
Research Article
Austin J Allergy. 2023; 9(1): 1044.
Analysis of Palynological Parameters of Selected Species of Family Lamiaceae explored from District Bhimber, Azad Kashmir Pakistan
Tanveer H*; Maryam N
Department of Botany, Mirpur University of Science and Technology (MUST), Mirpur-10250 (AJK), Pakistan
*Correspoing author: Tanveer H Department of Botany, Mirpur University of Science and Technology (MUST), Mirpur-10250 (AJK), Pakistan. Email: tanveer.botany@must.edu.pk
Received: November 06, 2023 Accepted: December 20, 2023 Published: December 27, 2023
Abstract
Purpose: Recent research work elaborated palynological study of some selected species of family Lamiaceae which was conducted in District Bhimber, Azad Kashmir.
Methods: The selected 6 species of family Lamiaceae were collected from District Bhimber. The flowers were plucked from the plants. The anthers were spaced apart and kept in a glass tube having acetic acid. The anthers were poisoned with the glass rod to set a homogeneous mixture and then purified it. Then slides were prepared and purified and add 1% safranin to stain the slides and study these slides under light microscope, and then add some drops of mixture on slides, which were covered with cover slip.
Results: Then observations were done under light microscope with both quantitative and qualitative characters. In qualitative characters pollen shape, number of Colpi, sculpturing types were examined. After qualitative analysis, quantitative analysis was applied for the measurement of Colpus length, polar and equatorial axis, polar to equatorial ratio. The study represented that the shape of pollen grains were prolate, spheroidal and sub-spheroidal which expressed no prominent change in pollen shapes of six studied taxa. The qualitative study indicated that pollens can be divided widely into two groups depended on the number of colpi, (1) hexa-zonocolpate and (2) tri-zonocolpate. The greatest size of pollen 38.73 was reported in Ocimum basilicum and the shortest 20.41 in Mentha longifolia. These change in size was occasionally is due to the eco-physiological changes in these habitats. It was also observed that the members of family Lamiaceae bireticulate perforate exine pollen surface. The microscopic micrographs of pollen showed diverse changes between the members of Lamiaceae family but some features were remained constant as tri-zonocalpate and reticulate exine. The quantitative characters of pollens were documented and indicated that highest colpus length was measured against Ocimum basilicum (38.73μm) while lowest was explored against Leucas aspera (13.33μm). Mentha longifolia and Ocimum basilicum indicated maximum number (6) of Colpi as compared to other four observed species. The polar axis measurement was also indicated highest (56.63 μm) by Ocimum basilicum and Leucas aspera expressed lowest (17.15μm). The equatorial axis value was maximum (55.81μm) shown by Ocimum basilicum plant while minimum equatorial axis value (11.66μm) was measured against Leucas cephalotes. It was observed that the fertility rate was maximum (63%) shown by Leucas aspera while maximum (42%) sterility rate shown by Mentha arvensis.
Conclusion: It was concluded that These findings were expressed a lot of variation in all characters of plant species. It means that the paleontological study depicted lot of diversity among plants species as indicated Ocimum basilicum Leucas aspera indicated minimum diversity among observed characters. This study will help us to explore taxonomic characters of family Lamiaceae.
Keywords: Palynological study; Family Lamiaceae; Quantitative characters; Qualitative characters
Introduction
The Lamiaceae family is by far the most prevalent family in practically all global habitats. The Lamiaceae family is the biggest of the Angiosperm families. The family has roughly 236 genera and 7,000 species spread over the globe. Family is incredibly important economically [1].
Asia's primary hub for salvia variety is Anatolia. 95 Salvia species can be found in Turkey, and 49 (52%) of them are indigenous [2]. The vast Lamiaceae (formerly Labiatae) family is widespread, with particularly rich variety in California, Mexico, and the Mediterranean area. Although many are drought-adapted, the plants may be found in a wide range of settings. As a triplet of characters with vegetative traits, this family is one of the few that can typically be identified. The fresh growth (not the old growth) of mints has square stems, and like many other families, mints have opposing leaves. The aromatic leaves of mints, which are also present in numerous other families, are what distinguish them from other plants [3].
In all aspects, the family Lamiaceae is very significant. The most significant plant families, it contains a huge number of plants with biological, pharmacological, and therapeutic purposes, as well as others that are utilised as a source of food. Basil, thyme, sage, mint, lemon balm, and other members of this family have a variety of functions as food, fodder, medications, and other pharmaceuticals, among others [4].
Numerous members of aromatic plants of the Lamiaceae family were helpful in medicine, the drug industry, and the food industry due to their biological characteristics. They can improve the central nervous system, stimulate blood flow and digestion, and act as an antispasmodic, antiseptic, diuretic and tonic. Oregano, rosemary, thyme, and sage are the most widely used members of this family of herbs [5].
The existence of several plants with a variety of various applications in District Bhimber is the basis for the choice of the Lamiaceae family. In Pakistan's flora, the Lamiaceae family was classified as one of the oldest and biggest. The identification and categorization of plants depend heavily on pollen morphology. To adjust the species in the proper taxonomic rank, researchers have employed these pollen morphological characteristics to identify flora [6].
Pollen grains, spores, and tiny planktonic creatures are all studied in the field of palynology. In systematic family studies at higher taxonomic levels, general palynological data is highly helpful. Pollen grains may be used to identify species because they contain distinctive biological properties that represent high genetic protection [7].
Systematic investigations employ pollen morphology, which is thought to reveal evolutionary connections [8]. The field of study known as taxonomy is concerned with the investigation, identifying, describing, and classifying of all creatures. It is an intricate and distinct field that is always founded on reliable scientific theory [9].
The morphology and palynological features of the family Lamiaceae have been the subject of much investigation [10]. In any case, several researchers have worked on pollen morphology, although there are still some flaws and unexplored taxa. The family Lamiaceae morphology and palynological study is particularly beneficial for description, identification, and upcoming research [11].
It was suggested that the pollen characteristics were helpful in differentiating certain areas and plants in their investigation on Stachys species. Marrubium is a genus found in Turkey where pollen morphological characteristics have taxonomic importance. Pollen from Ocimum species has bireticulate perforated tectum sculpture, which raises the possibility that their classification has to be reconsidered. The Ocimum species specialized in pollen Colpi examined several forms ranging from acolpate to octacolpate pollens that demonstrate there were considerable variances between the plants. The pollen sculpture from the Lallemantia species blooming in Turkey had taxonomic significance [12].
The exine ornamentation of Ajuga species, which is either granulate or reticulate, may be helpful in classifying the species within the genus. Since a long time in the systematic and evolution, pollen features were retained and usually employed in solving systematic difficulties at the family, genus, species, and variety level. Aperture characteristics of pollen and consistent exine ornamentation were determined to be relevant for the parent genus or species. This research provides a detailed microscopic and taxonomic analysis of earlier works on the Lamiaceae family from Pakistan [13].
The study was mainly focused on the following objectives as; i. To elaborate morphological characters of six selected species of family Lamiaceae with special reference to palynological assessment, ii. To documented the qualitative and quantitative elaboration of different characters of pollens family Lamiaceae and iii. To measure fertility and sterility rate of flowers of the selected species of the family.
Material and Methods
General analysis and field trips were carried out in different areas of District Bhimber Azad Kashmir to collect the selected species of the flora from different regions. The entire compositions of plants along with families were organized.
Collection, Investigation and Preservation
The plants were collected, dried, preserved and mounted on standard Herbarium sheets. Estimation of the life forms spectra, leaf size spectra and phonological forms were prepared and reported. After complete analysis, the specimens were submitted in the Herbarium of Mirpur University of Science and Technology, Bhimber Campus. The pollen grains of the selected species of family Lamiaceae were taken from District Bhimber Azad Kashmir. However, the pollens representing the family were extracted from fresh flowers of plant specimens gathered from different areas during spring.
For Light Microscopy (LM) examination, pollen grains were prepared by using method of Erdtman [14]. Pollen descriptions were depending on characters recognized at ×1000 magnifications and photographs of pollen grains were taken with an Olympus BX21 light microscope while pollen slides were prepared and kept save for further study. For LM, pollen grains were mounted on slides in glycerin jelly.
First of all, collected plant material such as 6 plants samples were gathered from many areas of District Bhimber, Azad Kashmir, Pakistan. The species of plants which were collected futher investigated and categorized with the help of taxonomists and practitioners and also correlated their morphological and palynological characters with the herbarium specimen of Mirpur University Herbarium (MUH), Department of Botany, (MUST), Bhimber Campus. The collected data that correlated and documented with their assessed habitat, environment, flowering time and the color of flowers. After correct investigation and description of the plants were protected and preserved.
Pollen Grains Observation by Light Microscope
The pollen slides were prepared from flowers of some plant species collected during field trips. The anthers were placed apart and kept in a tube having a solution of acetic acid and sodium chlorate (NaCIO3) in ratios of 1:2. The anthers were poisoned with the glass rod and then purified it. Slides were prepared and purified with glycerol jelly mixed with 1% safranin to stain the slides and study these slides under a light microscope, then a some drops of the mixture were placed on the slides, which were put down on a small section of simple fuchsin-stained jelly.
Then must be accurately put coverslip over it so that no air bubbles were come out. The glass cover was tightly attached to corners for long period for storage of the glass [15]. Pollen grains were calculated, evaluated, and micro-graphed under a Light Microscope at different resolutions of Leica Dialux 20. On the basis of five readings of grains, some morphological characters were calculated by using this process [16].
To calculate the average, different readings of pollen grains were taken for different (polar and equatorial) lengths, diameter of exine, thickness of colpi, and range of aperture. The appearance of pollen were depends on the ratio of the polar to equatorial area. The appearance and diameter of pollen grain will be calculated by using the terminologies [17].
Measurement of Fertility and Sterility
The percentage of fertility and sterility of pollen grains calculated by following formulas [18].
Fertility = Fertility/Fertility + Sterility × (100)
Sterility = Sterility/Sterility + Fertility × (100)
Statistical Analysis
To measurement values for example size and thickness of exine wall were checked with the help of SPSS software. These methods were also used to check the statistical analysis of pollen grains [16]. Measurable data were observed statistically (mean±standard error) for their further accurate validation.
Results
The different palynological qualities (Quantitative and Qualitative) of the research area were recorded. Structural changes of pollen grains were explained for size and shape of pollens, and the number of colpi, colpus length, polar and equatorial axis, polar to equatorial ratio and sterilty and fertility percentages were also examined.
The study based on shape, number of colpi, size, polar axis and equatorial axis and colpus length of pollen grains of 6 species. The study represents that the shape of pollen grains were prolate, spheroidal and sub-spheroidal which expressed no prominant change in pollen shapes of studied taxa. The study represents that these pollens can be divided widely into two groups depended on the number of colpi, viz; (1) hexa-zonocolpate and (2) tri-zonocolpate group. The pollen grain displays major changes in size between species. The greatest size of pollen 38.73 was reported in Ocimum basilicum and the shortest 20.41 in Mentha longifolia. These change in size was occasionally is due to the eco-physiological changes in these habitats. Despite the size of pollen grains were lightly different in Ocimum basilicum and Mentha longifolia species from the present research. This represented the size and change applicable in genus level. In different species of family Lamiaceae the pollen surface with bireticulate perforate exine was observed (Table 1).
S. No.
Species Name
Shape
No. of Colpi
Sculpturing type
1
Mentha longifolia L.
Spheroidal
6
Reticulate-perforate
2
Mentha arvensis L.
Oblate spheroidal
3
Bireticulate
3
Leucas aspera (Wild.)
Oblate spheroidal
3
Bireticulate
4
Leucas cephalotes (Roth)
Oblate spheroidal
3
Bireticulate
5
Coleus scutellarioides Loureiro.
Spheroidal
3
Reticulate-perforate
6
Ocimum basilicum L.
Spheroidal
6
Mega-reticulate
Table 1: Observation of qualitative characters of selected species of family Lamiaceae.
The pollen features determined between the specific lamiaceae family studied were explained. Examined Light microscopic micrographs of pollen were displayed. Most traits represent considerable changes between the lamiaceae family but some features, that was tri-zonocalpateand reticulate exine were showed constant. The pollen grains in all selected species were monad, isopolar, symmetrical, zonohexacolpate, prolate, tri-zonocalpate. The shapes of the pollens were represented as oblate spheroidal. The colpus orientation and mesocolpium were almost the same. Colpus broad and represented as verrucate to scabrate, the colpus tip was obtuse and the margins of colpus were irregular as indicated in Table 1.
The quantitative characters of pollens were documented with morphometric observation mentioned in Table 2. It was indicated that highest colpus length was measured against Ocimum basilicum (38.73μm) while minimum colpus length was measured against plant Leucas aspera (13.33μm). Mentha longifolia and Ocimum basilicum indicated maximum number (6) of Colpi as compared to other four observed plants (3). The polar axis measurement was also highest (56.63μm) Ocimum basilicum and Leucas aspera expressed lowest (17.15μm) polar axis value. The equatorial axis value was maximum (55.81μm) shown by Ocimum basilicum plant while minimum equatorial axis value (11.66μm) was measured against Leucas cephalotes.
S. No
Name of species
Colpus length (Ám)
Colpi
Polar axis (P) (Ám)
Equatorial axis (E) (Ám)
P/E Ratio
1
Mentha longifolia
20.41
6
28.74
28.32
1.01
2
Mentha arvensis
24.51
3
30.01
31.08
0.97
3
Leucas aspera
13.33
3
17.15
18.74
1.02
4
Leucas cephalotes
14.58
3
18.32
11.66
0.97
5
Coleus scutellarioides
15.82
3
22.91
21.24
1.07
6
Ocimum basilicum
38.73
6
56.63
55.81
1.01
Table 2: Quantitative characters of pollen morphological data of six plant of family Lamiaceae.
Measurement of number of fertile and sterile pollens of family Lamiaceae were mentioned in Table 3. It was observed that the fertility rate was maximum (63%) shown by Leucas aspera. While the lowest (57%) fertility rate was measured against Mentha arvensis. It was evaluated the sterility rate against six selected plants and indicated that maximum (42%) sterility rate by Mentha arvensis. The Leucas cephalotes indicated lowest (29%) sterility rate. These findings were expressed a lot of variation in all characters of plant species. It means that the paleontological study depicted lot of diversity among plants species.
S. No.
Name of Plant Species
Fertility (%)
Sterility (%)
No of Fertile pollens
No of Sterile pollens
1
Mentha longifolia
60
40
44
29
2
Mentha arvensis
58
42
45
32
3
Leucas aspera
63
37
48
26
4
Leucas cephalotes
71
29
53
22
5
Coleus scutellarioides
60
40
52
35
6
Ocimum basilicum
59
41
34
24
Table 3: Measurement of number of fertile and sterile pollens of family Lamiaceae.
The microscopic slides view of pollens characters of six plants; Mentha longifolia, Mentha arvencis, Ocimum basilicum, Leucas aspera, Coleus scutellariodes and Leucas cephalotes were indicated in Figure 3.
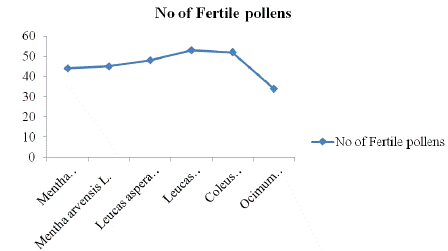
Figure 1: No. of fertile pollens of family Lamiaceae.
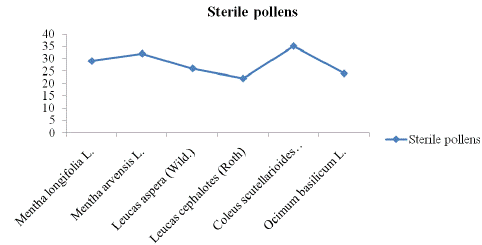
Figure 2: No. of sterile pollens of family Lamiaceae.
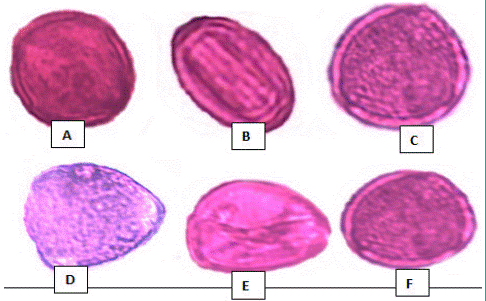
Figure 3: Microscopic slides view of pollen morphology of; A) Mentha longifolia; B) Mentha arvencis; C) Ocimum basilicum; D) Leucas aspera; E) Coleus scutellariodes; F) Leucas cephalotes.
Discussion
Palynology is one of the important taxonomic tools that were helpful in taxonomic problems for different families such as Lamiaceae. Furthermore, palynological tools has been represented a large range of changes and has a taxonomic importance of species identification of family Lamiaceae [19].
Pollen characters give a potential source of taxonomic traits because it represents very minute infraspecific changes. The different species represents considerable differences in pattern of sculpturing. The pollen study determined of family Lamiaceae examined by the light microscope, was found beneficial and helpful to assess phylogenetic relationships in the family Lamiaceae. Most of the species of family Lamiaceae have trizonocolpate pollen with different Colpus surface orientation, reticulate to micro-reticulate and bireticulate exine ornamentation [20].
The ecological studies revealed the detailed account of leaf size spectra and life forms of 25 species belonging to 13 families. The study is to provide information on life forms and leaf size spectra of different species including herbs, shrubs and trees. The change is due to anthropogenic pressure like grazing, trampling, invasive species, which are highly affecting the vegetation of the studied area. The overall vegetation in present studied was dominated life form by Therophytes followed by Megaphanerophytes, Nanophanerophytes and Hemicryptophytes. The dominated leaf size spectra were Nanophyll followed by Microphyll, Mesophyll and Leptophyll [21].
This study suggested extensive pollen characters of some selected species of family Lamiaceae examined under Light Microscope. In this study the pollen traits were organize specific for every studied level and has an important source in the classification and discrimination of the species. But, the species of family Lamiaceae carry little bit similarities in palynological features with more changes in pollen lamina, Colpus length make them different. Pollen characters were actually dependent taxonomic means and presenting distinct variability in genus and species levels. Further studies like genetic and phylogenetic analyses were suggested to accept and confirm the systematic of family Lamiaceae.
Conclusion
It was concluded that the qualitative study explored the shape of pollen grains which were prolate, spheroidal and sub-spheroidal as it expressed no prominent change in pollen shapes of six studied taxa. The greatest size of pollen 38.73 was reported in Ocimum basilicum and the shortest 20.41 in Men tha longifolia. It was finally concluded that a lot of variations in characters were observed in all characters of six plant species. It means that the paleontological study depicted lot of diversity among plants species as indicated Ocimum basilicum to Leucas aspera among observed characters. This study will help us to explore distinctive taxonomic characters of family Lamiaceae.
Author Statements
Acknowledgment
We would like to thank mentor for their unconditional support in our research experimental trials. We also acknowledge to co-supervisor for their kind help in experimental design and findings.
References
- Michel J, Abd Rani NZ, Husain K. A review on the potential use of medicinal plants from Asteraceae and Lamiaceae plant family in cardiovascular diseases. Front Pharmacol. 2020; 11: 852.
- Kahraman A, Dogan M, Celep F, Akaydin G, Koyuncu M. Morphology, anatomy, palynology and nutlet micromorphology of the rediscovered Turkish endemic Salvia ballsiana (Lamiaceae) and their taxonomic implications. Nord J Bot. 2010; 28: 91-9.
- Silva H. A descriptive overview of the medical uses given to Mentha aromatic herbs throughout history. Biology. 2020; 9: 484.
- Mahmood A, Mahmood A, Shaheen H, Qureshi RA, Sangi Y, Gilani SA. Ethno medicinal survey of plants from district Bhimber Azad Jammu and Kashmir, Pakistan. J Med Plants Res. 2011; 5: 2348-60.
- Arslan I, Celik A. Chemical composition and antistaphylococcal activity of an endemic Salvia chrysophyllaStapf naturally distributed Denizli Province (Turkey) and its vicinity. Pak J Bot. 2008; 40: 1799-804.
- Bano A, Ahmad M, Zafar M, Sultana S, Rashid S, Khan MA. Ethnomedicinal knowledge of the most commonly used plants from Deosai Plateau, Western Himalayas, Gilgit Baltistan, Pakistan. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014; 155: 1046-52.
- Song JH, Oak MK, Roh HS, Hong SP. Morphology of pollen and orbicules in the tribe Spiraeeae (Rosaceae) and its systematic implications. Grana. 2017; 56: 351-67.
- de Almeida VP, Raman V, Raeski PA, Urban AM, Swiech JN, Miguel MD et al. Anatomy, micromorphology, histochemistry of leaves and stems of Cantinoa althaeifolia (Lamiaceae). Microsc Res Tech. 2020; 83: 551-7.
- Rouhan G, Gaudeul M. Plant taxonomy: A historical perspective, current challenges, and perspectives. Molecular plant taxonomy. Methods Protoc. 2014: 1-37.
- Doaigey AR, El-Zaidy M, Alfarhan A, Milagy AES, Jacob T. Pollen morphology of certain species of the family Lamiaceae in Saudi Arabia. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2018; 25: 354-60.
- Ahlam AAW, Abdullah RD, Mohamed EZ. Pollen morphology of six species of subfamily Stachyoideae (Lamiaceae) in Saudi Arabia. Afr J Plant Sci. 2015; 9: 239-43.
- Boi M, Lazzeri V, Bacchetta G. Pollen micromorphological traits of the Tyrrhenian Stachys salisii Jord. & Fourr. (Lamiaceae). Ann Bot. 2013; 3: 231-5.
- Gul S, Ahmad M, Zafar M, Bahadur S, Sultana S, Begum N, et al. Taxonomic study of subfamily Nepetoideae (Lamiaceae) by palynomorphological approach. Microsc Res Tech. 2019; 82: 1021-31.
- Erdtman G. Pollen morphology and plant taxonomy IV. Labiatae Verbenaceae Avicenniaceae Svenk Bot Tidskr. 1945; 39: 279-85.
- Jiménez JA, Hockenbury JB. Spectroscopic properties of CuO, SnO, and Dy 2 O 3 co-doped phosphate glass: from luminescent material to plasmonic nanocomposite. J Mater Sci. 2013; 48: 6921-8.
- Nazish M, Zafar M, Ahmad M, Sultana S, Ullah R, Alqahtani AS, et al. Palyno-morphological investigations of halophytic taxa of Amaranthaceae through SEM from Salt Range of Northern Punjab, Pakistan. Microsc Res Tech. 2019; 82: 304-16.
- Punt W, Hoen PP, Blackmore S, Nilsson S, Le Thomas A. Glossary of pollen and spore terminology. Rev Palaeobot Palynol. 2007; 143: 1-81.
- Khan S, Jan G, Ahmad M, Gul F, Zafar M, Mangi JUD, et al. Morphopalynological assessment of some species of family Asteraceae and Lamiaceae of District Bannu, Pakistan on the bases of light microscope & scanning electron microscopy. Microsc Res Tech. 2021; 84: 1220-32.
- Talebi SM, Matsyura A, Behzadpour S, Tabaripour R. Infraspecific anatomical study of Salvia limbata CA Mey.(Lamiaceae) in Iran. Iranian Journal of Science. 2023; 47: 347-57.
- Koohdar F, Sheidai M, Poode ZM, Talebi SM. Pollen morphological analysis of the genus Lallemantia (Lamiaceae) of Iran. Acta Biol Sibirica. 2018; 4: 115-20.
- Díaz S, Kattge J, Cornelissen JH, Wright IJ, Lavorel S, Dray S, et al. The global spectrum of plant form and function. Nature. 2016; 529: 167-71.