
Research Article
Austin J Anal Pharm Chem. 2018; 5(1): 1098.
Electrochemical Determination of Deferiprone Using PVC Membrane Sensors
Attia KAM, E,l-Abasawi NM, El-Olemy A and Serag A*
¹Pharmaceutical Analytical Chemistry Department, Faculty of Pharmacy, Al-Azhar University, 11751 Nasr City, Cairo, Egypt
*Corresponding author: Serag A, Pharmaceutical Analytical Chemistry Department, Faculty of Pharmacy, Al-Azhar University, 11751 Nasr City, Cairo, Egypt
Received: March 21, 2018; Accepted: April 23, 2018; Published: April 30, 2018
Abstract
Anovel, simple, accurate and selective potontiometric method was developed to determine deferiprone; a chelating agent that chelates trivalent iron. The method is based on fabricating a PVC membrane sensor that selectively determine the studied drug. The method was linear over the concentration range of 10-2-10-5 M with a nernstian slope of 58.4mV. The accuracy and precision of the method was found to be within the acceptable limits. Furthermore, the methods were statistically compared to a reported method and good results were obtained.
Keywords: Deferiprone; Potontiometry; PVC membrane sensor
Introduction
Deferiprone (Figure 1), a chelating agent that chelates trivalent iron cations (Fe3+) in a 3:1 (deferiprone: iron) ratio. It is indicated for the treatment of iron overload in patients with thalassemia major for whom deferoxamine therapy is contraindicated [1]. The literature survey revealed that few methods were developed for the determination of deferiprone including spectrophotometry [2- 4], spectrofluorimetric [5], HPLC [6-9] and different voltametric techniques [10-13].
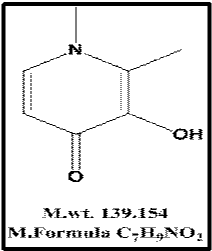
Figure 1: Structural formula of Deferiprone.
Modern ion - selective electrodes are based on membranes, across which material transport occurs, this material transport, includes both neutral and charged complex species or simple ions and electrons and leads to electrostatic potential differences across membranes. These so called membrane potentials reflect both composition and activities of ions in the exterior phase. The ion-selective electrode is capable of measuring selectivity and activity of a given ion regardless of other ions present in solution [14-17]. Potentiometric detection based on ion selective electrodes offers the advantages of speed and ease of preparation, fast response time, reasonable selectivity, wide linear dynamic range, online measurement and low cost [18].
The aim of the present work is to develop two novel ion selective electrodes based on poly (vinyl chloride) PVC membrane sensors for the potentiometric determination of deferiprone.
Experimental
Materials and reagents
- Pure deferiprone (99.77%) was kindly supplied by National Organization for Drug Control and Research, Giza, Egypt.
- Ferriprox® tablets each tablet claimed to contain 500 mg deferiprone (B.No. MK9814, manufactured by Apotex Inc., Toronto, Canada), supplied by National Organization for Drug Control and Research, Giza, Egypt.
- Methanol, tetrahydrofuran, dioctylphthalate (DOP), and (PVC) of high relative molecular weight (Sigma-Aldrich, Germany).
- Sodium tetraphenylborate (Sigma-Aldrich, Germany), prepared as 10-2M aqueous solution.
- Glucose, glycine, sucrose, urea, potassium chloride, calcium chloride, magnesium chloride, sodium chloride and nickel chloride (El-Nasr Company, Egypt), prepared as 10-3M aqueous solution.
- Sodium hydroxide (El-Nasr Company, Egypt), prepared as 0.1N aqueous solution.
- Hydrochloric acid (El-Nasr Company, Egypt), prepared as 0.1N aqueous solution.
- Monobasic potassium phosphate, potassium chloride, boric acid, glacial acetic acid and sodium acetate tri-hydrate (El-Nasr Company, Egypt).
- Buffers of different pH values prepared as prescribed in US pharmacopeia [19]:
- Hydrochloric acid buffer, pH 2.
- Acetate buffer pH range from 4 to 5.5.
- Phosphate buffer pH range from 6 to 8.
- Alkaline borate buffer pH range from 8 to 10.
Instruments
- Jenway pH meter 3510 (USA) with Ag/AgCl reference electrode no 924017-LO3-Q11C.
- Bandelinsonorox, Rx 510 S, magnetic stirrer (Hungarian).
Standard solutions
A stock standard solution of deferiprone (10-2M) was prepared by dissolving 0.139g of the drug powder in drug powder in 75ml of potassium chloride buffer pH (2.0) and complete to 100ml with the same solvent. Different working solutions of varying strengths ranging from (10-6 to 10-3 M) were prepared by suitable dilution from the stock standard solution with the same solvent.
Procedure
Preparation of deferiprone PVC membrane sensor: The ion association complex, deferiprone tetraphenylborate (DF-TPB) was prepared by mixing of 50ml of 10-2M of both deferiprone and sodium tetraphenylborate solutions. The resulting precipitate was left in contact with their mother liquor for 6h, then the precipitate was filtered and washed thoroughly with distilled water and left to dry at room temperature for 24h. In a glass petri dish (5-cm diameter), 0.184ml of DOP was thoroughly mixed with 184mg of PVC and 32mg of DF-TPB. The mixture was dissolved in 10mL of tetrahydrofuran. The petri dish was then covered with a Whatman No. 3 filter paper and left to stand overnight to allow for solvent evaporation at room temperature. A master membrane with a thickness of 0.1mm was obtained. From the master membrane, an 8mm diameter disk was cut out from the prepared membrane and glued using tetrahydrofuran to a transposable PVC tip that was clipped into the end of the electrode glass part. The resulting electrode body was filled with equal portions of 10-2M KCl and 10-2M deferiprone. The prepared sensor was preconditioned by soaking in 10-2M drug solution for 4h. When not in use, the sensor was stored in air.
Potential measurement conditions of the proposed sensors: The electrochemical system can be represented as following:
– For deferiprone PVC membrane sensor: internal reference electrode/internal filling solution/PVC membrane/test solution/ external reference electrode.
- Soaking time: 8h for deferiprone PVC membrane sensor,
- Response time: 45s for deferiprone PVC membrane sensor.
Sensors calibration: The conditioned sensor was immersed in conjunction with Ag/AgCl reference electrode in the solutions of deferiprone in the range of 10-6 to 10-2 M. They were allowed to equilibrate while stirring until achieving constant reading of the potentiometer. Then, the electromotive force values were recorded within ± 1mV. Calibration graph was plotted that related the recorded electrode potential values versus the negative logarithmic value of the drug concentration.
Application to pharmaceutical preparation: Ten Ferriprox® tablets (500mg of deferiprone per tablet) were weighted and finely powdered. The appropriate weight of the powder equivalent to 0.139g of deferiprone was accurately transferred to 100-mL volumetric flask and the volume was made up to 75ml with potassium chloride buffer. The solution was shaken vigorously for 15min then sonicated for 30min and completed to 100ml with the same solvent to obtain a solution labeled to contain 10-2M of deferiprone. The solution was filtered with 0.45µm membrane filter then aliquots covering the working concentration range were obtained by diluting the stock solution.
Results and Discussion
Electrochemical techniques are powerful and versatile analytical techniques that offer high sensitivity, accuracy, and precision as well as a large linear dynamic range, with relatively low-cost instrumentation. In the present study an ion selective membrane electrode based on PVC sensor has been constructed for selective determination of deferiprone. The method is based on the fact that, deferiprone behaves as a cation with an anionic type of ion exchanger such as tetraphenylborate to prepare water insoluble association complex using precipitation based technique. The resulting precipitates have low solubility product, suitable grain size and physically compatible with the matrix.
Performance characteristics of the developed sensor
The electrochemical performance of the investigated sensors was evaluated according to IUPAC recommendation data [20]. Calibration was carried out by immersing the developed sensor in conjunction with Ag/AgCl reference electrode in solutions of deferiprone in the concentration range of 10-6 to 10-2 M. The performance characteristics of the proposed sensor were summarized in Table 1. The profile of the potential in mV versus negative logarithmic molar concentration of deferiprone for the investigated sensors was plotted as shown in Figure 2.
Parameter
Deferiprone PVC sensor
- Regression equation
ya= bbx+ a
- Slope (b)
-58.4
- Intercept (a)
58.4
Coefficient of determination (r2)
0.9996
Linearity range (M)
10-5- 10-2
Working pH range
2–6
Response time (s)
45
LOD (M)
3.3x10-6
Stability (weeks)
3
Accuracy (%R)c
100.23
Repeatability
Precision (%RSD)c
1.186
Intermediate precision
1.387
ya is the recorded sensor potential.
xb is the molar concentration of the drug.
cValues for 3 determinations of 3 different concentrations.
Table 1: The performance characteristics of the proposed described sensors.
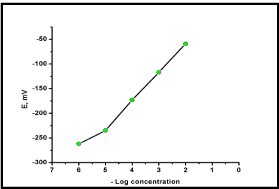
Figure 2: Profile of the potential in mV/- Log molar concentration of
deferiprone using PVC membrane sensor.
Optimization of the sensors composition
The ion association complex is the most important part of an ion selective sensor. It is the electro active ingredient which is responsible for the selective recognition of the ion in the developed sensor. The main components of a PVC membrane sensor are ion association complex, PVC and plasticizer. For the preparation of the membrane, the ion association complex, plasticizer and PVC should be taken in the appropriate percentage-weight ratios to improve the performance of the developed sensor. DF-TPB was prepared and tested as a modifier for the proposed sensor. It was studied by varying the percentages of the ion association complex, while keeping the percentages of the PVC and the plasticizer equal 1:1 as shown in Table 2. The sensor made of 8% (w/w) of DF-TPB exhibited a near Nernstian slope of -58.4mV/decade. Freshly prepared sensors must be soaked to activate the surface of the membrane to form an infinitesimally thin gel layer at which ion exchange occurs. The investigated sensors were soaked in 10-2M solution of the drug. Calibration graphs were constructed for the sensor after different time intervals (0, 2, 4, 6, 8 and 12 h) till the slope of the calibration graph deviated largely from the Nernstian value and the sensor. The results indicated that the optimum soaking time was 8h for deferiprone PVC membrane sensor.
Composition % (w/w)
Linearity rang
Slope (mV/decade)
r2
DOP
PVC
DF-TPB
(M)
48
48
4
1x10-5-1x10-2
-52.6
0.9993
46
46
8
1x10-5-1x10-2
-58.4
0.9996
45
45
10
1x10-5-1x10-2
-53.9
0.9994
44
44
12
1x10-5-1x10-2
-54.1
0.9994
Table 2: Optimization of the membrane composition (w/w %) of the deferiprone PVC memrane sensor.
The stability of the potential readings was investigated over a wide pH range (2 – 10) to determine the working pH range of the proposed sensor. The investigations were performed in 10-2 and 10-3 M of deferiprone solutions. The potential obtained at each pH value was recorded. Representative curve for the effect of pH on the proposed sensoris shown in Figure 3. The potential remained constant in the pH range (2 – 6). The influence of the related interfering compounds on the response of the investigated sensor towards the drug was investigated. The separate solution method (SSM) was applied based on measuring the potential of 10-3M solution of drug and the interfering ions separately. Then the selectivity coefficients were calculated. The interfering compounds were; potassium chloride, calcium chloride, magnesium chloride, sodium chloride, nickel chloride, glucose, urea, glycine and sucrose. The results of the calculated selectivity coefficients indicated that the proposed sensors were highly selective towards the studied drug.For analytical applications; the response time of the prepared sensor is of critical importance. The average time required for the electrode to reach a steady potential response within ±1mV of the final equilibrium value after successive immersion of a series of the drug solutions, each having a 10-fold difference in concentration, was investigated. Stable responses were achieved within 45 s for deferiprone PVC membrane sensor.
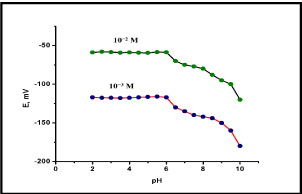
Figure 2: Effect of pH on the response of deferiprone using PVC membrane
sensor.
Method validation
Linearity and range: Under the described experimental conditions, the calibration graph for the sensor was constructed by plotting the recorded sensor potential versus negative logarithmic value of the drug concentration. The regression plots were found to be linear over the range of 10-5-10-2 M for the studied drug.
Limit of detection: Limit of detection was measured by interception of the extrapolated arms of Figure 2. It was found to be 3.3x10-6 for deferiprone PVC membrane sensor. The small value of LOD indicates good sensitivity of the described sensor.
Accuracy and precision: Accuracy of the described methods, calculated as the mean percent recovery (%R), was assessed by applying the described procedure for triplicate determination of three concentration levels covering the linearity range of deferiprone (0.5 x 10-2, 10,-3 and 10-4 M). The results in Table 1 indicated the accuracy of the proposed method.
Precision of the methods, calculated as the percent of relative standard deviation (%RSD), was assessed by triplicate determination of three concentration levels covering the linearity range of the drug (0.5 x 10-2, 10-3 and 10-4 M) within one day for repeatability and on three successive days for Inter mediate precision. The small values of %RSD indicated high precision of the method as shown in Table 1.
Application of the developed method
The described electrochemical method was applied for the determination of deferiprone in Ferriprox® tablets. Satisfactory results were obtained in good agreement with the label claim, indicating no interference from excipients and additives. The obtained results were statistically compared to those obtained by the reported method [8]. No significant differences were found by applying t-test and F-test at 95% confidence level, indicating good accuracy and precision of the proposed method for the analysis of the studied drug in its pharmaceutical dosage form, as shown in Table 3.
Parameters
Deferiprone PVC sensor
Reported method (8)
na
5
5
Average (%Recovery)
100.07
100.25
SD
0.93
2.04
%RSD
0.93
2.035
t
0.179
––
(2.306)b
F
4.81
––
(6.388)b
aNumber of measurements,
bThe values in parenthesis are tabulated values of “t “and “F” at (P = 0.05).
Table 3: Determination of deferiprone in Ferriprox® tablets by the described sensor and the reported method.
Conclusion
A PVC membrane sensor was applied for the selective potentiometric determination of deferiprone without prior separation or pretreatment. The proposed method is simple, sensitive, accurate and precise. It does not need any sophisticated apparatus and could be easily applied in quality control laboratories. Moreover, the proposed method does not require multiple steps or complicated handling associate with chromatographic methods.
References
- Kontoghiorghes G, Pattichis K, Neocleous K, Kolnagou A. The design and development of deferiprone (L1) and other iron chelators for clinical use: targeting methods and application prospects. Current medicinal chemistry. 2004; 11: 2161-2183.
- Barot H, Shah D, Maheshwari D. Development of stability indicating UV spectroscopy method for the estimation of deferiprone in pharmaceutical formulation. Am J Pharm Tech Res. 2015; 5: 621-632.
- Ahmed M, Jangade V, Shetty S, Aradhya V, Kuppast I, Kumar A. Development and validation of first order derivative spectrophotometric method for the estimation of deferiprone in bulk and capsule dosage form. Int J Univers Pharm Life Sci. 2015; 4: 169-176.
- Chavada VD, Bhatt NM, Sanyal M, Shrivastav PS. Pyrophosphate functionalized silver nanoparticles for colorimetric determination of deferiprone via competitive binding to Fe (III). MicrochimicaActa. 2017; 184: 4203-4208.
- Lashkar JM, Amjadi M, Soleymani J, Tamizi E, Panahi-Azar V, Jouyban A. Development and Validation of a Terbium-Sensitized LuminescenceAnalytical Method for Deferiprone. Iranian journal of pharmaceutical research. 2012; 11: 771.
- Manzoori JL, Amjadi M, Soleymani J, Tamizi E, Rezamand A, Jouyban A. Determination of deferiprone in urine and serum using a terbium-sensitized luminescence method. Luminescence. 2012; 27: 268-273.
- Abbas M, Nawaz R, Iqbal T, Alim M, Asi MR. Quantitative determination of deferiprone in human plasma by reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography and its application to pharmacokinetic study. Pakistan journal of pharmaceutical sciences. 2012; 25: 343-348.
- Limenta LMG, Jirasomprasert T, Tankanitlert J, Svasti S, Wilairat P, Chantharaksri U, et al. UGT1A6 genotype-related pharmacokinetics of deferiprone (L1) in healthy volunteers. British journal of clinical pharmacology. 2008; 65: 908-916.
- Song TS, Hsieh YW, Peng CT, Liu CH, Chen TL, Hour MJ. Development of a fast LC-MS/MS assay for the determination of deferiprone in human plasma and application to pharmacokinetics. Biomed Chromatogr. 2012; 26: 1575- 1581.
- Yadegari H, Jabbari A, Heli H, Moosavi-Movahedi A, Majdi S. Electrochemistry of deferiprone as an orally active iron chelator and HIV-1 replication inhibitor and its determination. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society. 2008; 19: 1017-1022.
- Yadegari H, Jabbari A, Heli H, Moosavi-Movahedi A, Karimian K. Electrooxidation and determination of deferiprone on a glassy carbon electrode. ChemAnal(Warsaw). 2008; 53: 5-16.
- Yadegari H, Jabbari A, Heli H, Moosavi-Movahedi A, Karimian K, Khodadadi A. Electrocatalytic oxidation of deferiprone and its determination on a carbon nanotube-modified glassy carbon electrode. ElectrochimicaActa. 2008; 53: 2907-2916.
- Hajjizadeh M, Jabbari A, Heli H, Moosavi-Movahedi A, Shafiee A, Karimian K. Electrocatalytic oxidation and determination of deferasirox and deferiprone on a nickel oxyhydroxide-modified electrode. Analytical biochemistry. 2008; 373: 337-348.
- Thomas JDR. Ion-selective electrode reviews: Elsevier; 2013.
- Morf WE. The principles of ion-selective electrodes and of membrane transport: Elsevier; 2012.
- Buck RP, Lindner E. Recommendations for nomenclature of ion-selective electrodes. Pure App Chem. 1994; 66: 2527-2536.
- Thévenot DR, Toth K, Durst RA, Wilson GS. Electrochemical biosensors: recommended definitions and classification. BiosnseBioelectron. 2001; 16: 121-131.
- Moody G, Saad B, Thomas J. The development of polymer matrix membranes for ion-selective electrodes. Sel Electrode Rev. 1988; 10: 71.
- United States Pharmacopoeia 30 and National formulary 25. Rockville (MD): United State Pharmacopoeia Convention; 2007.
- Buck RP, Cosofret VV. Recommended procedures for calibration of ionselective electrodes (Technical Report). Pure Appl Chem. 1993; 65: 1849- 1858.