Case Report
Austin J Anat. 2014;1(4): 1018.
Identifying Rare Human Anomalies Through Students Directed Dissection at Alfaisal University: Case Report
Mazhar MA, Qazi S, Kherallah S, AlDalati A, AlTinawi B, Azouz H, Ahmad JH and Ganguly P*
College of Medicine, Alfaisal University, Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
*Corresponding author: Paul Ganguly. MBBS, MD, FACA, Professor and Chairman, College of Medicine, Alfaisal University, Riyadh 11533, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Received: August 25, 2014; Accepted: September 23, 2014; Published: September 25, 2014
Abstract
Background: Dissection constitutes a fundamental attribute to learning, yet the limitations of resources oblige medical institutions sometimes to eradicate dissection. Alfaisal University is one of those institutions where the art of student-centred dissection is practiced under the supervision of well-trained faculty. It has been deduced that cadaveric dissection correlates well with the objectives of Alfaisal’s curriculum which is based on problem based learning and full comprehension of the clinical correlation. Consequently, this study elicits the importance of dissection in the field of medicine and emphasizes the concept of biological variations and demonstrates common pathological findings.
Objectives: 1) To reinforce and bolster traditional wet dissection among medical students. 2) To integrate some of the learning needs of clinical anatomy with anatomical variation and pathology observed through student-directed dissection.
Methods: Cadavers were dissected during student-centred integrated anatomy resource sessions at Alfaisal University. During dissection, students observed anomalies in some of the cadavers that provoked high yield of interest and triggered the sense of exploration among medical students.
Results: Anomalies discovered include: unusual origin of brachiocephalic trunk, large hiatus hernia and Giacomini vein.
Conclusion: Despite being a demanding exercise, dissection constitutes an essential technique in acquiring a comprehensive and inclusive understanding of anatomy. Dissection not only plays an effective technique in establishing a comprehensive understanding of anatomy but also serves an everlasting experience initiated by meticulous, diligent students.
Keywords: Anatomy dissection; Anomalies; Problem based learning; Medical students at Alfaisal University
Introduction
Dissection is a unique feature of medicine; yet recently, arguments emerged questioning the effectiveness of dissection in modern anatomical curriculums [1]. Cadaveric dissection fosters students curiosity, gives them chance to appreciate the three dimensional aspect of body structures, and illustrates the concept of biological variability [2,3]. Although many medical institutions are using this method of learning anatomy, there are newer schools who use a cadaver-free approach by relying on computer-assisted techniques [4]. Subsequently, one may question if this transformation may cause anatomical knowledge to fall below the required standards. This is particularly true for residents who often come back to the dissection hall to perfect the knowledge associated with surgical anatomy [5,6].
Alfaisal University has adopted newer teaching modalities in clinically-oriented understanding of human anatomy while giving dissection a priority. Dissection facilitates the learning in problem-based hybrid curriculum by assimilating information about clinical cases and conditions observed throughout medical history. Since dissection offers superlative results, students at Alfaisal are given free chances to dissect and, hence, promote the attributes of team work among them. The exposure to dissection also provides them an invaluable experience and perception of death and mortality.
This article elicits the importance of dissection in the field of medicine which is a compassionate art that can only be anticipated by the thorough investigation of internal bodily structures. Dissection also emphasizes the concept of normal and abnormal variations among human beings, and integrates anatomy with pathology and clinical medicine which remain a pivotal influence in future study [7].
Objectives
- To reinforce and bolster traditional wet dissection among medical students.
- To integrate some of the learning needs of clinical anatomy with anatomical variation and pathology observed through student-directed dissection.
Method
To promote full understanding of anatomy, twelve fully embalmed cadavers (M=7,F=5) of various ethnic origin were imported from Germany during Sept 2012 till Oct 2013. Our department is fully furnished to accommodate a good number of cadavers under ideal conditions. Students discovered anomalies throughout dissection under supervision which provoked a sense of curiosity and generated a stimulus for students to look for these anomalies. Hence, this bridged the gap between developmental malformation and the existing gross anatomical features. Students showed enthusiasm for active learning of this indispensable subject and its relationship with various clinical manifestations.
Results
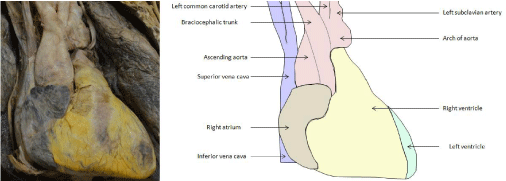
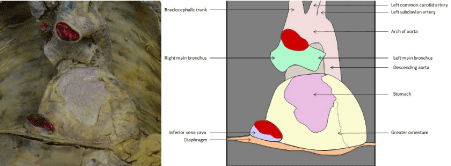
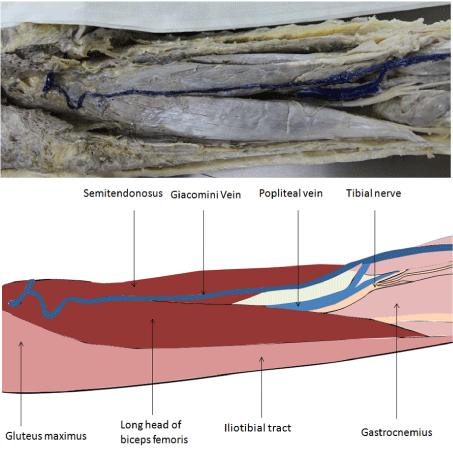
During dissection, students observed anomalies. Moreover, students performed further studies to reinforce the concept obtained from the discovered anomalies. Anomalies discovered include: unusual origin of brachiocephalic trunk (Figure. 1), hiatus hernia (Figure. 2) and Giacomini vein (Figure.3).
Figure 1: Unusual origin of brachiocephalic trunk.
Figure 2: Hiatus hernia.
Figure 3: Giacomini vein.
Discussion
“Seeing is believing” is perhaps the most ideal proverb which fits into the understanding of anatomy. Studies done by Patel and Moxham [8] and Moxham [9] and Azer SA et al. [10] found that “the order of preference for teaching methods was cadaveric dissection by students, prosection, living and radiological anatomy, computer aided learning (CAL), didactic lectures and the use of models”. Computer-aided simulating dissection programmes are useful tools in enhancing learning but they can never “fully replace the intellectual, educational and emotional experience afforded to medical students by cadaver dissection and even prosection.” Dissection was, therefore, ranked as a superior tool by anatomists [8,10].
The most common argument against dissection seems to be that it is expensive and time-consuming. As a result, medical institution would tend to compromise educational level to available reduced resources. Experience of learning anatomy through dissection is like “on the job” experience. Breaking bad news workshops or role play resuscitations cannot replace the actual experience gained in the wards; the same applies to the learning of anatomy through dissection.
During the last few decades new imaging techniques has evolved in living subjects and knowledge of anatomy has become increasingly important not only for interpretation of the images produced by the usual arrangement of structures but also to interpret any variations in it [11]. We are integrating the anatomical concepts of radiology and pathophysiology through cadaveric dissections [12,13]. Students are encouraged to present rare congenital findings as shown in this study. Students were able to find vascular problems such as brachiocephalic trunk originating from ascending aorta and Giacomini vein. It was reinforced that the defect of the neural crest cells was the key feature responsible for vascular malformations [14]. Also they found a rare form of hiatus hernia. Such activity engages student to use different learning modalities such as textbooks, atlases and computer programmes.
At Alfaisal University, anatomical knowledge is delivered to the students through anatomists as well through surgeons and clinicians who are highly experienced. Our curriculum is also characterized by the vertical integration of clinical anatomy throughout the medical course.
Conclusion
There is no doubt that the newer teaching modalities are convenient and hassle free to use than the cumbersome dissection exercises where extra hours and manpower are needed to maintain its integrity. However dissection is effective in establishing the core knowledge and is recognised as the most universal method for professional training and skill enhancement [15,16]. We strongly believe that the new teaching modes of learning anatomy should be tied up with the skill of dissection. It has been proven that the traditional wet dissection laboratory has inherent value in learning and teaching anatomy. It is probably true that the computer-assisted learning techniques cannot instil the feelings of mortality, humanity, and spirituality that dissection provokes. By combining the application of modern technology in teaching with the support of dissection, not by replacing it, our systems enable students to maximise their learning potential.
References
- Sugand K, Abrahams P, Khurana A. The anatomy of anatomy: a review for its modernization. Anat Sci Educ. 2010; 3: 83-93.
- Hasan T, Ageely H, Hasan D. The role of traditional dissection in medical education. Education in Medicine Journal. 2010; 2: e30-e34.
- Naz S, Nazir G, Iram S, Mohammad M, Umair, Qari IH, et al. Perceptions of cadaveric dissection in anatomy teaching. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2011; 23: 145-148.
- Winkelmann A. Anatomical dissection as a teaching method in medical school: a review of the evidence. Med Educ. 2007; 41: 15-22.
- Korf HW, Wicht H, Snipes RL, Timmermans JP, Paulsen F, Rune G, et al. The dissection course - necessary and indispensable for teaching anatomy to medical students. Ann Anat. 2008; 190: 16-22.
- Ahmed K, Rowland S, Patel V, Khan RS, Ashrafian H, Davies DC, et al. Is the structure of anatomy curriculum adequate for safe medical practice? Surgeon. 2010; 8: 318-324.
- Wood A, Struthers K, Whiten S, Jackson D, Herrington CS. Introducing gross pathology to undergraduate medical students in the dissecting room. Anat Sci Educ. 2010; 3: 97-100.
- Patel KM, Moxham BJ. Attitudes of professional anatomists to curricular change. Clin Anat. 2006; 19: 132-141.
- Moxham BJ, Moxham SA. The relationships between attitudes, course aims and teaching methods for the teaching of gross anatomy in the medical curriculum. Eur J Anat. 2007; 11: 19-30.
- Azer SA, Eizenberg N. Do we need dissection in an integrated problem-based learning medical course? Perceptions of first- and second-year students. Surg Radiol Anat. 2007; 29: 173-180.
- Machado JA, Barbosa JM, Ferreira MA. Student perspectives of imaging anatomy in undergraduate medical education. Anat Sci Educ. 2013; 6: 163-169.
- Prakash, Prabhu LV, Rai R, D'Costa S, Jiji PJ, Singh G, et al. Cadavers as teachers in medical education: knowledge is the ultimate gift of body donors. Singapore Med J. 2007; 48: 186-189.
- Campbell IS, Fox CM. Options for postgraduate anatomy education in Australia and New Zealand. N Z Med J. 2012; 125: 81-88.
- Conway SJ, Bundy J, Chen J, Dickman E, Rogers R, Will BM. Decreased neural crest stem cell expansion is responsible for the conotruncal heart defects within the splotch (Sp(2H))/Pax3 mouse mutant. Cardiovasc Res. 2000; 47: 314-328.
- Ramsey-Stewart G, Burgess AW, Hill DA. Back to the future: teaching anatomy by whole-body dissection. Med J Aust. 2010; 193: 668-671.
- Cowan M, Arain NN, Assale TS, Assi AH, Albar RA, Ganguly PK, et al. Student-centered integrated anatomy resource sessions at Alfaisal University. Anat Sci Educ. 2010; 3: 272-275.