
Review Article
Austin J Anal Pharm Chem. 2022; 9(3): 1150.
Estimation of Steroid Hormones in Biological Samples Using Micro Extraction and Advanced Chromatography Techniques
Anshuman Srivastava¹, Madan Madhav Godbole² and Ashutosh Shrivastava¹*
1Center for Advanced Research, King George’s Medical University, Lucknow, India
2Jawaharlal Nehru Medical College, KLE University, Belagavi, Karnataka, India
*Corresponding author: Dr. Ashutosh Shrivastava, Center for Advanced Research, Faculty of Medicine, King George’s Medical University, Lucknow, India
Received: September 27, 2022; Accepted: November 08, 2022; Published: November 15, 2022
Abstract
Steroid profiling plays an important role in the clinical setting and also in the diagnosis of various physiological disorders. Steroids in the research laboratory and patient care has been routinely measured by immunoassay. Limitations of immunoassay in quantifying steroids have been well documented and the advent of advanced mass spectrometry is offering a viable alternative to measure multiple steroids in single reaction. Analytes ranging from the steroid and their metabolites that are present in the body carry out various important functions and are relevant to maintaining homeostasis. Blood plasma and urine samples are the clinical material for such analysis, however, due to the difference in polarity of the target steroid, a major challenge exists as to how faithfully analyze different steroids in the given sample type. These steroids are usually present at very low concentrations in the body and are present in several forms leading to increased complexity. Achieving an excellent chromatographic separation for the analysis of steroids requires an effective sample preparation and analysis procedure. Hence various methods are developed to analyze the presence of steroids and to know their exact concentration in the body. This review covers various analytical methodologies such as chromatographic procedures and downstream mass spectrometry for the identification and measurement of the levels of steroid hormones. At the same time, this review also covers the most recent developments that have taken place in the recent past to cover the enhanced understanding of steroid hormone analysis.
Keywords: Steroid Hormone; Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry; Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry; Sample extraction procedure
Abbreviations
BSTFA, N, O-Bis(Trimethylsilyl)Trifluoroacetamide; DBS: Dried Blood Spot; DHEA: Dehydroepiandrosterone; DHT: Dihydrotestosterone; GC-MS/MS: Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry; LOD: Limit of Detection; LOQ: Limit of Quantification; LC-MS/MS: Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry; LLE: Liquid-Liquid Extraction; MALDI: Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization; MSTFA: N-Methyl-N-(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide: 17-OHP: 17 a-Hydroxyprogesterone; SPE: Solid Phase Extraction; UPLC: Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography; UPLC (QTOF) MS: Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography Quadrupole Timeof- Flight (QTOF) Mass Spectrometers; UHPSFC-MS/MS: Ultra- High Performance Supercritical Fluid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Introduction
Steroid hormones play a significant role in regulating different body functions, including salt and water balance, immune response, ability to endure illness and injury, and development of secondary sexual characteristics [1-3]. Steroid hormones are a biologically active group of molecules derived from cholesterol [4]. Any dysregulation in the biosynthesis, metabolism and excretion of steroids could lead to an endocrine disorder. Endocrine disease which is associated with the alteration of steroids can be diagnosed by the quantification of steroids and the ratio analysis of their specific pathway products.
The hyphenated chromatography technique, coupled with mass spectrometry, is gradually becoming a significant approach for the quantification and identification of steroid hormones in biological samples [5,6]. Fast analysis, improved selectivity, and the need for only a small sample volume make this type of technique superior in comparison to traditional and routinely used immunoassay methods [7]. Immunoassay methods are selective and helpful in the detection of a single steroid hormone. However, the robustness of the data, accuracy, and reproducibility of the immunoassay process is not high due to a lot of matrix interference and batch-to-batch variation in the antibodies [8,9].
Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS/MS) are advanced chromatography approaches in the field of steroid hormone analysis [10]. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry is an excellent tool in comparison to GC-MS/MS in respect of the determination of individual steroids, but in the case of metabolite identification, GCMS/ MS shows a better response [11,12]. A lot of research studies have been undertaken on the identification and quantification of steroids by using the above chromatography techniques, but only few of those studies are robust and reliable [10,13]. The additional recent analytical approach that has become more prevalent in the analysis of steroids over the past few years is Ultra-High Performance Supercritical Fluid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (UHPSFC-MS/MS) and Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization (MALDI-MS). These chromatography instruments are designed to resolve numerous challenging retention/separation problems.
Biological samples are complex and are not directly compatible with mass spectrometry. Therefore, a fast, selective, effective, and robust analytical sample extraction procedure is always important before the chromatographic separation and analysis of biological samples [14]. Generally, sample extraction is a time-consuming procedure and needs to be highly accurate. Sample extraction has conventionally been executed using Liquid-Liquid Extraction (LLE) [15,16], Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE) [17,18], and Protein Precipitation (PP) [9]. The manual operations associated with these techniques are labor-intensive and time-consuming. Modern trends in sample extraction procedures include Supported Liquid Extraction (SLE), Dried Blood Spot (DBS) [20,21], and Dispersive Liquid-Liquid microextraction (DLLME).
The measurement of steroid hormones is generally performed for public health assessment, patient care, diagnosis and clinical research. All steroid hormones are derivatives of cholesterol which is generally a waxy substance present in blood and animal tissue (Figure 1). The transportation of steroid hormones in bloodstream takes place with carrier globulin proteins in a bound form. Abnormalities in the production and metabolism of steroid hormones could potentially lead to various endocrine disorders. For the diagnosis, and treatment of endocrine-related diseases, the absolute quantification of steroid hormones and their metabolites is necessary. In this review, contemporary development in conventional and modern approaches for sample extraction for the analysis of steroids using chromatographic separation and mass spectrometry analysis have been drawn and reviewed. Attention has also been placed on different modern mass spectrometry instruments for the quantification of steroids in different biological samples.
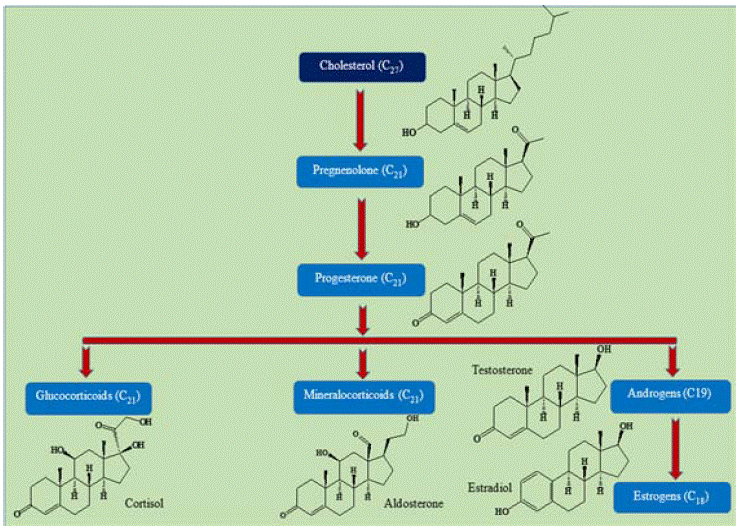
Figure 1: Relation of steroid hormone with cholesterol: In biosynthesis, cholesterol is converted to pregnenolone, which is not a hormone but an immediate
precursor for all steroid hormones Further, it converts into progesterone secreted by the corpus luteum of the ovary, but in the adrenal cortex, it is further
metabolized to steroid hormones (corticosteroids) such as cortisol and aldosterone. In both the ovary and testis, progesterone is transformed further to the
androgenic steroid androstenedione, then modified to the estrogen (estradiol) and androgen (testosterone).
Advanced Sample Preparation Techniques
Sample preparation is a crucial step for the proper extraction of analytes (Table 1). To quantify steroid hormones by using a mass spectrometry-based technique, a simple, effective, and robust sample preparation step is necessary to reduce the high matrix effect for better chromatographic separation [22,23]. The extraction techniques vary in terms of sample preparation and also have varying degrees of selectivity, time consumption, and convenience, all of which have a direct effect on the outcome of the final analysis.
S.No
Extraction technique
Advantages
Disadvantages
1
Solid-phase extraction
Easy automation, high recovery, low reagent consumption
Low reproducibility, costly, time-consuming, and many procedure steps
2
Liquid-liquid extraction
Easy operation, low extraction cost, simple instrumentation
High solvent consumption, laborious, time taking
3
Protein precipitation
Low solvent consumption, one-step reaction, high reproducibility
Removal of protein is not possible, the high matrix effect
4
Dried Blood Spot
Easier to transport, less blood needed, cost-effective
Storage problem, the possibility of contamination
5
Supported liquid extraction
Faster in comparison to LLE, effective for biological samples
Costly, time-consuming
6
Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction
Low solvent requirement, fast analysis,
long extraction time, limited solvent choice
Table 1: Advantages and disadvantages of the extraction technique.
Solid-phase extraction (SPE)
Solid-phase extraction is a highly used sample preparation and pre-treatment approach, especially for trace analytes. In comparison to other extraction procedures, it has a high recovery and robustness to achieve an effective preconcentration and consumes less solvent [24,25]. The selection of solvent and sorbent is a crucial factor in the SPE process. The range of sorbents for SPE varies from graphitized carbon to chemically bonded C8, and C18 silica, and different kinds of polymeric material among others [26,27]. Although SPE has many advantages, it also has some demerits such as its high cost and batchto- batch variation that affects reproducibility [28-30].
Quantification of steroids in urine samples by using solid-phase extraction on Oasis HLB sorbent and analysis was performed by UPLC-QTOF-MS. The developed method showed good linearity and recovery values, and the Limit of Quantification (LOQ) was in the range of 2 to 500 ng/ml [31]. Another study on the determination of steroid hormone in pediatric blood samples using LC-MS/MS found that the LOD of the developed method was 0.1 nmol/L. The gonadal steroids were extracted by using SPE Oasis MAX elution plates. Before the extraction procedure SPE plates were conditioned with 200μl of methanol after that acidified samples were loaded. Targeted analytes were eluted using 60 μl isopropanol, followed by 100 μl high-purity grade water [32]. For the analysis of estrone and its metabolites, a rapid and effective method was proposed, that utilized the LC-MS/ MS technique, and the developed method showed good accuracy between 88% and 108% [33].
The use of tandem mass spectrometry and hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography separation in combination with SPE extraction techniques also helped in analyzing the seven conjugated estrogens in urine. This approach produced a linear dynamic range of three orders of magnitude, 92-109 % recovery, 84-109 % intraday accuracy, 1-14 % intraday precision, 80-111 % inter day accuracy, and 1-22 % inter day precision [34].
Liquid-Liquid Extraction (LLE)
Liquid-liquid extraction is based on the separation of targeted analytes from one phase of solvent to another phase of another solvent based on polarity [35,36]. This technique can be used to extract nonpolar steroid hormones from serum or plasma into an organic solvent. Generally, one solvent is an aqueous medium and the other solvent or extraction solvent is non-polar resulting in phase separation [37,38]. In some LLE extraction protocols, sodium chloride is also mixed in the aqueous phase to aid the allocation of analytes into the organic phase, the procedure known as “salting out”. Extraction solvents having lower density in comparison to the aqueous medium may be separated by using a handheld pipette.
Liquid-liquid extraction is widely used for the quantification of steroids in different matrices. A study that was performed to determine the level of aldosterone in serum using methyl tertbutyl as an extraction solvent followed by LC-MS/MS system reported that the LOD and LOQ of the developed method were 22 pmol/L and 50 pmol/L, respectively [39]. Another study used the combination of hexane and ethyl acetate at a ratio of (3:2) for the quantification of T, DHT, E1, and E2 in serum samples using LC-MS/MS in the APPI mode [40]. In the LLE procedure pH play an important role, the use of an acidic or basic pH is vastly suggested so that contaminations such as phospholipids and cholesterol esters are removed. The measurement of T and DHT in serum samples using LLE as an extraction procedure required the adjustment of pH of the organic phase by adding 350 μL of 0.1 mol/L sodium hydroxide followed by LC-MS/MS in the ESI mode. The developed method showed good recovery for T and DHT of 100 to 113% and 98 to 107%, respectively [41]. The same extraction process was applied for the quantification of T in serum samples. The proposed method was found to provide high accuracy and excellent precision with a lower detection value LOD of 9.71 pmol/L [42].
Protein Precipitation (PP)
Protein precipitation is one of the simplest and most traditional sample preparation techniques for the extraction of analytes from biological material. Due to the effectiveness of the PP technique, it has been used in many recent applications [43]. The quantification of 12 steroid hormones in human serum samples was developed by using the PP method. The LOQ of the developed method was in the range of 0.005 ng/ml for estradiol to 1 ng/ml for cortisol. The average recovery of the developed method was in the range of 86.4 to 115.0% [44]. To determine 14 carbonyl-steroid hormones in human serum samples after protein precipitation, 2-hydrazinopyridine was used as a derivatization reagent. The correlation coefficient (R2) of the developed method was in the range of 0.9885 to 0.9998, and LOD was in the range of 0.07 to 65.25 ng/ml [45]. Doping analysis has been recognized as a challenge for testing laboratories. The present study focused on the analysis of steroids for doping control by using PP and the LC-MS/MS instrument. The method was validated by using 50 μl of human plasma and was found to show a functional recovery of between 80 to 112%, and at LOD in the range of 0.1 to 10 ng/ml [46]. Laura J. Owen et al. also developed a method by using the same extraction technique for the analysis of serum cortisol with LC-MS/ MS, in which only 20 μl of serum sample was used. The result showed a good R2 value (0.999), and the LOQ of the developed method was 12.5 nmol/L [47]. A method was proposed for the quantification of T, A, and DHEA in human serum samples, which also used LC-MS/ MS but which employed a combination of two different extraction procedures, LLE and PP, and methanol as an extraction solvent. The result showed that the LOD of the targeted analytes T, A, and DHEA was 0.22, 0.22, and 1.08 nmol/L, respectively [48].
Dried Blood Spot (DBS)
A dried blood spot type of bio sampling in which a blood sample is sucked onto a DBS card or filter paper and dried [49,50]. Dried blood spot sampling is an effective process, especially for screening neonates for metabolic disorders [51,52]. The collection of a blood sample through DBS is normally conducted by pricking the finger, heel, or toe with a lancet. A minimal quantity of typically 20 to 30 μl of blood is evenly spread across the spot. The sample is collected by punching out the spotted area and performing extraction by using a suitable extraction buffer or solvent (methanol or acetonitrile). After repeating the extraction step twice, the extract is centrifuged, and the supernatant is collected, dried in a concentrator, reconstituted in a suitable solvent, and then analyzed by using a chromatography instrument [53]. Most often, GC-MS/MS, UPLC, or LC-MS/MS are used in the DBS analysis [54-56].
A precise method was developed for the quantification and profiling of steroids in neonates by using an advanced DBS technique followed by LC-MS/MS. The R2 value of the developed method was greater than 0.99, and the LOQ for all steroids was in the range of 0.9 to 40.0 nmol/l. the developed method was successfully applied to quantify nine steroids in DBS for clinical diagnosis of congenital adrenal hyperplasia [57]. Recently, a study of neonatal screening for congenital adrenal hyperplasia with secondary steroid hormones using LCMS/MS was conducted. The method was developed by using diethyl ether as an extraction solvent combined with the DBS technique [58]. In another DBS-based study, seven steroid hormones were analyzed in the Korean population. The DBS card procedure was used for blood collection, and in the extraction step, 200 μl of 50% methanol + 50% acetonitrile was used. The proposed method shows good selectivity and sensitivity. The LOQ of all steroids is in the range of 0.5 ng/ml to 1.0 ng/ml [20]. A study was performed for screening of steroids in neonatal using UPLC-MSMS with ESI positive mode. The method was developed for five steroids, which shows recovery >64.1%. LOQ of the developed method was in the range of 2.8nmol/L to 4.3 nmol/L and had a short run time (1.25 min) [59].
Supported Liquid Extraction (SLE)
Supported liquid extraction (SLE) is similar to customary LLE in that it uses the same water-immiscible solvent methods to extract analytes from aqueous solutions, but the aqueous phase is coated onto a high surface area material typically diatomaceous earth within tubes, much like solid-phase extraction. In SLE, instead of shaking the two immiscible phases together as in LLE, the aqueous sample is immobilized on an inert carrier and the organic phase is flushed through the carrier matrix to extract the target analyte [60].
Recently, SLE has been used as an alternative to LLE and SPE for different biological matrices [61]. To date, several research papers have provided evidence of the utility of this method and its effectiveness as an alternative to methods such as SPE, PP, and LLE [62]. SLE cleanup provides an efficient recovery and decreased background noises. An SLE-based method for the analysis of hydrocortisone in mouse serum using LC-MS/MS was devised. The quality control samples’ intra and inter-day precision and accuracy at low, medium, and high concentration levels revealed > or =12.9% CV and 3.4-6.2 percent bias for the analyte in mouse serum [63]. Steroid profiling is used in clinical trials, but there is always room for improvement. Methods have been developed that include SLE technology and GCMS/MS that combine Selected Reaction Monitoring (SRM) with selected ion monitoring modes. Here, the LOD of serum steroids ranged from 0.2 to 5 ng/ml and R2 was higher than 0.999. Accuracy and accuracy ranged from 1.4 to 10.5% and 82.7 to 115.3%, respectively. The overall recovery of the 30 steroids ranged from 62.1% to 104.3%, while the recovery of the 7 sterols ranged from 44.7% to 75.7% [64].
Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Micro Extraction (DLLME)
Dispersive liquid-liquid micro extraction is a novel sample extraction procedure offering a high enrichment factor for the targeted analyte [65]. In the DLLME extraction procedure, extraction of the targeted analyte takes place in the dispersion of the extracting solvent prepared in an aqueous medium. The whole extraction procedure can be divided into two steps. In the first step, the mixture of extraction and disperser solvent is forcefully injected into the aqueous medium which leads to the formation of a cloudy solution and the second is the removal of the dispersed analyte by centrifugation. The extraction solvent containing analytes is suspended in the centrifuge tube and taken for analysis by using a micro syringe. This extraction process is associated with various advantages like selectivity, simplicity, low cost and high enrichment efficiency. Due to its high efficiency, DLLME is widely used in different environment toxicant analyses like pesticides [66-68], PAHs [69,70], and pharmaceutical products [71,72]. DLLME also deliver an advantage for the analysis of steroids analysis in biological samples. The extraction procedure for the isolation and pre concentration of 17β-estradiol, in human urine samples has been developed. A mixture of carbon tetrachloride and ethanol (1: 5; v / v) used as an extraction or dispersion solvent was quickly infused into a 2 ml urine sample with 8% NaCl added. The proposed method provides an efficient method for the analysis of estradiol in human pregnant urine samples [73]. To make this extraction method more effective, DLLME and Hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP) -alkyl carboxylic acid high-density super molecular solvent for extracting steroid sex hormones in human urine samples using HPLC MS / MS. A study using a combination of SUPRAS was proposed. In this process, octanoic acid was used as the extraction solvent and HFIP was used as the dispersion solvent. The detection limit of the developed method based on the signal-to-noise ratio of 3 was 0.010.10 μg / L. The recovery rate was 82.7-120.2% [74].
Advanced Chromatography Techniques
Role of mass spectrometry in the measurement of steroids
Mass spectrometry techniques have been utilized extensively in biomolecule identification, steroid analysis, and in chemical and the agricultural industry [75,76]. A predominant technique for steroid analysis based on mass spectrometry is gas or liquid chromatography (GCMS / MS or LCMS / MS) combined with mass spectrometry (Figure 2). Mass spectrometry is based on the movement of charged particles in an electric and magnetic field [77]. Only charged particles can be analyzed by using this technique, so the mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) is very important for the effective motion of a particle of interest [78,79]. Additionally UHPSFC-MS/MS and MALDI-MS are also discussed in this review.

Figure 2: Instrumentation of gas chromatography and liquid chromatography with a mass analyzer.
Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS): In recent years, the importance of LC-MS/MS has increased due to its specificity, high precision, selectivity, and accuracy compared to immunoassays. The main advantage of LC-MS/MS is that it can quantify a range of steroids in a single run. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry is a powerful analytical technique that is changing how steroids are analyzed in the clinical laboratory [80].
An overview of steroid analysis using different sample preparation techniques with LC-MS/MS is provided in Table 2. Comprehensive steroid hormone profiling is crucial for monitoring the occurrence and expansion of many related diseases [81]. A new LC-MS/MS method that was combined with an extraction procedure was proposed for the quantification of 17-OHP, AD, and T steroids in plasma. These steroids play an important role in the diagnosis and monitoring of hyperandrogenic disorders. The LOD of the developed method was in the range of 0.03 to 0.06 μg/L [82]. To quantify multiple steroid hormones in a single run, a rapid quantification method was proposed for the quantification of 13 steroids in human plasma by the combination SPE with LC-MS/Q-Trap. The LOD of the developed method was in the range of 0.02 to 9 μg/L [83]. For routine clinical analysis, an advanced method was developed for the analysis of 17-OHP in human serum samples [13]. The quantification of of pseudo-endogenous steroids in sports is very important. LC-MS/MS presents an extensive variety of evaluations in human serum, plasma, endometrium, and endometriotic tissue [84,85]. Similarly, a highly sensitive, effective, and easy quantification method was reported for the analysis of estrogen and progestogens in human serum samples. The developed method was found to be helpful for the analysis of both synthetic and endogenous sex-steroid hormones [86]. A comparative study was performed for postmenopausal women to examine the effectiveness of the analysis of estrogens in serum and plasma in a female breast cancer patient by using LC-MS/MS [87]. Postmenopausal women with elevated plasma or serum estrogens are considered to be at increased risk of breast and endometrial cancer, therefore an ultrasensitive quantification method exist using LCMS/ MS [88,89].
Analyte
LOQ
Sample and volume
Sample preparation technique used
Analytical instrument
Column
Mode of ionization
References
T, DHT, E2, E1
10 pg/ml, 50 pg/ml, 2.5 pg/ml, 1.5 pg/ml
Serum 200 μl
LLE
LC-MS/MS
(Supelcosil LC-8-DB, 7.5 cm× 3 mm, 3 μm
APPI
[40]
15 adrenal steroids
0.015 ng/mL to 20 ng/mL
Serum 250 μl
PP and SPE
LC-MS/MS
BEH C18 column
ESI
[113]
9 hydroxy-androgens
1.0 pg to 2.5 pg
Serum 200 μl
LLE
LC-MS/MS
Kinetex C18 (Phenomenex, Torrance, CA, USA) 100 mm x 2.1 mm, 2.6 μm, 100 Å column with a C18 guard column (2.1 mm internal diameter)
ESI
[114]
8 cortisol
0.9-40.0 nmol/L
Blood
DBS with LLE
LC-MS/MS
-
ESI
[57]
12 steroid hormone
0.005 ng/ml to 1 ng/ml
Serum 100 μl
LLE and PP
LC-MS/MS
Kinetex@ 2.6 μm PFP 100 Å column (100 × 3 mm)
ESI
[44]
E1,E2,E3,T,AD,DHEA, P
0.005 ng/ml for E1, E2, and, E3 0.01 ng/ml for T, P, and AD 0.25 ng/ml for DHEA
Serum 100 μl
LLE
LC-MS/MS
ACQUITY UPLC BEH Shield RP18 column (1.7 m, 2.1 × 50 mm)
ESI
[81]
14 carbonyl-steroid hormones
0.07 to 65.26 ng/ml
Serum 100 μl
PP
LC-MS/MS
ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 (100 mm × 2.1 mm, 1.7 μm)
ESI
[45]
A, T, DHEA
0.22, 0.22, and 1.08 nmol/L
Serum 100 μl
LLE and PP
LC-MS/MS
Phenomenex C18 column (100mm x 2.1 mm, Luna, 5 μm)
APCI
[48]
A, T, and DHT
0.1 nmol/L
Plasma 100 μl
SPE
LC-MS/MS
Waters Acquity UPLC BEH C18 analytical column of 100 2.1 mm and 1.7 um
ESI
[32]
Androgens and prostaglandins
0.01 to 2 ng/ml
Human urine 100 μl
SPE and LLE
LC-MS/MS
ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 (2.1 x 100 mm x 1.7 mm)
ESI
[115]
Steroids including doping agents
0.1 to 10 ng/ml
Human plasma 50 μl
PP
LC-MS/MS
Hypersil gold C18 analytical column (2.1 mm x 50 mm, 1.7 mm)
ESI
[46]
T and 5 alpha-DHT
0.2-40 ng/ml and 0.01-2ng/ml
Serum 300 μl
LLE and SPE
UPLC-MS/MS
Acquity BEH C18
ESI
[116]
Cortisol
12.5 nmol/L
Serum 20 μl
PP
LC-MS/MS
Phenomenex 30 x 2.1 mm C8 Kinetex analytical column
ESI
[47]
F, AD, 17 OHP
10 ug/L
Blood spot
DBS and LLE
LC-MS/MS
Waters C18; (50 mm x 2.1 mm)
ESI
[58]
Seven steroids
0.5 ng/ml to 1.0 ng/ml
Blood spot
DBS And LLE
LC-MS/MS
Kinetex 2.6 μm XB-C18 (2.1 mm×50 mm)
ESI
[20]
17-OHP, AD, T
0.03-0.06 ug/L
Plasma
Online SPE
LC-SMS/MS
Chromolith RP 18
APCI
[82]
11 steroids
-
Plasma 150 μl
LLE
LC-MS/MS
C18, bipheny
ESI
[117]
9 steroid
0.10 to 2.00 ng/ ml
Plasma and serum
SPE
GC-MS/MS
Zebron 5HT I (30 m x 0.25 mm, 0.25 μm )
EI
[93]
15 steroid
0.62 to 2.6 ng/ml
Rat blood
SPE
GC-MS/MS
Varian,VF-5 MS, (30 m x 0.25 mm x 0.25 μm
EI
[118]
T and nandrolone
10pg/ml
Plasma 500 μl
LLE
GC-CI-MS/MS
Agilent HP5MS
CI
[94]
15 estrogens, 6 androgens and 2 progestins
0.180 to 1.25pg
Breast tissue
-
GC-MS/MS
MXT-1 (30 m x 0.25 mm x 0.25 μm)
EI
[95]
22 steroids
0.1 to 20 ng/ml
Urine 1ml
SPE
GC-MS/MS
HP-Ultra1, (16 m x 0.2 mm x 0.11 μm)
EI
[97]
15 steroids
0.05 to 2 ng/ml
Urine
LLE
GC-MS/MS
TR-50MS (15 m, x 0.25 mm, 0.25 μm)
CIP
[98]
Estrogens their metabolites and T
0.25 pg and 2.5 pg
Urine 5ml
SPE
ID/GC-MS/MS
Optima-1-MS, (25 m x 0.2 mm x 0.10 μm)
EI
[99]
17-BE, 2-MEOE,
18.4 pg mL-1 and 5.5 pg mL-1
Plasma 0.5 ml
SPE
GC-MS/MS
ATTM-5MS (30 m x 0.25 mm x 0.25 μm)
ESI
[119]
40 steroids
= 50 nM
Urine 1.5 ml
SPE
GCxGC-TOF MS
RXI-1MS (15 m x 0.25 mm x 0.25 μm)
EI
[120]
13 steroids
0.025 to 2.50 ng/ml
Plasma 90 μl
Online –SPE
UHPLC-MS/MS
ProntoSIL 120 C18H (10 x 0.5 mm, 5 μm)
ESI
[121]
Aldosterone
1 pg
Serum 200 μl
SPE
LC-MS/MS
Cadenza CD-C18 (150 mm x 3 mm, 3 μm)
ESI
[122]
E1 and E2
0.5 pg/ml
Serum 0.25 to 1ml
SPE
LC-MS/MS
Cadenza CD-C18 (50 mm× 2 mm, 3 μm)
ESI
[123]
E1, E2, E3, T, AD, DHEA, and P
0.005 ng/ml to 0.25 ng/ml
Serum 100 μl
LLE
LC-MS/MS
ACQUITY UPLC BEH Shield RP18 column (1.7 m, 2.1 × 50 mm)
ESI
[124]
E1 and E2
1.3 ng/L and 1.2 ng/L
Serum 300 μl
PP
LC-MS/MS
Monolythic C18 (3×100 mm)
ESI
[125]
37 Steroids
0.2 ng to 5 ng/ml
Serum 100 μl
SLE
GCMS/MS
MTX-1 (30 m x 0.25 mm x 0.25 μm)
ESI
[75]
Aldosterone
40 pmol/L
Plasma 400 μl
SLE
LCMS/MS
Phenomenex Luna C18 (50 mm × 2.1μm, 5 μm)
ESI
[73]
glucuronide and sulfate steroids
0.1 ng/ml to 0.5 ng/ml
urine 2 ml
SPE
UHPSFC- MS/MS
Acquity UPC2 BEH (3.0×100mm, 1.7 μm)
ESI
[126]
Cortisol, testosterone, and progesterone
1.0 nmol/L to 25 nmol/L
Saliva 300 μl
LLE
LC-MS/MS
Phenomenex (25 x 4.6 mm) C18 column
ESI
[90]
Testosterone
5 pmol/L
Saliva 200 μl
LLE
LC-MS/MS
Waters C8 Kinetex 3.0 x 100 mm x 2.6um
ESI
[91]
Progesterone, estrone, 17β-estradiol,estriol, 17a-ethinylestradiol
0.01-0.10 μg/L
Urine 900 μl
DLLME
HPLC-MS/MS
Sepax BR-C18 column (150 mm × 2.1 mm, 3 μm
ESI
[74]
Table 2: Laboratory values at hospital admission.
Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry techniques provide an effective quantification method for the analysis of salivary steroids also. Recently a multiplexed analysis method for the analysis of steroid hormones in saliva was developed by combining the LLE and LC-MS/MS techniques. In this method, tannic acid was introduced as a new PP reagent for LC-MS/MS analysis in saliva samples [90]. Another method reported the use of an LC-MS/MS method for the quantification of salivary testosterone in adult males and females. The developed method was successfully applied for the analysis of 104 male and 91 female samples [91]. An alternative utilization of the LCMS/ MS technique using SPE as the extraction method was proposed for the diagnosis of late-onset hypogonadism which is a male-specific disorder caused by the age-related decline of testosterone [92].
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS/MS): Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry is widely used in the measurement of many steroid hormones across a wide concentration range and has provided a great opportunity to improve the standards of steroid analysis (Table 2).
GCMS/MS uses a targeted approach to analyze multiple steroids in a sample. Methods have been proposed to quantify nine major steroid hormones in plasma and serum, including T, E1, P, etc. The accuracy of the developed method was 50-112% [93]. For the analysis of steroid esters in human plasma, a highly sensitive method was developed using GC-MS/MS instrument. The method was optimized for the analysis of testosterone and nandrolone and showed a LOD value of 10 pg/ml. The developed method was validated with a range of concentrations from 100 to 2000 pg/ml [94]. The precision and accuracy of the analysis of different sex steroids in breast cancer tissue samples using a GC-MS/MS instrument reported a range of 4.2 to 26.8% with an acceptable recovery of 90.8 to 116.4% [95]. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry is the preferred analytical technique for the quantification of endogenous steroids in athletics. The glucuronide or sulfated conjugated steroid hormones first undergo deconjugation and then derivatization to make them suitable for GC-MS/MS analysis [96].
Urinary steroid hormone profiling is a primary and longestablished analytical technique that provides a vast range of information related to a disorder of human steroid biosynthesis and catabolism. The extraction was done by using a C18 SPE cartridge with 4 ml of methanol and 4 ml of water as an extraction solvent. The LOQ value was in the range of 0.1 to 20 ng/ml and the accuracy varied between 80 to 120% [97]. The same study was also performed for the quantification of 15 steroids in urine samples by using a capillary photoionization ion source equipped with GC-MS/MS. The relative standard deviation value was between 5 to 18%, while the LOD and LOQ ranged from 2 to 100 pg/ml and 0.05 to 2 ng/ml, respectively [98]. An advanced GC-MS/MS protocol (benchtop dilution/benchtop gas chromatography) showed good chromatography linearity and reproducibility with R2 value between 0.999 to 1.000 % [99].
A lot of research articles have demonstrated the efficacy of derivatization in the analysis of steroid hormones. A comparative study investigated the efficiency of several derivatization reagents e.g. BSTFA with TMCS, MSTFA, and BSA for steroid hormone analysis using GC-MS/MS. The results showed that MSTFA performed the best in comparison to others in metabolite analysis. A study performed by the same research group targeted the analysis of 12 steroids by separately using BSTFA+1% TMCS, MSTFA, and BSA as derivatization reagents, from which it was concluded that MSTFA was again more efficient in comparison to the other reagents [100]. In contrast, the analysis of E1 and EE2 by GC-MS/MS using MSTFA and BSTFA as a derivatization reagent showed that BSTFA has better performed [101]. On other hand, a rapid microwave-accelerated derivatization method was proposed for the simultaneous analysis of five natural and synthetic estrogenic steroids by using GC-MS/MS with BSTFA+TMCS in pyridine solution as the derivatization reagent. The developed method showed good recovery and reproducibility. The LOD of the developed method was 0.02 to 0.1 ng/L [102].
Ultra-High Performance Supercritical Fluid Chromatography- Tandem Mass Spectrometry (UHPSFC-MS/MS): Ultra-high performance supercritical fluid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry has the combined resolution power of GC and the high efficiency of UHPLC. Supercritical CO2 which has high solubility, effective dissolving capacity, and liquid-like density is used as a primary mobile phase. Generally, a UHPSFC system uses liquid organic modifiers of different polarities. When combined with supercritical CO2 and a high-range stationary phase it can provide effective and robust data [103].
A comparative study was undertaken to assess the performance of LC-MS/MS and UHPSFC-MS/MS in screening different molecules [104,105]. It was reported that this technique is highly effective for the analysis of clinically relevant steroids [103]. SFC-MS/MS technique is suitable for steroid analysis that covers different structural classes of endogenous steroids. Systematic investigations revealed that ESI is superior to other ionization processes [106]. A comparative study was also performed to examine the analysis capability of GC-MS/MS and UHPSFC-MS/MS in respect of endogenous steroid profiling to analyze glucuronide and sulfate steroids in urine samples and the former showed better sensitivity [107].
Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization (MALDI-TOF)
Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization is a highly sensitive and effective soft ionization technique that utilizes a laser and laser energy adsorbing solid matrix to ionize analytes with the least fragmentation. Although MALDI normally produces significantly fewer multi-charged ions, it is similar to Electrospray Ionization (ESI) in that both procedures are relatively gentle (low fragmentation) ways of getting ions of big molecules in the gas phase (Figure 3). The MALDI technique has been used in several studies to analyze steroid hormones. A method proposed for the quantitative analysis of endogenous estrone in human breast cancer cells. The method developed showed good linearity (R2> 0.99) with a LOQ of 11 f mol. Based on the results, it was successfully applied to monitor changes in estrone levels in MCF7 cells after treatment with an aromatase inhibitor [108]. To analyze the low concentrations of steroids in plasma samples, hydroxylamine was used as the derivatization agent. The resulting LOD ranged from 0.019 to 0.031 nM, the recovery varied from 86 to 108%, and the coefficient of variation (CV %) ranged from 4.59 to 11.90% [109]. In a different clinical context, the MALDI technique is a convenient way to analyze the free form of steroid hormones in saliva samples. In the case of MALDI analysis when traditional organic matrices are used, it is observed that nanomaterials are also used as a matrix to increase the selectivity of the method. Nanomaterials have a high surface area and good adsorption efficiency, furthermore, nanomaterials reduce the interferences and shows the best suitable for small molecules [110].

Figure 3: Schematic representation of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI).
Challenges in Mass Spectrometry Assays
While mass spectrometry appears to be becoming the gold standard for steroid hormone analysis, there are still some challenges that need to be addressed. The presence of tissue, biological fluids, and their interaction with steroid hormones of interest is a significant consideration when we develop a method for the quantification of a particular steroid. The major use of qualitative analysis is for the detection of synthetic anabolic steroids or their metabolites in the urine of sportspersons [111]. The list of synthetic and prohibited steroids continues to increase and create new challenges in the field of analytical chemistry [112]. Due to the increased specificity and sensitivity of various methods, various new tools are being developed for the analysis of complex spectra that is developed after analysis. The selective algorithm that can help identify new steroid progeny is crucial for such analysis. The selection of proper spectral analysis in light of high throughput and faster analysis is the key to overcoming the ever-growing complexity of steroid hormone analysis methods and analysis.
Conclusion
Clinical analysis of steroids is essential for the identification of the different hormones that can have adverse effects on human physiology. Several techniques are available, but they are all very costly and time-consuming. Advanced chromatography instruments can produce robust, precise, and high-quality results. In comparison to GC-MS/MS, recent data shows that LC-MSMS is more effective, faster, and more sensitive for routine laboratory analysis of steroid hormones whereas GC-MS/MS is more effective for steroid metabolite identification and steroid profiling analysis. Taken together, the results suggest that a MALDI-MS-based quantitative approach is effective in quantifying targeted steroid hormones that may reflect the clinical status and pathogenic mechanisms.
Acknowledgement
The laboratory of Dr. Ashutosh Shrivastava is supported by King George’s Medical University Intramural Grant Award and a research grant from CCRH, Ministry of AYUSH, Government of India (Z.28015/01/2018-HPC-EMR-AYUSH-D).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- Holst JP, Soldin OP, Guo T, Soldin SJ. Steroid hormones: relevance and measurement in the clinical laboratory. Clin Lab Med. 2004; 24: 105-118.
- Bereshchenko O, Bruscoli S, Riccardi C. Glucocorticoids, Sex Hormones, and Immunity. Front Immunol. 2018; 9: 1332-1332.
- Zubeldia-Brenner L, Roselli CE, Recabarren SE, Gonzalez Deniselle MC, Lara HE. Developmental and Functional Effects of Steroid Hormones on the Neuroendocrine Axis and Spinal Cord. J Neuroendocrinol. 2016; 28: 10.
- Hu J, Zhang Z, Shen WJ, Azhar S. Cellular cholesterol delivery, intracellular processing and utilization for the biosynthesis of steroid hormones. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2010; 7: 47-47.
- Matysik S, Liebisch G. Quantification of steroid hormones in human serum by liquid chromatography-high resolution tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2017; 1526.
- Konieczna L, Belka M, Okonska M, Pyszka M, Baczek T. New 3D-printed sorbent for extraction of steroids from human plasma preceding LC–MS analysis. Journal of Chromatography A. 2018; 1545.
- Klee G. Interferences in hormone immunoassays. Clin Lab Med. 2004; 24: 1-18.
- Wang Q, Mesaros C, Blair IA. Ultra-high sensitivity analysis of estrogens for special populations in serum and plasma by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry: Assay considerations and suggested practices. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016; 162: 70-79.
- Gao W, Stalder T, Foley P, Rauh M, Deng H, Kirschbaum C. Quantitative analysis of steroid hormones in human hair using a column-switching LCAPCI- MS/MS assay. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013; 928: 1-8.
- McDonald JG, Matthew S, Auchus RJ, Steroid profiling by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for adrenal diseases. Horm Cancer. 2011; 2: 324-332.
- Krone N, Hughes BA, Lavery GG, Stewart PM, Arlt W, et al. Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) remains a pre-eminent discovery tool in clinical steroid investigations even in the era of fast liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS). J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2010; 121: 496-504.
- Hansen M, Jacobsen N, Nielsen F, Björklund E, Halling-Sørensen B. Determination of steroid hormones in blood by GC-MS/MS. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011; 400: 3409-3417.
- Gaudl A, Kratzsch J, Ceglarek U. Advancement in steroid hormone analysis by LC-MS/MS in clinical routine diagnostics – A three-year recap from serum cortisol to dried blood 17a-hydroxyprogesterone. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.2019; 192: 105389.
- de Koning S, Janssen HG, Brinkman UAT. Modern Methods of Sample Preparation for GC Analysis. Chromatographia. 2009; 33.
- Keevil BG. Novel liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LCMS/ MS) methods for measuring steroids. Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2013; 27: 663-674.
- Deventer K, Eenoo PV, Delbeke FT. Screening for anabolic steroids in doping analysis by liquid chromatography/electrospray ion trap mass spectrometry. Biomedical Chromatography. 2006; 20: 429-433.
- Newman AEM, Chin EH, Schmidt KL, Bond L, Wynne-Edwards KE, et al. Analysis of steroids in songbird plasma and brain by coupling solid-phase extraction to radioimmunoassay. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2008; 155: 503- 510.
- Budzinski H, Devier MH, Labadie P, Togola A. Analysis of hormonal steroids in fish plasma and bile by coupling solid-phase extraction to GC/MS. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. 2006; 386; 1429-1439.
- Visser SAG, Smulders CJGM, Gladdines WWFT, Irth H, van der Graaf PH, et al. High-performance liquid chromatography of the neuroactive steroids alfaxalone and pregnanolone in plasma using dansyl hydrazine as fluorescent label: application to a pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic study in rats. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 2000; 745: 357-363.
- Kim B, Lee MN, Park HD, Kim JW, Chang YS, et al. Dried blood spot testing for seven steroids using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry with reference interval determination in the Korean population. Ann Lab Med. 2015; 35: 578-585.
- Choi R, Park HD, Oh HJ, Lee K, Song J, et al. Dried Blood Spot Multiplexed Steroid Profiling Using Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry in Korean Neonates. Ann Lab Med. 2019; 39: 263-270.
- Matysik S, Liebisch G. Quantification of steroid hormones in human serum by liquid chromatography-high resolution tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2017; 1526: 112-118.
- Gaudl A, Kratzsch J, Bae YJ, Kiess W, Thiery J, et al. Liquid chromatography quadrupole linear ion trap mass spectrometry for quantitative steroid hormone analysis in plasma, urine, saliva, and hair. J Chromatogr A. 2016; 1464: 64-71.
- Peng J, Tang F, Zhou R, Xie X, Li S, et al. New techniques of online biological sample processing and their application in the field of biopharmaceutical analysis. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2016; 6: 540-551.
- Srivastava A, Singh M, Singh S, Singh SP. Recent Advances in Microextraction Based Analytical Approaches for Pesticides Analysis in Environmental Samples, in: T. Gupta, S.P. Singh, P. Rajput, A.K. Agarwal (Eds.) Measurement. Analysis, and Remediation of Environmental Pollutants. Springer Singapore, Singapore. 2020; 281-318.
- Augusto F, Wang Hantao L, Mogollón N, Braga S. New Materials and Trends in Sorbents for Solid-phase Extraction. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry. 2013; 43: 14-23.
- Koren L, Ng ESM, Soma KK, Wynne-Edwards KE. Sample preparation, and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for multiple steroids in mammalian and avian circulation. PLoS One. 2012; 7: e32496-e32496.
- Koal T, Schmiederer D, Pham-Tuan H, Röhring C, Rauh M. Standardized LC-MS/MS based steroid hormone profile-analysis. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2012; 129: 129-138.
- Han X, Liu D. Detection and analysis of 17 steroid hormones by ultrahigh- performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS) in different sex and maturity stages of Antarctic krill (Euphausia Superba Dana). PLoS One. 2019; 14: e0213398-e0213398.
- Pang X, Bai L, Lan D, Guo B, Wang H, et al. Development of an SPE Method Using Ionic Liquid-Based Monolithic Column for On-Line Cleanup of Human Plasma and Simultaneous Determination of Five Steroid Drugs. Chromatographia. 2018; 81: 1391-1400.
- Badoud F, Grata E, Boccard J, Guillarme D, Veuthey JL, et al. Quantification of glucuronidated and sulfated steroids in human urine by ultra-high pressure liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011; 400: 503-516.
- Kulle AE, Riepe FG, Melchior D, Hiort O, Holterhus PM. A novel ultra pressure liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous determination of androstenedione, testosterone, and dihydrotestosterone in pediatric blood samples: age- and sex-specific reference data. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010; 95: 2399-2409.
- Guo T, Gu J, Soldin OP, Singh RJ, Soldin SJ. Rapid measurement of estrogens and their metabolites in human serum by liquid chromatographytandem mass spectrometry without derivatization. Clinical biochemistry. 2008; 41: 736-741.
- Qin F, Zhao YY, Sawyer MB, Li XF. Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry determination of estrogen conjugates in human urine. Anal Chem. 2008; 80: 3404-3411.
- Sajid M, Alhooshani K. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based binary extraction techniques prior to chromatographic analysis: A review. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry. 2018; 108: 167-182.
- de Kock N, Acharya SR, Ubhayasekera SJKA, Bergquist J. A Novel Targeted Analysis of Peripheral Steroids by Ultra-Performance Supercritical Fluid Chromatography Hyphenated to Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Sci Rep. 2018; 8: 16993-16993.
- Araujo P, Tilahun E, Breivik JF, Abdulkader BM, Frøyland L, et al. A simple liquid extraction protocol for overcoming the ion suppression of triacylglycerols by phospholipids in liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry studies. Talanta. 2016; 148: 463-471.
- Bahrami G, Mirzaeei S, Kiani A, Mohammadi B. High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of lamivudine in human serum using liquid-liquid extraction; application to pharmacokinetic studies. Journal of Chromatography B. 2005; 823 :213-217.
- Van Der Gugten JG, Dubland J, Liu HF, Wang A, Joseph C, et al. Determination of serum aldosterone by liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry: a liquid-liquid extraction method for the ABSCIEX API- 5000 mass spectrometry system. J Clin Pathol. 2012; 65: 457.
- Harwood DT, Handelsman DJ. Development and validation of a sensitive liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry assay to simultaneously measure androgens and estrogens in serum without derivatization, Clinica Chimica Acta. 2009; 409: 78-84.
- Shiraishi S, Lee PW, Leung A, Goh VH, Swerdloff RS, et al. Simultaneous measurement of serum testosterone and dihydrotestosterone by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, Clinical chemistry. 2008; 54: 1855-1863.
- Wang Y, Gay GD, Botelho JC, Caudill SP, Vesper HW. Total testosterone quantitative measurement in serum by LC-MS/MS. Clin Chim Acta. 2014; 436: 263-267.
- Márta Z, Bobály B, Fekete J, Magda B, Imre T, et al. Pushing quantitation limits in micro UHPLC-MS/MS analysis of steroid hormones by sample dilution using high volume injection. Journal of pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis. 2016; 129: 135-141.
- Yuan TF, Le J, wang ST, Li Y. An LC-MS/MS method to analyze the steroid metabolome with high accuracy and from small serum samples. Journal of Lipid Research. 2020; 61: 580-586.
- Bai YL, Hong ZD, Zhang TY, Cai BD, Zhang YZ, et al. A Method for Simultaneous Determination of 14 Carbonyl-Steroid Hormones in Human Serum by Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Journal of Analysis and Testing. 2020; 4: 1-12.
- Thomas A, Guddat S, Kohler M, Krug O, Schänzer W, et al. Comprehensive plasma-screening for known and unknown substances in doping controls. Rapid communications in mass spectrometry: RCM. 2010; 24: 1124-1132.
- Owen LJ, Adaway JE, Davies S, Neale S, El-Farhan N, et al. Development of a rapid assay for the analysis of serum cortisol and its implementation into a routine service laboratory. Annals of clinical biochemistry. 2013; 50: 345-352.
- Xu W, Li H, Guan Q, Shen Y, Cheng L. A rapid and simple liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the measurement of testosterone, androstenedione, and dehydroepiandrosterone in human serum. Journal of clinical laboratory analysis. 2017; 31.
- Sharma A, Jaiswal S, Shukla M, Lal J. Dried blood spots: Concepts, present status, and future perspectives in bioanalysis. Drug testing, and analysis. 2014; 6: 399-414.
- Zakaria R, Allen KJ, Koplin JJ, Roche P, Greaves RF. Advantages and Challenges of Dried Blood Spot Analysis by Mass Spectrometry Across the Total Testing Process. EJIFCC. 2016; 27: 288-317.
- Pitt JJ. Newborn screening. Clin Biochem Rev. 2010; 31: 57-68.
- Grüner N, Stambouli O, Ross RS. Dried blood spots--preparing and processing for use in immunoassays and in molecular techniques. J Vis Exp. 2015; 52619.
- Kim B, Lee MN, Park HD, Kim JW, Chang YS, et al. Dried blood spot testing for seven steroids using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry with reference interval determination in the Korean population. Ann Lab Med. 2015; 35: 578-585.
- Li W, Lee MS. Dried Blood Spots: Applications and Techniques. 2014; 1-363.
- Li W, Tse F. Dried spot sampling in combination with LC-MS/MS for quantitative analysis of small molecules. Biomedical chromatography. 2010; 24: 49-65.
- Matsumoto K, Uchida N, Sakurai A, Taniguchi S, Morita K. Clinical Application of the Dried Blood Spot Method in the Measurement of Blood Busulfan Concentration. Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation. 2016; 22: 1968-1973.
- Choi R, Park HD, Oh HJ, Lee K, Song J, et al. Dried Blood Spot Multiplexed Steroid Profiling Using Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry in Korean Neonates. Ann Lab Med. 2019; 39: 263-270.
- Lacey JM, Minutti CZ, Magera MJ, Tauscher AL, Casetta B, et al. Improved specificity of newborn screening for congenital adrenal hyperplasia by second-tier steroid profiling using tandem mass spectrometry. Clinical chemistry. 2004; 50: 621-625.
- Janzen N, Sander S, Terhardt M, Steuerwald U, Peter M, et al. Rapid steroid hormone quantification for congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) in dried blood spots using UPLC liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Steroids. 2011; 76: 1437-1442.
- Breitenbucher JG, Arienti KL, McClure KJ. Scope and limitations of solidsupported liquid-liquid extraction for the high-throughput purification of compound libraries. Journal of combinatorial chemistry. 2001; 3: 528-533.
- Ramesh B, Manjula N, Bijargi SR, Sarma VUM, Devi PS. Comparison of conventional and supported liquid extraction methods for the determination of sitagliptin and simvastatin in rat plasma by LC–ESI–MS/MS. J Pharm Anal. 2015; 5: 161-168.
- Owen L, Keevil B. Supported liquid extraction as an alternative to solidphase extraction for LC-MS/MS aldosterone analysis?, Annals of clinical biochemistry. 2013; 50: 489-491.
- Wu S, Li W, Mujamdar T, Smith T, Bryant M, Tse F. Supported liquid extraction in combination with LC-MS/MS for high-throughput quantitative analysis of hydrocortisone in mouse serum. Biomedical chromatography. 2009; 24: 632-638.
- Moon JY, Lee H, Kim J, Lee J, Choi M-H. Supported liquid extraction coupled to gas chromatography-selective mass spectrometric scan modes for serum steroid profiling. Analytica Chimica Acta. 2018; 1037:281-292.
- Rezaee M, Assadi Y, Milani Hosseini MR, Aghaee E, Ahmadi F, et al. Determination of organic compounds in water using dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. Journal of chromatography A. 2006; 1116: 1-9.
- Ahmad W, Al-Sibaai AA, Bashammakh AS, Alwael H, El-Shahawi MS. Recent advances in dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for pesticide analysis. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry. 2015; 72: 181-192.
- Zacharis CK, Rotsias I, Zachariadis PG, Zotos A. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of organochlorine pesticides residues in honey by gas chromatography-electron capture and ion trap mass spectrometric detection. Food chemistry. 2012; 134: 1665-1672.
- Andrašcíková M, Hrouzková S, Cunha SC. Combination of QuEChERS and DLLME for GC-MS determination of pesticide residues in orange samples. Food Additives & Contaminants: Part A. 2013; 30: 286-297.
- Zhao X, Fu L, Hu J, Li J, Wang H, et al. Analysis of PAHs in Water and Fruit Juice Samples by DLLME Combined with LC-Fluorescence Detection. Chromatographia. 2009; 69: 1-5.
- Ghasemzadeh-Mohammadi V, Mohammadi A, Hashemi M, Khaksar R, Haratian P. Microwave-assisted extraction and dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for isolation and determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in smoked fish. Journal of chromatography A. 2012; 1237: 30-36.
- Herrera-Herrera AV, Hernández-Borges J, Borges-Miquel TM, Rodríguez- Delgado M. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with nonaqueous capillary electrophoresis for the determination of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in waters. Electrophoresis. 2010; 31: 3457-3465.
- Mohebi A, Samadi M, Tavakoli HR, Parastouei K. Homogenous liquidliquid extraction followed by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the extraction of some antibiotics from milk samples before their determination by HPLC. Microchemical Journal. 2020; 157: 104988.
- Kupcová E, Reiffová K. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction as an effective preanalytical step for the determination of estradiol in human urine. Journal of separation science. 2017; 40: 2620-2628.
- Zong Y, Chen J, Hou J, Deng W, Liao X, et al. Hexafluoroisopropanol-alkyl carboxylic acid high-density supramolecular solvent-based dispersive liquidliquid microextraction of steroid sex hormones in human urine. Journal of chromatography A. 2018; 1580: 12-21.
- Patel KN, Patel JK, Patel MP, Rajput GC, Patel HA. Introduction to hyphenated techniques and their applications in pharmacy. Pharm Methods. 2010; 1: 2-13.
- Honour J. Mass spectrometry for steroids. Annals of clinical biochemistry. 2014; 51: 309-311.
- Burinsky DJ. Chapter 11 Mass spectrometry, in S. Ahuja, N. Jespersen (Eds.) Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry, Elsevier, 2006; 319-396.
- Rubakhin SS, Sweedler JV. A mass spectrometry primer for mass spectrometry imaging. Methods Mol Biol. 2010; 656: 21-49.
- Ponzetto F, Boccard J, Baume N, Kuuranne T, Rudaz S, et al. Highresolution mass spectrometry as an alternative detection method to tandem mass spectrometry for the analysis of endogenous steroids in serum. Journal of Chromatography B. 2017; 1052: 34-42.
- Keevil BG. LC-MS/MS analysis of steroids in the clinical laboratory. Clinical biochemistry. 2016; 49: 989-997.
- Yuan TF, Le J, Cui Y, Peng R, Wang ST, et al. An LC-MS/MS analysis for seven sex hormones in serum. Journal of pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis. 2019; 162: 34-40.
- Rauh M, Gröschl M, Rascher W, Dörr HG. Automated, fast and sensitive quantification of 17 alpha-hydroxy-progesterone, androstenedione and testosterone by tandem mass spectrometry with on-line extraction. Steroids. 2006; 71: 450-458.
- Ceglarek U, Kortz L, Leichtle A, Fiedler GM, Kratzsch J, et al. Rapid quantification of steroid patterns in human serum by online solid-phase extraction combined with liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole linear ion trap mass spectrometry. Clin Chim Acta. 2009; 401: 14-118.
- Häkkinen MR, Heinosalo T, Saarinen N, Linnanen T, Voutilainen R, et al. Analysis by LC-MS/MS of endogenous steroids from human serum, plasma, endometrium and endometriotic tissue. Journal of pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis. 2018; 152: 165-172.
- de la Torre X, Iannone M, Botrè F. Improving the detection of anabolic steroid esters in human serum by LC-MS. Journal of pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis. 2021; 194: 113807.
- Zhang J, Tang C, Oberly PJ, Minnigh MB, Achilles SL, et al. A sensitive and robust UPLC-MS/MS method for quantitation of estrogens and progestogens in human serum. Contraception. 2019; 99: 244-250.
- Blair IA. Analysis of estrogens in serum and plasma from postmenopausal women: past present, and future. Steroids. 2010; 75: 297-306.
- Wang Q, Bottalico L, Mesaros C, Blair IA. Analysis of estrogens and androgens in postmenopausal serum and plasma by liquid chromatographymass spectrometry. Steroids. 2015; 99: 76-83.
- Wang Q, Rangiah K, Mesaros C, Snyder NW, Vachani A, et al. Ultrasensitive quantification of serum estrogens in postmenopausal women and older men by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Steroids. 2015; 96: 140-152.
- Nadarajah N, Skadberg Ø, Adaway J, Brede C. Multiplexed analysis of steroid hormones in saliva by LC-MS/MS with 2-hydrazinopyridine derivatization. Clinical Mass Spectrometry. 2017; 4-5: 1-10.
- Keevil BG, MacDonald P, Macdowall W, Lee DM, Wu FCW, et al. Salivary testosterone measurement by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in adult males and females. Annals of clinical biochemistry. 2014; 51: 368-378.
- Shibayama Y, Higashi T, Shimada K, Odani A, Mizokami A, et al. Simultaneous determination of salivary testosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone using LC-MS/MS: Method development and evaluation of applicability for diagnosis and medication for late-onset hypogonadism. Journal of chromatography. B, Analytical technologies in the biomedical and life sciences. 2009; 877: 2615-2623.
- Hansen M, Jacobsen NW, Nielsen FK, Björklund E, Styrishave B, et al. Determination of steroid hormones in blood by GC-MS/MS. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011; 400: 3409-3417.
- Van Renterghem P, Viaene W, Van Gansbeke W, Barrabin J, et al. Validation of an ultra-sensitive detection method for steroid esters in plasma for doping analysis using positive chemical ionization GC-MS/MS. Journal of Chromatography B. 2020; 1141: 122026.
- Moon JY, McNamara KM, Lee JJ, Chung BC, Sasano H, et al. Improved detectability of sex steroids from frozen sections of breast cancer tissue using GC-triple quadrupole-MS. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2018; 178 : 185-192.
- Gomes RL, Meredith M, Snape CE, Sephton MA. Analysis of conjugated steroid androgens: deconjugation, derivatization, and associated issues. Journal of pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis. 2009; 49: 1133-1140.
- Robles J, Marcos J, Renau N, Garrostas L, Segura J, et al. Quantifying endogenous androgens, estrogens, pregnenolone and progesterone metabolites in human urine by gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta. 2017; 169: 20-29.
- Pöhö P, Scholz K, Kärkkäinen N, Haapala M, Räikkönen H, et al. Analysis of steroids in urine by gas chromatography-capillary photoionization-tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A. 2019; 1598: 175-182.
- Hoffmann P, Hartmann MF, Remer T, Zimmer KP, Wudy SA. Profiling estrogens and testosterone in human urine by stable isotope dilution/ benchtop gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Steroids. 2010; 75: 1067-1074.
- Bowden J, Colosi D, Stutts W, Mora D, Garrett T, et al. Enhanced Analysis of Steroids by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry using Microwave- Accelerated Derivatization. Analytical chemistry. 2009; 81: 6725-6734.
- Zhou YQ, Wang ZJ, Jia N. Formation of multiple trimethylsilyl derivatives in the derivatization of 17alpha-ethinylestradiol with BSTFA or MSTFA followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry determination. Journal of environmental sciences (China). 2007; 19: 879-884.
- Zuo Y, Zhang K, Lin Y. Microwave-accelerated derivatization for the simultaneous gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric analysis of natural and synthetic estrogenic steroids. Journal of chromatography. A. 2007; 1148: 211-218.
- Storbeck KH, Gilligan L, Jenkinson C, Baranowski ES, Quanson JL, et al. Taylor, The utility of ultra-high performance supercritical fluid Chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UHPSFC-MS/MS) for clinically relevant steroid analysis. Journal of Chromatography B. 2018; 1085: 36-41.
- Pinkston J, Wen D, Morand K, Tirey D, Stanton D. Comparison of LC/MS and SFC/MS for Screening of a Large and Diverse Library of Pharmaceutically Relevant Compounds. Analytical chemistry. 2006; 78: 7467-7472.
- Desfontaine V, Nováková L, Ponzetto F, Nicoli R, Saugy M, et al. Liquid chromatography and supercritical fluid chromatography as alternative techniques to gas chromatography for the rapid screening of anabolic agents in urine. Journal of Chromatography A. 2016; 1451.
- Parr MK, Wüst B, Teubel J, Joseph JF. Splitless hyphenation of SFC with MS by APCI, APPI, and ESI exemplified by steroids as model compounds. Journal of chromatography. B, Analytical technologies in the biomedical and life sciences. 2018; 1091 : 67-78.
- Doué M, Dervilly-Pinel G, Pouponneau K, Monteau F, Le Bizec B. Analysis of glucuronide and sulfate steroids in urine by ultra-high-performance supercritical-fluid chromatography hyphenated tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015; 407: 4473-4484.
- Kim KJ, Kim HJ, Park HG, Hwang CH, Sung C, et al. A MALDI-MS-based quantitative analytical method for endogenous estrone in human breast cancer cells. Sci Rep. 2016; 6: 24489.
- Song Z, Gao H, Xie W, Sun Q, Liang K, et al. Quantitative MALDI-MS assay of steroid hormones in plasma based on hydroxylamine derivatization. Analytical Biochemistry. 2021; 616: 114089.
- Chen CH, Bair MJ, Hsu CW, Chiu TC, Hu CC. Analysis of steroid hormones in human saliva by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anaytical Methods. 2015; 7: 486-489.
- Zhang Y, Tobias HJ, Brenna JT. Highly sensitive and selective analysis of urinary steroids by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography combined with positive chemical ionization quadrupole mass spectrometry. Analyst. 2012; 137: 3102-3110.
- Nielen MWF, Bovee TFH, van Engelen MC, Rutgers P, Hamers ARM, et al. Urine Testing for Designer Steroids by Liquid Chromatography with Androgen Bioassay Detection and Electrospray Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Identification. Analytical Chemistry. 2006; 78: 424-431.
- Travers S, Martinerie L, Bouvattier C, Boileau P, Lombès M, et al. Multiplexed steroid profiling of gluco and mineralocorticoid pathways using a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017; 165: 202-211.
- Zang T, Tamae D, Mesaros C, Wang Q, Huang M, et al. Simultaneous quantitation of nine hydroxy-androgens and their conjugates in human serum by stable isotope dilution liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017; 165: 342-355.
- Im E, Lew BL, Lee MY, Lee J, Paeng KJ, et al. Simultaneous determination of androgens and prostaglandins in human urine using ultra-highperformance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of chromatography. B, Analytical technologies in the biomedical and life sciences. 2019; 1109: 45-53.
- Licea-Perez H, Wang S, Szapacs ME, Yang E. Development of a highly sensitive and selective UPLC/MS/MS method for the simultaneous determination of testosterone and 5alpha-dihydrotestosterone in human serum to support testosterone replacement therapy for hypogonadism. Steroids. 2008; 73: 601-610.
- Häkkinen MR, Heinosalo T, Saarinen N, Linnanen T, Voutilainen R, et al. Analysis by LC–MS/MS of endogenous steroids from human serum, plasma, endometrium and endometriotic tissue. Journal of pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis. 2018; 152: 165-172.
- Chen J, Liang Q, Hua H, Wang Y, Luo G, et al. Simultaneous determination of 15 steroids in rat blood via gas chromatography-mass spectrometry to evaluate the impact of emasculation on adrenal. Talanta. 2009; 80: 826-832.
- Tsakalof AK, Gkagtzis DC, Koukoulis GN, Hadjichristodoulou CS. Development of GC-MS/MS method with programmable temperature vaporization large volume injection for monitoring of 17β-estradiol and 2-methoxyestradiol in plasma. Analytica Chimica Acta. 2012; 709: 73-80.
- Bileck A, Verouti SN, Escher G, Vogt B, Groessl M. A comprehensive urinary steroid analysis strategy using two-dimensional gas chromatography - time of flight mass spectrometry. Analyst. 2018; 143: 4484-4494.
- Márta Z, Bobály B, Fekete J, Magda B, Imre T, et al. Simultaneous determination of thirteen different steroid hormones using micro UHPLCMS/ MS with on-line SPE system. Journal of pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis. 2018; 150: 258-267.
- Yamashita K, Okuyama M, Nakagawa R, Honma S, Satoh F, et al. Development of sensitive derivatization method for aldosterone in liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry of corticosteroids. Journal of chromatography. A. 2008; 1200: 114-121.
- Yamashita K, Okuyama M, Watanabe Y, Honma S, Kobayashi S, et al. Highly sensitive determination of estrone and estradiol in human serum by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Steroids. 2007; 72: 819-827.
- Yuan TF, Le J, Cui Y, Peng R, Wang ST, et al. An LC-MS/MS analysis for seven sex hormones in serum. Journal of pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis. 2019; 162: 34-40.
- Pauwels S, Antonio L, Jans I, Lintermans A, Neven P, et al. Sensitive routine liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for serum estradiol and estrone without derivatization. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2013; 405: 8569-8577.
- Doué M, Dervilly-Pinel G, Pouponneau K, Monteau F, Le Bizec B. Analysis of glucuronide and sulfate steroids in urine by ultra-high-performance supercritical-fluid chromatography hyphenated tandem mass spectrometry. Analytical and bioanalytical chemistry. 2015; 407.