
Research Article
Austin J Anal Pharm Chem. 2018; 5(3): 1106.
Determination of Lomefloxacin Hydrochloride by Ion- Pair Complex Formation with Ammonium Reineckate using Atomic Absorption Spectrometry
Nassar MW, Attia KAM, Said RA, El-Olemy A andHasan MA*
Pharmaceutical Analytical Chemistry Department, Faculty of Pharmacy, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt
*Corresponding author: Mohamed Abd Allah, Assistant lecturer of Analytical Chemistry, Department of Pharmaceutical Analytical Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy, Al-Azhar University, Nasr City, Cairo, Egypt
Received: September 03, 2018; Accepted: October 08, 2018; Published: October 15, 2018
Abstract
Lomefloxacin hydrochloride is a fluorinated 4-quinolone or fluoroquinolone antibiotic. In this study, a rapid, specific, accurate and precise atomic absorption spectrometric method has been developed and validated for the determination of lomefloxacin hydrochloride in bulk powder and in pharmaceutical preparation depending on its ability to form stable ion pair complex with ammonium reineckate. This formed complex is insoluble in aqueous solution and can easily be separated by filtration. The precipitate could be dissolved in acetone. Then the amount of chromium in the formed complex of lomefloxacin-reineckate ion pair can be measured directly by atomic absorption spectrometer at 357.9nm. These amounts are corresponding directly to the concentrations of the reacted lomefloxacin hydrochloride. The linear regression analysis data for the calibration curve shows a good relationship in the range of 15 – 100 μg/ml. The developed method was validated according to the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) guidelines demonstrating good accuracy and precision. The results were statistically compared with those obtained by the reported method, and no significant difference was found.
Keywords: Lomefloxacin hydrochloride; Fluoroquinolone; Atomic absorption spectrometry; Ammonium reineckate and chromium
Introduction
Lomefloxacin hydrochloride is a fluoroquinolone antibacterial which chemically known as (RS)-1-ethyl-6,8-difluoro-1,4-dihydro- 7-(3-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid hydrochloride (Figure 1). Lomefloxacin hydrochloride is a white powder which is soluble in water and methanol with 387.81 molecular weigth [1]. Lomefloxacin exhibits antimicrobial effects on DNA gyrase (bacterial topoisomerase II) and bacterial topoisomerase IV. Inhibition of DNA gyrase results in relaxation of supercoiled DNA, promoting DNA strand breakage. Inhibition of topoisomerase IV impacts chromosomal stabilization during cell division, thus interfering with the separation of newly replicated DNA. It has wider spectrum of activity than nalidixic acid and more favorable pharmacokinetics, allowing its use in systemic infections. It has been used in the treatment of infections including bone and joint infections, gastroenteritis (including travelers’ diarrhea and campylobacter enteritis, cholera, salmonella enteritis, and shigellosis), gonorrhea, infections in immuno compromised patients (neutropenia), Q fever, lower respiratory-tract infections, typhoid and paratyphoid fever [2]. It’s non official drug, but literature survey reveals that many HPLC methods were reported for determination of lomefloxacin hydrochloride in pharmaceutical preparations and biological fluids [3-11]. Also atomic absorption [11], spectrophotometric [12-19], spectrofluorimetric [20-24] and electrochemical [25-30] methods were reported for determination of lomefloxacin hydrochloride alone or in presence of other fluoroquinolone antibiotics. Reviewing the literature on the determination of lomefloxacin hydrochloride revealed the lack of any atomic absorption spectrometric determination of lomefloxacin hydrochloride using ammonium reineckate as precipitating reagent. The aim of this work is to develop and validate simple, accurate and precise atomic absorption spectrometric method for determination of lomefloxacin hydrochloride in bulk powder and in pharmaceutical preparation depending on its ability to form stable ion pair complex with ammonium reineckate. The main goals of analytical atomic spectrometry are to attain the broadest dynamic range, suppress the matrix effect, eliminate spectral interferences, minimize the time and cost required for sample preparation.
Experimental
Instruments
GBC Elemental atomic absorption flame spectrometer, model: GBC 932 AA (Australia), equipped with air acetylene burner, spray chamber, adjustable nebulizer and computed with GBC AAS software. Chromium was measured at wavelength 357.9nm, slit width 0.2nm, relative noise 1nm, lamp current 10mA, integration time 4 seconds.
Elementar-Vario El (Germany) was used for elemental analysis of the ion pair.
FT-IR, Nicolet IR 200 (Thermo electron corporation, USA).
Analytical balance (Precisa, Switzerland).
Parameters
Proposed method
Wavelength (nm)
357.9
Linearity range (μg/ml)
15 ─ 100 (2.01-13.41 ppm chromium)
LOD (μg/ml)
1.893
LOQ (μg/ml)
5.735
Regression Equation
y a = b x b + a
- Slope (b)
0.0025
- Intercept (a)
0.0014
Coefficient of determination (r2)
0.9997
Accuracy (% R)c
100.62
Precisiond (% RSD)
- Repeatability
0.685
- Intermediate precision
1.027
Table 1: Regression and validation data for the determination of lomefloxacin hydrochloride by the proposed atomic absorption spectrometric procedure.
aThe absorbance at 357.9 nm.
bConcentration of lomefloxacin hydrochloride in µg/ml.
cAverage of nine determinations (three concentrations repeated three times).
d%RSD of nine determinations (three concentrations repeated three times).
Pharmaceutical taken (µg/ml)
Pharmaceutical founda (µg/ml)
Pure added (μg/ml)
Pure foundb (µg/ml)
Pure recovery (%R)
30
29.79
20
20.18
100.92
30
29.82
99.41
40
39.34
98.35
50
50.94
101.87
Mean ± %RSD
100.14±1.562
Table 2: Recovery study of lomefloxacin hydrochloride by standard addition technique using the proposed atomic absorption spectrometric procedure in Lomex® tablet.
aAverage of five determinations.
bAverage of three determinations.
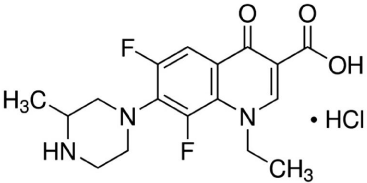
Figure 1: Structural formula of lomefloxacin hydrochloride.
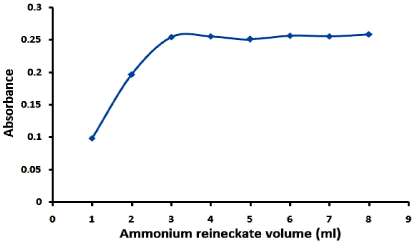
Figure 2: Effect of volume of ammonium reinckate (10-2 M) on the absorbance of its reaction product with lomefloxacin hydrochloride (100µg/ml).
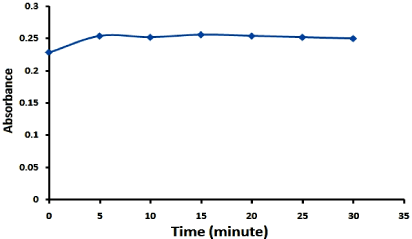
Figure 3: Effect of time required for complete reaction of lomefloxacin (100µg/ml) and ammonium reinckate (10-2 M).
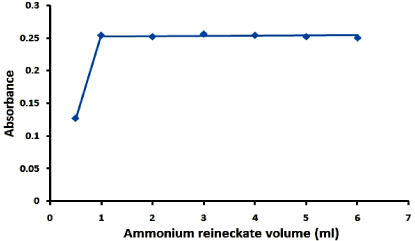
Figure 4: Stoichiometry of the reaction of lomefloxacin hydrochloride (2.6 x 10-2M) with ammonium reinckate (2.6 x 10-2M) by molar ratio method.
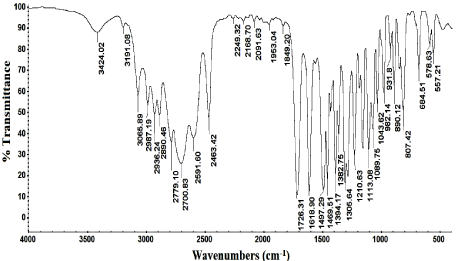
Figure 5: IR spectrum of lomefloxacin hydrochloride.
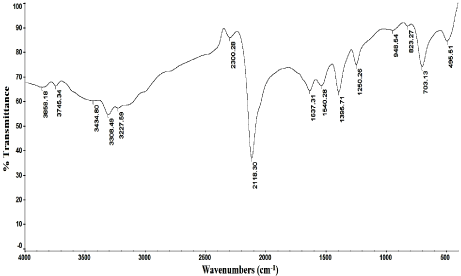
Figure 6: IR spectrum of ammonium reineckate.
Materials and reagent
All reagents used were of analytical grade, solvents were of HPLC grade and water used throughout the procedure was freshly distilled.
Pure lomefloxacin hydrochloride (99.65%) was kindly provided by Sigma Pharmaceutical Industries - Quesna City – Egypt.
Lomex® tablet: labeled to contain 442mg lomefloxacin hydrochloride per tablet equivalent to 400mg lomefloxacin, manufactured by Sigma Pharmaceutical Industries - Quesna City – Egypt; (batch number 40357), purchased from local market.
Ammonium reineckate (Sigma-Aldrich, Germany), prepared as 10-2 and 2.6 x 10-2 M aqueous solutions.
Hydrochloric (El-Nasr Company, Egypt), prepared as 0.1N aqueous solutions.
Acetone and petroleum ether, (Sigma-Aldrich, Germany).
Standard solutions
A standard solution of lomefloxacin hydrochloride 10mg/ml (2.6 x 10-2M) was prepared by dissolving 1g of the drug powder in 75ml of 0.1N hydrochloric acid and the volume was completed to 100ml with the same solvent.
Procedures
General procedure: Aliquots of standard lomefloxacin hydrochloride solution (10mg/ml) equivalent to (1.5–10 mg) were transferred into a series of 10ml volumetric flasks and 4ml of 10-2M ammonium reineckate solution was added. The mixture was left to stand for 15 minutes at room temperature to assure complete coagulation of the resulting precipitate which was then filtered off on Whatman filter paper and washed several times with water. The precipitate was separated and dissolved in least amount of acetone, and completed to the mark in a 100ml volumetric flasks with water. The solutions were then aspirated directly in the atomic absorption spectrometer and measured the chromium ion concentration at wavelength 357.9nm.
Optimization of experimental conditions:
Effect of volume of ammonium reineckate solution: The general procedure for the method was repeated using fixed amount of lomefloxacin hydrochloride (10mg) and different volumes (1–8 ml) of 10-2M ammonium reineckate solution.
Effect of time required for complete precipitation: The general procedure for the method was repeated using fixed amount of lomefloxacin hydrochloride (10mg) and the solution allowed to stand for different time intervals ranging from 0–30 minutes.
Determination of stoichiometry of the reaction by:
Elemental analysis and IR spectroscopy: Ion-associates synthesis protocol included addition of 50ml of 10-2M aqueous solution of ion pairing agent (ammonium reineckate) drop wise to 50ml of 10-2M lomefloxacin hydrochloride solution. The mixture was left for 15 minutes at room temperature to assure complete coagulation of the resulting precipitate which was then filtered off on Whatman filter paper and washed several times with distilled water. The compound was left to dry for 12 hours at 60oC, washed with petroleum ether to remove any residual moisture, and then ground to fine powder. Small sample portions were sent for elemental analysis and IR spectroscopy.
Molar ratio method: The general procedure for the method was repeated using 1 ml of lomefloxacin hydrochloride standard solution (2.6 x 10-2M) and different volumes (0.5–6 ml) of ammonium reineckate standard solution (2.6 x 10-2M).
Application to pharmaceutical formulation: Ten Lomex® tablets (442mg/tablet) were weighted and finely powdered. Appropriate weight of powder equivalent to 1g of lomefloxacin hydrochloride was accurately weighted, transferred to 100ml volumetric flask and the volume was made up to 75ml with 0.1N hydrochloric acid. The solution was shaken vigorously for 15min then sonicated for 30min and then filtered. The volume was completed to 100ml with the same solvent to obtain a concentration of 10mg/ml. Repeat the general procedure using aliquots covering the working concentration range. Lomefloxacin hydrochloride content of the tablets was determined from the corresponding regression equation.
Results and Discussion
In the present study, a simple atomic absorption spectrometric method was suggested for selective quantitative determination of lomefloxacin hydrochloride depending on its reaction with ammonium reineckate.
Ammonium reineckate salt NH4[Cr(NH3)2(SCN)4] is ammonium tetrathiocyanodiammonochromate having a high affinity towards the formation of water insoluble ion pair complex with lomefloxacin hydrochloride. This formed complex is insoluble in aqueous solution and can easily be separated by filtration. The precipitate could be dissolved in acetone. Then the amount of chromium in the formed complex of lomefloxacin-reineckate ion pair can be measured directly by atomic absorption spectrometer at 357.9nm. These amounts are corresponding directly to the concentrations of the reacted lomefloxacin hydrochloride.
Optimization of experimental conditions
The optimization of the method was carefully studied to achieve complete reaction formation, highest sensitivity and maximum absorbance.
Effect of volume of ammonium reineckate solution: Different volumes of ammonium reineckate solution (10-2M) were used and the results as shown in Figure 2 prove that; 4ml of 10-2M of ammonium reineckate solution is the optimum for complete precipitation.
Effect of time required for complete precipitation: Different time intervals were tried to choose the optimum reaction time and the results as shown in Figure 3 prove that; the time required for complete precipitation was found to be 5 minutes. The mixture was left for 15 minutes at room temperature to assure complete coagulation and aggregation of the resulting precipitate to facilitate its filteration and prevent any loss during filteration process.
Stoichiometry of the reaction
Molar ratio method was applied for the determination of the stoichiometry of the reaction which was found to be a 1:1 ratio of lomefloxacin hydrochloride and ammonium reineckate salt as shown in Figure 4. The results of molar ratio method was confirmed by the results of elemental analysis of the formed ion pair complex (C, 38.29; H, 4.03; N, 18.54; S, 18.92). Also the IR spectrum of lomefloxacin hydrochloride, Figure 5, showes a characteristic band corresponding to the stretching vibrations of C=O group, while the IR spectrum of ammonium reineckate, Figure 6, has a characteristic band at 2118cm- 1 due to ν (CN) “in the Cr-NCS link” stretching vibration, a band at 703cm-1 due to νsym (C-S) and at 495cm-1 due to δ (NCS) deformation vibration [31]. The IR spectrum of the formed ion associate, Figure 7, shows a weak band corresponding to νCH (aliphatic) at 2997cm-1. The band corresponding to the stretching vibrations of C=O shifted to a lower frequency by ~35cm-1. In addition, the peak due to νNCS is shifted to a lower frequency by 46cm-1. Peaks due to νsym (C-S) and δ (NCS) appear at 695 and 489 cm-1 respectively. The above IR interpretation indicates that an ion associate has been formed between lomefloxacin hydrochloride and ammonium reineckate. Hence, each 15μg/ml of lomefloxacin hydrochloride is equivalent to 2.01μg/ml of chromium. The following equation describes the reaction mechanism and the expected structure of the ion pair as shown in Figure 8.
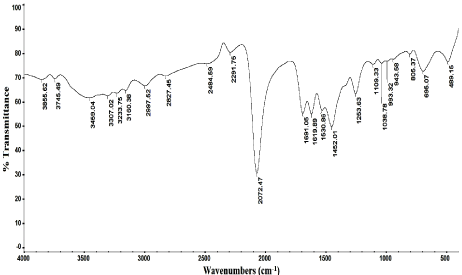
Figure 7: IR spectrum of lomefloxacin-reineckate ion pair complex.
Methods validation
Validations of the proposed method was assessed as per the ICH guidelines [32].
Linearity and range: Under the described experimental conditions, the calibration graph for the method was constructed by plotting the measured absorbance at 357.9nm versus the final drug concentrations in μg/ml. The regression plot was found to be linear over the range of (15-100 μg/ml) equivalent to (2.01-13.41 ppm) chromium. The regression data were presented in Table 1. The value of coefficient of determination indicated the good linearity of the calibration graph.
Limits of detection and quantitation: The limits of detection (LOD) and the limits of quantitation (LOQ) were calculated according to ICH guidelines from the following equations:
LOD = 3.3 σ / S; LOQ = 10 σ / S
Where σ is the residual standard deviation of the regression line and S is the slope of the calibration curve. LOD and LOQ values were mentioned in Table 1 and indicate good sensitivity of the method.
Accuracy and precision: Accuracy of the described method, calculated as the mean percent recovery (%R), was assessed by applying the described procedure for triplicate determination of three concentration levels covering the linearity range of the drug (30, 60 and 90 μg/ml). The results in Table 1 indicated the accuracy of the proposed methods. Precision of the method, calculated as the percent relative standard deviation (%RSD), was assessed by triplicate determination of three concentration levels covering the linearity range of the drug (30, 60 and 90 μg/ml) within one day for repeatability and on three successive days for intermediate precision. The small values of %RSD indicated high precision of the methods as shown in Table 1.
Specificity: Standard addition technique was applied to check the specificity of the described method. It was done by using aliquots of standard lomefloxacin hydrochloride solution (10mg/ml) containing (2, 3, 4 and 5 mg) with aliquot of already analyzed Lomex® tablets solution (10mg/ml) containing (3mg), then the percent recovery (%R) of pure added concentrations were calculated. The data listed in Table 2 proved that the proposed methods could selectively analyze the drug without any interference from any excipients.
Pharmaceutical applications
The proposed method was applied to the determination of lomefloxacin hydrochloride in Lomex® tablet. Satisfactory results were obtained in good agreement with the label claim, indicating no interference from excipients and additives which was confirmed by the results of standard addition technique. The obtained results were statistically compared to those obtained by the reported method [17]. No significant differences were found by applying student’s t-test and F-test at 95% confidence level [33], indicating good accuracy and precision of the proposed method for the analysis of the studied drug in its pharmaceutical dosage form, as shown in Table 3.
Parameters
Proposed method
Reported method* [17]
Number of measurements
5
5
Mean % recovery of lomefloxacin
99.31
100.48
% RSD
0.916
1.314
Variance
0.827
1.743
Student’s t-test**
1.636 (2.306)
——
F-value**
2.107 (6.388)
——
Table 3: Determination of lomefloxacin hydrochloridein Lomex® tablet by the proposed atomic absorption spectrometric and reported methods.
*Reported method is using first derivative spectrophotometric method with zero crossing point at 295.2nm.
**The values in parenthesis are tabulated values of “t” and “F” at (P = 0.05).
Conclusion
In this work accurate and precise atomic absorption spectrometric method for determination of lomefloxacin hydrochloride in bulk powder and in pharmaceutical preparation depending on its ability to form stable ion pair complex with ammonium reineckate. The method was validated according to the ICH guidelines and can be used for the routine analysis and for checking quality of pharmaceutical preparations containing lomefloxacin hydrochloride.
References
- Sweetman S. Martindale: the complete drug reference. 36th ed. London: The Pharmaceutical Press. 2009.
- The Merck Index 14th Ed. Published by Merck and CO. INC., Rahway, USA. 2006.
- Shibl AM, Tawfik AF, El-Houfy S, Al-Shammary FJ. Determination of lomefloxacin in biological fluids by high-performance liquid chromatography and a microbiological method. J Clin Pharm Ther. 1991; 16: 353-359.
- Carlucci G, Cilli A, Liberato M, Mazzeo P. Determination of lomefloxacin in human plasma by solid-phase extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography with UV detection. J Pharmaceut Biomed. 1993; 11: 1105-1108.
- Garcia MA, Solans C, Calvo A, Royo M, Hernandez E, Rey R, et al. Determination of lomefloxacin in plasma samples by HPLC with fluorescence detection. Application to pharmacokinetic studies. Chromatographia. 2001; 54: 577-580.
- Zendelovska D, Stafilov T. Development and validation of high-performance liquid chromatographic method for determination of ofloxacin and lomefloxacin in human plasma. J Serb Chem Soc. 2005; 70: 1451-1460.
- Tozo GC, Salgado HR. Determination of lomefloxacin in tablet preparations by liquid chromatography. J AOAC Int. 2006; 89: 1305-1308.
- Amran MS, Hossain MR, Amjad FM, Sultana S, Baki MA, Hossain MA. Development of a simple, sensitive and rapid quantitative analytical method for lomefloxacin by high performance liquid chromatography. Stamford J Pharm Sci. 2011; 4: 69-73.
- Chunyan S, Yaping Z, Jianghong G. Determination of Lomefloxacin and its related substances in lomeftoxacin hydrochloride dispersible tablets by HPLC. China Pharmacist. 2012; 9.
- Song S, Zhao D, Sun J, Miao Q, Liu X, Wang Y, et al. Development of a UPLC–MS/MS method for the determination of lomefloxacin in rabbit aqueous humor and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. J Chromatogr B. 2016; 1033-1034: 187-192.
- Jin T, Wu H, Gao N, Chen X, Lai H, Zheng J, et al. Extraction of quinolones from milk samples using bentonite/magnetite nanoparticles before determination by high‐performance liquid chromatography with fluorimetric detection. J Sep Sci. 2016; 39: 545-551.
- Salem H. Spectrofluorimetric, atomic absorption spectrometric and spectrophotometric determination of some fluoroquinolones. Am J Appl Sci. 2005; 2: 719-729.
- Issa YM, Abdel-Gawad FM, Abou Table MA, Hussein HM. Spectrophotometric determination of ofloxacin and lomefloxacin hydrochloride with some sulphonphthalein dyes. Anal lett. 1997; 30: 2071-2084.
- Feng T, Huiyun L, Yuan L. Extraction spectrophotometric determination of lomefloxacin. Chinese J Anal Chem. 2001; 5.
- Gomes GC, Salgado HRN. Validation of UV spectrophotometric method for determination of lomefloxacin in pharmaceutical dosage form. Acta Farm Bonaerense. 2005; 24: 406-408.
- Salem MY, EL-Guindi NM, Mikael HK, Abd El-Fattah LE. Stability indicating methods for the determination of some fluoroquinolones in the presence of their decarboxylated degradates. Chem Pharm Bull. 2006; 54: 1625-1632.
- Darwish IA, Sultan MA, Al-Arfaj HA. Kinetic spectrophotometric method for determination of ciprofloxacin and lomefloxacin in their pharmaceutical dosage forms. Int J Res Pharm Sci. 2010; 1: 43-50.
- Tieli Z, Huichun Z, Linpei J. Photochemical fluorescence enhancement of the terbium–lomefloxacin complex and its application. Talanta. 1999; 49: 77-82.
- Ulu ST. Highly sensitive spectrofluorimetric determination of lomefloxacin in spiked human plasma, urine and pharmaceutical preparations. Eur J Med Chem. 2009; 44: 3402-3405.
- Yi YN, Li GR, Wang YS, Zhou YZ, Zhu HM. Simultaneous determination of norfloxacin and lomefloxacin in milk by first derivative synchronous fluorescence spectrometry using Al (III) as an enhancer. Anal Chim Acta. 2011; 707: 128-134.
- Saleh GA, Askal HF, Refaat IH, Abdel-aal FAM. Chemiluminescence determination of some fluoroquinolones using NBS-Luminol system. Asian J Biomed Pharm Sci. 2014; 4: 39-49.
- Hongyan CEZYG. Adsorptive voltammetric behavior of lomefloxacin and its application. J Beijing Normal Univ. 2001; 2.
- Vı́lchez JL, Araujo L, Prieto A, Navalon A. Differential-pulse adsorptive stripping voltammetric determination of the antibacterial lomefloxacin. J Pharm Biomed anal. 2001; 26: 23-29.
- El ries MA, Wassel AA, Abdel Ghani NT, El-Shall MA. Electrochemical adsorptive behavior of some fluoroquinolones at carbon paste electrode. Anal Sci. 2005; 21: 1249-1254.
- Ramadan A, Mandil H. Determination of lomefloxacin in pharmaceuticals using differential pulse polarographic analysis. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2012; 4: 255-261.
- Ayad MM, Abdellatef HE, Hosny MM, Kabil NA. Conductometric determination of sibutramine HCl, sumatriptan succinate and lomefloxacine HCl and the solubility products of their ion associates with molybdophosphoric acid. Eur J Chem. 2013; 4: 297-302.
- Kumar N, Goyal RN. Gold-palladium nanoparticles aided electrochemically reduced graphene oxide sensor for the simultaneous estimation of lomefloxacin and amoxicillin. Sensors and Actuators B: Chem. 2017; 243: 658-668.
- Uivarosi V, Monciu CM. Studies on the gravimetric and spectrophotometric analysis of norfloxacin using ammonium reineckate. Rev Chim. 2009; 60: 132-136.
- International Conference on Harmonization, ICH Harmonized Tripartite Guideline. Validation of analytical procedure: text and methodology, Q2 (R1). Geneva: International Conference on Harm-onization. 2005.
- Armitage P, Berry G. Statistical methods in medical research. 3rd ed. Oxford (UK): Blackwell. 1994.
Srinivas LD, Prasad Rao KVS, Sastry BS. Spectrophotometric determination of lomefloxacin in pharmaceutical dosage form with citric acid acetic anhydride reagent. Int J Chem Sci. 2005; 3: 321-324.
Maheshwari M, Verma1 K, Soni K, Jain P. Difference spectroscopic estimation of lomefloxacin in marketed formulation. Asian J Pharm Educ Res. 2017; 6: 24-29.
Ling-boa QU, Jie Z, Jian-jun LI. Determination of lomefloxacin by flow injection chemiluminescence. Anal Chem Indian J. 2007; 4: 43-48.