
Research Article
Austin J Anal Pharm Chem. 2017; 4(1): 1079.
Study of Effect of Formulation Variables on Bifonazole Niosomes by Applying Plackett Burman Design
Pawar HA1* and Attarde VB2
1Assistant Professor and HOD (Quality Assurance), Dr. L. H. Hiranandani College of Pharmacy, Smt. CHM Campus, Opp. Ulhasnagar Railway Station, Ulhasnagar-421003, Maharashtra, India
2Research Scholar (M. Pharm.), Dr. L. H. Hiranandani College of Pharmacy, Ulhasnagar-421003, Maharashtra, India
*Corresponding author: Harshal Ashok Pawar, Assistant Professor and Head of Department (Quality Assurance), Dr. L.H. Hiranandani College of Pharmacy, Smt. CHM Campus, Ulhasnagar-421003, India
Received: January 01, 2017; Accepted: February 08, 2017; Published: February 10, 2017
Abstract
Vesicular systems are a novel drug delivery that can enhance bioavailability of encapsulated drug and provide therapeutic activity for a prolonged period of time in a controlled manner. Many factors affect niosomes formation such as millimole of surfactant and cholesterol, surfactant:cholesterol ratio, time of hydration, pH of hydration medium, tempertaure during hydration process and speed of rotation of round bottom flask. Bifonazole was selected as a model drug. It has a short half life of 1-2 hr and low permeability (BCS Class IV) which was good candidate for formation of niosomes to enhance the permeation and to prolong the action of drug. The aim of the study was to optimize the various parameters affectingniosomes formation. The statistical approach was used to optimize the parameters. The Plackett–Burman design described in this study was applied for the isolation of the significant factors to concentrate more on them. The process parameters among six factors influencing in vitro diffusion study were identified using Plackett Burman design. The vesicular sizing parameters, drug entrapment data and drug release characteristics were investigated. Among the various variables screened, millimole (mM) of surfactant and cholesterol, time of hydration, hydration temperature were found to be the most significant factors in the preparation of noisome .
Keywords: Bifonazole; Optimization; Plackett Burman; In vitro study; Niosomes; Gel
Introduction
The vesicular systems are highly ordered assemblies of one or several concentric lipid bilayer formed, when certain amphiphillic building blocks are confronted with water. The vesicular system such as liposomes, niosomes, sphingosomes, ethosomes, transferosomes and pharmacosomes are used to improve the therapeutic index of existing and new drug molecules by encapsulating an active medicament inside vesicular structure in one such system [1].
Niosomes are microscopic lamellar structures and hydrated vesicular systems containing nonionic surfactants along with cholesterol or other lipids delivering drug to targeted site which are non toxic, stable over a longer period of time in different conditions requiring less production cost [2]. Niosomes, a nonionic surfactant vesicular formulation, have been explored widely for topical application to enhance skin penetration as well as to improve skin retention of drugs [1]. Many factors affect niosomes formation such as the method of manufacture, nature of surfactant and drug, temperature at which the lipids are hydrated and the critical packing parameter [2]. Drug deposition, vesicle size and entrapment efficiency are the key parameters involved in formulation of topical niosomes [3].
Superficial fungal infections (dermatomycoses) of the skin are among the most common diseases seen in our daily practice and occur throughout the world. These infections are contagious diseases caused by either a human (anthropophilic) or animal (zoophile) species of dermatophyte fungi. Tinea pedis (Athlete’s foot or ringworm) is the most common dermatophytosis and may affect up to 70% of adults worldwide. Most cases of tineapedis respond to topical antifungal agents. Clinical efficacy of topical antifungal therapy depends on the drug ability to penetrate into the stratum corneum (SC) and the duration of treatment [4].
Bifonazole is a imidazole antifungal drug which has been used in many skin and nail infections caused by fungi. It is highly lipophilic drug with a very short half-life (1-2hr) and is minimally absorbed following dermal application (0.6% of an applied dose). Niosomes are excellent candidate as potential drug delivery system because of their improved drug solubilization, enhanced penetration power, long shelf life and ease of preparation and administration [5]. Experimental design is a powerful tool for optimizing different nonhomogenous parameters and conditions. Plackett-Burman designs are ideal for screening purpose in systems where it is desired to a few main factors affecting the outcome and where interactions are not significant. Plackett–Burman enables randomizing different variables aiming to get the best conditions where each variable coordinates with other variables to give the best expected results [6]. Plackett- Burman designs utilise two levels for each factor, the higher level being denoted “+” and the lower “ -” as usual. In the present study,the experimental design can be used in order to derive valid and robust statistical significance testsfor the examined factors with a minimum number of experiments. More specifically, with the Plackett-Burman designs one will have an estimate of the factors main effects only and no other information concerning higher order interactions [7]. In the present study, niosomal formulations were prepared by application of Plackett-Burman design using different process parameters and were evaluated for the significant factors which affect niosomes formation.
Materials and Methods
Materials
Bifonazole was obtained as gift sample from Wexford Laboratories, Banglore (India). Cholesterol AR was obtained from Himedia Laboratories, Mumbai (India). Sorbitanmonostearate (Span 60) and Polysorbate 80 (Tween 80), were purchased from Molychem, Mumbai, India. Dialysis membranewas purchased from Himedia Laboratories Pvt. Ltd., Mumbai, India.
Experimental design
The software used here for optimization was design expert 7.0.0. In the present study, Plackett-Burman (PB) design was used to identify the significant process variables. A screening of the effects of six independent variables namely, millimole of surfactant and cholesterol, surfactant: cholesterol ratio, time of hydration, pH of hydration medium, hydration temperature and speed of rotation were carried out. The high and low levels for independent variables were selected based on extensive literature review and preliminary trials. Niosomes were prepared by thin film hydration method. Plackett- Burman screening designs wasused to screen for important factors which significantly affect niosomes formation process for method optimization. thisdesigns allow to identify the effects of a relatively high number of factors, in a relatively small and feasible number of experiments. Therefore, these designs were extremely useful in preliminary studies where the aim was to identify formulation variables that can be fixed or eliminated [8].
Selection of high and low level of parameters used for optimization:
a) Initially different topical gels were prepared by incorporation of niosomal dispersion having molar ratio of surfactant: cholesterol as 1:1, 2:1, 5:1, 7:1. Based on results obtained in preliminary trials and extensive literature survey, 1:1 and 7:1 of surfactant: choletserol ratio was selected for further study.
b) Millimole of surfactant and cholesterol, time of hydration, pH of hydration medium, hydration temperaure and speed of rotation which may affect niosome formation process were initially selected based on literature survey [9-11].
Experimental design to optimize the process related variables: The different levels for the independent variables for the 12 run of Plackett-Burman designs are given in Table 1. All the variables were denoted as numerical factors and investigated at two widely spaced intervals designated as -1 (low level) and +1 (high level). Table 2 shows 12 run Placket-Burman experimental design for screening significant process variables affecting niosomes formulation.
Factors
Levels
-1
+1
A. Millimole (mM) of surfactant and cholesterol
10
30
B. Surfactant: cholesterol ratio
1:1
7:1
C. Time of hydration (hr)
0.5
1
D. pH of hydration medium
6.8
7.4
E. Hydration temperature (0C)
55
65
F. Speed of rotation (rpm)
60
80
Table 1: Factors and factor levels investigated in Plackett-Burman experimental design.
Preparation of niosomes: Niosomes were prepared by thin film hydration method. Span 60 and cholesterol were dissolved in ethanol in a round bottom flask. Drug was dissolved separately in methanol and mixed with above solvent. Using rotary evaporator the organic solvent wasremoved and a thin film layer of solid mixture was deposited on the wall of the flask. The film was rehydrated with appropriate phosphate buffer mentioned in Plackett Burman design with gentle agitation which results in formation of multilamellar niosomes [12]. The niosomes prepared using different conditions are mentioned in Table 2.
Formulation No.
Factors to be screened
A
(mM)
B
C
(hr)
D
E
(0C)
F
(rpm)
1
30
7:1
0.5
7.4
65
80
2
30
1:1
1
7.4
65
60
3
10
7:1
1
7.4
55
60
4
30
7:1
1
6.8
55
60
5
30
7:1
0.5
6.8
55
80
6
30
1:1
0.5
6.8
65
60
7
10
1:1
0.5
7.4
55
80
8
10
1:1
1
6.8
65
80
9
10
7:1
0.5
7.4
65
60
10
30
1:1
1
7.4
55
80
11
10
7:1
1
6.8
65
80
12
10
1:1
0.5
6.8
55
60
Table 2: Plackett-Burman experimental design for screening significant process variables affecting niosomes formation.
Determination of entrapment efficiency: The prepared dispersion was centrifuged at 15000rpm in refrigerated centrifuge (Remi CPR 24, Mumbai) for 30min in order to separate entrapped drug. Further centrifugation, supernatant was separated. The pellet obtained at bottom after centrifugation was washed with phosphate buffer pH 6.8. Further centrifugation, the wash obtained was mixed with former supernatant. The mixture was filtered and sufficiently diluted with methanol to determine the concentration of unentrapped drug spectrophotometrically at 254nm using methanol as blank. The entrapment efficiency was calculated using the following equation [13,14].
Preparation of carbopol gel: Carbopol 940 (1%) was weighed and sprinkled onto the dispersion containing drug was allowed to hydrate for 1-2 hours. Propylene glycol (3%) and oleic acid (3%) were added subsequently to the aqueous dispersion with continuous stirring [3]. Methyl paraben (0.1%) was used as preservative. Niosomal gel was prepared by adjusting pH of gel between pH 6 -7 using triethanolamine.
In vitro release study: In vitro drug release study on niosomal gel was performed using Franz-diffusion cell. The dialysis cellophane membrane was mounted between the donor and receptor compartment. Dialysis membrane was soaked in phosphate buffer pH 6.8 containing Tween 80 (1%) for overnight before use. A 0.2 gram of niosomal gel containing 2mg bifonazole drug was placed on one side of the dialysis membrane. Phosphate buffer pH 6.8 containing Tween 80 (1%) was taken in receptor compartment of volume 9ml. Heat supplied using a thermostat with magnetic stirrer. The diffusion cell was placed over a magnetic stirrer at 150rpm and temperature was maintained at 37±1°C. Aliquots (1ml) were withdrawn at predetermined time interval of 30mins, 1hr, 2hr, 3hr, 4hr,5hr, 6hr, 7hr and same volume was replaced with fresh buffer. The sink condition was maintained throughout the experiment [16]. The aliquotes were sufficiently diluted with methanol and evaluated spectrophotometrically at 254nm using methanol as blank.
Results and Discussion
Selection of excipients/method
Excipients selection was based on physicochemical properties of drug, release pattern and compatibility studies. Cholesterol influences the physical properties and structure of niosomes possibly due to interaction with nonionic surfactants. Cholesterol imparts rigidity to vesicles, which is important under severe stress conditions. The effect of cholesterol in lipid bilayers is to modulate their cohesion, mechanical strength and permeability to water [16].
Nonionic surfactant is basic component of the niosomes. Surfactant was selected based on various properties of nonionic surfactant like hydrophilic–lipophilic balance, the chain length and size of hydrophilic head group, effect of transition temperature. Span 60 has highest phase transition temperature (50°C) as compared to Span 40 and Span 20 and hence high entrapment efficiency. The length of alkyl chain of surfactant has a prominent effect on permeability of prepared niosomes as length of surfactant increases entrapment efficiency also increases and as length decreases entrapment efficiency also decreases [15]. Hence long chain surfactant results in high entrapment. As result Span 60 was selected as surfactant because of its good entrapment efficiency and its HLB value.
Screening of parameters using Plackett-Burman design
The experiment was conducted in 12 runs to study the effect of the selected variables on niosomes formation. Table 3 represents the results of the screening experiments using Plackett-Burman design and predicted response was calculated manually using values from Table 1 in following equation. Observed response in Table 3 is percent cumulative drug release at 7thhr. No significant effect of different process variables was found on entrapment of drug in niosomes. The entrapment efficiency of 12run of Plackett Burman was found in range of 75.14±0.74% to 99.76 ± 0.005%. Statistical analyses of the responses were performed and they are represented in Table 4. The high value (0.95) of correlation coefficient (R2) for following equation indicates a good fit. The model F value of 23.98 implies that the model is significant. The values of Prob< 0.05 indicate model terms are significant.Regression analysis was performed on the results and a first order polynomial equation was derived representing In vitro release study as function of the independent variables.
Run No.
In vitro release study (% Cumultive release)
Observed response* (%)
Predicted response (%)
Entrapment efficiency*
1
40.32±0.12
36.55
75.14±0.74
2
41.92±0.72
40.53
98.79±0.01
3
50.39 ±0.02
48.55
93.25±0.21
4
51.51±0.40
51.35
91.85±0.35
5
50.09±0.49
50.69
92.62±0.16
6
40.30±0.28
42.43
99.42±0.02
7
63.42±0.33
62.97
99.62±0.01
8
35.62±0.06
37.73
99.03±0.01
9
42.74±0.24
42.95
97.99±0.02
10
44.98±0.25
45.47
99.19±0.02
11
53.49±0.13
52.81
98.57±0.04
12
52.98±0.23
53.77
99.76±0.005
Table 3: Observed and predicted responses of In vitro drug release study at 7th hr for the experiments performed using Plackett- Burman design.
Source
Sum of squares
df
Mean square
F value
p- value
prob>F
Effect
Model
646.35
5
129.27
23.98
0.0007
significant
A-mM
94.10
1
94.10
17.45
0.0058
C-time
69.87
1
69.87
12.96
0.0114
E-temp
55.83
1
55.83
10.36
0.0182
BC
80.71
1
80.71
14.97
0.0083
BD
169.59
1
169.59
31.45
0.0014
residual
32.35
6
5.39
Cor total
678.70
11
R-Squared : 0.9523, Adj R-Squared: 0.9126, C.V. % : 4.
Table 4: ANOVA for selected factorial model.
In vitro release study = + 47.15 - 3.20 *A - 2.61 *C - 2.47 *E + 2.94 *B *C - 4.60 *B *D
The polynomial equation can be used to draw conclusions after considering the magnitude of each coefficient and the mathematical sign it carries (i.e., positive or negative). The magnitude of the effects indicates the level of the significance of the variable on in vitro drug release study. A negative sign of coefficient for millimole (mM) of surfactant and cholesterol (A) and hydration temperature (C) represents antagonistic effect of these variables. So at a low level of millimole (mM) of surfactant and cholesterol increase in the in vitro drug release value might occur. The positive coefficients (BC) for the interactions between two variables indicate a favorable effect on in vitro drug release.
Response surface and contour plots
The relationship between the dependent and independent variables can be further understood by response surface and contour plots. These plots are useful to study effectsof two factors on the response at one time. Considering the greatest difference in model first order polynomial functions response, the surface plots for responses obtained for in vitro drug release are presented in Figure 1(A). It indicated that as level of millimole of surfactant and cholesterol decreases from 30mM to 10mM, in vitro release increases and Surfactant: cholesterol ratio do not have significant effect. Figure 1(B) represents as level of time of hydration decreases from 1hr to 0.5hr, in vitro release increases and pH of hydration medium do not have significant effect. Figure 1(C) represents as level of hydration temperature decreases from 65 to 55°C, in vitro release increases and speed ofrotation do not have significant effect. Figure 1(D) and Figure 1(E) represents effect of interaction of Surfactant:cholesterol ratio (B) and time of hydration (C), also Surfactant:cholesterol ratio (B) and pH of hydration medium (D) on in vitro drug release.
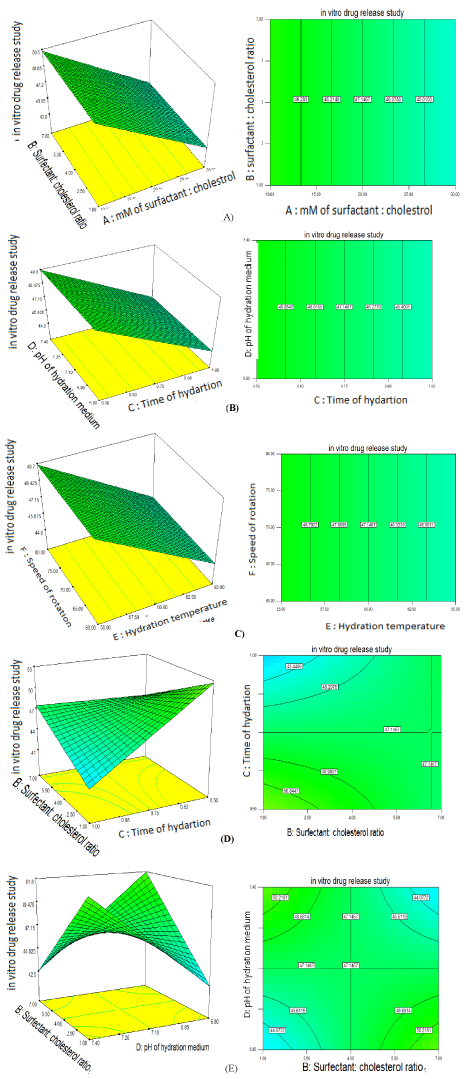
Figure 1: Response surface (3D) and contour plots showing the effects of independent variables on in vitro drug release.
Pareto charts of effects
Useful plot for identifying the factors that are important is the Pareto chart of effects. This graph shows the factors main effect estimates, rank ordered according to their significance, plotted against the horizontal axis [7]. The Pareto chart for the In vitro drug release study shows that most significant effect is millimole (mM) of surfactant and cholesterol, then time of hydration and hydration temperature (Figure 2).
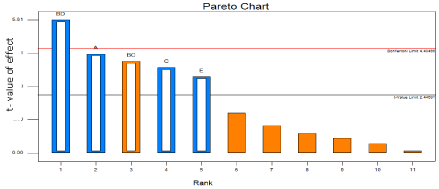
Figure 2: Pareto diagram showing effects of individual factors on in vitro drug
release study.
Conclusion
Vesicular formulation development process involves many factors which makes the interpretation of the system more complicated. In order to select the significant factors, it is suggested that processing factors are set at high and low levels, i.e., max and min settings of their operational ranges. Plackett-Burman design can be used for screening out numerous factors. The use of screening design, as described in the present study, diminished considerably the number of experiments and gave as much as possible information and useful conclusions for the main effects of the examined factors. Process parameter that impacts the In vitro drug release study significantly are millimole (mM) of surfactant and cholesterol, time of hydration, hydration temperature. Operational ranges of these parameters should be optimized in order to produce quality product in a repeatable manner. In order to examine further the isolated significant factors for their main effects and their interactions, other experimental design techniques should be followed, such as fractional factorial, central composite or full factorial designs, depending on the number of factors and the runs recommended.
References
- Jadhav S, Morey P, Karpe M. Novel Vesicular System: An Overview. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science. 2012; 02: 193-202.
- Dubey S, Jain A. Niosomes: The ultimate drug carrier. Drug Invention Today. 2010; 2: 72-77.
- Desai S, Doke A. Development and evaluation of antifungal topical niosomal gel formulation. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2011; 3: 224-231.
- Karpe M, Kadam V. Formulation and Evaluation of Topical Delivery Of Antifungal Drug Bifonazole Using Microemulsion Based Gel Formulations. World Journal Of Pharmacy And Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2013; 2: 6405-6422.
- Randa Z, Adel A. Formulation and In vitro Evalution of Diacerein Loaded Niosomes. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2014; 6: 515-521.
- Amro A, Salem-Bekhit M. Plackett–Burman randomization method for Bacterial Ghosts preparation form E. coli JM109. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal. 2014; 22: 273-279.
- Loukas Y. A Plackett–Burnam screening design directs the efficient formulation of multi component DRV liposomes. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2001; 26: 255–263.
- Zidan A, Rahman Z. Product and process understanding of a novel pediatric anti-hivtenofovir Niosomes with a high-pressure homogenizer. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2011; 44: 93–102.
- Vyas J, Vyas P, et al. Development of Topical Niosomal Gel of Benzoyl Peroxide. International Scholarly Research Network. 2011: 4-9.
- Mahale N, Thakkar P. Niosomes: Novel sustained release nonionic stable vesicular systems — An overview. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science. 2012; 183–184: 46–54.
- Chawda H, Jain C, Bhairwa N. Formulation, characterization, stability and in vitro evaluation of nimesulide niosomes. Pharmacophore. 2011; 2: 168-185.
- Lohumi A, Rawat S, Sarkar S. A Novel Drug Delivery System: Niosomes Review. Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics. 2012; 2: 129-135.
- Khalid M. El-Say, et al. Development and optimization of diclofenac sodium niosomes using response surface methodology. Az. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009; 40: 272-286.
- Verma A, Bindal Mc. A vital role of niosomes on Controlled and Novel Drug delivery. Indian Journal of Novel Drug delivery. 2011; 3: 238-246.
- Vyas J, Vyas P. Formulation and evaluation of topical niosomal gel of erythromycin. International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2011; 3: 123-126.
- Kumar G, Rajesh warrao P. Nonionic surfactant vesicular systems for effective drug delivery—an overview. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B. 2011; 1: 208–219.