
Research Article
Austin J Anal Pharm Chem. 2015; 2(4): 1048.
Design, Synthesis and Biological Screening of 2, 4- Disubstituted Quinolines
Ilango K¹*, Valentina P¹, Subhakar K¹ and Kathiravan MK¹
1Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University, Tamil Nadu, India
*Corresponding author: Ilango K, Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University, Kattankulathur, Kancheepuram Dist- 603203, Tamil Nadu, India.
Received: June 13, 2015; Accepted: September 02, 2015; Published: September 04, 2015
Abstract
A series of 2,4 disubstituted quinoline derivatives were synthesized though multi-step reactions. Aniline was reacted with benzaldehyde and pyruvic acid to form 2-Phenylquinolin-4-carboxylic acid 1 and converted to 2-Phenylquinolin- 4-carbonyl chloride 2, which on subsequent reaction with substituted amines gave 2-Phenylquinoline-4-substituted Phenylcarboxamide 3. The newly synthesized title compounds were evaluated for their antibacterial and antifungal activities against B. subtilis, K. pneumonia, E. coli, S. aureus, A. niger as well as anticancer activity. Preliminary results indicated that most of the 2,4 Diphenyl quinoline derivatives demonstrated good antibacterial and antifungalactivities. Among the newly synthesized compounds, N-2-Diphenyl quinolin-4- carboxamide 3a and N-p-Tolylquinolin-4-carboxamide 3f were found to possess maximum anticancer activity. It was concluded that two bulky aryl groups at 2 and 4 positions enhances the activity of synthesized quinoline derivatives. The compounds N-p-Tolylquinolin-4-carboxamide 3f and 2-Phenyl-N-(pyridin-2-yl) quinolin-4-carboxamide 3j were found to possess maximum activity against the tested strains of B. subtilis, K. pneumonia, E. coli, S. aureus and A. niger. It can be concluded that two bulky aryl groups at 2 and 4 positions enhances the activity of quinoline derivatives.
Keywords: 2, 4-disubstituted quinolines; Anticancer; Antibacterial; Antifungal
Introduction
Heterocyclic compounds play an important role in designing new classes of structural entities of medicinal importance with potentially new mechanisms of action. These heterocyclic compounds are well known to possess diverse pharmacological properties, viz. antimicrobial, anticancer, anticonvulsant, antimalarial activities etc. Quinoline nucleus occurs in several natural compounds and pharmacologically active substances displaying a broad range of biological activity. Quinolines exhibits wide range of activity such as antiprion [1], antimicrobial [2-5], antibacterial [6], antitubercular [7- 9] and anticancer activities [9-12]. Quinoline ring plays an important role in new anti-cancer agents development as their derivatives have shown excellent results through different mechanism of action such as growth inhibitors by cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, inhibition of angiogenesis, disruption of cell migration, and modulation of nuclear receptor responsiveness [13-15]. A review on anticancer potential of bioactive heterocyclic quinoline was published recently revealing the significance of quinoline [16]. Figure 1 illustrates promising structures of quinoline as biologically active nucleus.
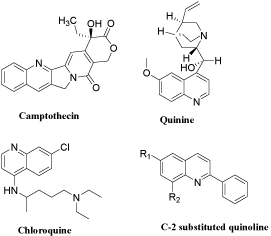
Figure 1: Promising structures of quinoline as biologically active nucleus.
Our interest was mainly focused on 2, 4-disubstituted quinolines due to its wide range of biological activities. Recently we found that C-2 quinoline derivatives possessing good antibacterial and antifungal activities. We identified structural similarities between our series of compounds and reported structures as antimicrobials [15]. So it was thought logically to screen this potential moiety for antibacterials as well as antifungal. In continuation to our ongoing work on quinoline derivatives, we here in report 2, 4-disubstituted quinolines as antimicrobials hitherto unreported.
Materials and Methods
General
Melting points of newly synthesized compounds were determined using VEEGO VMP-D. IR spectra were recorded in (KBr) on a Perkin Elmer FTIR, 1H-NMR on Bruker Avance, 400 MHz and Mass spectra on LC-MSD-Tranp-SL 2010A SHIMADZU. Purity of synthesized compounds were checked by precoated TLC aluminium sheets-silica gel 60 F254 (0.2mm).
General procedure for the synthesis of 2-Phenylquinolin- 4-substituted phenyl carboxamide (3a-3j)
Aniline (0.01mol), benzaldehyde (0.01mol) and pyruvic acid (0.01 mol) was refluxed in ethanol (20 ml) for 3 hours. The product formed was filtered and recrystallized from ethanol. 1 (0.01mol) was treated with phosphorus pentachloride (0.01 mol) and refluxed. The intermediate 2 (0.01 mol) was reacted with various amines (0.01 mol) at 10-15°C in presence of ethanol. The product was isolated by filtration and recrystallized from ethanol to yield 3a-3j (Table 1).
Sample code
Concentration
Live
cells
Dead
cells
Total cells
% Viability
% Mortality
3a
100 µg/mL
5
19
24
20.83
79.16
3b
100 µg/mL
9
15
24
39.73
61.32
3c
100 µg/mL
11
10
21
52.38
47.61
3d
100 µg/mL
10
11
21
47.61
52.38
3e
100 µg/mL
7
17
24
30.21
69.79
3f
100 µg/mL
5
16
21
23.80
76.19
3g
100 µg/mL
--
--
--
--
--
3h
100 µg/mL
6
14
20
30
70
3i
100 µg/mL
5
15
20
29.9
71.0
3j
100 µg/mL
5
11
16
31.25
68.75
Ara-c
10 µg/mL
4
21
25
7.83
92.46
Table 1: Anticancer activity-sensitivity testing 3a-3j.
Representative data: N-2-Diphenylquinolin-4-carboxamide (3a): pale white crystals; Yield 78%; mp 164-165°C; 1H-NMR δ (ppm): 7-8.0 (15H, m, Ar-H), 8.89 (1H, s, NH); FT-IR: 3311 (NH of CONH), 3060 (Ar-H), 1675 (C=O), 1599 (C=N), 1453 (C=C), 1445 (C-N) cm- 1; C22H16N2O (324.2); MS: m/z: 324 (M+), 163 (base peak), 130, 122, 114.
N-Benzyl-2-phenylquinolin-4-carboxamide (3b): white crystals; Yield 76%; mp 166-168°C; 1H-NMR δ (ppm): 4.1- 4.3 (2H, s, CH2), 7-7.9 (15H, m, Ar-H), 8.89 (1H, s, NH); FT-IR: 3311 (NH of CONH), 3060 (Ar-H), 2868 (C-H of CH2), 1675 (C=O), 1599 (C=N), 1453 (C=C), 1445 (C-N) cm-1; C23H18N2O (338.3); MS: m/z: 338 (M+), 174 (base peak), 142, 138, 130.
N-(4-Nitrophenyl)-2-phenylquinolin-4-carboxamide (3c): Pale yellow crystals; Yield 81%; mp 172-174°C; 1H-NMR δ (ppm): 7-7.9 (14H, m, Ar-H), 8.8 (1H, s, NH); FT-IR: 3311 (NH of CONH), 3060 (Ar-H), 1675 (C=O), 1599 (C=N), 1544 (Ar-NO2), 1453 (C=C), 1405 (C-N) cm-1; C22H15N3O3 (369.4); MS: m/z: 369 (M+), 184 (base peak), 142, 130, 126.
N-(3-Nitrophenyl)-2-phenylquinolin-4-carboxamide (3d): Deep brown crystals; Yield 82%; mp 176-178°C; 1H-NMR δ (ppm): 7-7.9 (14H, m, Ar-H), 8.8 (1H, s, NH); FT-IR: 3311 (NH of CONH), 3060 (Ar-H), 1675 (C=O), 1599 (C=N), 1544 (Ar-NO2), 1453 (C=C), 1405 (C-N) cm-1; C22H15N3O3 (369.4); MS: m/z: 369 (M+), 184 (base peak), 142, 130, 126.
N-(2-Nitrophenyl)-2-phenylquinolin-4-carboxamide (3e): Yellow crystals; Yield 74%; mp 178-180°C; 1H-NMR δ (ppm): 7-7.9 (14H, m, Ar-H), 8.8 (1H, s, NH); FT-IR: 3311 (NH of CONH), 3060 (Ar-H), 1675 (C=O), 1599 (C=N), 1544 (Ar-NO2), 1453 (C=C), 1405 (C-N) cm-1; C22H15N3O3 (369.4); MS: m/z: 369 (M+), 184 (base peak), 142, 130, 126.
2-Phenyl-N-p-tolylquinolin-4-carboxamide (3f): Yellow brown crystals; Yield 76%; mp 178-180°C; 1H-NMR δ (ppm): 2.5-2.7 (3H, s, CH3), 7-7.9 (14H, m, Ar-H), 8.8 (1H, s, NH); FT-IR: 3311 (NH of CONH), 3060 (Ar-H), 2916 (C-H of CH3), 1673 (C=O), 1599 (C=N), 1455 (C=C), 1406 (C-N) cm-1; C23H18N2O (338.2); MS: m/z: 338 (M+), 174 (base peak), 138, 120, 116.
Biological experiments
The newly synthesized compounds 3a-j were screened for antibacterial activity against freshly cultured strains of E. coli (EC), S. aureus (SA), K. pneumonia (KP) and B. subtilis (BS) using sterile nutrient agar media and antifungal activity against of A. niger (AN) using Sabeuraud’s agar medium. Disk diffusion method was used at a concentration of 3mg per mL using DMF as solvent. The results were recorded in duplicate using ciprofloxacin and ketoconazole at a concentration of 1 mg per mL as standards. The target compounds 3a-3j were screened for anticancer activity by Tryphan blue dye exclusion technique.
Results and Discussion
Chemistry
2-Phenylquinolin-4-carboxylic acid 1 was prepared by the reaction of aniline, benzaldehyde and pyruvic acid in ethanol under reflux condition. The aniline underwent nucleophilic addition across the carbonyl carbon of benzaldehye and resulted in the formation of imine, which on reaction with pyruvic acid formed 1. The acid function of 1 was converted into acid chloride by reacting it with phosphorus pentachloride forming 2-Phenylquinolin-4-carbonyl chloride 2. The active acid chloride was treated with variety of aromatic amines to yield the target compounds 2-Phenylquinolin-4- aryl substituted carboxamide 3a-3j (scheme-1). The aromatic amines were bearing EDG, EWG, Benzyl, Pyridyl, as well as halogen atoms such as Cl and Br.
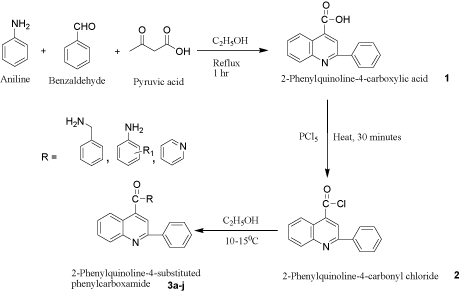
Scheme 1: Synthesis of 2-phenylquinolin-4-arylsubstituted carboxamide derivatives (3a-3j).
Biological activity
The newly synthesized compounds 3a-3j were screened for anticancer activity by Tryphan blue dye exclusion technique. The viable tumor cell count (tryphan blue test) was carried out with Neubauer Heamocytometer. Equal volume of cells (20μL) and equal volume (20 μL) of tryphan blue solution and the cells are carried in modified Neubauer’s chamber. Dead cells are stained with blue while live cells are unstained, followed by determination of percentage viablity and percentage mortality. The results were recorded in duplicate using Ara-c at a concentration of 10 μg per ml as standards. Among newly tested (Cytarabine) compounds, nine compounds showed % mortality above 50. However three compounds 3a, 3f and 3i were found to have 70 % mortality when compared with Ara-c against the tumour cells. All the newly tested compounds showed antibacterial and antifungal activities. Among newly synthesized derivatives, compounds 3f and 3j were found to possess good antibacterial and antifungal activities when tested against E. coli, S. aureus, B. subtilis, K. pneumonia and A. niger (Table 2).
Compound
code
Zone of inhibition in mm
Antibacterial activity
Antifungal activity
E. coli
S. aureus
B. subtilis,
K. pneumonia
A. niger
3a
16
16
16
16
18
3b
17
17
15
17
16
3c
18
18
16
15
15
3d
16
16
17
16
18
3e
17
18
16
15
16
3f
18
16
14
15
15
3g
16
17
15
16
14
3h
16
17
15
16
14
3i
15
17
17
18
16
3j
18
17
18
19
18
Ciprofloxacin
22
24
22
22
--
Ketoconazole
--
--
--
--
24
Table 2: Antimicrobial activity-sensitivity testing of 3a-3j.
Conclusions
From the result of anticancer testing the compounds 3a-3j, it can be concluded that the incorporation of two bulky aryl groups at 2 and 4 positions plays an important role in activity. The incorporation of amido group in quinoline derivatives enhanced their anticancer and antimicrobial activities. The presence of electron donating and electron withdrawing groups on the two aryl rings did not make any significant difference in their activity. However three compounds showed good potency 3a, 3f and 3j. Further studies to acquire more information about structure activity relationship are in progress in our laboratory.
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to The Management, SRM University Kattankulathur, for providing facilities to carry out this work.
References
- Cope H, Mutter R, Heal W, Pascoe C, Brown P, Pratt S, et al. Synthesis and SAR study of acridine, 2-methylquinoline and 2-phenylquinazoline analogues as anti-prion agents. Eur J Med Chem. 2006; 41: 1124-1143.
- Mamladesai SN, Katagi MS, Khare PV, Maddi VS, Bhat AR. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of 4-hydroxy-1-metnyl/phenyl-3-substituted quinolin-2-(1H)-ones. Indian J. Hetero. Chem. 2008; 17: 381-382.
- Kamel Metwally A, Lobna Abdel-Aziz M, El-Sayed Lashine M, Mohamed Husseiny I, Rania Badawy H. Hydrazones of 2-aryl-quinoline-4-carboxylic acid hydrazides: Synthesis and preliminary evaluation as antimicrobial agents. Biorg Med. Chem. 2006; 14: 8675-8682.
- Ola EI, Sayed A, Fatma EI-Beih M, Shada EI-Aqeel I, Badr AI-Bassam A, Maher Hussein E, et al. Synthesis of 2,4-disubstituted pyrimido[4,5-b]quinolines as potential antimicrobial agents. Indian J. Hetero. Chem. 2005; 14: 327-330.
- Kansagra BP, Bhatt HH, Parikh AR. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of substituted 4-thiazolidinones bearing 2-chloro quinoline nucleus. Indian J. Hetero. Chem. 2000; 10: 05-08.
- Santhosh Kumar S, Ajay N, Tiwari RP, Praveen J. Synthesis of novel substituted/unsubstituted-(2, 8-bis-triflouromethyl-quinolin-4-yloxy)-acetic acid: derivatives of cephalosphorin and their antibacterial activity. Indian J. Chem. 2006; 45: 1734-1739.
- Amit N, Rahul J. Synthesis and anti-tuberculosis activity of 2, 4-disubstituted quinolines. Indian J. Chem. 2008: 47; 117-128.
- Vangapandu S, Jain M, Jain R, Kaur S, Singh PP. Ring-substituted quinolines as potential anti-tuberculosis agents. Bioorg Med Chem. 2004; 12: 2501-2508.
- Vikramdeep M, Amit N, Balasubramanian V, Prakash PB, Sarbjit Singh J, Sukhraj K, et al. Synthesis and antimycobacterial activities of ring-substituted quinolinecarbohydrazide and ring-substituted quinolinecarboxamide analogues. Biorg Med. Chem. 2004: 12; 6465-6472.
- Tseng CH, Chen YL, Lu PJ, Yang CN, Tzeng CC. Synthesis and antiproliferative evaluation of certain indeno[1,2-c]quinoline derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008; 16: 3153-3162.
- Katarzyna S, Lukasz KS, Wojciech Szczepek J, Joanna W, Marta S, Wanda Peczynska, C. Synthesis and antiproliferative activity of diacetylenic thioquinolines. Institute Immun. Exper. Therp. 2007: 61; 41-200.
- Zhao YL, Chen YL, Chang FS, Tzeng CC. Synthesis and cytotoxic evaluation of certain 4-anilino-2-phenylquinoline derivatives. Eur J Med Chem. 2005; 40: 792-797.
- Firestone GL, Sundar SN. Anticancer activities of artemisinin and its bioactive derivatives. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2009; 11: e32.
- Lu JJ, Meng LH, Cai YJ, Chen Q, Tong LJ, Lin LP, et al. Dihydroartemisinin induces apoptosis in HL-60 leukemia cells dependent of iron and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation but independent of reactive oxygen species. Cancer Biol Ther. 2008; 7: 1017-1023.
- Kouznetsov VV, Rojas Ruíza FA, Vargas Méndeza LY, Gupta MP. Simple C-2-Substituted Quinolines and their Anticancer Activity. Letters in Drug Design & Discovery, 2012: 9; 680-686.
- Afzal O, Kumar S, Haider MR, Ali MR, Kumar R, Jaggi M, et al. A review on anticancer potential of bioactive heterocycle quinoline. Eur J Med Chem. 2015; 97: 871-910.