
Research Article
Austin J Anal Pharm Chem. 2019; 6(2): 1120.
Comparison of Assay Results by Two Methods, Urea on Cobas 6000 (Fully Automated Clinical Chemistry Analyzer) and Dirui DR-7000D (Semi-Automated Clinical Chemistry Analyzer)
Bikila D1,2*, Tewabe H1, Getahun T1,2 and Wolde M1
¹Addis Ababa University, Department of Medical Laboratory Sciences, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
²Ethiopian Public Health Institute, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
*Corresponding author: Bikila D, Addis Ababa University, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Received: July 18, 2019; Accepted: September 16, 2019; Published: September 23, 2019
Abstract
Background:| In different parts of Ethiopia, one laboratory may own more than one diagnostic device or reagent kit measuring the same analyte (around 42 different Clinical Chemistry analyzers throughout the country) and this situation causes great troubles for quality control and traceability. Therefore, a comparison of any two-assay results done by two different methods is of great importance in a clinical laboratory.
Objective: To compare the assay result of Urea on Dirui DR-7000D and Cobas 6000 chemistry analyzers.
Methods: Prospective cross-sectional study design was conducted at Addis Ababa University (AAU) and Ethiopian Public Health Institute (EPHI) in 2019. The collection of data was done with the data collection format prepared by the principal investigator containing Test method, Comparative Method and Urea test result by using convenience sampling technique from April 01-10/2019.The data was cleaned, edited, checked for completeness and entered into SPSS version 23 for analysis. The Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) document EP9-A2 guidelines were followed to evaluate the method comparison using 46 patient samples. The result was presented with tables and figures accordingly.
Results: Comparing Dirui DR-7000D (Semi-automated chemistry analyzer) and Cobas 6000 (Fully automated chemistry analyzer) for urea assay test result the regression parameter R2=0.814, Slope=0.48, intercept=15.15 was found. More importantly, Bland-Altman plots indicated that a positive bias (mean ± SD) was observed: Urea (3.1315 ± 9.655685 mg/dL).
Conclusion: Statistically Significant differences between two Chemistry analyzers (Dirui DR-7000D and Cobas 6000) at p value ‹0.01 were found. Even though, the difference found was statistically Significant, it is impossible to conclude that the two machines has no strong positive correlation due to some limitations of the study. To reach conclusion further experiment is needed by strictly following updated method comparison guidelines.
Keywords: Method Comparison; Dirui DR-7000D; Cobas 6000
Introduction
One of the final degradation end products of protein and amino acid metabolism in the human body is urea. The catabolism of protein yields amino acids and then the amino acids undergo deamination. The product of amino acid deamination, ammonia, is synthesized into urea in the liver. After urea is removed by the kidney, discharge in to the urine can take place. This is the most valuable mechanism by which excess nitrogen can be eliminated from the human body. Measurement of urea besides to creatinine is very useful for the assessment of renal complications [1].
Study conducted in china depicted that one laboratory may own more than one diagnostic device or reagent kit measuring the same analyte and this situation causes great troubles for quality control and traceability [2]. Therefore, a comparison of any two assay results done by two different methods is of great importance in a clinical laboratory [3]. Especially, this is very important in poor setting country like Ethiopia, for example, around 42 different Clinical Chemistry analyzers were found throughout the country (from recent assessment done by Ethiopian Public health Institute). As a part of assessment, to determine if the different devices yield equivalent results, the correlation coefficients between two chemistry analyzers which found at department of Medical Laboratory Sciences, Addis Ababa University and Ethiopian Public Health Institute were evaluated.
Materials and Methods
The Comparison of assay results by two Methods, Urea on Cobas 6000 (Fully Automated Clinical Chemistry Analyzer) and Dirui DR- 7000D (Semi-Automated Clinical Chemistry Analyzer was carried out at Addis Ababa University ,College of Health Sciences, Department of Medical Laboratory Sciences and Ethiopian Public Health Institute. The study design utilized was Prospective Cross-sectional study design done within a period from April 01, 2019 to April 10, 2019. The source population for the study was all participants willing to give blood at Ethiopian Public Health Institute for different Laboratory tests either for checkup purpose or diagnostic reason. Participants with complete Urea test results were considered as study population. Participants with complete urea test results were included in the study while others with laboratory test results other urea test results were excluded from the study.
Regarding sample size determination and techniques of sampling, 46 samples (as per guideline of CLSI requirement for method comparison) [4] were selected by using convenient sampling technique till the required sample size was achieved. In the comparison study, Test method (Dirui DR-7000D) and Comparative Method (Cobas 6000) were dependent variable and independent variable respectively. The collection of data was done with the data collection format prepared by the principal investigator containing Test method, Comparative Method and Urea test result. The study was carried out following permission obtained from Addis Ababa University college of Health sciences Department of Medical Laboratory Sciences and Ethiopian Public Health Institute. As part of data quality assurance, quality control and calibrations was done as per the manufacturer’s guideline and the collected data was cleaned, edited checked for completeness, clarity and consistency by the Principal Investigator on as appropriate. The Collected Data was carefully entered in to the computer to minimize errors due to transcription.
Biochemical methods (Test Principle) on Cobas 6000
The estimation of the concentration of Urea on comprehensive bio analytical system 6000 (Cobas 6000) was done with Enzymatic urea (Urease, Kinetic) Method. In the test principle of the Kinetic test with urease and glutamate dehydrogenase [5], the first reaction involves the hydrolysis of Urea by urease to yield ammonium and carbonate as a product. During the second Reaction, in the presence of glutamate dehydrogenase (GLDH) and the coenzyme NADH, 2-oxoglutarate reacts with ammonium to produce L-glutamate. The reaction involves the oxidation of two moles of NADH to NAD+ for each mole of urea hydrolyzed. The rate of decrease in the NADH concentration is directly proportional to the urea concentration in the specimen and is measured Photo-metrically.
Biochemical methods (Test Principle) on Dirui DR-7000D
During the analysis of urea on Dirui DR-7000D, Enzymatic colorimetric end point method was employed. The hydrolysis of Urea by urease into ammonia and carbon dioxide can take place. The product of the reaction, ammonia, reacts with alkaline hypochlorite and sodium salicylate in presence of sodium nitroprusside as coupling agent to give a green cromophore. The formation of color intensity is proportional to the concentration of the analyte being measured (urea) in the sample [6].
Statistical data analysis
Encoding of data was done by principal investigators into SPSS version 23 for data checking, cleaning, and analysis to compare the assay result of Urea on Dirui DR-7000D and Cobas 6000 chemistry analyzers. Difference plot was computed by using SPSS version 23 for visual inspection, Coefficient of Correlation (r), simple linear regression statistics was calculated as appropriate. The result was presented with tables, figures and graphs accordingly. P value less than 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
Results
As shown in Table 1, among a total of 46 samples analyzed by the test method, the minimum and maximum Concentration of urea measured was 19.39 and 47.16 respectively, among a total of 46 samples analyzed by the comparative method, the minimum and maximum Concentration of urea measured was 9.5 and 62.30 respectively and the mean concentration of urea analyzed by test method (26.2096) is greater than that of comparative method (23.078).
Descriptive Statistics of Dirui DR-7000D Versus Cobas 6000
N
Minimum
Maximum
Mean
Std. Deviation
Variance
Statistic
Statistic
Statistic
Statistic
Std. Error
Statistic
Statistic
Test Method(Urea)
46
19.39
47.16
26.21
0.6778
4.5973
21.135
Comparative Method(Urea)
46
9.5
62.3
23.078
1.2764
8.65664
74.937
Valid N (listwise)
46
Table 1: Descriptive Statistics of Test Method (Dirui DR-7000D) Versus Comparative Method (Cobas 6000).
Coefficientsa
Model
Unstandardized Coefficients
Standardized Coefficients
t
Sig.
B
Std. Error
Beta
1
(Constant)
18.93
1.57
12.051
0
Mean
-0.641
0.06
-0.843
-10.39
0
a. Dependent Variable: Difference
Table 2: T-test of the mean of the difference between the test method (Dirui DR- 7000D) and Cobas 6000.
As depicted on Figure 1. The R2=0.814-shows good positive (81.4%) correlation even though, the difference is statistically significant at P value ‹0.05 and the regression line equation (simple linear regression) is Y=0.48X+15.15which shows 52% proportional error and 15.15 constant error.
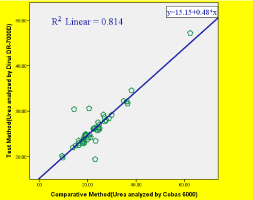
Figure 1: Linear regression plot of Test Method Dirui DR-7000D Versus
Comparative Method (Cobas 6000).
For the data set, the mean difference (mean bias) was found as 3.1315 with an SD of 4.92637.
As can be seen from the Figure 2. Some outliers exists above and below the specified limit (mean±1.96SD) which covers the 95% confidence interval, Therefore, whether the difference was statistically significant or not T-test is computed and the result were as follows:
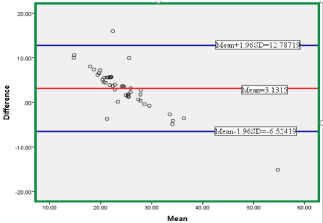
Figure 2: Agreement between Dirui DR-70000D and Cobas 6000 (Bland-
Altman Plot).
As shown in the Table the Mean difference is Statistically Significant (P-Value‹0.01), which depicted the existence of proportional bias.
Limitations of the Study
The difference between the Test Method (Dirui DR-7000D) and Comparative Method (Cobas 6000) is statistically Significant because of the following reasons: Unable to select the specified wavelength (600nm±10nm) on Dirui DR-7000D, because the machine has only limited inbuilt wavelength range that makes difficult to adjust to the desired wavelength and Since reagent was not ready made, Reagent preparation/Reconstitution may accounts for some of the differences observed between two methods/instruments.
Conclusion
Statistically Significant differences between two Chemistry analyzers (Dirui DR-7000D and Cobas 6000) were found at (P-Value‹0.01). Even though, the difference found was statistically Significant, it is impossible to conclude that the two machines has no strong positive correlation due to the above mentioned limitations of the experiment. The two machines shows Good Positive correlation (R2=0.814), but not accepted as per CLSI guideline [4]. To reach conclusion further experiment is needed by strictly following updated method comparison guidelines.
Recommendation
While comparing two methods/Instruments, it is important to use the same kind of reagents and conduct the comparison process according to the available guideline. Since the volume of sample needed for the analysis was very small (10μL), great care must be taken while taking those small volumes. Pipetting skill also has a prime importance to measure the desired volume accurately. While purchasing new equipment, it is important to consider the instrument specifications and its reagent requirements whether it is user friendly, and have adjustable inbuilt parameters as required.
Acknowledgment
We would like to thank Ethiopian Public Health Institute for providing us the chance to conduct the project in their Institute.
We would like to extend our thanks to School of Medical Laboratory Sciences, College of Health Sciences, Addis Ababa University, which allow us to conduct the project in their Laboratory.
References
- Urea Nitrogen CDC.
- Fu H, Yan S, Wang Y, Gu D, Li X, Yang G, et al. Methods Comparison and Bias Estimation of Three Distinct Biochemistry Analytical Systems in One Clinical Laboratory Using Patient Samples. Clinical laboratory. 2016; 62: 187- 194.
- Cai A, Qi S, Su Z, Yang Y, Shen H, Wang T, et al. Method Comparison and Bias Estimation of Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN), Creatinine (Cr), and Uric Acid (UA) Measurements between Two Analytical Methods. Clinical laboratory. 2017; 63: 73-77.
- EP9-A NC. Method comparison and bias estimation using patient samples; approved guideline. 1995.
- Manual of Medical Laboratory Techniques.
- UREA Berthelot - Linear Chemicals.