place for nesting and shelter for nymphs and adults inside each buccal.
Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Nano Silica Contact Tests
Plastic petri dishes with a diameter of 15 cm were used to perform the contact tests with nanosilica. The floor area of the petri was calculated, and the amount of nanosilica powder was poured as follows in grams per square meter on the floor surface of the petri dishes. For example, the value of 1g / m2 in Petri dish with a diameter of 15cm was calculated as follows:
To prepare 1 g of Nano silica per square meter for the above plate, 0.0176 g of Nano silica is required, which was measured with a precise scale…. And poured into the petri dish. The powder was spread inside the Petrie’s by hand stirring.
The inside of the petri dishes as placed in two small containers for food and water with 1 cm diameter and about 0.5cm depth, and the anesthetized cockroaches were transferred to a petri. On the outside cap, the date, time and size of the Nanosilica, as well as its amount in grams per square meter, were written and pasted, then, separation of male and female cockroaches was based on the physical characteristics of the end of the abdomen. Ootheca free cockroaches were used to perform the tests on adult females. To test the nymphs, the females having reached maturity each was transferred to a separate container. The nymphs were used for testing after a maximum of one week of opening the ootheca.
The selected cockroaches were first anesthetized with a mild CO2 and transferred to petri dishes containing the calculated amount of Nano silica. For the 24-hour exposure tests, the cockroaches remained in the petri dish for 24 hours, and after 24 hours, their deaths were recorded. To perform the 30-minute exposure test, the cap of the petri dish was punctured with a needle and small holes were made in the cap of the petri dish. The cockroaches were anesthetized with CO2 and transferred to the petri dishes. After half an hour, the petri dishes were placed in a buccal, then by inserting CO2 into the buccal, and penetrating into the petri dishes after cockroaches were anesthetized, they were transferred in clean petri dishes with dates and times listed on them, and their deaths were recorded after 24 hours. And measurement of samples weight with precise scale and spreading of powder in the petries were done by hand stirring.
So, in this investigation, the cockroaches that fell backwards and were unable to return were evaluated dead.
Data Analysis
The mortality rate was recorded at specific times, and the data were analyzed by probit analysis and regression analysis then LC50 was determined for male, females and nymphs that Expose with hydrophobic Nano silica. The mortality rate in all tests with 20nm-30nm and 12nm-14nm size of hydrophilic Nano silica after 24 hours was less than 10%, and given that, the time of exposure in the field isn’t justifiable, and it isn’t covered in this article.
Photos with SEM (Scanning Electron Microscope)
A sample of each of the cockroaches killed by the hydrophobic nanosilica, and the same numbers killed by CO2 were taken at specified times and investigated, photographed under the SEM from the antennae, pronotum, and abdomen, then the same numbers killed by co2were investigated under SEM.
Results
Effect of Hydrophobic Nanosilica on Male German Cockroaches with 24 hours of Exposure
After initial testing, the different amounts of hydrophobic Nano silica powder were in contact with German male cockroaches for 24 hours.
In Table 1. The results showed a significant effect of this substance on the German cockroach. The LD50 and LD90 of hydrophobic Nano silica was 0,1029 g / m2 in 24 hours and 0.2163 g / m2 respectively.
a
b ± SE
LD50 (g/m2) ± 95% C.L.
LD90 (g/m2) ± 95% C.L.
Χ2 calculated
Χ2 table (df)
p-value
3.9237
3.9736 ± 0.535
0.088
0.1846
1.626
12.592 (6)
0.05
0.1029
0.2163
0.1167
0.2746
Table 1: Analysis parameters of adult male cockroach mortality regression data in the exposure of hydrophobic Nano silica powder with 24-hour contact time.
The Effect of Hydrophobic Nano Silica on Female German Cockroaches with 24 hours of Exposure
After 24 hours of contact with hydrophobic Nano silica, the LD50 was 0.1344 g / m2 and a separate dose was 0.2362g / m2. This is the same as the male dose.
The Effect of Hydrophobic Nano Silica on 1st and 2nd Instars Nymph of German Cockroaches with 24-hour Exposure
All nymphs were dead after 24 hours exposure with 0.05 g/m2 of hydrophobic Nano silica. Figure 1 shows the regression line of both sexes of German cockroach exposed to Nano silica
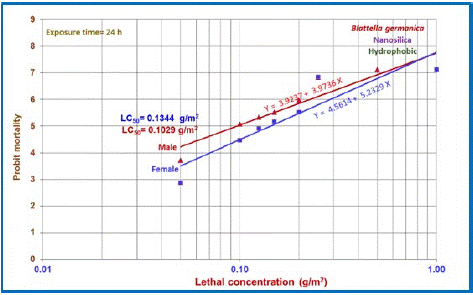
Figure 1: Line regression and equilibrium ratios of the males and female’s German cockroaches’ mortality in the exposure of different concentrations of hydrophobic Nano silica with 24-hour contact time.
The Effect of Hydrophobic Nano Silica on Male German Cockroaches with 30-minute Exposure after 24 hours
Due to the considerable mortality of cockroaches with 24-hour contact of Nano silica, its effect was evaluated in 30 minutes. The findings showed that the LD50 was 0.1469 g / m2 for this period of contact after 24 hours also LD90 gained 0.2528 g / m2 during this period.
The Effect of Hydrophobic Nano silica on a Female German Cockroach with 30 minutes after 24 hours
Lethal concentration was estimated about 50 percent for female cockroaches which in 30 minutes exposure equaled to 126 mg/m2, and during this time, 93.3 ratio of this mortality of cockroaches were recorded about 250 mg / m2 from hydrophobic nanosilica, and finally LD90 was calculated to be 0. 2760 g / m2 (Table 4 and Figure 2).
a
b ± SE
LD50 (g/m2) ± 95% C.L.
LD90 (g/m2) ± 95% C.L.
Χ2 calculated
Χ2 table (df)
p-value
4.5614
5.2329 ± 0.739
0.1207
0.2054
3.349
11.070 (5)
0.05
0.1344
0.2362
0.1481
0.2952
Table 2: Analysis parameters of adult female cockroach mortality regression data in the exposure of hydrophobic Nano silica powder with 24-hour contact time.
a
b ± SE
LC50 (g/m2) ± 95% C.L.
LC90 (g/m2) ± 95% C.L.
Χ2 calculated
Χ2 table (df)
p-value
4.527
0.4344 ± 0.785
0.1331
0.219
2.543
11.070 (5)
0.05
0.1469
0.2528
0.1617
0.3201
Table 3: Analysis parameters of male cockroach mortality regression data in exposure of hydrophobic Nano silica powder with 30-minute contact after 24 hours.
a
b ± SE
LD50 (g/m2) ± 95% C.L.
LD90 (g/m2) ± 95% C.L.
Χ2 calculated
Χ2 table (df)
p-value
3.8987
4.6805 ± 0.629
0.1316
0.2358
0.984
12.596 (6)
0.05
0.1469
0.276
0.1634
0.3536
Table 4: Analysis parameters of female cockroach mortality regression data in the exposure of hydrophobic Nano silica powder with 30-minute exposure after 24 hours.
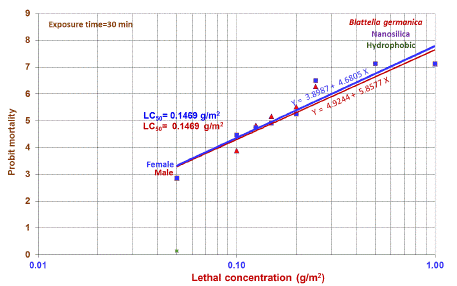
Figure 2: Lines regression and equilibrium ratios of the males and female’s German cockroaches’ mortality with 30-minute exposure of hydrophobic Nano silica after 24-hour contact time.
The Effect of Hydrophobic Nano Silica on Nymph 1-2 Instar of German Cockroaches with 30 minutes of Contact after 24 hours
The least dose used in this experiment, 50 mg / m2, was administered for 30 minutes and after 24 hours of exposure with hydrophobic Nano silica, 100% of nymph’s instar 1 - 2 were killed. Various parts of the German cockroaches killed by the hydrophobic Nano silica and killed by CO2 were scanned with a scanning electron microscope with different magnifications are shown in Figures 4-10.
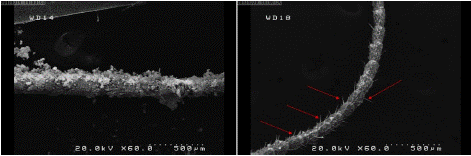
Figure 3: SEM photo of a Part of antenna in a German cockroach killed with hydrophobic (left) Nano silica compared with a
German cockroach killed with CO2 (right) with 60x magnification and 500μm Resolution. (Tiny hairs on the antenna are shown with an arrow).
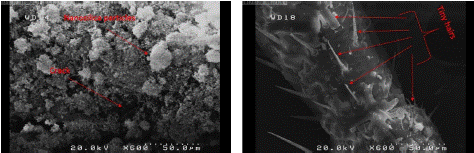
Figure 4: SEM photo of a German cockroach’s antenna killed with hydrophobic (left) Nano silica compared with an antenna of German cockroach killed with CO2 (right) with 600x magnification and 50μm Resolution. (Tiny hairs on the antenna are shown with an arrow).
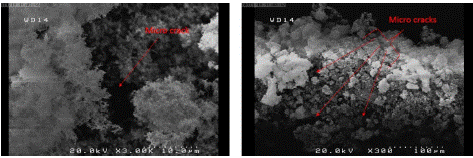
Figure 5: SEM photo of a German cockroach’s antenna killed with hydrophobic (left) with 30.0kx magnification and 10μm resolution and 300x magnification and 100μm resolution.

Figure 6: SEM photo of German cockroach’s Abdomen killed with hydrophobic Nano silica (left) compared with a German cockroach killed with CO2 (right) with 60x magnification and 500μm Resolution.
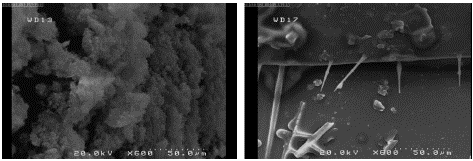
Figure 7: SEM photo of German cockroach’s Abdomen killed with hydrophobic Nan silica (left) compare with a German cockroach killed with CO2 (right) with 600x magnification and 50μm Resolution.
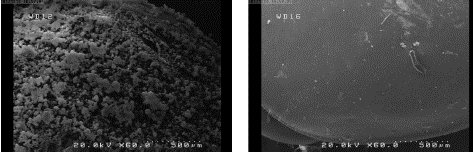
Figure 8: SEM photo of German cockroach’s pronotum killed with hydrophobic Nano silica (left versus with a German cockroach killed with CO2 (right) with 60x magnification and 500μm Resolution.
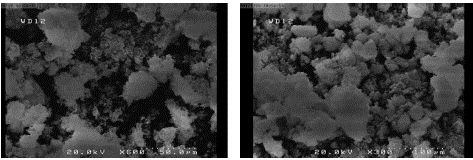
Figure 9: SEM photo of German cockroach’s pronotum killed with hydrophobic Nano silica with 600x magnification (left) and 300x right.
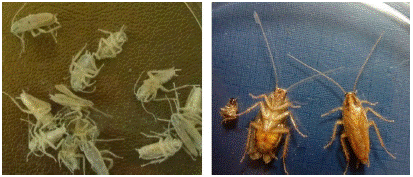
Figure 10: Photos of German cockroaches killed with a hydrophobic Nano silica without any magnification (left) and killed with CO2 (Right).
It is clear that the tiny hairs shed in the antenna of cockroach killed by the Nano silica, while in the cockroach killed by carbon dioxide these hairs are also present.
(Figure 6)
The surface of Abdomen is covered with Nano silica particles and the cracks are visible.
(Figure 7)
Discussion
Application of diatomaceous earth powder, which contains a significant amount of silica compounds, has long been studied for pests’ control [18], and studies have shown that there is a significantly positive correlation between the effect of diatomaceous earth powder and its silica on pests’ mortality [18]. Other studies have shown that Nano silica particles against the rice weevil Sitophilus oryzae, is more effective than bulk silica [19], also the higher the lethality- On silica nanoparticles found that the insecticide effect of nanoparticles of this material, with dimensions of 15-30 nm, is significantly higher than particles with sizes of 400-100 nm. Therefore, we used two different size of hydrophilic Nano silica with different sizes. 24 hours after exposure, the mortality rate was very low. After 14 days, direct exposure, although the mortality rate with Nano silica (12-14nm), was slightly higher than Nano silica (20-30 nm). However, due to the low mortality rate, its practical use in the field is inefficient. Another issue that was observed during the experiment was the behavior of avoiding contact with Nano silica powder. During the experiment, it was determined that the cockroaches were trying to place themselves in areas of the dish that are free of Nano silica, such as under or inside of water or food Container and keep themselves away from contacting with Nano silica. For that water and food were placed in the container for only 12 hours every 24 hours. It seems the activity of the cockroaches in the containers having Nano silica less than activity of the cockroaches in the control plates, which requires further investigation and in the case of the German cockroach contact test with hydrophobic Nano silica, the nanoparticles were rapidly absorbed by the insect's body surface, and when increased the cockroach's activity and movements, the greater the amount of material covered the insect's body, which could be realized with the naked eye. This also was examined under a stereo microscope and it was qualitatively observed that cockroaches exposed to hydrophobic Nano silica for a longer period of time or had higher doses were more covered with Nano silica than cockroaches having less contact time or exposing to lower doses. Rapid absorption of hydrophobic Nano silica on the surface of cockroaches’ body may be the main reason why hydrophobic Nano silica particles were more efficient than hydrophilic Nano silica. Electrostatic effects may also be involved between hydrophobic Nano silica particles and cockroaches' cuticles and plastic petri dish in terms of amount of Nano silica adsorption to the cockroaches' cuticle and their small body hairs. In a pilot test done in a glass petri dish, although the hydrophobic Nano silica had a significant mortality but the percentage of mortality was slightly lower than that of a plastic petri dish. This also needs further investigation. SEM photographs of cockroaches killed by hydrophobic Nano silica showed physical lesions, including micro cracking in the cuticle and the loss and fall of tiny hairs on the body, especially on the antennas. Owing to hydrophobic surface modification of hydrophobic Nano silica, its surface functional group can adsorb to the hydrophobic surface of Cuticle, as a result, nanoparticles can diffuse into Cuticle leading to rupture of the cuticle in cockroach’s body. High damages especially micro-hairs fall on antennae were observed in cockroaches with lower dose of Nano silica and after 14 days, they survived that probably has been done due to approaching, and contacting of antennae with Nano silica material for this investigation. Because the antennas and micro-hairs on antennas play an important role as chemical receptors in the insects’ food and mating searching behavior, the shedding of these micro-hairs can cause major disruption in their other behaviors, which need more investigation. Another notable point was the high mortality rate in the first and second instar of nymphs compared to adults, which is probably due to the more vulnerable cuticles of nymphs to adults or the greater susceptibility of nymphs to dehydration caused by physical cuticle damages, however, other unknown causes may be involve. Another point to note is that although the presence of physical damages in cockroaches that had killed by Nano silica has been investigated and confirmed by SEM, but it wasn’t done further investigation into possible lethal chemical damage that may occur between hydrophobic nanoparticles and lipids or epicuticle's fatty acids or the entry of Nano silica particles into the respiratory system of the insect or other possible injuries that can be considered in other experiments.
Conclusion
There are several reports on insecticide resistance in German cockroach. Replacement of novel approach will provide a solution for pest control.
Author Statements
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
This research is approved by the ethical committee of Tehran University of Medical Sciences,
Consent for publication: Publisher has the permission of the Author to publish the work.
Availability of Data and Material
It can be available by readers.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of Interest.
Funding
Tehran University of Medical Sciences under code number 97-01-27-32370.
Author’s Contributions
All the authors are involved for doing the research.
Acknowledgments
This research is financially supported by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
References
- Hamu H, Debalke S, Zemene E, Birlie B, Mekonnen Z, Yewhalaw D. Isolation of intestinal parasites of public health importance from cockroaches (Blattella germanica) in Jimma Town, Southwestern Ethiopia. J Parasitol Res. 2014; 2014: 186240.
- Fardisi M, Gondhalekar AD, Ashbrook AR, Scharf ME. Rapid evolutionary responses to insecticide resistance management interventions by the German cockroach (Blattella germanica L.). Sci Reports. 2019; 9: 8292.
- Rust MK, Owens JM, Reierson DA. Understanding and controlling the German cockroach: Oxford University Press on Demand; 1995.
- Wu X, Appel AG. Insecticide resistance of several field-collected German cockroach (Dictyoptera: Blattellidae) strains. J Eco Entomol. 2017; 110: 1203-9.
- Chung CY, Chang CC, Lee HJ. Adaptation of the cockroach Blattella germanica to human habitats: circadian and noncircadian factors. Physiol Entomol. 2016; 41: 307-12.
- Cochran DG. Monitoring for insecticide resistance in field-collected strains of the German cockroach (Dictyoptera: Blattellidae). J Econ Entomol. 1989; 82: 336-41.
- Keller J, Clark P, Lofgren C. Susceptibility of insecticide-resistant cockroaches to Pyrethrins. Pest Control. 1956; 24: 8292.
- Grayson JM. Recent developments in the control of some arthropods of public health and veterinary importance: Cockroaches. Bulletin of the ESA. 1966; 12: 333-8.
- Barson G, McCheyne N. Resistance of the German cockroach (Blattella germanica) to bendiocarb. Ann Appl Biol. 1987; 90: 147-53.
- Milio J, Koehler P, Patterson R. Evaluation of three methods for detecting chlorpyrifos resistance in German cockroach (Orthoptera: Blattellidae) populations. J Econ Entomol. 1978; 80: 44-6.
- Lee C, Yap H, Chong N, Lee R. Insecticide resistance and synergism in field collected German cockroaches (Dictyoptera: Blattellidae) in Peninsular Malaysia. Bull Entomol Res. 1966; 86: 675-82.
- Kristensen M, Hansen KK, Jensen K-mV. Cross-resistance between dieldrin and fipronil in German cockroach (Dictyoptera: Blattellidae). J Econ Entomol. 2005; 98: 1305-10.
- Zhu F, Lavine L, O’Neal S, Lavine M, Foss C, Walsh D. Insecticide resistance and management strategies in urban ecosystems. Insects. 2016; 7: 2.
- Rahayu R, Ahmad I, Ratna ES, Tan MI, Hariani N. Present status of carbamate, pyrethroid and phenylpyrazole insecticide resistance to German cockroach, Blattella germanica (Dictyoptera: Blattellidae) in Indonesia. J Entomol. 2012; 9: 361-7.
- Cochran DG. Effects of three synergists on pyrethroid resistance in the German cockroach (Dictyoptera: Blattellidae). J Econ Entomol.1994; 87: 879-84.
- Kah M, Hofmann T. Nanopesticide research: current trends and future priorities. Environ Inter. 2014; 63: 224-35.
- Barik T, Sahu B, Swain V. Nanosilica—from medicine to pest control. Parasitol Res. 2008; 103: 253.
- Shah MA, Khan AA. Use of diatomaceous earth for the management of stored-product pests. Inter J Pest Manag. 2014; 60: 100-13.
- Hayles J, Johnson L, Worthley C, Losic D. Nanopesticides: a review of current research and perspectives. New pesticides and soil sensors: Elsevier. 2017; 193-225.