
Research Article
Austin J Anal Pharm Chem. 2016; 3(3): 1068.
Stability-Indicating Method Development and Validation for the Assay of Hydrochlorothiazide and Determination of Impurities/Degradants in Hydrochlorothiazide Raw Material and Tablets using Reverse-Phase Liquid Chromatography
Urupina D and Al-Bazi S*
Department of Chemistry, Northeastern Illinois University, USA
*Corresponding author: Al-Bazi S, Department of Chemistry, Northeastern Illinois University, BBH 214, 5500 N. St. Louis Avenue, Chicago, IL 60625, USA
Received: June 28, 2016; Accepted: July 19, 2016; Published: July 21, 2016
Abstract
Hydrochlorothiazide is a drug that belongs to the class of diuretics used to treat hypertension and edema by inhibiting the ability of kidneys to retain water. A simple, accurate and precise reversed-phase liquid chromatography method was developed and validated to analyze Hydrochlorothiazide in raw material and determine impurities and degradants. A method was developed on a 15mm Luna Column C8, Particle size: 3μ, I.D. 4mm under ambient temperature. Mobile phase used: Monobasic Potassium Phosphate at pH 2.9 and Acetonitrile at a flow rate of 1.0 ml/min with UV-Vis detection at 273nm. Separation Mode: Isocratic elution 7/93% ACN/Buffer in 20min. Hydrochlorothiazide was subjected to the following stress conditions: acid hydrolysis, base hydrolysis, hydrogen peroxide oxidation, heat and UV light. The method was validated for specificity, robustness, linearity, accuracy, and precision, limit of detection and limit of quantitation. Linearity for active ingredient was investigated in the range from 250 to 1200 μg/mL with correlation coefficient found to be 0.9995. Linearity for impurities was studied in 0.001 to 1μg/mL range and gave a correlation coefficient of 0.9999. Calculated %Recovery for the active ingredient ranged from 95.0 to 98.0 percent. The method was then applied to quantify Hydrochlorothiazide in the Lisinopril and Hydrochlorothiazide tablets. Percent recovery of Hydrochlorothiazide in the finished product was calculated to be 98.7%. The molecular formula for degradant was established to be C6H8ClN3O4S2 corresponding to 4,6- sulfonylamido-3-chloroaniline, an ingredient used to prepare Hydrochlorothiazide raw material.
Keywords: Hydrochlorothiazide; Method development; Validation; HPLC; Impurities/degradants identification
Abbreviations
HPLC: High Performance Liquid Chromatography; LC-MS: Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectroscopy; ICH: International Conference on Harmonization; FDA: Food and Drug Administration; ACN: Acetonitrile; LOD: Limit of Detection; LOQ: Limit of Quantification
Introduction
Hypertension is a common medical condition characterized by high blood pressure. According to the World Health Organization it’s a principal cause of cardiovascular mortality [1]. Hypertension is a risk factor for heart attack, stroke, arterial disease, and is generally associated with lower life expectancy [1]. About one in three adults in the USA suffers from hypertension costing the nation almost 47.5 billion dollars annually in direct medical expenses and lost productivity [2].
Hydrochlorothiazide is one of the medications designed to lower high blood pressure and keep it under control. It is a white or off-white crystalline powder, melting point is 274°C, solubility in water is 722 mg/L (at 25 °C), pKa 7.9 [3]. Its chemical formula is C7H8ClN3O4S2 with molecular weight 297.74 and chemical structure shown in Figure 1.
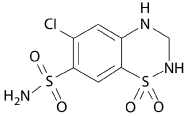
Figure 1: Structural formula of Hydrochlorothiazide.
Image generated using ACD/ChemSketch Freeware, version 10.00,
Advanced Chemistry Development, Inc., Toronto, ON, Canada, www.
acdlabs.com, 2012.
United States National Library of Medicine classifies Hydrochlorothiazide as a thiazide diuretic often considered to be the prototypical member of its class [4]. It works by reducing the reabsorption of electrolytes from the renal tubules resulting in increased excretion of water and electrolytes, including sodium, potassium, chloride, and magnesium [4]. It is also used to treat several other disorders including edema, hypertension, diabetes insipidus, and hypoparathyroidism [4]. The drug is available in tablets of 25 and 50 mg and as capsules of 12.5mg generically and under the trade names of Hydrodiuril, Microzide and Esidrix; or it can be combined with other active ingredients such as antihypertensive medications or with potassium-sparing diuretics [5].
Hydrochlorothiazide is synthesized in the following way: 3-Chloroaniline reacts with chlorosulfonic acid, forming 4,6-sulfonochloride-3-chloroaniline. Reaction with ammonia gives 4,6-sulfonylamido-3-chloroaniline. Cyclization of 4,6-sulfonylamido-3-chloroaniline using paraformaldehyde produces Hydrochlorothiazide [6]. Alternatively Hydrochlorothiazide can be produced from Chlorothiazide by reaction with Formaldehyde [6].
Exact mechanism of action is not fully understood [7]. Initially Hydrochlorothiazide lowers the kidneys’ ability to retain water, reducing the volume of extracellular fluid and plasma volume; that in turn reduces cardiac output and blood pressure [7]. In the long run though, some other factors might come into play. The fact that plasma and extracellular fluid volumes almost fully recover within 4–6 weeks of Hydrochlorothiazide initiation, but blood pressure remains lowered is evidence for some additional mechanism [7]. It’s known though that the site of action for Hydrochlorothiazide is the nephron, a basic structural unit of kidney, specifically distal convoluted tubule of nephron [7].
Few analytical methods for determination of Hydrochlorothiazide are available in the literature [8,9]. Stability-indicating method for simultaneous determination of active ingredients and potential degradants in Hydrochlorothiazide raw material and tablets is in high demand. It is needed for regulatory submissions and to set expiration dates for the active pharmaceutical ingredient or drug product [10, 11]. The motivation for this project was to develop and validate a simple, accurate and precise stability-indicating reversed-phase liquid chromatography method to analyze Hydrochlorothiazide in the raw material and tablets and determine impurities and degradants.
Materials and Methods
Chemicals and reagents
Hydrochlorothiazide was purchased from Waterstone (Carmel, IN). Lisinopril and Hydrochlorothiazide Tablets USP were manufactured by Lupin Limited (Goa, India) and obtained from Walmart Bentonville (Bentonville, AR). Acetonitrile HPLC Grade, Potassium Phosphate Monobasic, Potassium Phosphate Dibasic, Hydrogen Peroxide 30%, Hydrochloric Acid 12 N, and Sodium Hydroxide were purchased from Fischer Scientific (Pittsburgh, PA). Other chemicals and solvents of analytical grade were used during research. DI water was used throughout the investigation.
Instrumentation and chromatographic conditions
Chromatography equipment used to develop the method consisted of Agilent 1100 Series HPLC System with UV/VIS Detector equipped with G1322A degasser, G1311A quaternary pump, G1314A variable wavelength detector, and G1313A ALS auto sampler (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). Chem Station Data Acquisition System for LC (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara) was used to analyze the data. Analysis was performed using Phenomenex Luna Column C8, 3μ, Length 150mm, I.D. 4.00mm. The HPLC instrument was operated isocratically at ambient temperature using ACNPotassium Phosphate Buffer Monobasic 25mM, adjusted to pH 2.9 with phosphoric acid (7:93, v/v) mobile phase and run at a flow rate of 1 mL/min for 20min. The injection volume was 10μL. Detector was set at 273nm. Columns were cleaned for 30 minutes at the end of the experiment with ACN/water (50:50, v/v) in order to remove any buffer from the column.
Stability indicating studies were done using Spectroline UV light (Spectroline, Westbury, NY), Dry Bath Type 17600 (Barnstead International, Dubuque, IA). Validation studies were performed using 1100 Series HPLC System with DAD Detector (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA).
Degradant analysis was performed using Agilent Technologies 6130 Quadruple LC/MS, Agilent 1260 Infinity Series HPLC System with UV/VIS Detector equipped with Chem Station Data Acquisition System; and Agilent Technologies 6540 UHD Accurate-Mass Q-Tof LC-MS, Agilent 1100 Series HPLC System equipped with Mass Hunter Workstation Data Acquisition System for LC-MS 6200 (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA).
Preparation of solutions
Potassium Phosphate Buffer Monobasic 25mM, adjusted to pH 2.9 with phosphoric acid was vacuum filtered and degassed for 30min. Acetonitrile 100% was degassed for 30min.
Stock solution of Hydrochlorothiazide 5000 μg/mL, 25mL was prepared by weighting 0.125g of Hydrochlorothiazide, transferring it in a 25mL volumetric flask, adding 12.5mL of ACN, vortex-mixing until it completely dissolved, adding DI water to the volume and mixing well. Other concentrations of Hydrochlorothiazide were prepared from its stock solution through serial dilution with ACNwater (50:50 v/v).
To prepare a sample solution a tablet of Lisinopril and Hydrochlorothiazide containing 20mg of Lisinopril and 12.5mg of Hydrochlorothiazide was grinded in to a fine powder and transferred to 25mL volumetric flask. 12.5mL of ACN was added and the solution was mixed well. After the specified time, deionized water was added to the volume; the solution was mixed well, and filtered.
Degradation studies
As a part of forced-degradation studies, 1000 μg/mL Hydrochlorothiazide (final concentration) was subjected to the following stress conditions under the ICH and FDA guidelines [11]: acid hydrolysis, base hydrolysis, hydrogen peroxide oxidation, heat and UV light.
Acid degradation
In acid hydrolysis study 2 mL of 5000 μg/mL stock solution of Hydrochlorothiazide was combined with 2mL of 6M HCl. The solution was heated for 24 hours at 750C, cooled to room temperature, neutralized with 2mL of 6M NaOH, transferred to a 10mL volumetric flask and diluted to the volume with 50/50% ACN/water. The pH of the solution was checked with pH strips to make sure solution is neutral (pH 7), filtered and injected into the HPLC system.
Base degradation
Aliquot of 2mL of 5000 μg/mL stock solution of Hydrochlorothiazide was combined with an equivalent amount of various concentrations of NaOH in the range 0.03 – 6 M. The solutions were heated for 24 hours at 750C, cooled to room temperature, neutralized with corresponding concentration of HCl, transferred to a 10mL volumetric flask and diluted to the volume with 50/50% ACN/water. The pH of these solutions was checked with pH strips to make sure they are neutral (pH 7), filtered and injected into the HPLC system.
Hydrogen peroxide degradation
Oxidative studies were conducted by combining 2mL of 5000 μg/ mL stock solution of Hydrochlorothiazide with an equivalent amount of various concentrations of H2O2 in the range 0.1 – 3%, heated for 24 hours at 750C and cooled to room temperature. These solutions were transferred to a 10mL volumetric flask, diluted to the volume with 50/50% ACN/water, and filtered prior to their injection into the HPLC system.
Heat degradation
In this study, 2mL of 5000 μg/mL stock solution of Hydrochlorothiazide was heated for 41 hours at 750C and cooled to room temperature. This solution was transferred to a 10mL volumetric flask, diluted to the volume with 50/50% ACN/water, filtered and injected into the HPLC system.
UV light degradation
About 0.1g of Hydrochlorothiazide was placed on a watch glass, and exposed to the UV light for 5 days. Accurately, 0.01g of the exposed Hydrochlorothiazide was transferred to a 10mL volumetric flask and dissolved in 5mL of ACN. The solution was completed to the volume with DI water, and injected into the HPLC system.
Method validation
According to ICH and FDA guidelines the developed method was validated for system suitability, specificity, robustness, solution stability, linearity and range, accuracy, precision, limit of detection for impurities/degradants-LOD, and limit of quantitation for impurities/ degradants-LOQ.
System suitability
To make sure that equipment is working properly and consistently eight injections of the standard solution #1 of 1000 μg/ mL Hydrochlorothiazide were evaluated for area percent RSD and retention time percent RSD. Then 1000 μg/mL of the solution #2 of Hydrochlorothiazide was injected twice and also evaluated for area percent RSD and retention time percent RSD. Percent drift was then calculated using the following equation:
where As is average peak area of eight replicate injections of standard solution #1 and Ac is average peak area of two replicate injections of standard solution #2. System suitability test was performed before testing for each validation parameter.
Specificity
To ensure that the peak response is due to only one component and no co-elution occurs, Hydrochlorothiazide was degraded with 0.1% H2O2 (percent degradation 42.6%) and then analyzed by Agilent 1100 HPLC system equipped with Diode Array Detector.
Robustness
Robustness was investigated using a degraded sample of 1000 μg/mL Hydrochlorothiazide. To validate robustness of the method the following parameters were varied: %ACN (7±2%), pH (2.9±0.1), flow rate (1.0±0.1 mL/min), wavelength (273±2 nm). In order to observe how analyte of interest changes over time 1000 μg/mL Hydrochlorothiazide was prepared from the stock solution of 5000 μg/mL and injected into the HPLC system. The same solution was injected in 47 hours, 7 days, 15 days, and 22 days.
Linearity and range
To investigate linearity for the active ingredient, six different concentrations of Hydrochlorothiazide were prepared from 5000 μg/ mL stock solution of Hydrochlorothiazide in the range 250 – 1200 μg/mL. To explore linearity for impurities/degradants, ten different concentrations of Hydrochlorothiazide, which was used as surrogate, were prepared in the range 0.001-01.0 μg/mL and injected into the HPLC system.
Accuracy
To investigate method accuracy for the active ingredient, two solutions of Hydrochlorothiazide were prepared at 25% of nominal concentration and triplicate solutions were prepared at 100 and 120% of nominal concentration. To investigate method accuracy for impurities/degradants triplicate solutions were prepared at 1, 0.5 and 0.075% of nominal concentration.
Precision
Injection precision was tested to measure sensitivity of the method towards errors coming from the instrument itself: the column, the detector, the injector, the integration device. Method precision was conducted to measure sensitivity of the method towards errors that may result from preparation of the samples during analysis. To evaluate method precision for active ingredient, eight samples at 1000 μg/mL were prepared from 5000 μg/mL of Hydrochlorothiazide stock solution. Intermediate precision was tested by preparing 1000 μg/mL Hydrochlorothiazide from 5000 μg/mL stock solution by a different analyst and injected into a different HPLC system on a different day.
LOD and LOQ
Limit of detection for impurities/degradants was investigated to determine the lowest concentration of Hydrochlorothiazide as surrogate that can be detected but not quantified and it was found based on signal to noise ratio of three [11]. Limit of quantitation was studied to determine the lowest level of the analyte concentration that can be accurately quantified and was determined by the concentration corresponding to signal-to-noise ratio of more than ten [11].
Assay of hydrochlorothiazide in lisinopril and hydrochlorothiazide tablet
A tablet of Lisinopril and Hydrochlorothiazide containing 20mg of Lisinopril and 12.5mg of Hydrochlorothiazide was grinded in to a fine powder and transferred to 25mL volumetric flask. About 12.5mL of ACN was added to the powder, sonicated for 10min, completed to 25mL with deionized water, and mixed well. The resulting solution (500 μg/mL Hydrochlorothiazide and 800 μg/mL Lisinopryl) was filtered and injected into the HPLC system. ICH acceptance criterion is recovery of 95 to 105% of the theoretical value for the active ingredient [11].
Identification of the potential degradant
To identify the main degradant of Hydrochlorothiazide, a 100 μg/mL solution of Hydrochlorothiazide was analyzed by Quadruple LC-MS instrument in positive MS Mode, Fragmentor 70 on a Phenomenex Kinetex C18 column , 2.6μ, Length 50mm, I.D. 2.1mm. The HPLC instrument was operated isocratically at 273nm wavelength at ambient temperature using ACN- Trifluoroacetic acid 0.1% (7:93, v/v) mobile phase at a flow rate of 0.4 mL/min for 5min. The injection volume was 5μL. Analysis of the mass spectrum of Hydrochlorothiazide degradant was done using Molecular Weight calculator in Isotopic Distribution Mode.
To confirm accuracy of the results, the experiment was repeated on Agilent 6540 Accurate-Mass Q-Tof LC-MS instrument in positive MS Mode, and Fragmentor 100 using a Phenomenex Synergi Hydro- RP C18 column, 4μ, Length 150mm, I.D. 4.60mm. Aliquot of 5μL of 100 μg/mL Hydrochlorothiazide was injected under isocratic elution at ambient temperature using ACN- Trifluoroacetic acid 0.1% (20:80, v/v) mobile phase and run at a flow rate of 0.4 mL/min for 10min.
Results and Discussion
Solubility of Hydrochlorothiazide in different proportions of water, methanol, and acetonitrile was investigated. It was observed that Hydrochlorothiazide dissolved well in 100% each of ACN and methanol, while being poorly soluble in pure water. ACN was considered to be first choice as a primary solvent due to low UV cut-off range (192 nm) and low viscosity of ACN/water mixture [12]. To determine the appropriate wavelength, a diluted solution of Hydrochlorothiazide in ACN was run between 200 and 600 nm on the UV-VIS spectrophotometer. Although maximum absorbance was observed at 225nm, however another peak at 273nm was found more desirable to minimize generated at lower wavelength. Different columns were tested to determine the conditions that will result in a peak with a minimum of 2000 theoretical plates and tailing factor between 0.9 and 2 for the active ingredient [11]. Phenomenex, Luna C8, 3μ, Length 150mm, I.D. 4.00mm resulted in tailing factor of 1.026, the number of theoretical plates equal to 8253 and was used in further studies. A pH of 2.9 was selected to minimize secondary interaction that may result in peak tailing [12]. Different proportions of ACN/ buffer were investigated to optimize solvent strength that will result in retention time around 10-12 min and was observed at a ratio of 7/93% ACN/buffer as shown in Figure 2.
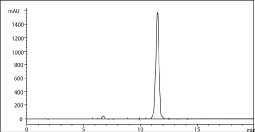
Figure 2: Chromatogram of 1000 μg/mL Hydrochlorothiazide.
Conditions: 1) Mobile phase: solvent A: 25mM Potassium Phosphate buffer,
monobasic, pH 2.9; Solvent B: ACN. 2) Isocratic elution 7/93% ACN/Buffer in
20 min. 3) Flow rate: 1 mL/min. 4) Temperature: ambient. 5) Injection volume
10μL. 6) Wavelength 273 nm.
Hydrochlorothiazide was found to be resistant to acid hydrolysis, UV light and heat but sensitive to base hydrolysis and oxidative stress in forced-degradation studies (Table 1). One potential degradant of Hydrochlorothiazide was observed at 6.5min and was well resolved from the Hydrochlorothiazide peak which eluted around 11min (Figure 3).

Figure 3: Chromatogram of 1000 μg/mL Hydrochlorothiazide.
Conditions: 1) Mobile phase: solvent A: 25mM Potassium Phosphate buffer,
monobasic, pH 2.9; Solvent B: ACN. 2) Isocratic elution 7/93% ACN/Buffer in
20 min. 3) Flow rate: 1 mL/min. 4) Temperature: ambient. 5) Injection volume
10μL. 6) Wavelength 273 nm.
Stress Condition
Exposed Time
Temperature
Degradation %
6M HCl
24 hours
750C
5.6
0.03 M NaOH
24 hours
750C
16.4
0.1% H2O2
40 hours
750C
42.6
Heat
41 hour
750C
7.2
UV-light
5 days
---
1.7
Table 1: Degradation Study Results.
Method Validation Studies
System suitability
The results of system suitability test are shown in Table 2. The acceptance criteria for system suitability test are: the number of theoretical plates ≥ 2000, tailing factor ≤ 2, resolution between the peak of interest and the closest potential interfering peak by rs> 2 , %drift ≤ 2%, area % RSD and retention time %RSD of ≤ 1% for number of injections n ≥ 5 [11]. All peaks were well resolved. The method fulfilled the system stability requirements for tailing factor, number of theoretical plates, percent RSD for area, percent RSD for retention time, and percentage drift.
Standard #1 Injection
Peak Area
Retention Time (min)
Plate Count
Tailing Factor
Peak Area %RSD
Retention Time %RSD
%Drift
1
33804.1
11.867
9200
1.034
0.10
0.52
-1.93
2
33895.5
11.886
9545
1.064
3
33837.7
11.791
9393
1.056
4
33851.2
11.763
9348
1.052
5
33815.6
11.714
9271
1.045
6
33869.5
11.723
9285
1.048
7
33814.4
11.78
9067
1.039
8
33872.3
11.797
9093
1.049
Standard #2 Injections
1
34487.3
11.931
8435
1.028
0.05
0.37
2
34511.8
11.868
8903
1.027
Table 2: System Suitability results for Hydrochlorothiazide raw material.
Specificity
Hydrochlorothiazide degraded with 0.1% H2O2 (percent degradation 42.6%) showed no interfering peaks. All peaks were well separated from the analyte peak. Peak purity factor was found to be 998.198.
Robustness
Method proved to be robust against changes in %ACN (7±2%), pH (2.9±0.1), flow rate (1.0±0.1 mL/min), and wavelength (273±2 nm). All peaks were separated from the peak of interest by Rs>2. In addition, number of theoretical plates was more than 2000 and tailing factor was below 2.0. Solution stability results obtained from injecting 1000 μg/mL Hydrochlorothiazide on different days are shown in Table 3. There were no peaks lost; new peaks were not observed.
Parameters
Time
Peak Area
% Change
Control
0
34778.6
---
47 h
34039.2
-2.1
7 d
33664.7
-3.2
15 d
34686.1
-0.27
22 d
35025.8
+0.71
Table 3: Stability study results for 1000 μg/mL Hydrochlorothiazide.
Linearity and range
The plot of peak area versus concentration for Hydrochlorothiazide raw material in the 250-1200 μg/mL range gave linear regression equation y=33.853x+594.98 with correlation coefficient of 0.9995. Linear regression curve for impurities/degradants in 0.001-1 μg/mL range resulted in a linear regression equation y=35.758x+0.425 with correlation coefficient of 0.9999. The resulted correlation coefficients are in agreement with the accepted guidelines of 0.999 for the active ingredient and 0.99 for impurities/degradants based on ICH guidelines [11].
Accuracy
The results of accuracy study for the active ingredient are presented in Table 4. Calculated %Recovery for the active ingredient was between 95.0 and 98.0 percent; calculated %Recovery for impurities/degradants were between 80.9 and 97.8 percent.
Concentration (µg/mL)
Peak Area
Percent Recovery (%)
Average Percent Recovery
%RSD
250
8620.6
94.8
95.0
0.3
8662.8
95.2
1000
32798.8
95.1
96.8
1.5
33570.8
97.4
33687.1
97.8
1200
40976.0
99.4
98.0
1.2
40137.2
97.3
40170.2
97.4
Table 4: Accuracy study for Hydrochlorothiazide active ingredient.
Precision
While conducting system suitability test, injection precision was calculated to be 0.10%. Criterion for the injection precision is %RSD≤1% for n ≥ 5 [11]. The %RSD for method precision for active ingredient as reported in Table 5 was found to be 0.58, which is in agreement with the criterion for method precision of %RSD for active ingredient ≤ 2.0% [11]. The results of the intermediate precision for determination of the active ingredient expressed as %RSD was found to be 1.41% (Table 6). The acceptance criterion for intermediate precision is %RSD≤2% on overall results [11].
Preparation
Peak Area
Average
Standard Deviation
%RSD
1
33635.4
33625.7
194.4
0.58
2
34001.4
3
33655.7
4
33543.0
5
33714.3
6
33570.3
7
33579.8
8
33305.4
Table 5: Method Precision study for 1000 μg/mL Hydrochlorothiazide.
Operator
Preparation
Peak Area
Average
Standard Deviation
%RSD
Analyst 1
1
33505.8
33490.13
472.8
1.41
2
32677.0
3
33220.7
Analyst 2
1
33804.1
2
33895.5
3
33837.7
Table 6: Intermediate Precision study for Hydrochlorothiazide.
Limit of detection (LOD) and Limit of quantitation (LOQ)
LOD for determination of impurities/degradants using Hydrochlorothiazide as surrogate and corresponding to signalto- noise ratio of 6 to 1 was found to be 0.025 μg/mL. LOQ for determination of impurities/degradants using Hydrochlorothiazide as surrogate was found to be 0.075 μg/mL based on signal to noise ratio of 12 to 1.
Method application
The developed method was applied to determine Hydrochlorothiazide in the Lisinopril/Hydrochlorothiazide tablet. The dissolution time up to 120min of the grinded tablet was investigated using mechanical shaking. Hydrochlorothiazide immediately dissolved as shown in Table 7. Similar results were obtained with sonication and 10min was found appropriate dissolving time. Dissolution precision was validated by injecting seven solutions of the tablet each containing 500 μg/mL of Hydrochlorothiazide. %RSD was calculated to be 1.52%, which is in agreement with the criterion for method precision of %RSD for active ingredient ≤ 2.0% [11].
Preparation
Peak Area
Average
Standard Deviation
%RSD
1
17569.1
17598.8
268.3
1.52
2
18043.9
3
17794.4
4
17505.1
5
17188.5
6
17622.7
7
17468.1
Table 7: Dissolution studies for Lisinopril and Hydrochlorothiazide tablet containing 500μg/mL Hydrochlorothiazide.
Validated method was used to assay Hydrochlorothiazide in Lisinopril/Hydrochlorothiazide tablet. A 500 μg/mL Hydrochlorothiazide tablet solution was prepared and injected into the HPLC system. Using linear regression equation for Hydrochlorothiazide raw material (y=33.705x+1071.7) and the peak area of the injected sample of 17707.9, the amount of Hydrochlorothiazide in the tablet was calculated to be 12.34mg which corresponded to percent recovery of 98.7%. ICH acceptance criterion is recovery of 95 to 105% of the theoretical value for the active ingredient [11].
Identification of the degradant
To identify the potential degradant of Hydrochlorothiazide, a 100 μg/mL solution of Hydrochlorothiazide was analyzed by Quadruple LC/MS instrument. The resulted spectra of the degradant corresponded to the molecular formula C6H8ClN3O4S2 as simulated by Molecular Weight calculator in Isotopic Distribution Mode. To improve sensitivity of detection, this study was repeated on Agilent 6540 Accurate-Mass Q-Tof LC-MS. The formula C6H8ClN3O4S2 proposed in the previous experiment was compared to the reference from the database. Compound with a molecular formula C6H8ClN3O4S2 had a target score of 95.48 and a mass error of 0.15. A target score of more than 90 with a mass error of less than 5 μg/mL confirms the proposed molecular formula of the potential degradant of C6H8ClN3O4S2. This molecular formula corresponds to 4,6-sulfonylamido-3-chloroaniline used to prepare Hydrochlorothiazide active ingredient [6].
Conclusion
A reversed-phase HPLC method was developed and validated for the assay of Hydrochlorothiazide raw material and for determination of its impurities/degradants. The method was developed on a Phenomenex Luna Column [C8, 3μ, Length 150mm, I.D. 4.00mm] under ambient column temperature using isocratic elution 7/93% ACN/Buffer [25mM Potassium Phosphate buffer, monobasic, pH 2.9] in 20min. A flow rate of 1ml/min with 10μL injected volume, and detection wavelength of 273nm were used. The developed method was validated based on FDA and ICH guidelines for the System Suitability, Specificity, Robustness, Stability, Linearity, Accuracy, Precision, LOD and LOQ. The developed method was successfully applied to assay Hydrochlorothiazide in the finished product with percent recovery of 98.7%. The potential degradant was identified as 4,6-sulfonylamido-3-chloroaniline.
References
- Hypertension [Internet]. Wikipedia. 2016 [cited 4 November 2014].
- High Blood Pressure Facts | cdc.gov [Internet]. Cdc.gov. 2016 [cited 4 November 2013].
- Drug Bank: Hydrochlorothiazide [Internet]. Drugbank.ca. 2016 [cited 23 March 2013].
- Drug Information Portal - U.S. National Library of Medicine - Quick Access to Quality Drug Information [Internet]. Druginfo.nlm.nih.gov. 2016 [cited 2 March 2013].
- Thiazide Diuretics [Internet]. Livertox.nlm.nih.gov. 2016 [cited 23 June 2016].
- Vardanyan RS, Hruby V. Synthesis of essential drugs. 1st ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2006. p.281.
- Duarte JD, Cooper-DeHoff RM. Mechanisms for blood pressure lowering and metabolic effects of thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics. Expert Review of Cardiovascular Therapy. 2010; 8: 793-802.
- Kamble R, Singh S, Singh S. Development and Validation of a Stability Indicating LC Method for the Determination of Hydrochlorothiazide in Pharmaceutical Formulations. Journal of Pharmacy Research. 2010; 3: 2949-2952.
- Bhagwate S, Gaikwad N. Stability Indicating HPLC Method for the Determination of Hydrochlorothiazide in Pharmaceutical Dosage form. J App Pharm Sci. 2013; 3: 88-92.
- ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology Q2(R1). International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use [Internet]. ICH Expert Working Group; 1996 [cited 23 June 2016].
- Reviewer Guidance Validation of Chromatographic Methods. [Internet]. Center for Drug Evaluation and Research; 1994 [cited 23 June 2016].
- Meyer V. Practical high-performance liquid chromatography. 4th ed. Chichester: John Wiley; 2004. P.71, 114: 163.
Citation: Urupina D and Al-Bazi S. Stability-Indicating Method Development and Validation for the Assay of Hydrochlorothiazide and Determination of Impurities/Degradants in Hydrochlorothiazide Raw Material and Tablets using Reverse-Phase Liquid Chromatography. Austin J Anal Pharm Chem. 2016; 3(3): 1068.