
Review Article
Austin J Anal Pharm Chem. 2015;2(2): 1037.
Analytical Techniques in Simultaneous Estimation: An Overview
Pragya Nand Badyal1, Chetan Sharma1, Navdeep Kaur1, Ravi Shankar2, Abhay Pandey1 and Ravindra K. Rawal1*
1Department of Pharmaceutical Analysis, Indo-Soviet Friendship College of Pharmacy (ISFCP), Moga-142001, India
2Medicinal Chemistry Division, Indian Institute of Integrative Medicine (CSIR), Jammu-180001, India
*Corresponding author: Ravindra K. Rawal, Department of Pharmaceutical Analysis, Indo-Soviet Friendship College of Pharmacy (ISFCP), Moga-142002, India.
Received: March 18, 2015; Accepted: April 16, 2015; Published: April 17, 2015
Abstract
Simultaneous estimation plays a very important role in pharmaceutical world as it is very feasible and time saving. For the multi component analysis various techniques like spectrophotometric techniques (UV-VIS, IR, NMR and MASS spectrometry) and chromatographic techniques (Thin Layer Chromatography, High Performance Liquid Chromatography, Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography, High Pressure Thin Layer Chromatography and Gas Chromatography) is used. These techniques provide high degree of specificity and selectivity and further provide the high degree of assurance that these techniques fit for the simultaneous estimation of the pharmaceutical dosage form. Chromatographic and spectrophotometric techniques together develop new hyphenated techniques which are useful for the simultaneous estimation and impurity profiling. The simultaneous analytical analysis provides specificity and assurance for the identification of the chemical entities in the pharmaceutical formulation. The main objective behind the analytical estimation is to provide the assurance that the particular formulation contains the equal amount of active pharmaceutical ingredient as mentioned in the label.
Keywords: Analytical techniques; Spectrophotometric; HPTLC; Hyphenated techniques; Gas Chromatography
Abbreviations
API's: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients; UV-VIS: Ultra Violet -Visible; I.R: Infra Red; I.P: Indian Pharmacopoeia; B.P: British Pharmacopoeia; USP: United States Pharmacopoeia; NMR: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance; MALDI: Matrix- Asisted Laser desorption Ionization; GAA: Glacial Acetic Acid; HPLC: High Performance Liquid Chromatography; PAD: Pulsed Amperometric Detection; PDA: Photo Diode Array; NS,CD: Non-suppressed Conductometric Detection; ACN: Acetonitrile; KOH: Potassiun Hydroxide; TLC: Thin layer Chromtography; HPTLC: High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography; UPLC: Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography; TFA: Triflouro Acetic Acid; GC-MS: Gas Chromatography - Mass Spectrometry; LC-IR: Liquid Chromatography- Infra Red; LCMS: Liquid Chromatography- Mass Spectroscopy; GC-IR: Gas Chromatography-Infra Red; GC-MS-MS: Gas Chromatography- Mass spectroscopy-Mass spectroscopy; LC-MS-MS: Liquid Chromatography-Mass spectroscopy-Mass spectroscopy; GCGC- MS: Gas Chromatography-Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectroscopy; GC-NMR: Gas Chromatography-Nuclear Magnetic Resonance; GC-AES: Gas Chromatography-Atomic Emission Spectroscopy.
Introduction
The development of pharmaceuticals and their analysis has brought the world to the revolutionary extent in health sciences. The process of drug molecule discovery and pharmaceutical investigation or analysis of the formulation provides the safety and therapeutic effect to a high extent. To make API and formulation safe a large number of analytical techniques have been developed. During various stages of preparation of pharmaceutical formulation, the addition of impurities or development of impurities makes the preparation harmful for the administration and may cause other disorders and disease like cancer(mainly from solvents like benzene) [1,2]. In formulation the analytical techniques play the great role in the identification of physical and chemical properties of the formulation. The analytical techniques provide the important description for the evaluation of the toxicity and other impurities [1]. Presently various combinations in dosage forms are present in enormous amount and are increasing rapidly. These multi component formulations provide the increased therapeutic index, multiple actions, less side effects and quicker relief. The analytical process deals with two parts of chemical characterization either it is qualitative or quantitative. The qualitative analytical analysis provides quality and identity of the sample and quantitative analytical analysis provides the amount of chemical identities present in the formulation. The main objective behind the analytical estimation is to provide the assurance that the particular formulation contains the equal amount of active pharmaceutical ingredient as mentioned in the label [3].
For the estimation of multi component in formulation the various instrumental techniques like spectrophotometric and chromatographic techniques are used due to their advantages viz. less time consuming, cheap, specific and accurate which provides result up to high extent [3] (Figure 1).
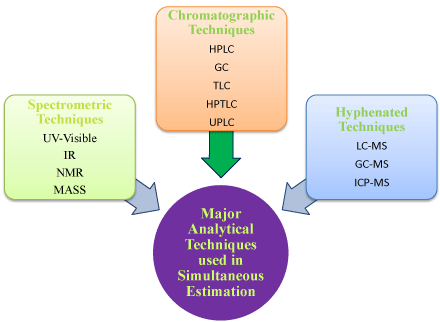
Figure 1: Different types of analytical techniques used in pharmaceutical world.
Spectrophotometric Techniques
Spectrophotometric techniques are the important instrumental techniques which are available to pharmaceutical analyst. The basics of spectrophotometric techniques are that they measure the interaction of electromagnetic radiations with sample in quantized form [4]. There are various spectrophotometric techniques which are used in the pharmaceutical world for the analysis of the API's and pharmaceutical ingredients.
UV/VIS Spectroscopy
It is the cheapest and easiest working analytical tool available that is used in the pharmaceutical laboratories and research. The analytical applications of the UV spectroscopy are qualitative and quantitative. As most of the pharmaceutical contains chromophore they can be determined directly. However UV/VIS spectroscopy is not much suitable for the simultaneous estimations with spectral overlapping. The derivative spectroscopy provides the enhancement of specificity and sensitivity in pharmaceutical formulations [5].
The ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry techniques is one of the most frequently used techniques in the analysis which involves the measurement of amount of ultraviolet and visible radiations absorbed by the pharmaceuticals in a solution. Various techniques has been used in simultaneous estimation by UV/VIS spectroscopy such as: (i) Simultaneous Equation method; (ii) Absorbance ratio method; (iii) Geometric correction method; (iv) Orthogonal polynomial method; (v) Difference spectroscopy; (vi) Derivative spectroscopy [4]. The advantages of the UV/VIS spectroscopy techniques are that they have low time and labor consumption. The precision and accuracy of analyst by using the UV/VIS spectroscopy is up to a high limit [1].
Derivative Spectrophotometry
It is one of the most highly developed spectrophotometric techniques. The origin of derivative spectrophotometry is linked with appearance of spectrophotometers enabling recording of derivative spectra [6]. The derivative spectrophotometry involves the change of normal spectrum to its first, second or higher derivative spectrum [4]. The derivative spectra can be obtained by optical, electronic and mathematical methods. In optical method there is wave length modulation where the wavelength of incident light is quickly modulated over a narrow wavelength range by electromechanical device [6].
If the derivative spectrum is expressed as absorbance (A) as function of wavelength (λ), the derivative spectra are:
Zero order: A = f (λ)
First order:
Second order:
The derivative spectra are employed to get the better differences among spectra to resolve the overlapping bands in qualitative analysis and to reduce the outcome of scattering matrix [4].
The strong positive and negative bands with maximum and minimum at same wavelength of an absorption band as inflection point in absorbance band governs the odd (first and second) derivative spectrum whereas the strong positive and negative bands with minimum or maximum at same wavelength as λ max of absorbance band governs the even (second and fourth) derivative spectrum.
Number of bands = derivative order +1
The merits of derivative spectroscopy are to increase the resolution permitting identification of analyte with close λmax, to decline the baseline shift arising from instrument or sample handling and diminish the scattering effect thus helpful for analyte present in turbid solution [7] (Table 1,2,3).
Drug combination
Wavelength (nm)
References
Adrenaline and Noradrenaline
394 and 342
[8]
Amiloride and Furosemide
241.4 and 343.6
[9]
Amitryptyline and Chlorpromazine hydrochloride
254 and 260
[10]
Amoxicillin and Bromohexine hydrochloride
278.8 and 326.2
[11]
Analgin and Adamon
600 and 310.5
[12]
Analgin and Hyoscine N-butyl bromide
291.8 and 219.8
[13]
Atenolol and Nifedipine
276 and 340
[14]
Cephalothin and Cefoxitin
235 and 236.7
[15]
Cilazapril and Hydrochlorothiazide
242.8 and 282.8
[16]
Table 1: Simultaneous estimation of drugs in pharmaceutical combination by first-order derivative UV spectrophotometric method.
Drug combination
Wavelength (nm)
References
Acrivastine and Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride
288 and 270.2
[17]
Cefatoxime sodium and Cefadroxil monohydrate
257 and 279
[18]
Telmisartan and Metoprolol
224 and 299.5
[19]
Prasugrel and Asprin
252.4 and 267.6
[20]
Ibuprofen and Famotidine
272.8 and 290
[21]
Citicoline and Piracetam
274.6 and 206.8
[22]
Diclofenac sodium and Thiocolchicoside
249 and 246
[23]
Table 2: Simultaneous estimation of drugs in pharmaceutical formulation by second-order derivative UV spectrophotometric method.
Drug combination
Wavelength (nm)
References
Atenolol and Amlodipine
264 and 308
[24]
Amitryptyline and Chlorpromazine hydrochloride
254 and 260
[10]
Table 3: Simultaneous estimation of drugs in pharmaceutical estimation by thirdorder derivative UV spectrophotometric method.
IR Spectroscopy
Pharmaceutical quality control and quality assurance depends on monitoring the composition and uniformity of the drug substance during processing and in the pharmaceutical product. Various tests have been used to determine identity, quality and strength. Vibrational spectroscopic techniques, including Mid-infrared, Near-infrared and Raman, have been proposed as other alternative approaches [25]. Infra-red is an important technique which gives sufficient information about the structure and its functional groups of a compound. This technique provides a spectrum containing large number of absorption bands i.e. functional groups can be derived from which the structures of organic compound can be studied or demonstrated. The absorption of infra-red radiations (quantized) causes the various bands in a molecule to stretch and bend with respect to one another [26]. The most important region for the organic chemist is 2.5μ to 15μ in which molecular vibrations can be detected. The ordinary infra-red region extends from 2.5μ to 15μ. The region from 0.8μ to 2.5μ is called Near IR region and that from 15μ to 200μ is called Far IR region. When the electromagnetic radiations are passed through sample which are absorbed by the bonds of the molecules in the sample causing them to stretch or bend. The wavelength of the radiation absorbed is characteristic of the bond absorbing it (Table 4).
Drug name
Near IR
Mid IR
Far IR
Property Description
References
Indomethacin-saccharin
Characterization of cocrystals
[27]
Enalapril
Characterization of six salt forms
[27]
Celecoxib
Characterization of polymorphs
[27]
Omperazole sodium
Characterization of API in salt form
[27]
Acyclovir and lactose
Drug excepient compatibility
[27]
Bicifadine HCl
Characterization of polymorphs
[27]
Piroxicam monohydrate
Quantification during
isothermal dehydration
[27]
Troglitazone
Drug (crystalline versus amorphous) distribution in
solid dispersion
[27]
Theophylline and caffeine
Characterization of hydrate formation during wet Granulation
[27]
Sulfathiazole
Polymorph screening and processing-induced
transformation (PIT)
screening
[27]
Prediction of DNA
Oligonucleotide of DNA
[28]
Table 4: Determination of pharmaceutical drugs by IR spectroscopy.
Shortcomings and limitations of infrared spectroscopy
Infra-red spectroscopy has proved to be one of the most important and needy methods for characterization of both quantitatively and qualitatively of large number of inorganic compounds encountered in research as well as in industry yet it suffers some shortcomings which are mentioned below:
- It is impossible to determine the unknown substance from the individual IR spectrum. Example a mixture of paraffin and alcohol will give the same IR spectrum as by the higher molecular weight alcohols.
- In case of Near IR region technique extensive method development is required before the technique can be used for analysis of pharmaceuticals. Development of method requires a highly trained professional analyst with computing knowledge [29].
Application of IR spectroscopy
Various pharmacopoeias like IP, BP and USP are used to identify API's and to check the purity at short interval of the time which indirectly increases the productivity eg: Amylobarbitone, Betamethasone, Dexamethasone, Cyclophosphamide, Sulphalene. Assay of pharmaceutical dosage form: A few remarkable examples are codeine phosphate in tablet, aspirin-phenacetein-caffeine tablet, meprobamate in tablet have been reported [30].
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance is a division of analytical chemistry and spectroscopy which deals with the radio frequency waves which produces transitions among magnetic energy levels of nuclei of a molecule. The magnetic energy levels are created by keeping the nuclei in magnetic field. The first observation of NMR was observed and studied by Purcell and Bloch at 1945. Ethyl Alcohol was the first compound which was studied and demonstrated by this technique in 1951 [31].
When the energy in the form of radiofrequency is applied, the applied energy is equal to the precessional frequency, the adsorption of energy takes place and NMR spectrum is obtained. On increasing the strength of magnetic field it will cause raise in precessional frequency but it does not cause the transition from ground state to excited state. Without the magnetic field and radiofrequency there will be no reason to cause the formation of NMR spectrum. NMR is used for the quantitative and qualitative analysis to determine the impurities of the drug, to elucidation of natural drug products and to determination metabolites of drugs in body fluids. The enhancement or power of NMR can be increased by following ways:
- Hyper-polarization
- Two dimensional(2D)
- Three dimensional(3D) and higher dimension multifrequency techniques
- Distortionless enhancement by polarization transfer (DEPT)
- Correlation spectroscopy (COSY)
- Nuclear overhouser enhancement spectroscopy (NOESY)
Incredible natural abundance double quantum transfer experiment (INADEQUATE), and with the addition of chromatographic techniques ie hyphenated techniques [32].
Application of NMR
- Food Chemistry: It is used for the authentication of the wine aging and identification of the fatty oil's constituents in food and other beverages.
- Clinical application: It is used for the identification and studies of metabolites in biological fluids in vivo or in vitro and used for diagnosis and helpful in treatment of diseases [33].
- Study of the Hydrogen Bonding: Hydrogen bonds in the metal chelates as well as in organic compounds can be determined by this technique. Hydrogen bonding results in the decrease in the electron shield protons and signal is shifted towards low field.
- Impurity profiling of the pharmaceuticals: NMR play has an important role in the impurity profiling of pharmaceuticals (Table 5).
Drugs
Impurity
References
Heparin
Galactosamine
[34]
Fluticasone propionate
Monomeric or dimeric impurity
[35]
Ropivacaine hydrochloride
Drug associated impurity
[36]
Anastrozole
Degradation associated impurity
[37]
Table 5: Simultaneous estimation of drugs in presence of impurity by NMR spectroscopy.
Mass Spectrometry
In mass spectroscopy the compound or a complex molecule is ionized, the ions are separated on the basis of their mass/charge ratio, and the number of ions generated during the ionization represents mass/charge unit which is recorded as the spectrum. Commonly electron impact mode is applied for bombarding the molecules in vapour phase with high energy electron beam and records as a spectrum of positive ions, which have been separated on the basis of mass/charge [38]. Some important features of mass spectroscopy are such as (i) small quantity of sample is used in this process which is ionized by the ion source which generally produces cations; (ii) the mass analyzers used in the mass spectrometer separate ions according to their mass to charge ratio; (iii) the ions which are formed are detected by the detector and displayed, which is called mass spectrum.
Advantages of mass spectrometry
- It is highly sensitive and accurate technique.
- Small amount of sample is required from nanogram to microgram can be analyzed.
- Resolution time is up to high extent.
- Highly specific due to fragmentation and helps in study of structure.
Disadvantages of mass spectrometry
- Sample recovery cannot be achieved due to destructive nature of the process.
- Very costly and required high maintenance.
Introduction of sample is difficult due to small sample size [29].
Application of mass spectrometry
- Determination of molecular mass of the compounds: peak having highest m/e ratio shows the molecular mass of the compound
- Characterization of polymers: Determination of polymers and elucidation of polymer structure can be done by this technique. The structure of the polymer can be distinguished on the basis of arrangement of atoms.
- Impurity profiling in pharmaceuticals by Mass spectrometers: Mass spectrometry is the finest and latest technique used for the detection of impurities in the complex compounds. If the molecular weights of the impurities are larger than major components their detection is easier due to their higher mass peaks which are free from major constituents. For example: i) Determination of impurity (toxic elements) in Hydroxyapatite [39]; ii) Determination of impurity (Anhydro-simvastatin, Simvastatin dimer) in Simvastatin [40].
- Mass spectrometry is also used for the analysis of simple or complex proteomes using quantitative mass spectrometry [41].
- Analytical biological quantitative estimation: Quantitative analysis of antiretroviral drugs (Ritonavir. Saquinavir, Amprenavir, Indinavir, Nelfinavir, Tipranavir, Carbamazepine. As internal standard, carbamazepine for nevirapine, indinavir for amprenavir, lopinavir for tipranavir, indinavir for nelfinavir, saquinavir for ritonavir, nelfinavir for indinavir, and tipranavir for lopinavir were used) in lysates of peripheral blood mononuclear cells using MALDI-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry have been reported [42].
Chromatography
Chromatography is moderately a new technique which was developed by M. Tswett, a botanist in 1906 in Warsaw. In that year he was successful in elucidating chlorophyll, xanthophylls and several other colored substances from vegetable extracts through a column of calcium carbonate. The calcium carbonate act as an adsorbent and other various dissimilar substances get adsorbed to different extent and give rise to colored bands at different positions on the column. Tswett named this system of colored bands as the Chromatogram and the method as Chromatography after the Greek words chroma and graphos meaning "color" and "writing" respectively. In 1930's chromatography in the form of TLC and Ion Exchange chromatography was introduced as separation techniques. In 1941, Martin and Synge introduced Partition and Paper chromatography. They introduce Gas chromatography in 1952.
Chromatography is a non-destructive method from which multi component can be derived and separated chromatography is the most important single analytical technique used today and will most expected continue to be so far for the predictable future. It is the foundation stone of molecular and pharmaceutical analytical chemistry and recently it is coupled with atomic absorption and Mass spectroscopy which has extended its application in the world pharmaceutical analysis.. Various chromatographic techniques have been used for simultaneous estimation of API's or pharmaceutical dosage forms such as (i) Paper chromatography; (ii) High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC); (iii) Thin layer chromatography (TLC); (iv) High performance liquid chromatography (HPTLC); (v) Gas chromatography (GC ); (vi) Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UPLC); (vii) Column chromatography.
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
Chromatography is the most commonly used analytical technique in pharmaceutical analysis. The technique is used by the chemists to separate and determine species in variety of organic, inorganic, and biological materials [26]. HPLC has been around for about 35years and it is the major separation technique use. HPLC is one of the best method of choice for analyzing various varieties of natural and synthetic compounds [43]. Various types of HPLC's have been used for simultaneous estimations e.g. normal phase HPLC, reversed phase HPLC, size exclusion HPLC, ion-exchange HPLC, bio-affinity HPLC.
In case of normal phase HPLC, the stationary phase is polar and mobile phase is non polar. Adsorption extends with increase in polarity, and the interaction with polar analyte and polar stationary phase increases the elution time [44]. Few drugs enlisted in Table 6 which is simultaneously estimated by normal phase HPLC.
Drugs
Mobile phase
References
Drotaverine hydrochloride and Omperazole
n-heptane: Dichloromethane: Methanolic Ammonia (5%) : MeOH(50:25:1:4) v/v/v
[45]
Benzoyl peroxide and Benzoic Acid
MeOH : water (65:35) v/v
[46]
Tocopherols and Tocotrienols
Hexane : 1,4-dioxane (95.5:4.5) v/v
[47]
Table 6: Simultaneous estimation of drugs by normal phase HPLC.
Furthermore, RP-HPLC is opposite to normal phase HPLC. The polarities of the mobile and stationary phase are reversed. It is the most popular mode of liquid chromatography. Almost 90% of all analysis of low molecular weight sample is carried out using RPHPLC [48] (Table 7).
Drugs
Mobile phase
References
Aceclofenac and Paracetamol
MeOH and water (70:30) v/v
[49]
Losartan potassium and Amlodipine besylate
0.02% Triethylamine in water: ACN (60:40)v/v
[50]
Naproxen and Esomeprazole
Part A: Mixing buffer, ACN and MeOH in the ratio of (70:20:10) v/v/v
Part B: Mixing buffer, ACN in the ratio of (20:80) v/v
Buffer is prepared by dissolving 0.71 g (0.005M) of sodium perchlorate in 1000 mL of water, added with 5 mL of N-butyl amine. The pH of the buffer is adjusted to pH to 8.7 using diluted solution of Perchloric acid.
[51]
Paracetamol and Etroricoxib
MeOH : ACN: Phosphate buffer (40:20:40)v/v
[52]
Cefixime and Cloxacilin
Phosphate buffer : ACN: MeOH (80:17:3)v/v
[53]
Metoprolol and Hydrochlorothiazide
Di-sodium hydrogen phosphate: MeOH: ACN (525:225:250) v/v
[54]
Chlorpheniramine Maleate and Phenylephrine
ACN: Phosphate buffer (55:45) v/v
[55]
Lansoprazole and Domperidone
ACN and MeOH (81:19) v/v
[56]
Ambroxal hydrochloride and Loratidine
ACN and Ammonium acetate (50:50) v/v
[57]
Table 7: List of few drugs estimated simultaneously by RP-HPLC.
Size Exclusion HPLC
Size exclusion or Gel chromatography is one of the latest types of the liquid chromatographic procedures. It is the most potent technique that is particularly applicable to high molecular-weight species [58]. It separates biomolecules on the basis of true size difference; small molecules of analyte can enter the pores of gel without difficulty and therefore spend more time in these pores escalating their retention time. On the other hand, large analyte spend little time in the pores and elute quickly [59].
Ion-exchange HPLC
In ion exchange chromatography, the stationary phase is ion exchange resin and ions of the opposite charge are electro statically attached to the surface of the resin. When the mobile phase is passed through resin, the electro statically bound ions are free as other ions which are bounded preferentially. This technique involves the exchange equilibria between ions in solution and ions of like sign on the resin [60] (Table 8).
Analyte
Column
Eluent
Detection
Method
References
Amikacin
Anion Exchanger
0.115 N NaOH
PAD
Assay
[61]
Bethinicol chloride injection
Weak cation Exchanger
20 mM CH3SO3H
NS,CD
Assay
[61]
Erythromycin
Cation Exchanger
Mixture of ACN, NaOH and water
PAD
Assay
[61]
Kanamycin sulfate
Anion Exchanger
0.115 N NaOH
PAD
Assay
[61]
Fenoldopam
Anion Exchanger
2.8mM NaHCO3 + 2.2mM Na2CO3+ 0.8mM 4-cyanophenol+2% ACN
NS,CD
Assay
[61]
Paracetamol
Waters IC-PAK A HR
5 mM LiOH in 5% ACN at 1mL/min
UV at 300nm
Quantitation in solid dosage form
[62]
Oxytetracycline,
tetracycline,
chlortetracycline,
doxycycline.
Dionex OmniPac PCX 100 (250 × 4mm)
0.2M HCL in ~28% ACN at 1 mL/min
Direct UV at 300 nm
Method developed for primarily residual testing
[63]
Caffeine, Theobromine, Theophylline
DionexHPLC-CS3(cationic coloumn)
Dionex OmniPac PAX-100(anionic)
100mM HCL at1mL/min(cation)
15mM KOH in 1% ACN at 1mL/min
Direct UV at 274nm
Quantitation in injections and tablets .
[64]
Flucloxacillin and Amoxicillin
Zorbax 300-SCX (Agilent)
250×4.6 mm, 5µm particles
0.025M ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (pH 2.6)-ACN (95/5) at 1.5mL/min
UV at 225nm
Used in QC test in pharmaceutical injection products.
[65]
Methenamine, Methenamine mandelate, Methenamine hippurate
Zorbax SCX-300(Agilent), 150×4.6 mm, 5µm
ACN-sodium perchlorate monohydrate (0.1M, pH05.8), 1mL/min
UV at 212nm
Assay of pharmaceutical tablets
[66]
Simultaneous determination of chloride, bromide and iodide in food stuff .
Anion-Exchange resin column (0.6 cm × 13 cm)
4.0 mM Na2CO3 with flow rate of 0.70mL/min
Optical detector
Simultaneous Estimation
[67]
Table 8: Pharmaceutical compounds estimated by Ion-exchange chromatography.
Bio Affinity HPLC
Affinity chromatography is a precious tool in areas such as biochemistry, pharmaceutical science, clinical chemistry, and environmental testing, where it has been used for both the purification and analysis of compounds in complex sample mixtures. Affinity chromatography is a liquid chromatographic technique that uses a "biologically related" agent as a stationary phase for the purification or analysis of pharmaceutical components. The method of analysis is usually based on the same types of specific, reversible interactions and reactions that are initiated in biological system, such as the binding of an enzyme with a substrate or an antibody with an antigen. These interactions are exploited in affinity chromatography by immobilizing (or adsorbing) one of a pair of molecules on to a solid support which is called as a stationary phase. This immobilized molecule provides the site for binding to particular compounds in a sample [68].
Thin Layer Chromatography
In 1958, Stahl demonstrated purpose and use of TLC in analysis, a method based on adsorption chromatography. Presently TLC is an important analytical tool for the qualitative and quantitative analysis, of number of natural as well as synthetic products. The TLC technique is very important tool in analysis of alkaloids, glycosides, isoprenoids, lipid components, sugars and derivatives and practically all bio constituents.. In TLC sample is spotted on the plate with micropipette and the chromatogram is developed by placing the bottom of the plate or strip. The solvent or the mobile phase is drawn up by the phenomenon of capillary action, and the sample components move up the plate at different rates, depending on their solubility and their degree of affinity towards mobile phase. The spots will generally move at certain fraction of the rate at which the solvent moves, and they are characterized by the Rf value: Rf = distance solute moves /distance solvent from moves [69] TLC plays important role in the analysis of different groups of drugs. The last few years shows that interest in TLC application in pharmaceutical analysis has increased with improvements in TLC instrumentation such as TLC combined with densitometry or with MS and IR. As TLC has some advantages as comparison to HPLC and GC methods are absence of UV activity or when absence of volatility in compounds, TLC is cheap equipment and easy to work in comparison to HPLC and GC and allows parallel separation and quantitative determination of many samples at the same time [70]. The application of TLC has been limited due to low sensitivity and does not appropriate for volatile compounds. Mainly, TLC is frequently used by BP monographs as part of number of identity tests performed on pure substances or used to identify the marker compounds. There are some examples of TLC based identity tests described in pharmacopoeial monographs as shown in Table 9. Various impurities present in the pharmaceutical API's can be detected by TLC. Some drugs with impurities which can be detected by TLC can be detected (Table 10).
Drug examined
Stationary phase
Mobile phase
Visualization reagent
Reference
Polymyxin B, Framycetin, and Dexamethasone
Silica gel 60 and F254 silica gel 60 plates
MeOH and MeOH-n-butanol-Ammonia (25%)-Chloroform (14:4:9:12) v/v/v/v
0.3% Ninhydrin solution
[71]
Oxo-steroids
Silicagel GF254
Chloroform: MeOH(97:3) v/v/
Dansylhydrazine was used as a prelabeling reagent.
[72]
Aceclofenac, Paracetamol, and Chlorzoxazone
Silica gel 60 F 254
Toluene:2-Propanol: Ammonia (4:4:0.4 )v/v/v
Detection at 274nm
[73]
Levamisole
Silica gel 60F254
MeOH:Toluene:Chloroform (14:36:50 )v/v/v
UV light 223nm
[74]
Table 9: List of some drugs estimated by TLC.
Drugs
Impurity
Reference
Ethambutol
2-amino butanol
[75]
Framycetin sulphate
Neamine
[75]
Norgestrel
3,17a-diethinyl-13-ethyl-3,5-gonadiene-17-ol
[75]
Clopidogrel
(+)-(S)-(o-chlorophenyl)-6,7-dihydrothieno3,2-c.pyridine-5(4H)-acetic acid
[76]
Table 10: Impurity profiling by TLC
Simultaneous identification of drugs: TLC provides the identification of drugs simultaneously in various pharmaceutical dosage forms which is very reliable. Some examples of the drugs which are identified by TLC method are described in Table 11.
Drug
Dosage Form
Stationary phase
Mobile phase
Identification
References
Clotrimazole, Miconazole, and Ketoconazole
Creams and Ointments
Silica gel F254
n- hexane: Chloroform: MeOH: Diethylamine (50:40:10:1) v/v
By UV at 220nm
[77]
Neomycin sulfate, Polymixin B sulfate, Zinc bacytracin and Methyl and Propyl hydroxybenzoates
Opthalmic Ointment
Silica gel
MeOH:n-butanol: Ammonia 25%-Chloroform (14:4:9:12)v/v/v/v for determination of antibiotics and n-pentane:Glacial Acetic Acid (66:9)v/v for methyl and propyl hydroxybenzoates.
Antibiotic were identified by using ninhydrin ethanol solution, while densitometric measurements were made at ?=550nm. Hydroxy benzoates were identified by UV measurements at ?=260 nm
[78]
Atorvastatin calcium and Fenofibrate
Pharmaceutical Dosage form
Silica gel 60 F254
Toluene:MeOH:Triethylamine (7:3:0.2 v/v
densitometrically at 258 nm
[79]
Table 11: Simultaneous Identification of Drugs by TLC.
Determination of the amino acids: Various amino acids can be detected by application of TLC. Various amino acids which are detected by TLC are Glycine, Alanine, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Serine, Threonine, Aspartic acid, Aspargine, Glutamic acid, Glutamine, Lysine, Histidine, Arginine, Phenylalanine, Tyrosine, Tryptophan, Cysteine, cystine, Methionine, Proline and Hydroxy Proline [80] and analysis of essential constituents of food by TLC (Table 12)
Food sample
Analyte determined
Stationary phase
Mobile phase
Determination
Refernces
Green salad
Ascorbic Acid
Silica Gel F254
Ethanol:1.0% acetic Acid(9:1) v/v
By UV at 254 nm
[81]
Potatoes
Vitamin C
Kiesel gel-G
Oxalic acid, MeOH, Chloroform (2gm:20:60)
UV radiation
[82]
Fish Liver
Vitamin A
Alumina
Cyclohexane
Molybdophosphoric acid
[82]
Vegetable oils
VitaminE
Kiesel gel-G
Dichloromethane, trichloroethylene
sbCl2
2,2-bipyridyl Fecl3
[82]
Coca butter
Triglyceride
Silica impergnated by silver nitrate
Carbon tetrachloride: Chloroform: Acetic Acid and small volumes of ethanol (60:40:0.5) v/v/v
0.2% Ethanolic solution of dibromo-R-fluorescein
[83]
Ziziphusmauritiana
Sugar
Silica gel
Butanol: Water : Acetic Acid (55:30:15) v/v/v
Visulaized under UV the sprayed with 80% Folin -C phenyl reagent
[84]
Table 12: Determination of various important constituents of food used on daily basis.
High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography (HPTLC)
Among the significant modern analytical tools HPTLC is a powerful analytical method equally appropriate for qualitative and quantitative analytical tasks (Table 13). HPTLC is playing important role in today pharmaceutical analytical world, not in competition to HPLC [85]. Separation may result due to adsorption or partition or by both phenomenons's depending upon the nature of adsorbents used on plates and solvents system used for development. Different aspects on HPTLC fundamentals such as qualitative and quantitative analysis have been reported such as phytochemical analysis, biomedical analysis, herbal drug quantification, analytical analysis, finger print analysis and potential for hyphenation (HPTLC-MS, HPTLC- FTIR and HPTLC-Scanning Diode Laser) have been reported [86].
Drugs
Stationary phase
Mobile phase
Detection
Reference
Valsartan and Hydrochlorothiazide
Silica gel 60F254
Chloroform : MeOH : Toluene : Glacial acetic acid (6:2:1:0.1) v/v/v/v
By UV at 260 nm.
[88]
Emtricitabine and Tenofovir
Silica gel 60F254
Chloroform: MeOH (9:1) v/v
By UV at 265nm.
[89]
Telmisartan and Ramipril
Silica gel 60F254
Acetone: Benzene : Ethyl acetate : Glacial acetic acid in the proportion of (5:3:2:0.03) v/v/v/v
Densitometrically using a UV detector at 210 & 296 nm.
[90]
Diosgenin and Levodopa
Silica gel 60F254
Toluene : Ethyl acetate: Formic acid : GAA in the ratio (2:1:1: 0.75 ) v/v
194 nm for Diosgenin and 280 nm for Levodopa using absorbance reflectance mode.
[91]
Diclofenac Sodium and Misoprostol
Silica gel 60F254
Toluene : Ethyl Acetate : Ethanol : Glacial Acetic acid (8:2:1:0.1) v/v/v/v
Densitometric evaluation of the separated zones was performed at 220 nm
[92]
Pseudoephedrine and Cetirizine
Silica gel 60F254
Ethyl Acetate : MeOH : Ammonia (7:1.5:1) v/v/v
Spectrodensitometric scanning at a wavelength of 240nm
[93]
Telmisartan and Amlodipine
Silica gel 60F254
Ethyl acetate : 1, 4 Dioxane : MeOH : 25% Ammonia (15:1.5:3:1.5) v/v/v/v
By UV detection at 323 nm.
[94]
Perindopril Erbumine and Indapamide
Silica gel 60F254
Dichloromethane : MeOH : Glacial acetic acid (9.5:0.5:0.1) v/v/v
By UV detection at 215 nm.
[95]
Atorvastatin calcium and Ezetimibe
Silica gel 60F254
Toluene: MeOH (8:2) v/v
Densitometric evaluation was performed at 240 nm
[96]
Table 13: Simultaneous estimation of drugs by HPTLC.
There are several advantages of using HPTLC for the analysis of compounds as compared to other techniques, like HPLC, spectrophotometry, titrimetry, etc. Some of the advantages of HPTLC are:
- Capability to analyze crude samples containing multicomponents.
- In this process, it is easy to separate colored compounds.
- Several samples can be divided parallel to each other on the same plate resulting in a high output, time saving, and a rapid low-cost analysis.
- Two dimensional separations of the natural as well as pharmaceutical compounds are easy to perform.
- HPTLC can combine and it can be used for different modes of evaluation, allowing identification of compounds having different light absorption characteristics or different colours.
- HPTLC method may help to minimizes exposure risk of toxic organic effluents and significantly reduces its disposal problems as a result reducing environment pollution [87] (Table13).
Gas Chromatography
Gas chromatography is a technique used for separation of mixtures into single entities by a process which lies on the redistribution of components between a stationary phase or supporting material in the form of a liquid-solid or combination of both and gaseous mobile phase. Mechanism of the GC is based on adsorption, mass distribution or size exclusion [97].
Application of GC in quantitative analysis
Assay of pharmaceuticals products: B.P., U.S pharmacopoeia and the European pharmacopoeia are based on the GC as well as on other estimation techniques for the assay of various pharmaceutical products. Some of the pharmaceutical product which are assayed or determination of related substances by the GC are mentioned below:
- Analysis of methyl testosterone and related substances in API and Tablet.
- Assay of atropine in eye drops.
- Quantification of ethanol in a formulation.
Estimation of degradation product in the pharmaceuticals or impurity profiling: GC is the only technique used for the estimation of volatile degradation products in the pharmaceutical preparations and in impurity profiling of the drugs For example
- Estimation of pivalic acid in dipivefrin.
- Dimethylanaline in bupivacaine injection.
- Determination of residual glutaraldehyde in polymeric form [26].
- Impurity profiling of cocaine [98].
Use of GC in bio analysis: Use of GC in the bio analysis of the drugs in the plasma and its metabolism increase the efficacy of this type of chromatography.
- Determination of Valproic acid in the plasma can be determined by this method.
- Quantification of bupivacaine in plasma [26].
- Measurement of isoprene solubility in water, human blood and plasma [99].
- Simultaneous determination of 3,4-Dihyroxyphenylglycol, Catecholamines and 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine in plasma [100].
Environment analysis: Use of GC-GC played important role in investigation of Oil-Sand Napthenic acid which are waste products formed during the the Oil-sand digestion and extraction processes [101].
Simultaneous estimation by GC: Simultaneous estimation of the pharmaceutical formulations can be done by this technique which provides the use of less time and increase in the sensitivity. For example:
Simultaneous estimation Miconazole Nitrate and Metronidazole in Different Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms [102].
Simultaneous estimation of the amino acids in the food suppliments [103].
Simultaneous estimation of Turpentine oil, Chlorbutol, Para- Dichlorobenezene and Benzocaine [104].
Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography
Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) has marked a radical and outstanding change through opening new doors intended for analyst to fetch rapid analytical separation techniques without sacrificing high-quality results obtain former from high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The principle is based on the principal of use of stationary phase consisting of particles less than 2μm while HPLC columns are typically filled with particles of 3 to 5μm. The underlying principles of this evaluation are governed by the Van Deemter equation, which is an empirical formula that describes the relationship between linear velocities (flow rate) and plate height (HETP or column efficiency) [105].
The potential of UPLC is to get better analysis of the samples that are encountered during pharmaceutical development and manufacturing. UPLC generated higher separating efficiencies through the make use of smaller diameter particle packing and higher operating pressures. A commercial system competent of generating much higher pressures than used in standard HPLC has been evaluated to determine its potential in routine analysis. UPLC has been shown to generate high peak capacities in short times and this is found to be quite beneficial in analyzing the complex mixtures that comprise metabolism samples. The application of UPLC resulted in the detection of additional drug metabolites, improved the spectrum quality and separation efficiency [106]. UPLC is one of the advantageous analytical techniques in less run time, high sensitivity, high resolution; faster analysis due to fine particle size, cost effective, less solvent consuming and real time analysis is possible with the manufacturing processes in pharmaceutical industries as well as in research programs. But it has some restrictions also such as increased pressure requires for high maintenance, less column life [107] and non regenerable phases of size 1.7μm [108] (Table 14).
Drugs
Mobile phase
Detection
Reference
Abacavir Sulphate and Lamivivudine
Triethylamine phosphate buffer (pH 2.5) and MeOH (50:50%) v/v
UV detection at 230 nm
[109]
Aspirin and Dipyidamole
Triethylamine phosphate buffer (pH 2.5) and MeOH (50:50) v/v
UV detection at 230 nm
[110]
Losartan potassium, Atenolol and Hydrochlorothiazide
Water : ACN : Triethyl amine: Ortho phosphoric Acid (60:40:0.1:0.1) v/v/v/v
UV detection at 225 nm
[111]
Ceftriaxone and sulbactum injection
0.05M Sodium di-hydrogen ortho-phosphate dehydrate : ACN (86:14) v/v
PDA detection at 254 nm and 195 nm
[112]
Bambuterol Hydrochloride and Montelukast
0.025 % TFA in water as aqueous and 0.025% TFA in ACN as organic solvent
PDA detection at 210 nm
[113]
Impurities in Telmisartan and Chlorthalidone
The mobile phase A consists pH 4.5 buffer & ACN in the ratio 90:10 (v/v). Mobile phase B consists pH 4.5 buffers & ACN in the ratio 20:80 v/v
Detection at 290 nm
[114]
Metformin and pioglitazone
0.2% Triethylamine in water: ACN (70:30) v/v ph adjusted with orthophosphoric acid .
Detection at 243 nm
[115]
Thiocolchicoside and Aceclofenac
5% ammonium acetate buffer and MeOH in the ratio of (40:60) v/v
PDA detection at 276 nm
[116]
Vitamins, caffeine and
Preservatives
The mobile phase consisting of A : buffer (0.1% Trifluoro acetic acid in water) and B : a mixture of 50% ACN and 50% MeOH with a timed gradient programme
Detection at 200, 254, and 290 nm
[117]
Table 14: Application of UPLC in simultaneous estimation.
Hyphenated Techniques
A hyphenated technique is combination or coupling of two different analytical techniques with the help of proper or various interfaces. The word Hyphenated technique comes from the combination of separation-separation, separation-identification and identification-identification techniques. The term "hyphenation" was first adapted by Hirschfield in 1980 to describe a possible combination of two or more instrumental analytical techniques in a single run. The main objective of coupling of different analytical techniques to obtain an information-rich detection for both identification and quantification compared to that with a single analytical technique [118].
Hyphenated technique is usually comprised of separation and detection technique which are coupled to give a new technique. The use of hyphenated technique provides the high degree of assurance for the pharmaceutical estimation and impurity profiling (Figure 2).
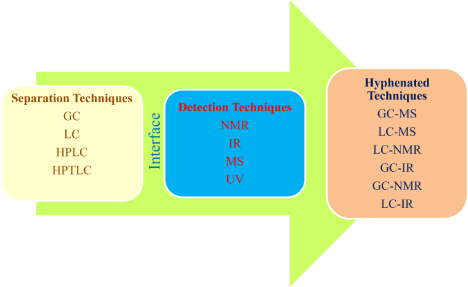
Figure 2: Diagram representing coupling of two techniques using different interfaces.
GC-MS
This hyphenated technique developed from the coupling of GC and MS, was the first of its type to become functional for research and development purposes. Mass spectra obtained from this hyphenated technique presents more structural information based on the interpretation of fragmentations. Compounds that can be easily volatile, small, and stable in high temperature in GC conditions can be easily analyzed by GC-MS. The most common derivatization technique is the conversion of the analyte to its trimethylsilyl derivative which provides the accurate and precise results.
LC-IR
The hyphenated technique is a coupling of an LC and IR or FTIR and is known as LC-IR or HPLC-IR. While HPLC is one of the most dominant separation techniques available today, the IR or FTIR is a useful spectroscopic technique for the identification of organic compounds, because the mid-IR region provides maximum possibilities of functional groups e.g., -OH, -COOH, and so on. However, combination of HPLC and IR is difficult and the evolution in this hyphenated technique is extremely slow because of large number of bands of the mobile phases thus it is difficult to understand the small signal generated by the sample components [119].
LC-MS
Hyphenated techniques LC-MS or HPLC-MS is composed of an LC (Liquid chromatography) with a mass spectrometer (MS). The information obtained from a single LC-MS run, on the structure of the compound is limited in use because the ionization techniques used in this technique are soft ionization techniques which present the molecular ion species with only a few fragment ion. Hyphenated techniques such as HPLC coupled with UV and Mass spectrometry (LC-UV-MS) has been proved to be more useful in biological screening for rapid survey of natural products [120].
LC-NMR
The on-line coupling of high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) principles to high-resolution NMR spectrometers offers a powerful tool for analyzing and characterizing complex chemical mixtures without the need of chemical separation. LC-NMR promises to be of great value in the analysis of complex compounds of all types, particularly the analysis of natural products and drugrelated metabolites in biofluids. The major advancement have been made in LC-NMR technology, a strong case can be made that HPLC purification of metabolites followed by conventional tube NMR is equally useful and may provide results in very less time and show very high sensitivity [121]. Hyphenated techniques provide the high degree of word for the compounds purity and impurity (Table 15).
Drug
Impurity
Techniques
Reference
Quetiapine
Degredation impurities
LC-MS/MS
[122]
Lopinavir
Methanesulfonate and Ethyl Methanesulfonate
LC-MS/MS
[123]
Acyclovir
Drug associated impurity
LC-MS
[124]
Irbesartan
Degredation impurity
LC-NMR
[125]
N-acetylcysteine
Cysteine, cystine, N,N-diacytylcysteine
LC-UV-MS
[126]
Triton
1,4-dioxane
GC-MS
[127]
Selenium
Elemental impurities
ICP-MS
[128]
Table 15: Impurity profiling of some compounds by hyphenated techniques.
Simultaneous Estimation by Hyphenated Techniques
Use of hyphenated techniques in the pharmaceuticals, environmental sciences and study of pharmacokinetic parameters by simultaneous estimation played an important role. Few examples of the various hyphenated techniques which are reported and their role in different fields are enlisted below.
Simultaneous determination of opiates, cocaine and major metabolites of cocaine in human hair by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) [129].
Differentiation of the regioisomeric 2-, 3-, and 4-trifluoromethyl phenylpiperazines (TFMPP) by GC-IRD and GC-MS [130].
Simultaneous determination of melamine, ammelide, ammeline and cyanuric acid in milk and milk products by gas chromatographytandem mass spectrometry [131].
Rapid sensitive speciation analysis of butyl- and phenyltin compounds in water by capillary gas chromatography atomic emission spectrometry (GC-AES) after in-situ ethylation and in-liner preconcentration [132].
Investigation of the composition of Pinus peuce needle oil by GCMS and GC-GC-MS [133].
Simultaneous determination of rosuvastatin and fenofibric acid in human plasma by LC-MS/MS with electrospray ionization [134].
Identification of the major constituents of Hypericum perforatum by LC/SPE/NMR and/or LC/MS [135].
Simultaneous determination of pioglitazone and its two active metabolites in human plasma by LC/MS/MS [136].
Simultaneous Bioanalytical Techniques used in the Medical Diagnosis
The application of analytical tools in the clinical as well as in diagnostic fields is up to the mark. The bioanalytical techniques like GC-MS, HS-GC/MS, Gas chromatography-thermal conductivity are used in the diagnosis of the diseases. All these technique are noninvasive techniques and have a great potential in medical as well as in the development of medical biomedical analytical method. The various approaches of bioanalytical tools like chromatography, spectroscopy, and immunoassay have advantages in the field of narcotics and toxicology. Diseases like AIDS, Hepatitis, Acute respiratory disorders can be diagnosed by the use of analytical tools [137-139]. In future these hybrid techniques like LC-NMR, LC-MS/MS, GC-MS/MS etc can be used in field of medical and forensic science (Table 16).
Medical conditions
Analytical Techniques
Reference
Coronory heart diseases
MRI
[140]
Overdose of Barbiturate Amphetamine,Cocaine Heroine and Cannabis.
LC-MS, EIA, GC-MS, LC-MS/MS,LC-NMR, ELISA
[141-145]
Detection of cadmium, cobalt, chromium, iron, molybdenum, nickel, selenium, titanium, vanadium and zinc in blood
Neutron activation Analysis
[146]
Asphyxia
Gas chromatography-thermal conductivity
[147]
Table 16: Analytical tools used in toxicology and medical diagnosis.
Conclusion
From the above studies, it has been concluded that analytical techniques can be used successfully for the simultaneous estimation of many drug combinations as medicines which are given to the patients should be free from impurity and other interferences which can affect the therapeutic index and may show harmful effects to the patients. Above techniques are also used to elucidate and determine the structure of natural compounds. The advantages of the simultaneous estimation are fast, simple, less time consuming, accurate and sensitive for research purpose where no new method of estimation and analysis has been reported yet. This review also represents the advancement of chromatographic and spectroscopic techniques to hyphenated techniques. Hence, the simultaneous estimation of chemical entities using various analytical techniques are very much valuable for the future needs in pharmaceutical as well as other fields of investigation. Nevertheless, more expansion and advancement is needed in these techniques which will be beneficial to the analytical and bioanalytical researchers in developing strategies for new analytical method and high output results in the laboratories.
Acknowledgements
The authors express their sincere thanks to Mr. Parveen Garg (Chairman), I.S.F. College of Pharmacy, Ferozepur Road, Moga- 142001, India for providing the necessary support and motivation for this study.
References
- Siddiqui MR, AlOthman ZA, Rahman N. Analytical techniques in pharmaceutical analysis: A review. Arabian J Chem. 2013: In press.
- Rao NR, Kiran S, Prasanthi N. Pharmaceutical impurities: An overview. Indian J Pharm Edu Res. 2010; 44: 301-310.
- Chaudhary J, Jain A, Saini V. Simultaneous estimation of multicomponent formulation by UV-visible spectroscopy: An overview. Int Res J Parmacy. 2011; 2: 81-83.
- Beckett AH, Stenalake JB. Pharmaceutical Chemistry Part 2. 4 ed: CBS Publishers distributers Pvt. Ltd; 2007.
- Willard HH, Jr LLM, John.A.Dean, Frank.A.Seattle. Instrumental Method of Analysis. 7 ed: CBS Publishers and Distributors; 1988.
- Bonfilio R, De Araujo MB, Salgado HRN. Recent applications of analytical techniques for quantitative pharmaceutical analysis: a review. WSEAS Trans Bio Biomed. 2010; 7: 316-338.
- Patel KN, Patel JK, Rajput GC, Rajgor NB. Derivative spectrometry method for chemical analysis: A review. Scholars Res Lib Der Pharm Lett. 2010; 2: 139-150.
- Rivas G, Ortiz SL, Calatayud JM. Simultaneous determination of adrenaline and noradrenaline by first derivative spectrophotometry in a FIA assembly. Anal Lett. 1996; 29: 2115-2124.
- Ines Toral M, Pope S, Quintanilla S, Richter P. Simultaneous determination of amiloride and furosemide in pharmaceutical formulations by first digital derivative spectrophotometry. Int J Pharm. 2002; 249: 117-126.
- Karpinska J, Suszynska J. The spectrophotometric simultaneous determination of amitryptyline and chlorpromazine hydrochlorides in their binary mixtures. J Trace Microprobe Techniques. 2001; 19: 355-364.
- Gupta A, Kaskhedikar S. Derivative spectrophotometric estimation of amoxycillin and bromhexine hydrochloride in tablets. Asian J Chem. 2003; 15: 977-980.
- Acar N, Onur F. Spectrophotometric simultaneous analysis of analgin-adamon mixture in injection preparations. Anal Lett. 1996; 29: 763-773.
- Erk N, Onur F. Spectrophotometric simultaneous determination of analgin and hyoscine N-butyl bromide in sugar-coated tablets. Anal Lett. 1996; 29: 369-380.
- Sachan A, Trivedi P. Estimation of atenolol and nifedipine in multicomponent formulations by ultraviolet spectroscopy. Asian J Chem. 1999; 11: 970-974.
- Murillo JA, Lemus JM, García LF. Analysis of binary mixtures of cephalothin and cefoxitin by using first-derivative spectrophotometry. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 1996; 14: 257-266.
- Erk N, Onur F. Simultaneous determination of cilazapril and hydrochlorothiazide in tablets by spectrophotometric methods. Anal Lett. 1996; 29: 1963-1974.
- Dinç E, Onur F. Application of derivative and ratio spectra derivative spectrophotometry for the determination of pseudoephedrine hydrochloride and acrivastine in capsules. Anal Lett. 1997; 30: 1179-1191.
- Morelli B. Derivative spectrophotometry in the analysis of mixtures of cefotaxime sodium and cefadroxil monohydrate. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2003; 32: 257-267.
- Patel P, Marolia B, Shah S, Shah D. Second order derivative spectrophotometric method for simultaneous estimation of telmisartan and metoprolol in tablet dosage form. Int Res J Pharmacy. 2012; 3: 259-262.
- Alvi Shahabuddin N Patel, Mehul N Kathiriya PBP, Bhavna A Parmar, J S. Simultaneous determination of Prasugrel and Aspirin by second order and ratio first order derivative ultraviolet spectrophotometry. J Spectro. 2013; 2013: 1-7.
- Shah DA, Suthar DJ, Nagda CD, Chhalotiya UK, Bhatt KK. Estimation of ibuprofen and famotidine in tablets by second order derivative spectrophotometery method. Arabian J Chem. 2012: In press.
- Dhoru MM, Surani S, Mehta P. UV-Spectrophotometric methods for determination of citicoline sodium and piracetam in pharmaceutical formulation. Der Pharm Lett. 2012; 4: 1547-1552.
- Choksi V, Vasava D, Chaudhari R, Patel B, Parmar S. Method development and validation of second order derivative spectrophotometric method for simultaneous estimation of diclofenac sodium and thiocolchicoside from its pharmaceutical formulation. J Applied Pharm Sci. 2013; 3: 97-100.
- Kasture A, Ramteke M. Simultaneous UV-spectrophotometric method for the estimation of atenolol and amlodipine besylate in combined dosage form. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2006; 68: 394-396.
- Lyon RC, Lester DS, Lewis EN, Lee E, Lawrence XY, Jefferson EH, et al. Near-infrared spectral imaging for quality assurance of pharmaceutical products: analysis of tablets to assess powder blend homogeneity. AAPS Pharm SciTech. 2002; 3: 1-15.
- Watson JT, Sparkman OD. Introduction to mass spectrometry: instrumentation, applications, and strategies for data interpretation: John Wiley & Sons; 2007.
- Chieng N, Rades T, Aaltonen J. An overview of recent studies on the analysis of pharmaceutical polymorphs. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2011; 55: 618-644.
- Bykhovskaia M, Gelmont B, Globus T, Woolard DL, Samuels AC, Duong TH, et al. Prediction of DNA far-IR absorption spectra based on normal mode analysis. Theor Chem Acc. 2001; 106: 22-27.
- Gurdeep.K.Chatwal, Sham.K.Ananad. Instrumental Method of Chemical Analysis. 6 ed: Himalaya Publishing House; 2004.
- Parke T, Ribley A, Kennedy E, Hilty W. Infrared Analysis of Pharmaceutical Products. Analytical Chemistry. 1951; 23: 953-957.
- Gerothanassis IP, Troganis A, Exarchou V, Barbarossou K. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy: basic principles and phenomena, and their applications to chemistry, biology and medicine. Chem Edu Res Practice. 2002; 3: 229-252.
- Kamboj S, Kamboj N, K Rawal R, Thakkar A, R Bhardwaj T. A Compendium of Techniques for the Analysis of Pharmaceutical Impurities. Curr Pharm Anal. 2014; 10: 145-160.
- Evanochko WT, Ng TC, Glickson JD. Application of in vivo NMR spectroscopy to cancer. Magn Reson Med. 1984; 1: 508-534.
- Beni S, Limtiaco JF, Larive CK. Analysis and characterization of heparin impurities. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011; 399: 527-539.
- Mistry N, Ismail IM, Duncan Farrant R, Liu M, Nicholson JK, Lindon JC. Impurity profiling in bulk pharmaceutical batches using 19F NMR spectroscopy and distinction between monomeric and dimeric impurities by NMR-based diffusion measurements. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 1999; 19: 511-517.
- Parmar K, Mahato A, Patel R, Prajapati S. Quantitative application of NMR in ropivacaine hydrochloride and its related impurity-A with correlation by alternate techniques. Int J ChemTech Res. 2013; 5: 312-321.
- Sitaram C, Rupakula R, Reddy BN. Determination and characterization of degradation products of anastrozole by LC-MS/MS and NMR spectroscopy. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2011; 56: 962-968.
- Silverstein R, Webster F. Spectrometric identification of organic compounds: John Wiley & Sons; 2005.
- Steblevskii A, Berlyand A, Alikhanyan A, Prokopov A. Determining impurity elements in hydroxyapatite by laser mass spectrometry. Pharm Chem J. 2011; 45: 299-301.
- Reddy GV, Kumar AP, Reddy BV, Sreeramulu J. Application of ion-trap mass spectrometry for identification and structural determination of an unknown impurity in simvastatin. Pharmazie. 2009; 64: 638-641.
- Bantscheff M, Schirle M, Sweetman G, Rick J, Kuster B. Quantitative mass spectrometry in proteomics: a critical review. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2007; 389: 1017-1031.
- Kampen JJAV. Mass spectrometry to dtermine intracellular concentration of antiretroviral drugs: From chemistry to clinical application: Optima Grafi sche Communicatie, Rotterdam, The Netherlands; 2009.
- Arya V, Bhardwaj A, Sharma V. HPLC: a versatile chromatographic approach used for qualitative and quantitative purposes-A review. 2011; 2: 298-307.
- Bansal V. High performance liquid chromatography: a short review. J Global Pharma Tech. 2010; 2
- Topagi KS, Jeswani RM, Sinha PK, Damle MC. A validated normal phase HPLC method for simultaneous determination of drotaverine hydrochloride and omeprazole in pharmaceutical formulation. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. 2010; 3: 20-24.
- Hamdu HH. An isocratic normal-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the simultaneous determination of benzoyl peroxide and benzoic acid in one pharmaceutical preparation and their stability in different solvents. IOSR J Pharmacy Bio Sci. 2014; 9: 4-12.
- Amaral JS, Casal S, Torres D, Seabra RM, Oliveira BP. Simultaneous determination of tocopherols and tocotrienols in hazelnuts by a normal phase liquid chromatographic method. Anal Sci. 2005; 21: 1545-1548.
- Kazakevich Y, LoBrrutto R. HPLC for Pharamceutical Scientists: A John Wiley and Sons INC Publications1; 2007.
- Godse V, Deodhar M, Bhosale A, Sonawane R, Sakpal P, Borkar D, et al. Reverse phase HPLC method for determination of aceclofenac and paracetamol in tablet dosage form. Asian J Res Chem. 2009; 2: 37-40.
- Patil PR, Rakesh SU, Dhabale P, Burade K. RP-HPLC method for simultaneous estimation of losartan potassium and amlodipine besylate in tablet formulation. Int J Chem Tech Res. 2009; 1: 464-469.
- Reddy PS, Sait S, Vasudevmurthy G, Vishwanath B, Prasad V, Reddy SJ. Stability indicating simultaneous estimation of assay method for naproxen and esomeprazole in pharmaceutical formulations by RP-HPLC. Der Pharma Chemica. 2011; 3: 553-564.
- Pattan S, Jamdar S, Godge R, Dighe N, Daithankar A, Nirmal S, et al. RP-HPLC method for simultaneous estimation of paracetamol and etoricoxib from bulk and tablets. J Chem Pharm Res. 2009; 1: 329-335.
- Rathinavel G, Mukherjee P, Valarmathy J, Samueljoshua L, Ganesh M, Sivakumar T, et al. A Validated RP-HPLC method for simultaneous estimation of cefixime and cloxacillin in tablets. J Chem. 2008; 5: 648-651.
- Brijesh S, Patel D, Ghosh S. Development of reverse-phase HPLC method for simultaneous analysis of metoprolol succinate and hydrochlorothiazide in a tablet formulation. Tropical J Pharm Res. 2009; 8: 539-543.
- Maithani M, Raturi R, Gautam V, Kumar D, Chaudhary AK, Gaurav A, et al. Development and validation of a RP-HPLC method for the determination of chlorpheniramine maleate and phenylephrine in pharmaceutical dosage form. Int J Comprehen Pharm. 2010; 1: 1-4.
- Patel B, Dedania Z, Dedania R, Ramolia C, Vidya Sagar G, Mehta R. Simultaneous estimation of lansoprazole and domperidone in combined dosage form by RP-HPLC. Asian J Res Chem. 2009; 2: 210-212.
- Nagappan KV, Meyyanathan S, Raja RB, Reddy S, Jeyaprakash M, Birajdar AS, et al. RP-HPLC Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Ambroxol Hydrochloride and Loratidine in Pharmaceutical Formulation. Res J Pharm and Tech. 2008; 1: 366-369.
- Skoog D, West D, Holler F, Crouch S. Fundamentals of analytical chemistry: Cengage Learning; 2013.
- Khanvilkar V, Chitnis A, Shirode A, Kadam V. Slalom chromatography: An overview. Int J Res Pharmacy Chem. 2012; 2: 66-76.
- Chavan M, Sutar M, Deshmukh S. Significance of various chromatographic techniques in drug discovery and development. Int J Res Pharmacy Chem. 2013; 3: 282-289.
- Bhattacharyya L. Ion chromatography in biological and pharmaceutical drug analysis: USP perspectives, presented at the Intl. IC Symp Baltimore: September2002.
- Pérez JL, Bello MA. Determination of paracetamol in dosage forms by non-suppressed ion chromatography. Talanta. 1999; 48: 1199-1202.
- Ding X, Mou S. Ion chromatographic analysis of tetracyclines using polymeric column and acidic eluent. J Chromatogr A. 2000; 897: 205-214.
- Chen Q-c, Mou S-f, Hou X-p, Ni Z-m. Simultaneous determination of caffeine, theobromine and theophylline in foods and pharmaceutical preparations by using ion chromatography. Anal Chim Acta. 1998; 371: 287-296.
- Liu H, Wang H, Sunderland VB. An isocratic ion exchange HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of flucloxacillin and amoxicillin in a pharmaceutical formulation for injection. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2005; 37: 395-398.
- Pavitrapok C, Williams DA. Determination of methenamine, methenamine mandelate and methenamine hippurate in pharmaceutical preparations using ion-exchange HPLC. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2006; 40: 1243-1248.
- Yu L, ZhaNg X, Jin J, Che S, Yu L. Simultaneous Determination of Chloride, Bromide and Iodide in Foodstuffs by Low Pressure Ion-Exchange Chromatography with Visible Light Detection 2011.
- Cazes J. Encyclopedia of Chromatography: Taylor & Francis; 2004.
- Evans WC. Trease and Evans' pharmacognosy: Elsevier Health Sciences; 2009.
- Gary. D. Christian. Analytical Chemistry. 6 ed: John Wiley and Sons,INC; 2003.
- Krzek J, MaÅlanka A, Lipner P. Identification and quantitation of polymyxin B, framycetin, and dexamethasone in an ointment by using thin-layer chromatography with densitometry. J AOAC Int. 2005; 88: 1549-1554.
- Bhawani S, Sulaiman O, Hashim R, Ibrahim M. Thin-layer chromatographic analysis of steroids: A review. Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research. 2010; 9.
- Mahajan V, Bari S, Shirkhedkar A, Surana S. Simultaneous densitometric TLC analysis of aceclofenac, paracetamol, and chlorzoxazone in tablets. Acta Chromatographica. 2008; 20: 625-636.
- Asghari B, Ebrahimi SN, Mirzajani F, Aboul-Enein HY. Development and validation of a simple stability-indicating TLC method for the determination of levamisole in pharmaceutical tablet formulation. JPC-Journal of Planar Chromatography-Modern TLC. 2011; 24: 419-422.
- Bari SB, Kadam BR, Jaiswal YS, Shirkhedkar AA. Impurity profile: Significance in active pharmaceutical ingredient. Eurasian J Anal Chem. 2007; 2: 32-53.
- Antic D, Filipic S, Agbaba D. A simple and sensitive TLC method for determination of clopidogrel and its impurity SR 26334 in pharmaceutical products. Acta Chromatogr. 2007; 18: 199-206.
- Roychowdhury U, Das SK. Rapid identification and quantitation of clotrimazole, miconazole, and ketokonazole in pharmaceutical creams and ointments by thin-layer chromatography-densitometry. J AOAC Int. 1996; 79: 656-659.
- Krzek J, Starek M, Kwiecien A, Rzeszutko W. Simultaneous identification and quantitative determination of neomycin sulfate, polymixin B sulfate, zinc bacytracin and methyl and propyl hydroxybenzoates in ophthalmic ointment by TLC. Journal of pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis. 2001; 24: 629-636.
- Shirkhedkar AA, Surana SJ. Simultaneous densitometric TLC analysis of atorvastatin calcium and fenofibrate in the bulk drug and in pharmaceutical formulations. JPC-Journal of Planar Chromatography-Modern TLC. 2009; 22: 355-358.
- Sen S, Sarkar S, Kundu P, Laskar S. Separation of Amino Acids Based on Thin-Layer Chromatography by a Novel Quinazoline Based Anti-Microbial Agent. Am J Anal Chem. 2012; 3: 669-674.
- HIMESH S, K. SA, SARVESH S, NAYAK G, PRIYANKA S. Quantification of Ascorbic Acid in Salad Components. Int J Curr Pharm Res. 2012; 4: 43-47.
- Cimpoiu C, Hosu A. Thin layer chromatography for the analysis of vitamins and their derivatives. Journal of liquid chromatography & related technologies. 2007; 30: 701-728.
- Barrett C, Dallas M, Padley F. The quantitative analysis of triglyceride mixtures by thin layer chromatography on silica impregnated with silver nitrate. Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society. 1963; 40: 580-584.
- Muchuweti M, Zenda G, Ndhlala AR, Kasiyamhuru A. Sugars, organic acid and phenolic compounds of Ziziphus mauritiana fruit. European Food Research and Technology. 2005; 221: 570-574.
- Andola Harish Chandra, Kant PV. High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography (HPTLC): A modern analytical tool for biological analysis. Nat Sci. 2010; 8: 58-61.
- Bimal N, Sekhon BS. High Performance Thin layer Chromatography: Application in Pharmaceutical Science. PhTechMed. 2013; 2: 323-333.
- Shivatare RS, Nagore DH, Nipanikar SU. HPTLC an important tool in standardization of herbal medical product: A review. J Sci Innovative Res. 2013; 2: 1086-1096.
- Shah NJ, Suhagia BN, Shah RR, Patel NM. HPTLC Method for the Simultaneous Estimation of Valsartan and Hydrochlorothiazide in Tablet Dosage Form. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2009; 71: 72-74.
- Joshi M, Nikalje AP, Shahed M, Dehghan M. HPTLC Method for the Simultaneous Estimation of Emtricitabine and Tenofovir in Tablet Dosage Form. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2009; 71: 95-97.
- Patel V, Patel P, Chaudhary B, Rajgor N, Rathi S. Development and validation of hptlc method for the simultaneous estimation of telmisartan and ramipril in combined dosage form. Int J Pharm Bio Res. 2010; 1: 18-24.
- Kshirsagar V, Deokate U, Bharkad V, Khadabadi S. HPTLC method development and validation for the simultaneous estimation of diosgenin and levodopa in marketed formulation. Asian J Res Chem. 2008; 1: 36-39.
- Dhaneshwar SR, Bhusari VK. Validated HPTLC Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Diclofenac Sodium and Misoprostol in Bulk Drug and Formulation. Asi J Phar Biol Res. 2011; 1: 15-21.
- Makhija SN, Vavia PR. Stability indicating HPTLC method for the simultaneous determination of pseudoephedrine and cetirizine in pharmaceutical formulations. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2001; 25: 663-667.
- Chabukswar AR, Jagdale SC, Kumbhar S, Kadam VJ, Patil VD, Kuchekar BS, et al. Simultaneous HPTLC estimation of telmisartan and amlodipine besylate in tablet dosage form. Arch Appl Sci Res. 2010; 2: 94-100.
- Dewani MG, Bothara KG, Madgulkar AR, Damle MC. Simultaneous Estimation of perindopril erbumine and indapamide in bulk drug and tablet dosage form by HPTLC. Int J Comprehen Pharmacy. 2011; 2: 1-4.
- Dhaneshwar S, Dhaneshwar S, Deshpande P, Patil M. Development and validation of a method for simultaneous densitometric estimation of atorvastatin calcium and ezetimibe as the bulk drug and in tablet dosage forms. Acta Chromatogr. 2007; 19: 141-148.
- Indian Pharmacopoeia Ghaziabad: The Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission; 2007.
- Casale J, Waggoner R. A chromatographic impurity signature profile analysis for cocaine using capillary gas chromatography. Journal of Forensic Sciences. 1991; 36: 1312-1330.
- Mochalski P, King J, Kupferthaler A, Unterkofler K, Hinterhuber H, Amann A. Measurement of isoprene solubility in water, human blood and plasma by multiple headspace extraction gas chromatography coupled with solid phase microextraction. Journal of breath research. 2011; 5: 046010.
- Eisenhofer G, Goldstein DS, Stull R, Keiser HR, Sunderland T, Murphy DL, Kopin IJ. Simultaneous liquid-chromatographic determination of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylglycol, catecholamines, and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine in plasma, and their responses to inhibition of monoamine oxidase. Clin Chem. 1986; 32: 2030-2033.
- Pažitná A, Jánošková N, Špánik I. Multidimensional gas chromatography and its applications in food and environmental analysis. Acta Chimica Slovaca. 2013; 6: 133-140.
- Ashour S, Kattan N. Simultaneous determination of miconazole nitrate and metronidazole in different pharmaceutical dosage forms by gas chromatography and flame ionization detector (GC-FID). Int J Biomed Sci. 2010; 6: 13-18.
- Obreshkova DP, Tsvetkova DD, Ivanov KV. Simultaneous identification and determination of total content of aminoacids in food supplements-tablets by gas chromatography. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. 2012; 5: 57-68.
- Pandya S, Hamane S, Mulla T, Kambale M, Gandhi N, Vairagkar R. Simultaneous estimation of turpentine oil, chlorbutol, para-dichlorobenzene and benzocaine by capillary gas chromatography. Int J Comprehen Pharmacy. 2012; 5: 1-5.
- Seelam SC, Priyanka G, Dhanalakshmi K. Switch from HPLC to UPLC: A Novel Achievement in Liquid Chromatography Technique-A review. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res. 2013; 21: 237-246.
- Sridhar S, Divya S, Madhuri R, Sudhakar M. UPLC-A dynamic and expeditious approach to liquid chromatography. Int J Pharm Chem Bio Sci. 2013; 3: 1139-1152.
- Patil V, Tathe R, Devdhe S, Angadi S, Kale S. Ultra performance liquid chromatography: A review. Int J Pharmacy. 2011; 2: 39-44.
- Kumar A, Saini G, Nair A, Sharma R. UPLC: a preeminent technique in pharmaceutical analysis. Acta Pol Pharm. 2012; 69: 371-380.
- Sarat M, Krishna PM, Rambabu C. Development and Validation of RP-UPLC Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Abacavir Sulphate and Lamivudine in Combined Tablet Dosage Form. Development. 2012; 4: 939-944.
- Rajput A, Sonanis MC. Development and validation of a rapid RP-UPLC method for the determination of aspirin and dipyridamole in combined capsule formulation. Int J Pharmacy Pharm Sci. 2011; 3: 156-160.
- Rao DD, Satyanarayana N, Sait S, Reddy YR, Mukkanti K. Simultaneous determination of losartan potassium, atenolol and hydrochlorothiazide in pharmaceutical preparations by stability-indicating UPLC. Chromatographia. 2009; 70: 647-651.
- Patel Nirav B, Arvadiya Alpesh C, Jansari Sneha K, Mistry Vipul D, Desai Hemant T. Development and Validation of Stability Indicating Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Ceftriaxone and Sulbactam Injection using RP-UPLC Method. Development. 2012; 2: 29-37.
- Yanamandra R, Vadla CS, Puppala UM, Patro B, Murthy YL, Parimi AR. Development and Validation of a Rapid RP-UPLC Method for the Simultaneous Estimation of Bambuterol Hydrochloride and Montelukast Sodium from Tablets. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2012; 74: 116-121.
- Marineni B, Sreenivasulu Reddy T. Simultaneous Determination of Telmisartan Impurities and Chlorthalidone impurities by UPLC. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res. 2014; 26: 226-230.
- Babu S. Method development and validation of simultaneous estimation of metformin and pioglitazone in bulk and pharmaceutical formulation by UPLC. Int Res J Pharm Applied Sci. 2012; 2: 91-96.
- Balan P, Kannappan N. Development and validation of stability-indicating RP-UPLC method for simul-taneous estimation of thiocolchicoside and aceclofenac in combined dosage form. Int Curr Pharm J. 2014; 3: 296-300.
- Nagamallika G, Devi MA. A validated stability indicating rp-uplc method for simultaneous determination of water soluble vitamins, caffeine and preservatives in pharmaceutical formulations. Int J Res Pharmacy Chem. 2013; 3: 456-463.
- Phalke P, Kavade S. Review on Hyphenated Techniquoes. Int J Chem Studies. 2013; 1: 157-165.
- Joshi RR, Gupta KR, Patil SS. Hyphenated technique-a boon to analytical world. Int J Pharm Sci Res. 2012; 3: 4184-4194.
- Patel KN, Patel JK, Patel MP, Rajput GC, Patel HA. Introduction to hyphenated techniques and their applications in pharmacy. Pharm Methods. 2010; 1: 2-13.
- Sakhreliya BD, Kansara S. LC-NMR: A Powerful Tool For Analyzing And Characterizing Complex Chemical Mixtures Without The Need Of Chemical Separation. J Pharm Biosci Res. 2013; 3: 115-121.
- Stolarczyk EU, Kutner A. Use of hyphenated LC-MS/MS technique for characterization of impurity profile of quetiapine during drug development. Acta Pol Pharm. 2010; 67: 599-608.
- Kakadiya P, Reddy BP, Singh V, Ganguly S, Chandrashekhar T, Singh D. Low level determinations of methyl methanesulfonate and ethyl methanesulfonate impurities in Lopinavir and Ritonavir Active pharmaceutical ingredients by LC/MS/MS using electrospray ionization. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2011; 55: 379-384.
- Huidobro AL, Rupérez FJ, Barbas C. LC methods for acyclovir and related impurities determination. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2005; 37: 687-694.
- Shah RP, Sahu A, Singh S. Identification and characterization of degradation products of irbesartan using LC-MS/TOF, MS(n), on-line H/D exchange and LC-NMR. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2010; 51: 1037-1046.
- Toussaint B, Pitti C, Streel B, Ceccato A, Hubert P, Crommen J. Quantitative analysis of N-acetylcysteine and its pharmacopeial impurities in a pharmaceutical formulation by liquid chromatography-UV detection-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2000; 896: 191-199.
- Poss M, Couch T, Odufu A, McCann J, Mellon J, Melnick B, et al. Determination of 1,4-dioxane impurity levels in Triton X-100 raw material by gas chromatography with mass spectrometric detection. J Chromatogr Sci. 2003; 41: 410-417.
- Toda E, Hioki A. Determination of impurities in high-purity selenium by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry after matrix separation with thiourea. Anal Sci. 1995; 11: 115-118.
- Kintz P, Mangin P. Simultaneous determination of opiates, cocaine and major metabolites of cocaine in human hair by gas chromotography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS). Forensic Sci Int. 1995; 73: 93-100.
- Maher HM, Awad T, Clark CR. Differentiation of the regioisomeric 2-, 3-, and 4-trifluoromethylphenylpiperazines (TFMPP) by GC-IRD and GC-MS. Forensic Sci Int. 2009; 188: 31-39.
- Miao H, Fan S, Wu YN, Zhang L, Zhou PP, Li JG, et al. Simultaneous determination of melamine, ammelide, ammeline, and cyanuric acid in milk and milk products by gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Biomed Environ Sci. 2009; 22: 87-94.
- Ceulemans M, Lobinski R, Dirkx W, Adams F. Rapid sensitive speciation analysis of butyl-and phenyltin compounds in water by capillary gas chromatography atomic emission spectrometry (GC-AES) after in-situ ethylation and in-liner preconcentration. Fresenius' J Anal Chem. 1993; 347: 256-262.
- Hennig P, Steinborn A, Engewald W. Investigation of the composition ofPinus peuce needle oil by GC-MS and GC-GC-MS. Chromatographia. 1994; 38: 689-693.
- Trivedi RK, Kallem RR, Mullangi R, Srinivas NR. Simultaneous determination of rosuvastatin and fenofibric acid in human plasma by LC-MS/MS with electrospray ionization: Assay development, validation and application to a clinical study. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2005; 39: 661-669.
- Tatsis EC, Boeren S, Exarchou V, Troganis AN, Vervoort J, Gerothanassis IP. Identification of the major constituents of Hypericum perforatum by LC/SPE/NMR and/or LC/MS. Phytochemistry. 2007; 68: 383-393.
- Lin ZJ, Ji W, Desai-Krieger D, Shum L. Simultaneous determination of pioglitazone and its two active metabolites in human plasma by LC-MS/MS. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2003; 33: 101-108.
- Saville RD, Constantine NT, Cleghorn FR, Jack N, Bartholomew C, Edwards J, et al. Fourth-generation enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the simultaneous detection of human immunodeficiency virus antigen and antibody. Journal of clinical microbiology. 2001; 39: 2518-2524.
- Bressler AM, Nolte FS. Preclinical evaluation of two real-time, reverse transcription-PCR assays for detection of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Journal of clinical microbiology. 2004; 42: 987-991.
- Pawlotsky JM. Pathophysiology of hepatitis C virus infection and related liver disease. Trends Microbiol. 2004; 12: 96-102.
- Chughtai A, Kazerooni EA. CT and MRI of acute thoracic cardiovascular emergencies. Crit Care Clin. 2007; 23: 835-853, vii.
- Neiman J, Haapaniemi HM, Hillbom M. Neurological complications of drug abuse: pathophysiological mechanisms. Eur J Neurol. 2000; 7: 595-606.
- Rusyniak DE. Neurologic manifestations of chronic methamphetamine abuse. Neurol Clin. 2011; 29: 641-655.
- Brown E, Prager J, Lee HY, Ramsey RG. CNS complications of cocaine abuse: prevalence, pathophysiology, and neuroradiology. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1992; 159: 137-147.
- Maurer HH. Screening procedures for simultaneous detection of several drug classes used for high throughput toxicological analyses and doping control. A review. Combinatorial chemistry & high throughput screening. 2000; 3: 467-480.
- Teixeira H, Verstraete A, Proença P, Corte-Real F, Monsanto P, Vieira DN. Validated method for the simultaneous determination of ? 9-THC and ? 9-THC-COOH in oral fluid, urine and whole blood using solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry with electrospray ionization. Forensic science international. 2007; 170: 148-155.
- Lavi N, Alfassi Z. Determination of trace amounts of cadmium, cobalt, chromium, iron, molybdenum, nickel, selenium, titanium, vanadium and zinc in blood and milk by neutron activation analysis. Analyst. 1990; 115: 817-822.
- Schaff JE, Karas RP, Marinetti L. A gas chromatography-thermal conductivity detection method for helium detection in postmortem blood and tissue specimens. Journal of analytical toxicology. 2012; 36: 112-115.