
Review Article
Austin J Anal Pharm Chem. 2023; 10(3): 1164.
Current Strategies in Treating Alzheimer and Nano-Based formulation of Curcumin as new Drug Delivery Systems against Alzheimer: A Review of in-vivo and in-vitro Evidences
Sharif Bakhtiar L1; Sharif Bakhtiar S2; Mohammadi Firouz Z3; Dokhai M3; Kamali P4; Rostami Z5
1Department of Nanobiotechnology, Protein Research Institute, Shahid Beheshti University, G.C. Evin, Tehran, Iran
2Department of Computer science, Computer and mathematic Institute, Shahid Beheshti University, G.C. Evin, Tehran, Iran
3Department of Genetic, Cellular and Molecular Institute, Medical Branch of Azad University, Tehran, Iran
4Department of Nanobiotechnology, Protein Research Institute, Shahid Beheshti University, GC Evin, Tehran, Iran
5Department of Reproductive Biomedicine and Stem, Rooyan Institute, Tehran, Iran
*Corresponding author: Sharif Bakhtiar L Department of Nanobiotechnology, Protein Research Institute, Shahid Beheshti University, GC Evin and Tehran, Iran. Tel: 09120621647; Fax: 02122704474 Email: l.sharifb@gmail.com
Received: November 01, 2023 Accepted: December 15, 2023 Published: December 22, 2023
Abstract
Alzheimer’s is a neurodegenerative disease that have caused many problems for the global health system.. Today, due to the increase in life expectancy and the age of the population, the number of people diagnosed with Alzheimer›s Disease (AD) is increasing [1]. AD is usually identified by cognitive dysfunction and disruption in behavioral abilities, leading to the decrease in humans productivity and function in daily life [3]. Indeed there is a growing necessity for prevention and treatment of AD [4]. Progression of AD is linked with numerous neuropathological features such as accumulation of Amyloid-ß (Aß) etc. Development of promising treatments for AD have been challenging, with no drugs approved to date. Although in trials some drugs such as Aducanumab was effective in reducing Aß plaques in the brain, clinical out-comes were not considerable [5-8]. Due to failure of multiple trials on different drugs, many researchers have focused on natural compounds [9-11]. Curcumin as one of the most popular polyphenols, have received interests due to its unique properties in targeting Aß’s aggregation [12,13]. However curcumin has disadvantages such as poor bioavailability and chemical instability [14]. To overcome these disadvantages, Nano-drug delivery systems have shown trusting results such as appropriate targeting, high bioavailability and reducing side effects [15]. In this study we have investigated novel curcumin loaded Nano particles to highlight the advantages and disadvantages of Nanoparticles in delivery of Curcumin in AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer; Curcumin; Nano; Nanoparticle; Drug; Brain
Introduction
What Cause Alzheimer?
Due to researches done on this subject, in common regions with prevalence of Dementia; Alcohol, Physical activity and Diabetes and in the next place other factors such as smoking, social engagement, anxiety, hormones, hyper/hypotension are the main cause of Dementia [16].
Alcohol
Alcohol could affect neurotransmitter in different ways which causes to harmful consequences to these pathways. Ethanol triggers inhibitory γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors, followed by the stimulation, the excitatory glutamate receptors will be suppressed. Chronic alcohol consumption can change the microbiome and causes the neuroinflammation [17]. External negative life aspects can change gut microbiome. Negative life habits such as poor die t and alcohol consumption are considered as critical risk factors for development of spordiac AD [18,19].
Physical Activity
The brain has high sensitivity to exercise, exercise in rodent models causes the neurogenesis within hippocampal and dentate gyrus’s areas, also it will enhance learning and memory abilities [20]. Evidences in this area suggested the beneficial effect of physical activity and exercise intervention on AD [21].
Diabetes
Diabetes is associated with various problems like nephropathy, neuropathy, retinopathy, diabetic foot, cognitive impairment, and many more. Age-related memory impairment is a complication having its major effect on people suffering from diabetes and Alzheimer's. As compared with normal individuals Patients suffering from diabetes are at two times higher risk of developing cognitive dysfunction [22]. In recent years Many researches have been done on correlation between Diabetes and Alzheimer, Due to the significant correlation between two diseases the term " diabetes type 3 "or "brain diabetes" have been proposed [23]. Today it is confirmed that type 2 diabetes is associated with greater brain atrophy and cognitive decline [24].
Smoking
Among other risk factors, smoking is one of the important ones that is associated with Dementia and also can be related to currency and mortality of AD [25]. Smoking may result in cerebral oxidative stress which causes the production of Amyloid beta (Aß) or tau protein pathology. In contrast never smokers had 18% lower risk of AD in compare to continuous smokers which confirms the destructive effect of smoking on cognitive decline [26].
Social Engagement
Life style intervention including social engagement has considerable effect on AD and Cognitive abilities [27]. Low social engagement may be a marker of neurocognitive vulnerability in older adults who are cognitively normal but have evidence of AD pathophysiologic change [28]. Dyer et al. [29] in a research have suggested that in patients with AD it is important to maintain the social network. in contrast poor social network in associated with experiencing serious negative symptoms.
Anxiety
AD can result into neuropsychiatric symptoms. Among AD patients, the prevalence of anxiety is about 40% and it can be a prelude of AD. Anxiety can be seen in patients with mild cognitive impairment, mild dementia, or early-onset forms of the disease and may result to clinical syndrome of Alzheimer’s disease [30]. It is reported that anxiety convey the risk of AD up to 53%. A meta-analysis done by Santebarbara et al. [31] it has been confirmed that anxiety increases the risk of AD.
Hormone
There is noticeable fact that Alzheimer’s and dementia’s prevalence are considerably different between sexes. The rate and incidence of AD is notably higher in females. Due to the findings, researchers have now begun to search about the role of sex-dependent hormones in the pathogenesis and cause of the AD [32]. Sex hormones such as estrogen changes rapidly during the female lifespan, these hormones are high during the reproductive years and it will decline naturally during the transition to menopause. Estrogen production during Women life span may increase the risk of AD [33]. Also by the research done by Quinalan et al. [34] it have been confirmed that Thyroid hormones were moderately changed in mild AD dementia with increased serum FT4, and a also there is a decrease in peripheral conversion of T4 to T3 which confirms the reduction of T3. Brain structures involved in AD development was correlated to Serum T3 levels.
Hypertension/Hypotension
Hypertension decreases the structural and functional integrity of the cerebral microcirculation and also causes microvascular rarefaction, cerebromicrovascular endothelial dysfunction and neurovascular uncoupling, which disrupts cerebral blood supply, as a conclusion hypertension considerably increases the risk of both vascular cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease [35]. Among the different types of hypotension, it has been reported that the Orthostatic hypotension is common in patients with AD [36]. It is also reported that the prevalence of Orthostatic hypotension was more significant with progression of AD [37].
Amyloid Beta, Tau Protein, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Dysregulation of Calcium Homeostasis, Proliferation of Microglia
Amyloid Beta
Aß plaques are made in neuronal endosomes by process of hydrolysis of amyloid precursor protein and this operation is done by two main enzymes: ß-secretase and γ-secretase. Under normal condition Aß has two responsibilities: profusion of activation of synapses and also reducing the synaptic excitotoxicity [38]. But under pathological condition mostly two Aß, Aß40 and Aß42 are produced by abnormal processing of ß- and γ-secretase what makes the accumulation of Aß plaques, is imbalancement of the pathway clearance and production. These small 4 kDa peptides (A4) that are mainly contained of 38 and 43 amino acids, fold into a beta-pleated sheet structures that are highly fibrillogenic. Aß42 is the most fibrillogenic and the greatest component of amyloid plaques in AD [39].
Tau Protein
Tau belongs to the family of microtubule-associated proteins MAPs that can emerge in brain cells. Alternative splicing of the human microtubule-associated protein gene MAPT leads to six tau isoforms which are contained of 352 to 451 amino acids. A normal tau isoform ratio is necessary for maintaining brain cell homeostasis and preventing neurodegenerative diseases [40]. Tau extracted from healthy adult brains is moderately phosphorylated but in contrast, detergent-insoluble NFT Tau isolated from AD brain, is unusually and highly phosphorylated [41].
Mitochondrial Dysfunction
The mitochondrion is a cellular organelle with a special structure that is formed by two membrane that is called: outer mitochondrial membrane and inner mitochondrial membrane. Inner membrane surrounds the matrix. Mitochondria is known as powerhouse of cell and contain its own DNA. During recent decades researches have suggest new hypothesis for explaining AD pathology [42].
Mitochondrial cascade hypothesis stated that mitochondrial function may affect the accumulation of Aß. Also Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) is responsible for most of the oxidative stress in body. There are evidences that confirms Due to mitochondrial Damage in AD, the production of ROS increases. ROS is responsible for most of the oxidative stress in body [43].
Dysregulation of Calcium Homeostasis
One of the major secondary messengers is Calcium ion which is involved in cell survival, proliferation, differentiation, transcription and apoptosis. In AD, G protein coupled receptors generate secondary messengers which regulate calcium homeostasis inside cell. But in AD and pathological condition the homeostasis get damaged [44]. In normal condition, During neurotransmission, an increase in intracellular’s calcium, following membrane depolarization, transmits the signal to synapses. Therefor calcium signaling is important for neurotransmission, maintaining the synaptic plasticity and generating long term potentiation which is the basis of learning and memory [45].
Proliferation of Microglia
Microglia are the major phagocytic cells in the Central Nervous System (CNS). These cells develop from yolk sac progenitors, migrate into the developing brain, and generate a population of brain-resident phagocytes that persist for life through self-renewal [46]. Microglia cells have different responsibilities in brain as clearing apoptotic cells, releasing growth factors and nurturing neuronal metabolism and development in neurodegenerative diseases, microglia restrain extracellular protein aggregates and clear damaged neurons [47]. Still in pathological condition of AD, at first microglia was thought to be triggered by amyloid deposit. But in recent studies majority of AD risk loci are found near or in genes that in microglia are highly expressed which rises the theory of alteration in microglia ‘s genes may lead to AD [48].
Current Strategies in Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease
As it was mentioned, AD is one of the most common neurodegenerative diseases. Despite increasing number of Alzheimer cases, there is still no effective treatment to cure or slow down the progression of the disease. Until now only six drugs have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA): Aducanumab, Donepezil, Galantamine, Rivastigmine, Memantine, and a manufactured combination of Memantine and Donepezil. the main limitations of current AD treatment are low blood–brain barrier permeability, severe off-target of drugs, and immune abnormality [49,50].
Aducanumab
Aducanumab is a fully human IgG1 monoclonal antibody with a high affinity that acts by breaking down these ß-amyloid aggregates into smaller oligopeptides or amino acids. Aducanumab has been shown to selectively bind to parenchymal amyloid over vascular amyloid. The medicine at a high dose has the potential to slow down the cognitive decline linked with Alzheimer’s in patients with early-onset disease. However, aducanumab does not reverse memory loss [51]. Also aducanumab did not show positive effect on AD patients in comparison to placebo in control trials. The reports have shown that patients treated with Aducanumab have had several side effects such as headache, falls and diarrhea [52,53]. To conclude based on researches in this area, aducanumab can slow down a few symptoms of AD but until now there is no trusted research that shows the strong efficiency of Aducanumab on AD patients.
Donepezil
Donepezil is used to treat symptomatically AD. This drug specifically inhibits the enzyme Acetylcholinesterase (AChE). The main physiological function of AChE is to hydrolyze the neurotransmitter acetylcholine [54]. Unfortunately, due to the presence of Blood Brain Barrier (BBB), donepezil makes severe side effects after continuous administration at a high dose of 5 mg/day, such as diarrhea, bradycardia, vomiting, insomnia and anorexia. BBB in Alzheimer patients is more hindrance which makes the drug delivery to this area even more difficult [55]. Based on researches done on Donepezil, the medicine can improve the cognitive function to a certain degree. However, there is no evidence of significantly delaying the progression of the disease, and it can easily cause side effects on patients [56,57].
Galantamine
Galantamine is an alkaloid phytochemical which can inhibit the AChE activity. the advance feature of Galantamine in this field is the ability of Galantamine in crossing the blood brain barrier. galantamine can significantly reduces mortality and cognitive decline and also improved daily routine activity in mild cognitive decline patients [58]. But it is not clinically proven that galantamine can have disease modifying effect in humans. Also, galantamine does not have the ability to strongly break the vicious circle of Aß accumulation. It is suggested that early usage of galantamine has efficiency in prevention of AD but there is a strong doubt that Galantamine can be useful in treatment of AD patients [59].
Rivastigmine
Rivastigmine is one of the approved agent for the management of dementia of mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease. this medicine is the only cholinesterase inhibitor which inhibits both AChE and butyrylcholinesterase enzymes in the brain [60,61]. This molecule also has a short half-life and a hydrophilic nature, which makes it difficult for the medicine to pass through the Blood Brain Barrier (BBB) and Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) which results to low bioavailability of the drug [62]. Oral consumption of Rivastigmine shows different adverse effects such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and cholinomimetic effects. Also, it have been reported that large plasma fluctuation happens after oral administration which is the main reason for higher incidence of cholinergic side effects [63].
Memantine
Memantine is an oral drug which functions as a noncompetitive N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist and is approved for treatment of moderate to sever AD. Unfotunatly, studies on mold to moderate and sever AD have shown that memantine has a mild but not considerable effect on clinical symptoms [64,65].
Combination of Memantine and Donepezil
In a network meta-analysis done by Gou et al [66]. it is suggested that combination of both memantine and donepezil is effective on cognitive and neuropsychiatric symptoms but in comparison to memantine alone or placebo is less acceptable [67].
NPs Type
Study Type
Author
Effect On
Curcumin loaded liposome coupled with Sialic acid
In vivo study on mice
Chen et al. (87)
High permeation rate Through blood-brain barrier
Curcumin loaded Liposomes
In vitro study on microglia and astrocyte of human cell culture / In vivo study on murine acute brain slices
Schmitt et al. (88)
Reduction in glial scarring associated microglia and astrocyte reactions
Curcumin micelles
In vitro study on mitochondrial function in PC12 cell line/ In vivo study on NMRI mice / ex vivo in isolated mouse brain mitochondria
Hagl S et al. (91)
In isolated mouse brain, Curcumin micelles are efficient in mitochondrial swelling. Curcumin micelles are more efficient in protecting PC12 cells from nitrosative stress.
Curcumin- cocrystal micelles
In vitro cytotoxicitystudy on U87MG cell line/ In vivo pharmacokinetic and biodistribution studies in rodent model
Preshita P et al. (92)
Curcumin-cocrystal micelle have high brain distribution and also improves bioavailability, brain uptake, retention and it would delay clearance of curcumin in brain.
Encapsulated curcumin in hydroxypropyl- β-cyclodextrin
In vitro study on
BV-2 and SH-SY5Y cell line / In vivo study on mice modelsZhan et al. (94)
Encapsulated curcumin in hydroxypropyl- β-cyclodextrin, decreases TNF-a and IL-6 levels. And also the complex showed high bioavailability and brain distribution
Cyclodextrin-solubilized curcuminoids
In vitro study on NT2/D1 cells/ in vivo study on female APPSWE, PS1dE9 transgenic mice
Quitschke et al. (95)
Curcuminoids solubilized in 10% HP-γ-CD in NT2/D1 cells shows less binding compare to curcuminoids in solubilized in mouse serum/
intravenous injection of cyclodextrin-solubilized curcuminoids, reduces the plaque load to approximately 70% of the control valueβ-cyclodextrin-curcumin conjugates
In vitro study on Primary cultures of cortical neurons from rat fetuses/ In vivo study on rat embryonic cortical neurons
Ben mihoub et al. (96)
Water solubility of Curcumin- β-Cyclodextrin in nanoconjugates were evaluated compare to sole curcumin also the complex reduces cell toxicity of curcumin
Curcumin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticle
In vivo study on Wild Type and in TgCRND8 mice models
Campisi et al. (100)
The expression levels of Bcl-2, Cyclin-D1, and caspase-3 cleavage was evaluated after administering curcumin-solid lipid nanoparticle to animal models. Also the complex modulates the TG2 isoforms which repairs cellular damage in AD mice models. Thus significant improvement of cognitive performance and memory function was observed in TgCRND8 mice models
Curcumin encapsulated in solid-lipid-nanoparticle
In vitro study on neuron cells from hippocampus/ In vivo study on Pregnant mice and C57BL/6 mice
R Huang et al. (101)
Curcumin-solid lipid nanoparticle reduced neuronal apoptosis through Bcl2 family and P38 MAPK pathways compare to sole Curcumin through in vitro and in vivo study
Curcumin-loaded PLGA-PEG nanoparticles
In vivo study on brain injured neonatal rats
Pontes-Quero et al. (108)
The curcumin- loaded nanoparticles were able to overcome the impaired blood–brain barrier, diffuse effectively through the brain parenchyma, localize in regions of injury, and deliver a protective effect in the injured neonatal brain
Table 1: Nanoparticle-curcumin formulation effect on AD related biomarkers and cell line; in-vivo and in-vitro studies.
Although today, main treatment strategy of Alzheimer is prescribing approved FDA drugs, many studies are focusing on plant based compounds as they have shown less side effect, and in some cases more efficiency in in vitro and in vivo studies [68].
Polyphenols Effect on Alzheimer Disease
Polyphenols are plant compound derivation with antioxidant properties. Studies on animals have proved that polyphenols could impact accumulation and reduction of oxidative stress in patients with AD [69]. Fruits, Vegetables, beverages (tea,wine,juices), plants and some herbs have plenty of antioxidants polyphenols [70]. Veriety of mechanisms, such as free radical scavenging, metal chelation and the modulation of enzyme activities may explain the positive effect of polyphenols on brain [71]. Curcumin is one of the most famous polyphenols which could be one of the potential pharmaceutical agent for protecting brain function [72].
Curcumin and Its Therapeutic Effect
Curcumin a yellow- orange pigment belongs to a chemical class of polyphenols; it is known as diferuloylmethane with a chemical formula of C21H20O6 and a molecular weight of 368.38. Curcumin has several biological activities which is due to its special chemical structure [73,74]. There are three chemical group in Curcumin molecule: two aromatic ring systems containing o-methoxy phenolic groups linked by a seven-carbon spacer consisting of an a,ß-unsaturated ß-diketone moiety. The diketo group shows the tautomerism between two form of keto and enol. This feature indicates Curcumin could exist in equilibrium between the keto and the enol tautomer [75]. Curcumin is derived from a plant named Tumeric (Curcuma longa). Tumeric is an aromatic plant from the ginger family (Zingiberaceae). It can usually be found in Iran, Malaysia, India, China, Polynesia and Thailand. Curcumin isolated from turmeric two centuries ago. This polyphenol has been studied in numerous researches on natural compounds and have shown wide therapeutic potential in in vitro studies [76]. The compound belongs to a group of plant derivations named Flavnoids. Flavnoid among the medical herbs are a huge subgroup of the family of polyphenolic compounds that are result of secondary metabolism in plants. Various researches in recent years has shown that flavonoids could be effective in prevention and control of common diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, Alzheimer’s, stroke, diabetes, Osteoporosis and rheumatoid arthritis [77]. It is proven that curcumin as one of the most famous flavonoids has beneficial effect on neurological diseases such as AD and it can alter and decrease the disaggregation of amyloid-ß plaques, weaken the hyperphosphorylation of tau and provoke the clearance of tau protein [78]. Although curcumin can change the pathological factors of AD’s initiation and progression, it has some limitations such as low stability and low bioavailability which can weaken the positive effect of the compound on cells [79]. Also another blockage for curcumin delivery is blood–brain barrier. BBB is the major hindrance for the delivery of curcumin into the brain, resulting into decreasing its therapeutic effects [80]. One of the main solutions to overcome the Weaknesses of curcumin as a therapeutic agent is nanotechnology. Some of the major disadvantages of curcumin-based medication delivery has been alleviated by Curcumin nano formulation [81]. Today numerous studies on Alzheimer are focusing on designing the nano formulation with the most beneficial effect on brain health. Due to the hydrophobicity and low bioavailability of curcumin, encapsulated formations such as liposomes, micelles, cyclodextrin, solid lipid and polymeric NPs could increase sole curcumin’s biodistribution and bioavailability [82-84] (Figure 1).
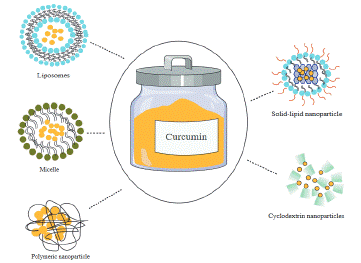
Figure 1: Five different types of important nanocarriers for delivering Curcumin in Alzheimer disease.
Curcumin-Liposome Nano Particles
Lipososmes are structured of lipid components with two parts: hydrophobic head and hydrophilic tail. Liposomes differ from their size, shape and also the number of lipid bilayers. They may have single bilayer (unilamellar), a few bilayers (oligolamellar), or multiple bilayers (multilamellar). We can also modify the rigidity, fluidity and surface charge of the liposomes which makes them a good candidate for delivering drugs in different environment [85]. Lipid nanoparticles, especially liposomes and lipid/nucleic acid complexed nanoparticles are promising formulations due to their stable drug loading, reducing side effects, enhancing efficiency in targeting and also their ability to pass the BBB or plasma membrane barriers. According to these features, liposomes are effective formulations for current untreatable illnesses [86]. In a study done by Chen et al. [87] Curcumin loaded liposome with different kind of Sialic acid coupled formulation, shows high permeation rate crossing BBB. Also Schmitt et al. [88] in a in vitro study, experimented the effect and efficacy of Curcumin loaded liposomes in specific brain cells in human. The results have should that the formulation reduces the reactivity of human microglia and actrocytes and also in in vivo study, the designed complex could preserve the tissue integrity in organotypic cortex slices in mice.
Curcumin-Micelle Nano Particles
Micelle NPs are usually formed by self assembly of block of copolymers. These type of drug delivery is usually used for encapsulating highly hydrophobic drugs and improving their solubility. Block co polymers can self assemble in solution and make micelles with different size range [89]. Moreover Micelle NPs could improve provide passive and acrive targeting and reducing the side effects of loaded drug on normal cells [90]. Hagl S et al. [91] in a in-vivo and in-vitro study have found that Curcumin-micelle formulation could improve the Curcumin bioavailability in plasma 1- to 40 times more compare to sole Curcumin. Also in this study it have been proved that curcumin micelles are promising formulation for prevention of mitochondrial damage in Neurodegenerative diseases and brain aging. In another research Preshita P et al. [92] designed Curcumin- cocrystal micelles in aim of enhancing the therapeutic efficiency of Curcumin in brain. The results have shown that Curcumin-cocrystal micelle have high brain distribution and also improves bioavailability, brain uptake, retention and moreover could delay clearance in brain.
Curcumin- Cyclodextrin Nano Particles
Cyclodextrins are cyclic oligosaccharides which are obtained from enzymatic process on stratch. There are three form of cyclodextrin a-, ß- and γ- cyclodextrins containing 6, 7 and 8 glucopyranose units. Cyclodextrin is widely used in pharmaceutical application due to their low toxicity. Also Cyclodextrins increases the solubility of hydrophobic drugs in water [93]. Zhan et al. [94] in a research encapsulated curcumin in hydroxypropyl- ß-cyclodextrin (CUR/HP- ß-CD). The in vitro experiment showed that CUR/HP- ß-CD has higher cellular uptake in compare with CUR-encapsulated chitosan-coated poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles. Also CUR/HP- ß-CD reduces cellular cytotoxicity and decreases inflammation markers such as TNF- a and IL-6. In a study done by Quitschke et al. [95] cyclodextrin solubilized curcuminoids was injected to mice and after 11 and 12 months, the plaque concentration is reduced up to 70% in compare with control value. Ben mihoub et al. [96] in a study synthetized Cur- ß-Cyclodextrin nanoconjugates to improve the solubility and reduce cell toxicity of Cur. At last the finding revealed that the nano formulation has better water solubility and in vitro biocompatibility in compare with sole Cur. The results indicated that Cur- ß-Cyclodextrin nanoconjugates could have positive effect in prevention of neurodegenerative diseases.
Curcumin-Solid Nanoparticles Complex
Solid Lipid Nanoparticle (SLNs) commonly have spherical shape with a diameter in the range of 50 to 1000 nm. The most important parts of SLN formulations include lipids, which in the room temprature are at solid state, emulsifiers and sometimes a mixture of both, active pharmaceutical ingredients and an adequate solvent system [97]. SLNs can hold both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs. They can be made up of biocompatible ingredients and due to these features, SLNs are one of the most considered choices for drug delivery. SLN’s surface modification may provide unique features to them such as mucoadhesiveness and targeting capability [98]. Gupta et al. [99] in a research for controlling the oral bioavailability of curcumin had fabricated a curcumin loaded with solid nanolipid particle by using tristearin and polyethylene glycol (PEG)ylated emulsifiers, the results suggested that bioavailability of curcumin can be improved by altering interfacial properties of SLNs which can be used in functional foods and pharmaceuticals. Also Campisi et al. [100] in a experiment done on Alzheimer mice models, have observed that the curcumin loaded solid nanoparticles can trigger the apoptotic pathway or modulate the ability of protein in repairing cellular damage in brain. R Huang et al. [101] in a study had capsulated curcumin in solid lipid nanoparticle for better neuroprotective efficacy. In vitro experiment proved that Cur-SLNs by significantly decreasing the level of free radical and reversing mitochondrial activity, functioned much better against neuronal apoptosis than sole Cur. To conclude curcumin loaded solid nanoparticles can be much more effective in Alzheimer’s disease than curcumin by itself. The efficiency is mostly due to increased bioavailability features of curcumin when is loaded with solid nanoparticles.
Curcumin-Polymeric Nanoparticle Complex
Polymeric nanoparticles are blocks of co-polymers with natural and synthetic sources such as albumin and polysaccharides [102]. These particles have the size range between 1 to 1000 nm and can make complex with active compounds. Nanoparticles are divided into two groups: nanocapsules and nanospheres. These two polymeric subgroups are mainly different by their morphological shape [103]. NPs as drug carrier has various advantages such as strong bioavailability, improving the drug therapeutic index, controlled release and the ability to protect the drug from unwanted interaction with environment [104,105]. There are several researches that have showed the therapeutic effect of Polymeric NPs in combined with antitumor drugs. Polymeric NPs would enhance antitumor efficiency, inhibiting metastases and also reduce the side effects [106]. In a research done by Pontes-Quero et al. [107] Curcumin loaded on polymeric nanoparticles shows good encapsulation efficiency and good curcumin release profile. Also, curcumin loaded on polymeric nanoparticle were not cytotoxic in different range of concentration and were effective in reducing inflammatory markers. Joseph et Al. [108] in a research have loaded curcumin into poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)-poly(ethylene glycol) particles to examine the effectiveness of drug delivery to the brain. The examiners have concluded that CUR-polymeric NPs had overcome the BBB and also the complex has passed through parenchyme in brain.
Conclusion and Perspective
In last decades, AD patients have been increasing due to change in lifestyle. Numerous medical and psychological factors may cause AD, such as lack of physical activity, Consuming alcohol, Diabetes, smoking loneliness etc. There is no proved evidence that what may cause AD but there are several theories that indicates the pathological cause of AD including accumulation of Aß plaques, tau proteins, mitochondrial dysfunction, Dysregulation of Calcium homeostasis and Proliferation of microglia. Due to difficulties of drug delivering into the brain aria in AD, such as existence of BBB and rapid clearance of molecules in this area, until now treatment of AD has been challenging for medical system and scientists. Today nano based biomaterials have drawn attention for efficient drug delivery in brain. Most NPs have unique physical and chemical properties which make them a great candidate for safe deliver of drugs. Many NPs have the ability to cross BBB due to their small size or interaction with endothelial cells in BBB. Moreover, today there are few drugs which have been approved by medical system such as Aducanumab and Donepezil etc. But there are a lot of doubts about their efficiency in crossing BBB, also they would cause numerous side effects in patients with low positive effect on delaying the symptoms. Today it has been proved that plant-based compounds such as polyphenols have antioxidant and anti inflammatory effects in brain. Cur is one of the potent polyphenols with strong properties in reducing brain inflammatory with least side effects compare to approved drugs. However, Cur molecules are hydrophobic which makes it hard for them to cross cells. Also, Cur molecules have low stability and low bioavailability which decreases effectiveness of Cur in treatment of AD. Loading Cur on NPs would make Cur to overcome negative features in crossing BBB and in addition, adding NPs to the complex, improves stability and bioavailability of Cur. In this review different NPs-Cur formulations for treatment of AD which have been designed in recent related articles have been mentioned and discussed.
References
- Poudel P, Park S. Recent advances in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease using nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14: 835.
- Reitz C, Rogaeva E, Beecham GW. Late-onset vs nonmendelian early-onset Alzheimer disease: A distinction without a difference? Neurol Genet. 2020; 6: e512.
- Cammisuli DM, Cipriani G, Castelnuovo G. Technological solutions for diagnosis, management and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease-related symptoms: a structured review of the recent scientific literature. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022; 19: 3122.
- Griñán-Ferré C, Bellver-Sanchis A, Izquierdo V, Corpas R, Roig-Soriano J, Chillón M, et al. The pleiotropic neuroprotective effects of resveratrol in cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease pathology: from antioxidant to epigenetic therapy. Ageing Res Rev. 2021; 67: 101271.
- Uddin MS, Kabir MT, Rahman MS, Behl T, Jeandet P, Ashraf GM, et al. Revisiting the amyloid cascade hypothesis: from anti-Aß therapeutics to auspicious new ways for Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21: 5858.
- Roda AR, Serra-Mir G, Montoliu-Gaya L, Tiessler L, Villegas S. Amyloid-beta peptide and Tau protein crosstalk in Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen Res. 2022; 17: 1666-74.
- Tolar M, Abushakra S, Sabbagh M. The path forward in Alzheimer’s disease therapeutics: reevaluating the amyloid cascade hypothesis. Alzheimers Dement. 2020; 16: 1553-60.
- Synnott PG, Whittington MD, Lin GA, Rind DM, Pearson SD. The effectiveness and value of aducanumab for Alzheimer’s disease. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2021; 27: 1613-7.
- Phan HTT, Samarat K, Takamura Y, Azo-Oussou AF, Nakazono Y, Vestergaard MC. Polyphenols modulate alzheimer’s amyloid beta aggregation in a structure-dependent manner. Nutrients. 2019; 11: 756.
- Henríquez G, Gomez A, Guerrero E, Narayan M. Potential role of natural polyphenols against protein aggregation toxicity: in vitro, in vivo, and clinical studies. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020; 11: 2915-34.
- Zheng Q, Kebede MT, Kemeh MM, Islam S, Lee B, Bleck SD, et al. Inhibition of the self-assembly of Aß and of tau by polyphenols: mechanistic studies. Molecules. 2019; 24: 2316.
- Maleki Dana P, Sadoughi F, Mansournia MA, Mirzaei H, Asemi Z, Yousefi B. Targeting Wnt signaling pathway by polyphenols: implication for aging and age-related diseases. Biogerontology. 2021; 22: 479-94.
- Azam S, Jakaria M, Kim IS, Kim J, Haque ME, Choi DK. Regulation of toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling pathway by polyphenols in the treatment of age-linked neurodegenerative diseases: focus on TLR4 signaling. Front Immunol. 2019; 10: 1000.
- Zheng B, McClements DJ. Formulation of more efficacious curcumin delivery systems using colloid science: enhanced solubility, stability, and bioavailability. Molecules. 2020; 25: 2791.
- Fang X, Cao J, Shen A. Advances in anti-breast cancer drugs and the application of nano-drug delivery systems in breast cancer therapy. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2020; 57: 101662.
- Anstey KJ, Ee N, Eramudugolla R, Jagger C, Peters R. A systematic review of meta-analyses that evaluate risk factors for dementia to evaluate the quantity, quality, and global representativeness of evidence. J Alzheimers Dis. 2019; 70: S165-86.
- Peng B, Yang Q, B Joshi R, Liu Y, Akbar M, Song B-J, Zhou S, Wang X. Role of Alcohol Drinking in Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease, and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21: 2316.
- Askarova S, Umbayev B, Masoud AR, Kaiyrlykyzy A, Safarova Y, Tsoy A, et al. The links between the gut microbiome, aging, modern lifestyle and Alzheimer’s disease. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020; 10: 104.
- Frausto D. The impact of the intestinal microbiome on microglial inflammation. Alzheimers Dement. 2020; 16: e046964.
- Kou X, Chen D, Chen N. Physical activity alleviates cognitive dysfunction of Alzheimer’s disease through regulating the mTOR signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 20: 1591.
- Jia RX, Liang JH, Xu Y, Wang YQ, Y, et al. Effects of physical activity and exercise on the cognitive function of patients with Alzheimer disease: a meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2019; 19: 181.
- Jash K, Gondaliya P, Kirave P, Kulkarni B, Sunkaria A, Kalia K. Cognitive dysfunction: A growing link between diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. Drug Dev Res. 2020; 81: 144-64.
- Stanciu GD, Bild V, Ababei DC, Rusu RN, Cobzaru A, Paduraru L, et al. Link between diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease due to the shared amyloid aggregation and deposition involving both neurodegenerative changes and neurovascular damages. J Clin Med. 2020; 9: 1713.
- Callisaya ML, Beare R, Moran C, Phan T, Wang W, Srikanth VK. Type 2 diabetes mellitus, brain atrophy and cognitive decline in older people: a longitudinal study. Diabetologia. 2019; 62: 448-58.
- Kim S, Son Y. Astrocytes stimulate microglial proliferation and M2 polarization in vitro through crosstalk between astrocytes and microglia. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22: 8800.
- Jiang Y, Man Q, Liu Z, Wang Y, Suo C, Jin L, et al. Temporal trends in the mortality rate of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias attributable to smoking, 1990-2017. Environ Res. 2020; 184: 109183.
- Zhang XX, Tian Y, Wang ZT, Ma YH, Tan L, Yu JT. The epidemiology of Alzheimer’s disease modifiable risk factors and prevention. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2021; 8: 313-21.
- Ko Y, Chye SM. Lifestyle intervention to prevent Alzheimer’s disease. Rev Neurosci. 2020; 31: 817-24.
- Biddle KD, d’Oleire Uquillas F, Jacobs HIL, Zide B, Kirn DR, Rentz DM et al. Social engagement and amyloid-ß-related cognitive decline in cognitively normal older adults. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2019; 27: 1247-56.
- Dyer AH, Murphy C, Lawlor B, Kennelly SP, Study Group FTN. Social networks in mild-to-moderate Alzheimer disease: longitudinal relationships with dementia severity, cognitive function, and adverse events. Aging Ment Health. 2021; 25: 1923-9.
- Mendez MF. The relationship between anxiety and Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2021; 5: 171-7.
- Santabárbara J, Lipnicki DM, Bueno-Notivol J, Olaya-Guzmán B, Villagrasa B, López-Antón R. Updating the evidence for an association between anxiety and risk of Alzheimer’s disease: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. J Affect Disord. 2020; 262: 397-404.
- Wu M, Li M, Yuan J, Liang S, Chen Z, Ye M, et al. Postmenopausal hormone therapy and Alzheimer’s disease, dementia, and Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and time-response meta-analysis. Pharmacol Res. 2020; 155: 104693.
- de Lange A-MG, Barth C, Kaufmann T, Maximov II, van der Meer D, Agartz I, et al. Women’s brain aging: effects of sex-hormone exposure, pregnancies, and genetic risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Brain Mapp. 2020; 41: 5141-50.
- Quinlan P, Horvath A, Eckerström C, Wallin A, Svensson J. Altered thyroid hormone profile in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2020; 121: 104844.
- Ungvari Z, Toth P, Tarantini S, Prodan CI, Sorond F, Merkely B, et al. Hypertension-induced cognitive impairment: from pathophysiology to public health. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021; 17: 639-54.
- Isik AT, Erken N, Yavuz I, Kaya D, Ontan MS, Ates Bulut E, et al. Orthostatic hypotension in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Neurol Sci. 2022; 43: 999-1006.
- Isik AT, Kocyigit SE, Smith L, Aydin AE, Soysal P. A comparison of the prevalence of orthostatic hypotension between older patients with Alzheimer’s disease, Lewy body dementia, and without dementia. Exp Gerontol. 2019; 124: 110628.
- Huang YR, Liu RT. The toxicity and polymorphism of ß-amyloid oligomers. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21: 4477.
- DeTure MA, Dickson DW. The neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurodegener. 2019; 14: 32.
- Penke B, Szucs M, Bogár F. Oligomerization and conformational change turn monomeric ß-amyloid and tau proteins toxic: their role in Alzheimer’s pathogenesis. Molecules. 2020; 25: 1659.
- Wegmann S, Biernat J, Mandelkow E. A current view on Tau protein phosphorylation in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2021; 69: 131-8.
- Cenini G, Voos W. Mitochondria as potential targets in Alzheimer disease therapy: an update. Front Pharmacol. 2019; 10: 902.
- Liu PP, Xie Y, Meng XY, Kang JS. History and progress of hypotheses and clinical trials for Alzheimer’s disease. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2019; 4: 29.
- Sushma AC, Mondal AC. Role of GPCR signaling and calcium dysregulation in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2019; 101: 103414.
- Ryan KC, Ashkavand Z, Norman KR. The role of mitochondrial calcium homeostasis in Alzheimer’s and related diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21: 9153.
- Pías-Peleteiro JM, de Vries HE, Castillo J, Sobrino TCustodia A, Ouro A, Romaus-Sanjurjo D Endothelial Progenitor Cells and Vascular Alterations in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022; 13: 811210.
- Hemonnot AL, Hua J, Ulmann L, Hirbec H. Microglia in Alzheimer disease: well-known targets and new opportunities. Front Aging Neurosci. 2019; 11: 233.
- Ouyang Q, Meng Y, Zhou W, Tong J, Cheng Z, Zhu Q. New advances in brain-targeting nano-drug delivery systems for Alzheimer’s disease. J Drug Target. 2022; 30: 61-81.
- Pardo-Moreno T, González-Acedo A, Rivas-Domínguez A, García-Morales V, García-Cozar FJ, Ramos-Rodríguez JJ et al. Therapeutic approach to Alzheimer’s disease: current treatments and new perspectives. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14: 1117.
- Karthivashan G, Ganesan P, Park SY, Kim JS, Choi DK. Therapeutic strategies and nano-drug delivery applications in management of ageing Alzheimer’s disease. Drug Deliv. 2018; 25: 307-20.
- Aducanumab at a high dose has the potential to slow down the cognitive decline linked with Alzheimer’s in patients with early-onset disease. However, aducanumab does not reverse memory loss.
- Wojtunik-Kulesza K, Rudkowska M, Orzel-Sajdlowska A. Aducanumab—hope or disappointment for Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2023; 24: 4367.
- Cummings J, Aisen P, Apostolova LG, Atri A, Salloway S, Weiner M. Aducanumab: appropriate use recommendations. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2021; 8: 398-410.
- Zambrano P, Suwalsky M, Jemiola-Rzeminska M, Strzalka K, Sepúlveda B, Gallardo MJ, et al. The acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor and anti-Alzheimer drug donepezil interacts with human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2019; 1861: 1078-85.
- Zhang H, Zhao Y, Yu M, Zhao Z, Liu P, Cheng H, et al. Reassembly of native components with donepezil to execute dual-missions in Alzheimer’s disease therapy. J Control Release. 2019; 296: 14-28.
- Zhang X, Lian S, Zhang Y, Zhao Q. Efficacy and safety of donepezil for mild cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2022; 213: 107134.
- Cheng J, Yang H, Zhang J. Donepezil’s effects on brain functions of patients with Alzheimer disease: a regional homogeneity study based on resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2019; 42: 42-8.
- Metz CN, Pavlov VA. Treating disorders across the lifespan by modulating cholinergic signaling with galantamine. J Neurochem. 2021; 158: 1359-80.
- Saito T, Hisahara S, Iwahara N, Emoto MC, Yokokawa K, Suzuki H, et al. Early administration of galantamine from preplaque phase suppresses oxidative stress and improves cognitive behavior in APPswe/PS1dE9 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019; 145: 20-32.
- Eldufani J, Blaise G. The role of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors such as neostigmine and rivastigmine on chronic pain and cognitive function in aging: a review of recent clinical applications. Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2019; 5: 175-83.
- Nguyen K, Hoffman H, Chakkamparambil B, Grossberg GT. Evaluation of rivastigmine in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurodegener Dis Manag. 2021; 11: 35-48.
- Cunha S, Costa CP, Loureiro JA, Alves J, Peixoto AF, Forbes B, et al. Double optimization of rivastigmine-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) for nose-to-brain delivery using the quality by design (QbD) approach: formulation variables and instrumental parameters. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12: 599.
- Salimi A, Gobadian H, Sharif Makhmalzadeh B. Dermal pharmacokinetics of rivastigmine-loaded liposomes: an ex vivo–in vivo correlation study. J Liposome Res. 2021; 31: 246-54.
- Marotta G, Basagni F, Rosini M, Minarini A. Memantine derivatives as multitarget agents in Alzheimer’s disease. Molecules. 2020; 25: 4005.
- Balázs N, Bereczki D, Kovács T. Cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine for the treatment of Alzheimer and non-Alzheimer dementias. Ideggyogy Sz. 2021; 74: 379-87.
- Guo J, Wang Z, Liu R, Huang Y, Zhang N, Zhang R. Memantine, donepezil, or combination therapy—what is the best therapy for Alzheimer’s disease? A network meta-analysis. Brain Behav. 2020; 10: e01831.
- Briguglio G, Costa C, Pollicino M, Giambò F, Catania S, Fenga C. Polyphenols in cancer prevention: new insights. Int J Funct Nutr. 2020; 1: 1.
- Colizzi C. The protective effects of polyphenols on Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review. Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2019; 5: 184-96.
- Singh M, Arseneault M, Sanderson T, Murthy V, Ramassamy C. Challenges for research on polyphenols from foods in Alzheimer’s disease: bioavailability, metabolism, and cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Agric Food Chem. 2008; 56: 4855-73.
- Schaffer S, Halliwell B. Do polyphenols enter the brain and does it matter? Some theoretical and practical considerations. Genes Nutr. 2012; 7: 99-109.
- Mythri RB, Harish G, Dubey SK, Misra K, Bharath MM. Glutamoyl diester of the dietary polyphenol curcumin offers improved protection against peroxynitrite-mediated nitrosative stress and damage of brain mitochondria in vitro: implications for Parkinson’s disease. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011; 347: 135-43.
- Smirnova E, Karthikeyan A, Moniruzzaman M, Kalaiselvi S, Nam K, Le Goff G, et al. The impact of curcumin on livestock and poultry animal’s performance and management of insect pests. shbabu A. Front Vet Sci. 2023; 10.
- Shen L, Ji HF. Theoretical study on physicochemical properties of curcumin. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2007; 67: 619-23.
- Del Prado-Audelo ML, Caballero-Florán IH, Meza-Toledo JA, Mendoza-Muñoz N, González-Torres M, Florán B et al. Formulations of curcumin nanoparticles for brain diseases. Biomolecules. 2019; 9: 56.
- Uroševic M, Nikolic L, Gajic I, Nikolic V, Dinic A, Miljkovic V. Curcumin: biological activities and modern pharmaceutical forms. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022; 11: 135.
- Mansouri K, Rasoulpoor S, Daneshkhah A, Abolfathi S, Salari N, Mohammadi M, et al. Clinical effects of curcumin in enhancing cancer therapy: A systematic review. BMC Cancer. 2020; 20: 791.
- Vijh D, Imam MA, Haque MMU, Das S, Islam A, Malik MZ. Network pharmacology and bioinformatics approach reveals the therapeutic mechanism of action of curcumin in Alzheimer disease. Metab Brain Dis. 2023; 38: 1205-20.
- Hosseini-Zare MS, Sarhadi M, Zarei M, Thilagavathi R, Selvam C. Synergistic effects of curcumin and its analogs with other bioactive compounds: A comprehensive review. Eur J Med Chem. 2021; 210: 113072.
- Askarizadeh A, Barreto GE, Henney NC, Majeed M, Sahebkar A. Neuroprotection by curcumin: a review on brain delivery strategies. Int J Pharm. 2020; 585: 119476.
- Gayathri K, Bhaskaran M, Selvam C, Thilagavathi R. Nanoformulation approaches for curcumin delivery-a review. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2023; 82: 104326.
- Alagawany M, Farag MR, Abdelnour SA, Dawood MAO, Elnesr SS, Dhama K. Curcumin and its different forms: a review on fish nutrition. Aquaculture. 2021; 532: 736030.
- Trigo-Gutierrez JK, Vega-Chacón Y, Soares AB, Mima EGO. Antimicrobial activity of curcumin in nanoformulations: a comprehensive review. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22: 7130.
- Naksuriya O, Okonogi S, Schiffelers RM, Hennink WE. Curcumin nanoformulations: a review of pharmaceutical properties and preclinical studies and clinical data related to cancer treatment. Biomaterials. 2014; 35: 3365-83.
- Kamaly N, Miller AD. Paramagnetic liposome nanoparticles for cellular and tumour imaging. Int J Mol Sci. 2010; 11: 1759-76.
- Fan Y, Marioli M, Zhang K. Analytical characterization of liposomes and other lipid nanoparticles for drug delivery. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2021; 192: 113642.
- Chen MH, Chiang BH. Modification of curcumin-loaded liposome with edible compounds to enhance ability of crossing blood brain barrier. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects. 2020; 599: 124862.
- Schmitt C, Lechanteur A, Cossais F, Bellefroid C, Arnold P, Lucius R, et al. Liposomal encapsulated curcumin effectively attenuates neuroinflammatory and reactive astrogliosis reactions in glia cells and organotypic brain slices. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020; 15: 3649-67.
- Tyrrell ZL, Shen Y, Radosz M. Fabrication of micellar nanoparticles for drug delivery through the self-assembly of block copolymers. Prog Polym Sci. 2010; 35: 1128-43.
- Sutton D, Nasongkla N, Blanco E, Gao J. Functionalized micellar systems for cancer targeted drug delivery. Pharm Res. 2007; 24: 1029-46.
- Hagl S, Kocher A, Schiborr C, Kolesova N, Frank J, Eckert GP. Curcumin micelles improve mitochondrial function in neuronal PC12 cells and brains of NMRI mice–Impact on bioavailability. Neurochem Int. 2015; 89: 234-42.
- Desai PP, Patravale VB. Curcumin cocrystal micelles—multifunctional nanocomposites for management of neurodegenerative ailments. J Pharm Sci. 2018; 107: 1143-56.
- Varan G, Varan C, Erdogar N, Hincal AA, Bilensoy E. Amphiphilic cyclodextrin nanoparticles. Int J Pharm. 2017; 531: 457-69.
- Zhang L, Yang S, Wong LR, Xie H, Ho PCL. In vitro and in vivo comparison of curcumin-encapsulated chitosan-coated poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles and curcumin/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes administered intranasally as therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Pharm. 2020; 17: 4256-69.
- Quitschke WW, Steinhauff N, Rooney J. The effect of cyclodextrin-solubilized curcuminoids on amyloid plaques in Alzheimer transgenic mice: brain uptake and metabolism after intravenous and subcutaneous injection. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2013; 5: 16.
- Ben Mihoub A, Acherar S, Frochot C, Malaplate C, Yen FT, Arab-Tehrany E. Synthesis of new water soluble β-cyclodextrin@curcumin conjugates and in vitro safety evaluation in primary cultures of rat cortical neurons. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22: 3255.
- Duan Y, Dhar A, Patel C, Khimani M, Neogi S, Sharma P, et al. A brief review on solid lipid nanoparticles: part and parcel of contemporary drug delivery systems. RSC Adv. 2020; 10: 26777-91.
- Paliwal R, Paliwal SR, Kenwat R, Kurmi BD, Sahu MK. Solid lipid nanoparticles: a review on recent perspectives and patents. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2020; 30: 179-94.
- Gupta T, Singh J, Kaur S, Sandhu S, Singh G, Kaur IP. Enhancing bioavailability and stability of curcumin using solid lipid nanoparticles (CLEN): A covenant for its effectiveness. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020; 8: 879.
- Campisi A. Campisi A, Sposito G, Pellitteri R, Santonocito D, Bisicchia J, Raciti G, et al. Effect of unloaded and curcumin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles on tissue transglutaminase isoforms expression levels in an experimental model of Alzheimer’s disease. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022; 11: 1863.
- Huang R, Zhu Y, Lin L, Song S, Cheng L, Zhu R. Solid lipid nanoparticles enhanced the neuroprotective role of curcumin against epilepsy through activation of Bcl-2 family and P38 MAPK pathways. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020; 11: 1985-95.
- La Barbera L, Mauri E, D’Amelio M, Gori M. Functionalization strategies of polymeric nanoparticles for drug delivery in Alzheimer’s disease: current trends and future perspectives. Front Neurosci. 2022; 16: 939855.
- Zielinska A, Carreiró F, Oliveira AM, Neves A, Pires B, Venkatesh DN, et al. Polymeric nanoparticles: production, characterization, toxicology and ecotoxicology. Molecules. 2020; 25: 3731.
- Owens III DE, Peppas NA. Opsonization, biodistribution, and pharmacokinetics of polymeric nanoparticles. Int J Pharm. 2006; 307: 93-102.
- Soppimath KS, Aminabhavi TM, Kulkarni AR, Rudzinski WE. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles as drug delivery devices. J Control Release. 2001; 70: 1-20.
- Gagliardi A, Giuliano E, Venkateswararao E, Fresta M, Bulotta S, Awasthi V, et al. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles for drug delivery to solid tumors. Front Pharmacol. 2021; 12: 601626.
- Pontes-Quero GM, Benito-Garzón L, Pérez Cano JP, Aguilar MR, Vázquez-Lasa B. Amphiphilic polymeric nanoparticles encapsulating curcumin: antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and biocompatibility studies. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021; 121: 111793.
- Joseph A, Wood T, Chen CC, Corry K, Snyder JM, Juul SE, et al. Curcumin-loaded polymeric nanoparticles for neuroprotection in neonatal rats with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Nano Res. 2018; 11: 5670-88.
- Available from: http://smart.servier.com.