
Mini Review
Austin J Anal Pharm Chem 2022; 9(3): 1152.
An Overview about the Relationship between Cystatin C and Inflammatory Diseases
*Corresponding author: Yixin Huang College of Biological Science and Technology, Agricultural University Of Hunan, 410128, China
Received: November 21, 2022; Accepted: December 23, 2022; Published: December 29, 2022
Abstract
Cystatin C (Cys-C) is a protease inhibitor that can be produced by nuclear cells in the human body. Its principal function is to inhibit the activity of various cysteine proteases in vivo. In addition, Cys-C also plays an essential role in regulating antigen presentation, extracellular matrix degradation, and the balance of protein production and decomposition in living cells. Cys-C is involved in the pathophysiological processes of chronic inflammatory diseases, including cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, and respiratory diseases. This article reviews the effects of Cys-C on chronic inflammatory diseases and its therapeutic prospects.
Keywords: Cystatin C; Inflammatory diseases
Abbreviations: Cys-C; AS; Cat-K; ACS; AMI; MIRI; SA-AKI; COPD
Introduction
The cystatin super family includes three families, I, II, and III. The members of the family I are single-stranded proteins composed of more than 100 amino acid residues without disulfide bonds and carbohydrates; Members of family II are composed of 120 amino acid residues lacking carbohydrates but containing two disulfide Bridges; Members of family III are activators of large multifunctional glycoproteins in plasma. Among them, cystatin C belongs to family II, encoded by the gene CST3 on the short arm of chromosome 20. It has a molecular mass of 13 kD, an isoelectric point of 9.3, and contains 122 amino acids. It is an intrinsic inhibitor of cysteine proteases such as cathepsin B, elastase, and please (Figure 1) [1].
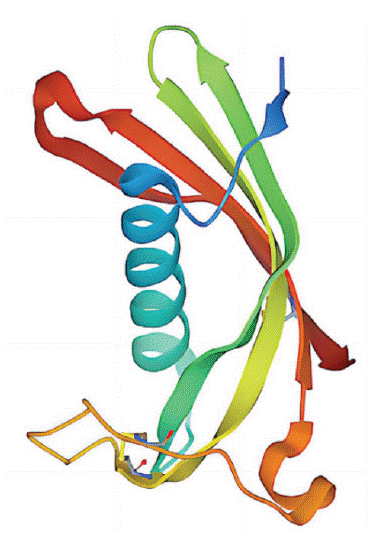
Figure 1: Biochemical structure of Cystatin C [1].
Cys-C is not affected by age, sex, or protein intake and has no tissue specificity. Cys-C is stably produced by all nucleated cells in the human body. At the same time, the kidney is the only organ that can clear circulating Cys-C. Cys-C is used as a biomarker of renal function in clinical practice. Due to its small size, 99% of Cys-C cannot be detected in routine urine due to glomerular filtration and glomerular absorption. When renal function is damaged, the glomerular filtration rate is affected, and the Cys- C level is increased, which can be used as an evaluation index of the severity of renal function [2]. However, more and more studies have shown that Cys-C is also involved in the physiological and pathological processes of many chronic inflammatory diseases, such as cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, severe infectious diseases, respiratory diseases, and so on. This article reviews the function and clinical application of Cys- C. These results collectively indicate that Cys-C is an essential breakthrough in treating inflammatory diseases.
The Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Cystatin C
Anti-Proteolytic Activity
Cys-C, as a cysteine protease inhibitor, can prevent cells from being affected by endogenous or exogenous proteases by regulating intracellular and extracellular proteins, thereby inhibiting various cysteine protease activities in vivo, including improper hydrolysis of endogenous proteases or exogenous proteases promoting pathogen growth [3]. Due to the differences in the structure and properties of different proteases, Cys-C has different degrees of inhibitory activity against different proteases. Cys-C showed potent inhibition of cathepsins B, L, K, and S but almost no inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases and serine proteases. Cathepsins are a class of target proteases found in tissue cells, mainly from autolysin. 11 kinds of cathepsins in the human body are closely related to various inflammatory diseases. For example, when an inflammatory reaction occurs in the arterial wall, Cys-C can inhibit the secretion of cathepsins and then promote the remodeling of the vascular wall matrix to slow down the disease [4].
Anti-Inflammatory Activity
Cys-C exhibits anti-inflammatory properties through other mechanisms. Studies have found that Cys-C can reduce the severity of inflammation by promoting neutrophil chemotaxis, adhesion, degranulation, and reactive oxygen species production [5]. This mechanism is related to many inflammatory diseases. When pro-inflammatory factors are increased in adipose tissue under obesity, increasing the Cys-C level can reduce the concentration of pro-inflammatory factors, thereby offsetting the deterioration of glucose metabolism and reducing the degree of inflammation [6]. In addition, Cys-C plays an essential role in the pathophysiological process of cardiovascular and inflammatory diseases by inhibiting oxidative low-density lipoprotein and zymogens [7].
Cystatin C Associated Diseases
Cardiovascular Inflammatory Disease
Atherosclerosis: Atherosclerosis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by the massive degradation of extracellular matrix proteins in the arterial wall [8]. Under the activation of vascular endothelial cells and the interaction of various inflammatory factors, monocyte aggregation and macrophage differentiation, lipid infiltration into the subendothelium, and the formation of atherosclerotic plaques [9]. The lumen stenosis caused by atherosclerotic plaque and the thrombus formed by plaque detachment eventually lead to acute cardiovascular events [10]. When Cys-C secretion is relatively low, atherogenesis occurs at a faster rate. Studies have found that Cys-C regulates protein hydrolysis and metabolism by regulating the activity of cysteine cathepsin and then affects the degradation of the extracellular matrix, thereby alleviating the progression of the disease to malignancy. It has also been found that Cys-C can inhibit the increase of the Cathepsin K (Cat-K) level, which stimulates the transition of atherosclerotic plaque from a stable to an unstable state [11]. In addition, the fluctuation of Cys-C level can be used as a marker of atherosclerosis to evaluate the severity and prognosis of atherosclerosis.
Acute Coronary Syndrome: Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) is a clinical syndrome caused by acute myocardial ischemia, including unstable angina pectoris, non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, and ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Studies have proved that the increase of inflammatory factors affects the disease and lesion degree of ACS and plays an essential role in the occurrence and development of ACS [12]. Some studies have shown that the increase in Cys-C concentration is associated with increased number of stenosed coronary arteries in ACS patients. Cys-C can predict the severity of ACS patients so that patients can be treated in time [13,14].
Acute Myocardial Infarction: Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) is a type of myocardial necrosis caused by acute or persistent coronary ischemia and hypoxia [15]. The pathological basis of AMI is coronary atherosclerotic stenosis. Some studies have found that aging is an independent risk factor for poor prognosis in patients with AMI. Elderly patients with AMI are more likely to present with multiple clinical manifestations and multi-branch lesions than younger patients with AMI [16]. Cys- C can induce myocardial injury and acute myocardial infarction through the ROS/ mitochondrial signaling pathway, disrupting the production of hypoxic cardiomyocytes [17]. In addition, the Cys-C level can be used as a marker to evaluate the severity and prognosis of AMI.
Cardiac Failure
When patients have an acute myocardial infarction, timely reperfusion to restore the coronary artery can save ischemic cardiomyocytes’ survival and reduce patients’ mortality. However, it may also cause Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (MIRI), which may reduce the efficacy of reperfusion therapy in patients with AMI and eventually develop into heart failure. The serum level of Cys-C increased with the increase in the severity of the cardiac failure, indicating that Cys-C was closely related to AMI and MIRI [18]. Cys-C can reduce the injury of cardiomyocytes, inhibit the activity of the NF-κB signaling pathway, and then reduce the oxidative stress and apoptosis of H9C2 cells, thereby reducing the injury of H9C2 cells and alleviating the severity of MIRI [19]. Cys-C has value in the evaluation of AMI and its complications (Figure 2).
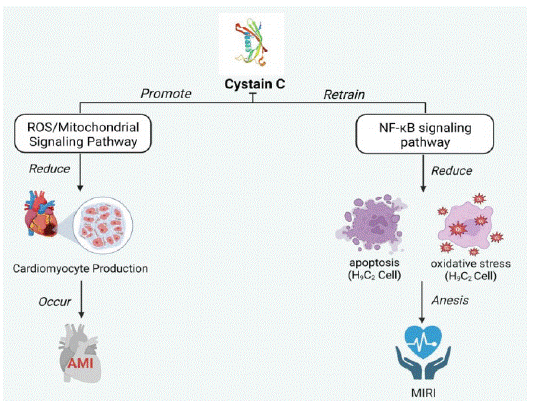
Figure 2: Mechanism of Cys-C in myocardial infarction and heart
failure. (Created with BioRender.com).
Cerebral Vasculitis Disease
Ischemic Stroke: Stroke is a group of acute cerebrovascular diseases, including ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke, which are caused by the sudden rupture of cerebral blood vessels or blood cannot flow into the brain due to vascular obstruction, and the proportion of patients with ischemic stroke is up to 87% ammatory diseases [20]. Ischemic stroke is caused by the stenosis or occlusion of the supply vessels of the brain, leading to necrosis or softening of the local brain tissue, resulting in persistent neurological dysfunction. Atherosclerosis is the primary pathological basis of it [21]. Cys-C is a risk factor for ischemic stroke. The severity of ischemic stroke increases with the increase of serum Cys-C level. It has been found that the serum level of Cys-C in patients with ischemic stroke is significantly higher than that in patients without ischemic stroke, and the degree of neurological deficit increases with the increase of Cys-C level. At the same time, other studies have found that high-density lipoprotein, a protective factor of ischemic stroke, decreases with the increase of Cys-C level, which leads to an increase in the incidence of ischemic stroke [22].
Severe Infectious Inflammatory Disease
Sepsis: Sepsis is a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection [23]. An excessive inflammatory response caused by infection induces a large release of proinflammatory factors, which is the main factor in increasing sepsis's severity [24]. Because of the critical role of cystatin in parasite immune escape, Yang X et al. found that Schistosoma japonicum-derived Cys-C cloned from Japanese blood-sucking adults could inhibit the release of inflammatory factors such as TNF-a [25]. Subsequently, Wan Y. K. et al. found that Schistosoma japonicum-derived Cys-C could ameliorate LPS-induced sepsis [26]. Schistosoma japonicum-derived Cys-C induces monocytes to become Mg macrophages. These macrophages inhibit the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines IFN-γ and IL-6 and produce anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10 and TGF-β, significantly reducing the severity of sepsis and the pathological injury of other organs [27]. In addition, acute kidney injury is a common complication that increases mortality in patients with sepsis. Some studies have found that Cys-C has a diagnostic and predictive role in sepsis complicated with acute kidney injury (SA-AKI). Cys-c can diagnose SA-AKI in advance than creatinine and is more suitable as a biomarker of sepsis and complications than creatinine (Figure 3) [28].
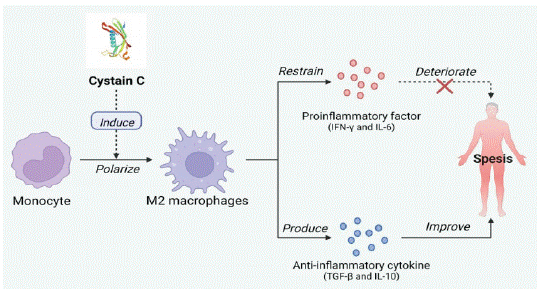
Figure 3: Mechanism of action of Cys-C in sepsis. (Created with Bio-
Render.com).
Respiratory Inflammatory Disease
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is characterized by incompletely reversible airflow obstruction, chronic airway inflammation, and systemic effects or comorbidities associated with long-term chronic inflammatory responses to harmful gases and particulate matter [29,30]. Elevated serum cysteine C levels may indicate increased severity of COPD. Studies have found that elevated COPD levels correlate with inflammatory factors such as IL-6, resist in, tumor necrosis, and CRP. Cys-C levels in COPD patients are higher than those without the disease [31,32]. It was also found that Cys-C is involved in the pathological process of COPD by inhibiting cathepsin synthesis [33]. When COPD is combined with pulmonary infection, the inflammatory cells will release a large amount of Cys-C, significantly increasing the serum Cys-C level in the patients [34]. Moreover, serum Cys-C can be abnormally increased when the blood creatinine is still in the normal range before further systemic deterioration [35]. The Cys-C level can be used as a detection indicator for judging COPD. It can detect changes in COPD severity faster than the creatinine. It can also be an early warning marker for other tissue or organ failure caused by COPD [36].
Bronchial Asthma: Bronchial asthma is a heterogeneous chronic inflammatory respiratory disease mainly characterized by chronic non-specific inflammation and airway hyperreactivity. Studies have found that Cys-C levels are highly expressed in asthma patients' bronchial epithelial cells, respiratory tract gland endothelial cells, lung fibroblasts, airway and vascular smooth muscle cells, and surrounding inflammatory cells [37]. Serum Cys-C was positively correlated with the extent of lungderived asthma. It shows that the serum Cys-C level can provide diagnostic value for assessing asthma severity and provide intervention treatment with particular clinical significance.
Conclusion
Cys-C is an endogenous protease, and Cys-C is more sensitive than creatinine in evaluating renal function. In addition to antiproteolytic activity, it also has functions to inhibit inflammatory factors or promote inflammatory factors in different inflammatory disease responses. Importantly, Cys-C can be produced by any nucleated cell in the human body and is not affected by age, sex, or protein intake. It is expected that Cys-C has great potential in treating chronic inflammatory diseases and being a biomarker of renal function in humans. However, many challenges remain in the development of Cys-C. Firstly, many studies have shown that the level of Cys-C fluctuates significantly in the occurrence and development of chronic inflammatory diseases, which can be used as a prognostic marker of the disease. However, the specific anti-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory mechanisms of Cys-C are still unclear, and further studies are needed. Second, the current clinical application of Cys-C is limited to a marker to assist in diagnosing and treating diseases, and its great potential has not been promoted.
Moreover, its application in animal models of related diseases is still in the initial research stage, and there is still a long way to go before its clinical application. However, the correlation between Cys-C levels and the risk, severity, and prognosis of chronic inflammatory diseases has been continuously explored in recent years. More in-depth research in this area will provide new ideas for the prevention and treatment of chronic inflammatory disorders and benefit more people.
References
- Orlikowska M, Jankowska E, Behrendt I, Borek D, Otwinowski Z, Skowron P, et al. Hinge-loop mutation can be used to control domain swapping of human cystatin C. Acta Crystallographica a- Foundation and Advances. 2011; 67: C310-C.
- Zi M, Xu YJIl. Involvement of cystatin C in immunity and apoptosis. 2018; 196: 80-90.
- Zhang WJ, Zi MT, Sun L, Wang FG, Chen S, Zhao YF, et al. Cystatin C regulates major histocompatibility complex-II-peptide presentation and extracellular signal-regulated kinase-dependent polarizing cytokine production by bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. Immunology and Cell Biology. 2019; 97: 916-30.
- Li X, Zhu H, Li P, Xin Q, Liu J, Zhang W, et al. Serum cystatin C concentration as an independent marker for hypertensive left ventricular hypertrophy. 2013; 10: 286.
- Wu HX, Du QN, Dai QY, Ge JB, Cheng XW. Cysteine Protease Cathepsins in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases. Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis. 2018; 25: 111-23.
- Dedual MA, Wueest S, Challa TD, Lucchini FC, Aeppli TRJ, Borsigova M, et al. Obesity-Induced Increase in Cystatin C Alleviates Tissue Inflammation. Diabetes. 2020; 69: 1927-35.
- Dandana A, Gammoudi I, Chalghoum A, Chahed H, Addad F, Ferchichi S, et al. Clinical utility of serum cystatin C in predicting coronary artery disease in patients without chronic kidney disease. 2014; 28: 191-7.
- Ross R. Mechanisms of disease - Atherosclerosis - An inflammatory disease. New England Journal of Medicine. 1999; 340: 115-26.
- Martinez E, Martorell J, Riambau V. Review of serum biomarkers in carotid atherosclerosis. Journal of Vascular Surgery. 2020; 71: 329-41.
- Grover SP, Mackman N. Tissue factor in atherosclerosis and atherothrombosis. Atherosclerosis. 2020; 307: 80-6.
- Zhao HY, Qin XJ, Wang S, Sun XW, Dong B. Increased cathepsin K levels in human atherosclerotic plaques are associated with plaque instability. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine. 2018; 15: 2693.
- Collison LW, Workman CJ, Kuo TT, Boyd K, Wang Y, Vignali KM, et al. The inhibitory cytokine IL-35 contributes to regulatory T-cell function. 2007; 450: 566-9.
- Ma L, Dai WQ, Lin YB, Zhang ZY, Pan YH, Han HY, et al. Leukocyte Rho kinase activity and serum cystatin C affect cardiovascular events in acute coronary syndrome. Medicine. 2020; 99: e20060.
- Jin S, Xu J, Shen G, Gu PJSJoC, Investigation L. Predictive value of circulating cystatin C level in patients with acute coronary syndrome: a meta-analysis. 2021; 81: 1-7.
- Henderson G, Abdallah M, Johnson M, Anabila M, Kravitz K, Rajeswaran J, et al. RECURRENT ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION AFTER AN ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2019; 73: 228.
- Wang JW, Li L, Ma N, Zhang XH, Qiao YY, Fang GG, et al. Clinical investigation of acute myocardial infarction according to age subsets. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine. 2020; 20: 120.
- Shen J, Li Y, Jiao Y, Wang J, Hou X, Su Y, et al. Wnt 3a Protects Myocardial Injury in Elderly Acute Myocardial Infarction by Inhibiting Serum Cystatin C/ROS-Induced Mitochondrial Damage. Front Physiol. 2022; 13: 950960.
- Pinsino A, Jennings DL, Mahoney I, Sweat A, Kim A, Mondellini GM, et al. Serum Cystatin C versus Creatinine Based Assessment of Renal Function in Heart Transplant Patients. Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation. 2020; 39: S256-S.
- Su B, Bu SD, Kong BH, Dai RX, Su Q. Cystatin C alleviates H2O2- induced H9c2 cell injury. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences. 2020; 24: 6360-70.
- Andrabi SS, Parvez S, Tabassum HJP. Ischemic stroke and mitochondria: mechanisms and targets. 2020; 257: 335-43.
- Huang L, Yao SG. Carotid artery color Doppler ultrasonography and plasma levels of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 and cystatin C in arteriosclerotic cerebral infarction. Journal of International Medical Research. 2019; 47: 4389-96.
- Watanabe J, Kakehi E, Kotani K, Kayaba K, Nakamura Y, Ishikawa SJAPJoPH. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and risk of stroke subtypes: Jichi Medical School Cohort Study. 2020; 32: 27-34.
- Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). Jama-Journal of the American Medical Association. 2016; 315: 801-10.
- Kaukonen KM, Bailey M, Pilcher D, Cooper DJ, Bellomo R. Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome Criteria in Defining Severe Sepsis. New England Journal of Medicine. 2015; 372: 1629-38.
- Yang X, Liu J, Yue Y, Chen W, Song M, Zhan XM, et al. Cloning, expression and characterisation of a type II cystatin from Schistosoma japonicum, which could regulate macrophage activation. Parasitology Research. 2014; 113: 3985-92.
- Wan Y-K, Li H-H, Zuo L, Wang X-L, Wang L-Y, He W-X, et al. Intervention with Schistosoma japonicum cysteine protease inhibitor for treatment of lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis in mice. 2018; 38: 625-9.
- Xie H, Wu LQ, Chen XZ, Gao SF, Li HH, Yuan Y, et al. Schistosoma japonicum Cystatin Alleviates Sepsis Through Activating Regulatory Macrophages. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology. 2021; 11: 617461.
- Moradkhani A, Samimagham HR, Tamaddondar M, Farshidi H, Khayatian M, Soleimani SJJoN. The efficiency of remote ischemic preconditioning on serum cystatin C-based acute kidney injury in patients undergoing coronary angiography; a randomized controlled trial. 2020; 10: e09-e.
- Singh D, Agusti A, Anzueto A, Barnes PJ, Bourbeau J, Celli BR, et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive lung disease: the GOLD science committee report. Eur Respir. 2019; 53: 1900164.
- Wang C, Xu J, Yang L, Xu Y, Zhang X, Bai C, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in China (the China Pulmonary Health [CPH] study): a national cross-sectional study. 2018; 391: 1706-17.
- Takayuki Nakajima. Plasma cathepsin S and cathepsin S/cystatin C ratios are potential biomarkers for COPD: Keio University; 2018.
- Telo S, Kuluöztürk M, Deveci F, Kirkil G, Öner Ö, Kaman DJJomb. Serum cystatin C levels in COPD: potential diagnostic value and relation between respiratory functions. 2018; 37: 434-440.
- Song Q, Chen P, Liu X-MJRR. The role of cigarette smoke-induced pulmonary vascular endothelial cell apoptosis in COPD. Respir Res. 2021; 22: 39.
- Qu J, Yue L, Gao J, Yao HJJoP, Therapeutics E. Perspectives on Wnt signal pathway in the pathogenesis and therapeutics of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Pharmacol Exp. 2019; 369: 473- 80.
- Chai L, Feng W, Zhai C, Shi W, Wang J, Yan X, et al. The association between cystatin C and COPD: a meta-analysis and systematic review. BMC Pulm Med. 2020; 20: 182.
- Hirai K, Tanaka A, Homma T, Goto Y, Akimoto K, Uno T, et al. Serum creatinine/cystatin C ratio as a surrogate marker for sarcopenia in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clinical Nutrition. 2021; 40: 1274-80.
- De Vooght V, Smulders S, Haenen S, Belmans J, Opdenakker G, Verbeken E, et al. Neutrophil and eosinophil granulocytes as key players in a mouse model of chemical-induced asthma. 2013; 131: 406-18.