
Research Article
Austin J Anat. 2017; 4(4): 1075.
A Morphometric Study of Ventricular System of Human Brain by Computerised Tomography in an Indian Population and its Clinical Significance
Honnegowda TM¹*, Nautiyal A² and Deepanjan M²
¹Human Anatomy, Department of Plastic Surgery and Burns, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal, Manipal University, India
²Nuclear Medicine Physicist, Institute of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, AMRI Hospitals, India
*Corresponding author: Dr. Honnegowda TM Ph.D, Department of Human Anatomy, Kannur Medical College, Kannur, Kerala, India
Received: September 30, 2017; Accepted: December 15, 2017; Published: December 22, 2017
Abstract
Background and Aim: The human brain undergoes many gross and histopathological changes with regression of the brain tissue leading to the enlargement of the ventricles as age advances. Knowledge of morphometric and size of normal ventricular system of brain is of paramount importance to understand these changes.
Methods: For the present perspective study, Computerized Tomography (CT) for 250 patients (Males-130 and Females-120) were studied for the measurements of lateral ventricle, third ventricle and fourth ventricle and it was statistically analyzed.
Results: The antero -posterior extent of the body of the lateral ventricles on the right side was 77.45 ± 8.6 and 71.36 ± 9.4 in the males and females and on the left side was 76.6 ± 8.4 and 71.09 ± 9.4mm in the males and females; the length of the frontal horns on the right side was 30.54 ± 3.4 and 28.4 ± 4.2mm in the males and females and on the left side was 30.14 ± 4.7 and 27.4 ± 3.2 mm in the males and females respectively. The width and height of the fourth ventricle were 13.0 ± 1.9 and 10.0 ± 2.1 mm in the males and 12.0 ± 2.0 mm and 9.6 ± 2.2 mm in the females respectively. The width of the third ventricle was 5.9 ± 1.5 and 5.5 ± 1.9 mm in the males and females respectively.
Conclusion: The present study has defined the morphometric measurements of the lateral ventricles, third ventricle, and fourth ventricle of the brain which has clinical correlations in diagnosis and for appropriate treatment.
Keywords: Brain; Morphometry; Ventricular System; Size; Subjects; Tomography
Introduction
The cavity with in the brain is ventricles filled with Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF). The lateral ventricles are the largest paired ventricles present within the cerebrum; the third ventricle is in the diencephalon of the forebrain between the thalami; and the fourth ventricle is located posterior to the Pons and open part of the medulla oblongata of the hindbrain [1].
Objective and morphometric studies of human brain ventricles is under limelight, recently due to it is relation with several pathologies evidences such as schizophrenia, hydrocephalus, tumors, Trauma and as well as gender and aging which could lead to dementia [2]. By CT scanning ventricles of the brain can be studied and well visualized, and their overall configuration can be reconstructed from a series of contiguous slices [3]. Knowing the normal measurements of the cerebral ventricles in the living human has great importance in the diagnosis and monitoring of several pathologies [4]. It should be noted that there is a continuous debate in the literature of neuroanatomy, psychiatry, neuroradiology and neurology over the best method of assessing the various parts of the cerebral ventricular system and the information known regarding the accurate measurements of the brain ventricles is limited [5]. Since very few work has been done on measurement of cerebral ventricular system in india the present work is undertaken to study morphometric analysis of the lateral, third and fourth ventricles of the brain in normal Indian subjects using CT scan.
Materials and Methods
Selection and study Population
This prospective study population composed of 250 patients (130 males and 120 females) in the age group of 12 to 81 years, attending the department for Brain PET/CT procedure at Institute of Nuclear Medicine & Molecular Imaging, AMRI Hospital, Kolkata.
These patients were selected randomly and clinically confirmed no history of cerebral infarction, local mass lesions, probable communicating hydrocephalus, alcoholism, drug abuse, trauma or previous intra-cranial surgery and other hereditary diseases and were not on medication at the time of this study. All patients were in fasting condition (minimum 6 hrs) before undergone for the CT procedure. PET /CT scan of all patients were reported by expert nuclear Medicine physician scoring as normal.
Procedure of CT scanning technique
The CT scanner used in this study was the General electric GE discovery 690 PET/CT (64 slices). The selected exposure factors for the CT scan were 80-120 kvp and 250-450 mAs, the slice thickness was 3 mm and the noise index was 3. All CT Scans was performed in axial mode with iterative reconstruction algorithm.
The patient was placed on the PET/CT table and the head was centralized and supported for correct positioning and to avoid blurring of images. A lateral scout image was taken to confirm correct positioning of patient. Orbito-meatal line was drawn and a line at an angle of 15 - 20 degrees to and 1 cm above it was drawn, representing the lowest tomographic section, which passed through the base of skull. Total time of CT scan was 20-30 second followed by PET. A total of 8 to 10 sections were obtained without any overlap [6,7]. All processing and measurement of axial CT images were performed in ADW work station.
Method of measuring the brain ventricle
The measurements were taken as follows:
1) Lateral Ventricle Measurement
a) Length of right lateral ventricular body inclusive of level of interventricular foramen. Frontal horn (taken from tip of frontal horn to the atrium).
b) Length of left lateral ventricular body inclusive of frontal horn (taken from tip of frontal horn to the atrium) can be seen in (Figure 1).

Figure 1: CT axial image of the brain showing the length of the left lateral
ventricle and body of right ventricle. The three lines show the length of body of
right ventricle, length of the whole left ventricle and width of the third ventricle
respectively.
2) Level of Interventricular Foramen
a) Length of frontal horns of right lateral ventricle in Foramen (measured from its tip to the interventricular foramen).
b) Length of frontal horns of left lateral ventricle in cm (measured from its tip to the interventricular foramen) can be seen in (Figure 2).
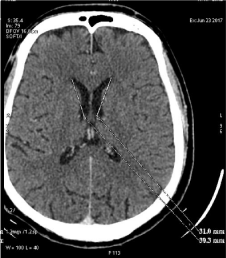
Figure 2: CT axial image of the brain showing the length of body of the
lateral ventricles. The gray lines indicate the length of the body of both lateral
ventricles.
3) Level of Third Ventricle
a) Greatest width of third ventricle in mm can be seen in (Figure 3).

Figure 3: CT axial image of the brain showing the length of the left lateral
ventricle and body of right ventricle. The three lines show the length of body of
right ventricle, length of the whole left ventricle and width of the third ventricle
respectively.
4) Level of Fourth Ventricle
a) Greatest height of fourth ventricle in mm (Figure 4).

Figure 4: CT axial image of the brain showing the width and height
measurement of the 4th ventricle. The gray lines indicate the height and the
width.
b) Greatest width of fourth ventricle in mm (Figure 4).
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed and expressed in mean ± SD. paired t test was performed between male and female group for a set of parameters, using the SPSS 16th version. The p-value is less than 0.05 were considered to be significant.
Results
It was observed that the anteroposterior extent of the body of the right and left ventricles was equal in the female 71.36 ± 9.4 mm whereas, it was larger in the right side 77.45 ± 8.6 mm than the left side 76.6 ± 8.4 mm in the males. The length of the frontal horns on the right side was 29.53 + 3.88 mm and 27.16 + 4.21 mm in the males and females and on the left side were 30.54 ± 3.4 mm and 28.4 ± 4.2 mm in the males and females (Table 2). The mean height and width of the fourth ventricle were 10.0 ± 2.1 and 13.0 ± 1.9mm in the males and 9.6 ± 2.2 mm and 12.0 ± 2.0mm in the females respectively as shown in (Table 1). On correlation between width of third and fourth ventricle with age showed positive correlation which was statistically significant as shown in (Table 3). The measurement of the ventricles was obtained from the CT monitor using the curser were shown in (Figures 1-4).
Parameters
Sample size (n)
Mean ± SD
(Max– Min in mm)
Length of body of the right ventricle
250
76.23 ± 9.4
(105-40)
Length of body of the left ventricle
250
72.43 ± 8.78
(106-20 mm)
Length of right frontal horn of Lateral ventricle
250
29.2 ± 3.72
(37-15mm)
Length of left frontal horn of lateral ventricle
250
28.7 ± 2.9
(37-16 mm)
Width of the third ventricle
250
5.8 ± 2.10
(11-3 mm)
Height of the fourth ventricle
250
9.9 ± 1.5
(19-4 mm)
Width of the fourth ventricle
250
12.4 ± 1.08
(13.5- 8 mm)
Table 1: List of measurements and statistical details of lateral, third and fourth ventricles.
Parameters
Mean ± SD (Max- Min)
P- value
Males (n=130)
Females (n=120)
Length of body of the right ventricle
77.45±8.6
71.36±9.4
0.004
Length of body of the left ventricle
76.6±8.4
71.09±9.4
0.022
Length of right frontal horn of Lateral ventricle
30.54±3.4
28.4±4.2
0.034
Length of left frontal horn of lateral ventricle
30.14±4.7
27.4±3.2
0.002
Width of the third ventricle
5.9±1.5
5.5±1.9
0.011
Height of the fourth ventricle
10.0±2.1
9.6±2.2
0.556
Width of the fourth ventricle
13.0±1.9
12.0±2.0
0.007
Table 2: List of ventricular measurements (mean ± SD) in males and females.
Pearson Correlation coefficient
P value
Width of 4th ventricle and age
0.235
0.045
width of the third ventricle and age
0.392
0.039
Table 3: Correlation study between age and width of the 4th and 3rd ventricles.
Discussion
The ventricular size of the brain is likely to be an increased in number of circumstances of several neurological disorders such as hydrocephalus, cerebral atrophy, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, in which precise measurements will be of value [8]. Morphometric study of cerebral ventricles provides useful indices of cerebral asymmetry and atrophy [9]. A study by Matsuzua, Goldestien et al. shown that the left lateral ventricle was larger than the right one and both were larger in the female [10]. In the present study anteroposterior extent of the body of the right lateral ventricle 77.89 ± 9.86 mm and 71.06 ± 8.83 mm males and females, on the left side was 75.89 ± 8.56 mm and 69.56 ± 10.00 mm.
Both left and right ventricles were large in males compared to females. This is because males skull were heavier and bigger, the capacity of the skull is more compared to female skull and also because the brain size is more in males compared to females [11].
Our study results revealed that the length of the right frontal horns was 30.54 ± 3.4 mm in the males and 28.4 ± 4.2mm in the females and that the length of the left frontal horns was equal to the right one in the males but slightly shorter than the right one in the females 27.4 ± 3.2 mm. Studies by D’Souza and Natekar revealed that the height of the fourth ventricle was 11.8 mm and 11.1 mm for the male and female respectively [12]. Older studies by Gawler et al. [13] revealed that the greatest distance between the roof and the floor of the fourth ventricle was less than 10.8 mm [14]; however in our study this distance was significantly smaller, (9.66 ± 0.22 mm) in males and (9.70 ± 0.28 mm) in the females with the mean 9.68 ± 0.17 mm).
In the present study, the width of the fourth ventricle was found to be greater than the height in both genders and was more in males (13.0 ± 1.9) than in females 12.0 ± 2.0 ) with the mean 12.4 ± 1.08 mm. Gawlar J et al. and others measured the width of third ventricle [13,14]. Soininen et al. [14], D’Souza et al, [12], Meshram, P et al [15], Brinkman et al. [16] found that the maximum mean width of the third ventricle was 5.9 mm, 9.2 mm, 4.2 mm. In present study, we found this measure was significantly higher in males (5.9 mm) as compared to females (5.5 mm) with mean (5.8 mm). On performing paired‘t’ test to all the parameters between male and female the p value is significant (P<0.05) except height of fourth ventricle (p = 0.556).
Conclusion
The study provided useful morphometric data to better understand the lateral, third and fourth ventricles while diagnosing clinical problems associated with the various types of ventricular enlargement such as hydrocephalus, schizophrenia, psychotic disorders, Parkinsonism and other pathologic disorders.
References
- Gyldensted C. Measurements of the normal ventricular system and hemispheric sulci of 100 adults with computed tomography. Neuroradiology 1977; 14: 183-192.
- Duffner F, Schiffbauer H, Glemser D. Anatomy of the cerebral ventricular system for endoscopic neurosurgery: a magnetic resonance study. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2003 ;145: 359-368.
- Soni JPBD, Gupta M, Soni RN. Normal Parameters of Ventricular System in Healthy Infants. Indian Pediatric. 1994; 32: 549–555.
- Schmahmann JD, Smith EE, Eichler FS, Filley CM. Cerebral white matter: neuroanatomy, clinical neurology, and neurobehavioral correlates. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2008; 1142: 266–309.
- Smith EE, Salat DH, Jeng J. Correlations between MRI white matter lesion location and executive function and episodic memory. Neurology 2011; 76: 1492–1499.
- Haaga JR, Sartoris DJ, Lanzieri CF, Zerhouni EA. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of the whole body. In: Normal CT and MRI anatomy of the brain. 1994; 75-102.
- Gawler J, Du Boulay GH, Bull JW, Marshall J. Computerized tomography (the EMI Scanner): a comparison with pneumoencephalography and ventriculography. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1976; 39: 203-211.
- Kido DK, Caire ED, Le May M. Temporal lobe atrophy in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: A CT study. Am Jour of Neuroradiology. 1989; 10: 551–555.
- Peter F Buckley. Neuroimaging of schizophrenia: structural abnormalities and pathophysiological implications. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2005; 3: 193–204.
- Takeda S, Matsuzawa T. Age-related change in volumes of the ventricles, cisternae, and sulci: a quantitative study using computed tomography. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1985; 33: 264-268.
- Williams PL, Bannister LH, Berry MM, Collins P, Dyson M, Dussek JM. Gray’s Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Medicine and Surgery. 38th Edition, Elsevier Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh. 1955; 1205-1209.
- D’ Souza DMC, Natekar PE. Morphometric study of the ventricular system of Brain by Computerised Tomography. J Anat Soc India. 2007; 56: 19-24.
- Galwar J, Bull JWD, Du Boulay GH, Marshall J. Computerized axial tomography: the normal EMI scan. Jour of Neurol, Neurosurgery and Psy 1975; 38: 935-947.
- Soininen H, Puramen M, Riekkinen PJ. Computed Tomography Findings in Senile Dementia and Normal Ageing. Jour of Neurol, Neurosurgery and Psy. 1982; 45: 50-54.
- Meshram P, Hattangdi S. The Morphometric Study of Third Ventricle and Diencephalon by Computerized Tomography. Indian Journal of Applied Basic Medical Science 2012; 14: 8-13.
- Brinkman SD, Sarwar M, Levin H, Morris HH. Quantitative Indices of Computed Tomography in Dementia and Normal Ageing. Radiology. 1981; 138: 89-92.