
Research Article
Analysis. Austin J Anat. 2017; 4(3): 1074.
Role of Withania Somnifera (Ashwagandha) in Ischemic Stroke Rat Model Produced by Unilateral Internal Carotid Artery Ligation: A Histological Staining with 2,3,5 Triphenyltetrazolium Chloride and a Behavior Analysis
Koirala S¹*, Shah S¹, Rouniar GP², Koirala B² and Khanal L¹
¹Department of Human Anatomy, B.P. Koirala Institute of Health Sciences, Nepal
²Department of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, B.P. Koirala Institute of Health Sciences, Nepal
*Corresponding author: Koirala S, Department of Human Anatomy, B.P. Koirala Institute of Health Sciences, Nepal; Email: koirala_sarun@yahoo.com, sarun.koirala@bpkihs.edu
Received: November 08, 2017; Accepted: December 15, 2017; Published: December 22, 2017
Abstract
Introduction: A stroke is a medical emergency and can cause permanent neurological damage. The more extensive the area of brain affected, the more functions that are likely to be lost.
Objectives: To access and compare neurological deficits after 60 min of induction of stroke and 14 days after treatment with ashwagandha in different groups and to see infract area in brain using 2,3,5 Triphenyltetrazolium Chloride (TTC) stain.
Materials and Methods: 21 Male wistar albino rats were randomly allocated to form 3 groups. Commercially available Withania somnifera root extract (Vitamin world. Inc. NY, USA) was used as intra peritoneal route for 14 days and neurological deficits was assessed. Brain of coronal section of 2mm thickness, immersed in TTC (Sigma Aldrich, Merck Group Germany) solution and incubated at 37°C for 20 min. Inferential analysis was done by t- test to see the significant level at p < 0.05 with 95% confidence interval and ANOVA, Post Hoc test was applied to compare between different groups, regression and correlation was seen.
Results: There was significant differences in area of infract between Withania somnifera treated group and non-medicated group p = 0.017. Latency of fall off time in Rota rod test was seen significant (p = 0.000) in between the group. Similarly, 14 days after the induction of stroke, significant differences was present in different groups in rota rod fall off latency time (p = 0.043) and Grid walking test (p =0.002).
Conclusion: Ashwagandha showed improved neurosensorimotor activities in stroke model produced after unilateral ligation of internal carotid artery.
Keywords: Neurological deficits behavior tests; Ashwaganda
Abbreviations
TTC: 2,3,5 Triphenyltetrazolium Chloride; ICA: Internal Carotid Artery; IP: Intraperitoneal
Introduction
A stroke, known medically as a cerebrovascular accident, is the rapidly developing loss of brain function due to disturbance in the blood supply to the brain which is due to ischemia, lack of blood flow, caused by blockage, thrombosis, arterial embolism or a hemorrhage leakage of blood [1]. As a result, the affected area of the brain is unable to function, which might result in an inability to move one or more limbs on one side of the body, inability to understand or formulate speech, an inability to see one side of the visual field [2].
Ischemia induces production of oxygen free radicals and other reactive oxygen species which damage a number of cellular and extracellular elements and blood vessel endothelium as free radicals directly initiate elements of the apoptosis cascade by means of redox signaling, many antioxidant neuroprotectants drugs works at the level of the endothelium (National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke [3,4].
The Primary objectives of the study was to use the acute stroke model of rat produced by unilateral ligation of internal carotid artery, to see the neuroprotective effect of ashwagandha by conducting neurological deficits behavior tests. Secondary objectives were to access the neurological deficits after 60 min of induction of stroke, to compare the neurological deficits in different groups, 14 days after the i.p. injection of ashwagandha and to see the brain infraction area after unilateral ligation of ICA by using 2,3,5 Triphenyltetrazolium Chloride (TTC) stain.
Materials and Methods
Type of study: Experimental, Quantitative type of animal study
Sample size was calculated by using Resource Equation Method in which, a value E was measured, which is degree of freedom of Analysis Of Variance (ANOVA).
E = Total number of animals - Total number of groups
In this study to see the role of ashwagandha in rat stroke model and we had three groups (one group as control and two experimental groups); where value of E was assumed to be 18.
Then; the total number of animals or sample size (n) is:
E= n-3
18= n-3
N= 21, total sample size= 21, 7 in each group
By Resource Equation Method total 21 Male wistar albino rats weighing 200–220 gm, 7 in each group were randomly allocated to form 3 groups.
Animal Housing and Caring: Male wistar albino rats weighing 200–220g was obtained from the departmental animal house of BPKIHS. All procedures was approved by the IRC, BPKIHS. Animal handling for this research was done in accordance to the Guidelines given by Ethical Review Board for the Care and Use of Animals (ERBA) of the Nepal Health Research Council (NHRC, and NIH publication no. 80- 23 revised 1996). Rats were housed in standard plastic cages under room temperature (22–24°C) with a 12-h light/dark cycle. Unless otherwise stated standard laboratory food and water was provided throughout the experiments. Animals were allowed to acclimatize to the laboratory conditions for seven days prior to the experimental procedures. All efforts were made to minimize the number of animals used and their suffering.
Ethical consideration: Ethical clearance was obtained from Institutional Review Committee (IRC) and approval from Research Committee, BPKIHS, IRC/ 476/ 015.
Requirements and materials: Normal saline, surgical gloves, adhesive tapes, curved scissors, surgical blade, curved forceps, small scissors, cotton, surgical thread, 4.0 silk sutures, 1, 3ml, 5 ml syringe, 2% lidocaine HCl (Xylocaine), 16 number needle, betadine solution and ointment, magnifying glass, razors, cidex solution.
Surgical procedures and experimental design
Animals were anesthetized with Ketamin 50mg/ kg/ i.p. and turned supine position, and fixed to the surgical table using a adhesive tape
The incisional site was shaved and betadine solution was applied in the skin to make aseptic area for surgical process.
Three different experimental groups were made as below:
• Control group was made with only skin incision in neck region coded as Group A0,
• Unilateral internal carotid artery ligation only coded as Group A1
• Unilateral internal carotid artery ligation and treatment with ashwaganda 10 mg/kg i. pt. for 14 days coded as Group A2
A midline neck incision was made and the soft tissue over the trachea was retracted gently.
The Right common carotid artery was carefully isolated from the vagus nerve and the internal carotid artery was ligated using a 4.0 silk suture to create a acute model of stroke in rat model and the skin was sutured.
After 60 min the silk suture was removed to re-vascularize the brain. The mid line neck incision was then sutured.To relief pain and discomfort in the post-operative period, topical 1% lidocaine gel was applied on the sutured area and 0.5 ml saline i.p. was given for volume replenishment after surgery. Ashwagandha 10mg/kg/ i. p. (Root extract-Vitamin world. Inc. NY, USA) was injected in Group coded as Code: A2 for 14 days.
After 14 days of treated in Group A2,at the end of the study neurological deficits was assessed in Group A1, and A0, values were filled in data collection sheet and the animal was given high dose of sodium pentobarbitol (40 mg/ kg/ i.p) to deeply anesthetized, decapitated and brain was removed carefully.
Neurological deficits test and scoring
The acute neurological deficit of the animals in each group was evaluated after reperfusion after 60 min, by placing the rat in the floor, Grid walking test, Grip test and Rota rod test was done at the end of day 14 and values were filled in data collection sheet.
Staining method and image analysis
Properties of stain: 2,3, Triphenyltetrazolium chloride
Chemical structure of 2,3, 5 TTC is. (T8877, Sigma Aldrich Company) (Figure 1).
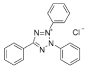
Figure 1: It is in powder form, faint yellow in color, water soluble, Molecular
weight is: 334.80, Chemical formula is: C19H15CIN4.
It is in powder form, faint yellow in color, water soluble, Molecular weight is: 334.80, Chemical formula is:
C19 H15CIN4
All groups of animal were anesthetized by high dose sodium pentobarbitol (40 mg/kg/i.p) injection to deeply anesthetized, decapitated and brain was removed carefully. The brain was removed and the edematous brain was stored in -20°C in deep freeze for 20 min, cut in coronal section of 2mm thickness by commercially supplied blade and immersed in TTC (Sigma Aldrich, Merck Group Germany) solution and incubated at 37°C for 20 min. TTC stain was prepared fresh by mixing 5gm with 250ml 0.9 % NACl. Since TTC stain is light sensitive it was prepared in dark room and stored in aluminum foil covered bottle. The TTC stain was then replaced with 10 % formalin.
Images of brain section was captured using Nikkon DSC 501 model digital camera and the infract area was calculated using KLONK Image Measurement computarized Software Softonic. Company, USA, version: 15.1.1.5.
Statistical analysis: Inferential analysis was done by t- test to see the significant level at p < 0.05 with 95% confidence interval and One-way ANOVA, Post Hoc test was applied to compare between different groups.
Grid walking Test for assessing motor impairement of the limb functioning which demonstrate the motor coordination deficits and rehabilition effects after stroke. Animal was placed on a grid and the foot fault was recorded. This test is suggestive of sensitive indicator for detecting impairments of sensorimotor functions after ischemia.
Grip Test: In this test the time for the suspension in the rod/ beam was noted
Forelimb flexion Test/ Sensorimotor Test: Normally the rat flexes both the limb towards the ground. Rat was suspended by its tail and the flexion of the limb to the contralateral side was noted, along with the head raised to the contralateral side.
Rota rod test is used to assess motor coordination and balance alteration in rodents first introduced by Dunham and Miya to study neurological functions in stroke model. The rota rod apparatus is a rod which rotates at an adjustable speed. The time of animal staying (fall off time) in the spinning rod is recorded.
Results
The 2mm thickness brain slices of control group were TTC stained and incubated at 370 C for 20 min (Table 1). The presence of red color in the brain slices indicates the normal brain tissue. In normal brain tissue with blood supply, 2,3,5 Triphenyltetrazolium Chloride - TTC was reduced to Formazen and gave red color (Figure 4).
Group Normal walk
(0)
Inability to walk straight (1)
Circling to paretic side (2)
Fall to the paretic side (3)
Flexion of forelimb to contralateral side (4)
A0 +
_
_
_
_
A1 _
_
+
+
+
A2 _
_
+
+
+
Table 1: Neurological deficits test scoring.
Larger size white color (unstained) was seen in brain slices of group coded as A1. There was clear demarcation between the red color stained and unstained area in the cortex, striatum area in right hemisphere which indicated the presence of infarct area created in different sections of brain in this group after artery ligation. The infarct area was unstained, remained white because of reduced activity of succinate dehydrogenase in ischemic area of brain and the presence of white unstained area was because of lack of conversion of TTC to formazen (Figures 2,3 and 5).
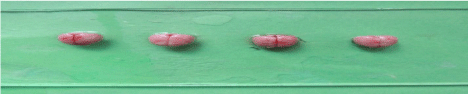
Figure 2: Brain Code: A1 prepartion for storage in – 20°C for 20 min.
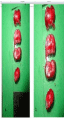
Figure 3: Brain slice showing infarct area 2,3,5 TTC staining: code A1.

Figure 4: Brain slice showing infarct area 2,3,5 TTC staining: code A1.

Figure 5: Shows the red color stained brain slices of control group. The 2mm
thickness brain slices were TTC stained and incubated at 370C for 20 min.
More red color stained and small size white color (unstained) in brain slices of Experimental group (coded A2) was seen. There was poor demarcation between the red color stained and unstained area (white) in the cortex, and few part of straitum in right hemisphere which indicated the presence of small infarct area in brain, 14 days after the i.p injection of ashwagandha in this group. The small infarct area was unstained, remained white because of poor activity of succinate dehydrogenase to convert of TTC to formazen (Figure 6).
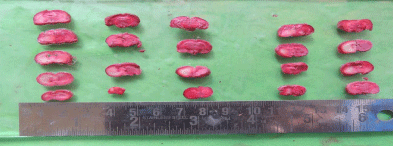
Figure 6: After 2,3,5 Triphenyltetrazolium chloride - TTC staining Group
coded as shows the red color stained and larger size white color (unstained)
brain slices of Experimental group (coded A1).
Significant difference was present in comparison of area of infarct between group A1, A2 (unpaired t- test), p < 0.05 (Table 2). Significant difference was present in Rota rod fall off time (sec) between Group A1 and Group A2, p< 0.05. No significant differences was seen in grip test and grid walking test in between Group A1, and A2 (p>0.05). Similarly significant difference was present between Rota rod test for fall off time between Group A2 and Ao, Grip test between Group A2 and Group A0, p < 0.001. Similarly grid walk test between Group A0 and A1, Group A2 and Ao was significant (p < 0.001), 60 min after induction of stroke (one –way ANOVA) and post hoc analysis. (Table 3, Figures 7 and 8). There was significant differences seen between 3 groups A0, A1, A2 in Grid walk test 14days after treatment with ashwaganda i.p. where p <0.001 (Table 4). Negative Correlation between area of infract and Rota rod fall off time (sec) was seen in with aspect to Rota rod, which was significant p < 0.001 but with respect to Rota rod fall of time 14 days after treatment, not much significance was seen which may be because of use of ashwaganda i.p. as medication for 14 days (Table 5, Figures 9-13).
Group
Mean
Std. Deviation of mean
Mean difference
95% Confident interval of mean difference
Sig. (2-tailed)
Area of Infarct
Group A1
24.44
4.457
8.9700
1.949 to 15.99
0.017
Group A2
15.47
7.266
*The mean difference is significant at the 0.05 level
Significant difference is present in comparison of area of infarct between group A1, A2 (unpaired t- test), where P< 0.05
Table 2: Comparison of area of infarct between group A1 and A2 experimental group applying unpaired t-test.
Dependent Variable
Group
Group
Mean Difference
Std. Error
Sig.
Group A0
Group A1
-2.714*
0.223
0
Group A2
-2.286*
0.223
0
Group A1
Group A0
2.714*
0.223
0
Grid Walk 1
Group A2
0.429
0.223
0.071
Group A2
Group A0
2.286*
0.223
0
Group A1
-0.429
0.223
0.071
Group A0
Group A1
6.4286*
0.5345
0
Group A2
7.2857*
0.5345
0
Grip Test 1
Group A1
Group A0
-6.4286*
0.5345
0
Group A2
0.8571
0.5345
0.126
Group A2
Group A0
-7.2857*
0.5345
0
Group A1
-0.8571
0.5345
0.126
Group A0
Group A1
6.5714*
0.4041
0
Group A2
7.5714*
0.4041
0
Group A1
Group A0
-6.5714*
0.4041
0
Rota Rod Test 1
Group A2
1.0000*
0.4041
0.024
Group A2
Group A0
-7.5714*
0.4041
0
Group A1
-1.0000*
0.4041
0.024
*The mean difference is significant at the 0.05 level.
Table 3: Table showing multiple comparisons between the groups: A0, A1 and A2 after 60 minute of induction of stroke (test: Post hoc analysis after one way ANOVA).
Variables
Groups
Mean
Std. Deviation
Std. Error
95% Confidence Interval for Mean
Difference between the groups
(Sig.)
Lower Bound
Upper Bound
Grid Walk 2
Group A0
1.14
0.378
0.143
.79 to 1.49
Group A1
3
0.816
0.309
2.24 to 3.76
Group A2
2
0
0
2.00 to 2.00
<0.001
Total
2.05
0.921
0.201
1.63 to 2.47
Grip Test 2
Group A0
13.857
6.7188
2.5395
7.643 to 20.071
Group A1
2.286
0.7559
0.2857
1.587 to 2.985
Group A2
22.429
17.501
6.6148
6.243 to 38.614
0.01
Total
12.857
13.309
2.9043
6.799 to 18.915
Rota Rod Test 2
Group A0
63.429
31.2136
11.7976
34.561 to 92.296
Group A1
49.143
28.0501
10.602
23.201 to 75.085
Group A2
82.857
27.6672
10.4572
57.269 to 108.445
0.12
Total
65.143
30.9585
6.7557
51.051 to 79.235
Significant difference is seen between 3 groups A0, A1, A2 in Grid walk test 14 days after treatment with ashwaganda i.p. p < 0.001.
Table 4: Table showing descriptive statistics and significance of difference between the three groups: A0, A1 and A2 after 14 days of induction of stroke (Test: one way ANOVA).
Variables
Area of infarct
Rota Rod Test 1
Pearson Correlation
-0.730
Sig. (2-tailed)
<0.001
Rota Rod Test 2
Pearson Correlation
-0.016
Sig. (2-tailed)
0.945
Table 5 reveals Negative Correlation between area of infract and Rota rod fall off time (sec) is seen in with aspect to Rota rod, which is significant p < 0.001.
Table 5: Correlation between area of infarct and Rota rod fall off time. (test: bivariate Pearson correlation test).

Figure 7: Shows the red color stained and small size white color (unstained)
brain slices of Experimental group (coded A2) arranged in 7 different rows.
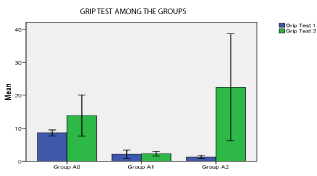
Figure 8: p < 0.05 in Group A2 (significant).
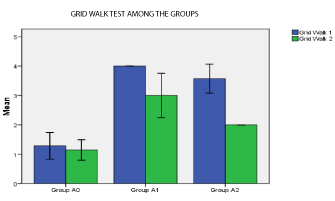
Figure 9: p < 0.01 in Group A1, A2 (significant).
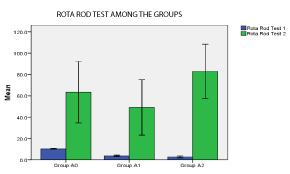
Figure 10: p < 0.05 in Group A0, A1, A2 (significant).
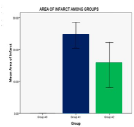
Figure 11: p < 0.05 in Group A1, A2 (significant).
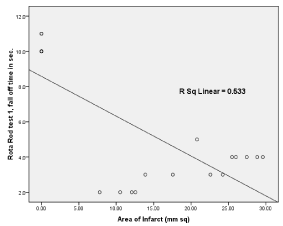
Figure 12: Simple linear regression graph showing the relationship between
area of infarct in X-axis and Rota Rod fall off time (sec) in Y-axis.
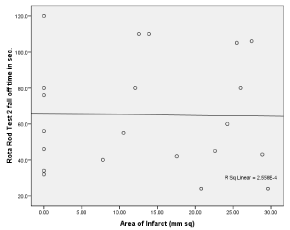
Figure 13: Simple linear regression graph showing the relationship between
area of infarct in X-axis and Rota Rod fall off time (sec) in Y-axis.
Discussion
Ischemia induces production of oxygen free radicals and other reactive oxygen species. Tissue injury caused by ischemia can be reduced to some extent if process of free radicals is inhibited by drugs which scavenge reactive oxygen species, inhibit apoptosis, or inhibit excitatory neurotransmitters. The symptoms depend on the area of the brain affected. The more extensive the area of brain affected, the more functions that are likely to be lost. So various behavior test are conducted to see the changes and to see for neuroprotective properties.
In this study, 14 brains were taken for TTC staining, which showed distinct demarcation between infarct and normal area suggesting reduced mitochondrial enzymes activity and 2,3 TTC was not reduced to formazen and thus formed white infarct area was visualized morphologically. Our study has similar finding with research conducted by Swanson RA et al, 1990 [6]. Similar other study for immediate TTC staining, the normal brain tissue was stained deep red and infarcted tissue with loss of succinate dehydrogenase activity appeared white [7]. The border between stained and unstained tissues was well demarcated and identified easily by visual inspection [8]. Similar finding in brain was present after TTC staining in study conducted by Sin Young, Park et al, 2014 [9].
In our study there was increased latency in rota rod fall off time in two different experimental group two weeks after ligation of artery in which time was seen more in the ashwagandha treated group. The rota rod test effectively asses motor impairment following ischemic injury. Increase in latency of rota rod fall time may be because of recovery after treatment and antioxidant properties of ashwagandha as well as motor learning with repetitive trails.
Similar finding of increased latency of rota rod fall off time was seen in a study conducted by Sin Young Park et al. [9]. This is because the active principles of ashwagandha, consisting of sitoindosides VII-X and withaferin-A isolated from root extract have shown to exhibit significant antioxidant effect in rat brain frontal cortex and striatum and improved behavior test to show neuroprotective properties [10].
Thus, few above findings indicate the traditional use of ashwagandha has a logical and scientific basis as a neuroprotective and antioxidant medication.
Keeping in view of its beneficial antioxidative properties and worldwide consumption present study was conducted to evaluate the neuroprotective properties of ashwagandha based on neurological deficits examination test are commonly employed behavioral paradigms of despair. These findings provide tremendous hope that ashwagandha extracts may one day help as a neuroprotective agents freeing patients from the ischemic strokes.
Conclusion
Ashwagandha showed its neuroprotective properties by neuro behavioral tests and improved the neurosensorimotor activities in stroke model produced by unilateral ligation of internal carotid artery.
Limitations of the Study
Cerebral Blood Flow (CBF) measurement was not conducted due to lack of CBF machine and magnetic resonance imaging for area of infracts and regular changes in between days were not calculated.
Acknowledgement
Department of Human Anatomy, Department of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, BPKIHS, Nepal, Urau Satya, Yadav Bhupendra, Limbu Harka, Sushil Kamat.
Conflict of Interest
No Conflict of Interest.
Fund Support
BPKIHS research grant.
References
- Sims NR, Muyderman H. Mitochondria, oxidative metabolism and cell death in stroke. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 2009; 1802: 80–91.
- Donnan GA, Fisher M, Macleod M, Davis SM. Stroke. Lancet. 2008; 9624: 1612–1623.
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS). Stroke: Hope through Research. National Institutes of Health.
- Feigin VL. Stroke epidemiology in the developing world. Lancet. 2005; 9478: 2160-2161.
- Uttara B, Singh Paolo AV, Zamboni, Mahajan RT. Oxidative Stress and Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Review of Upstream and Downstream Antioxidant Therapeutic Options. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2009; 7: 65–74.
- Swanson RA, Morton MT, Tsao-Wu G. A Semi automated Method for Measuring Brain Infarct Volume. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism. 1990; 2: 290-293.
- Liszczak TM. Limitations of Tetrazolium Salts in Delineating Infarcted Brain. Acta Neuropathol. 1984; 65: 150-157.
- Bederson JB. Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic examination. Stroke. 1986; 17: 472-476.
- Park SY, Marasini S, Kim GH. A Method for Generate a Mouse Model of Stroke: Evaluation of Parameters for Blood Flow, Behavior, and Survival. Exp Neurobiol. 2014; 23: 104–114.
- Gupta GL, Rana AC. Protective effect of Withania somnifera dunal root extract against protracted social isolation induced behavior in rats. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol. 2007; 51: 345-353.
Citation: Koirala S, Shah S, Rouniar GP, Koirala B and Khanal L. Role of Withania Somnifera (Ashwagandha) in Ischemic Stroke Rat Model Produced by Unilateral Internal Carotid Artery Ligation: A Histological Staining with 2,3,5 Triphenyltetrazolium Chloride and a Behavior Analysis. Austin J Anat. 2017; 4(3): 1074.