Abstract
Blast injuries result in high morbidity and mortality in the general population. The mechanism of injury may lead to single organ or multisystem trauma
A 27-year-old adult male patient presented to our department with severe degloving injury to the penis along with loss of scrotal skin with exposure of the right testicle following a blast from an air conditioning refill cylinder. Patient was sitting beside the cylinder and sustained a direct blow to the pelvis and had associated injuries including comminated fractures of the radius and ulna on the right side.
Keywords: Blast Injury; Degloving; Penis; Trauma
Introduction
Blast injuries are seen in accidents that involve pressurized containers like gas cylinders, acts of terrorism and improvised explosive devices. Poor handling of equipment and inadequate safety precautions are associated factors that lead to significant injuries.
The pressurized container produces a sudden gas expansion, which subsequently releases the potential energy hence creating a pressurized shock wave [1].
As per the EUA guidelines in event of penile avulsion injuries after initial resuscitation, surgical re-implantation of the penis is recommended if it has been recovered and is not too badly damaged [2].
Surgical re-implantation should be considered for all patients and should be performed within 24 hours of amputation [3]
A 27-year-old adult male patient presented to our department with severe degloving injury to the penis along with loss of scrotal skin with exposure of the right testicle following a blast from an air conditioning refill cylinder. Patient was sitting beside the cylinder and sustained a direct blow to the pelvis and had associated injuries including comminated fractures of the radius and ulna on the right side. Patient was hemodynamically stable with no major abdominal injuries.
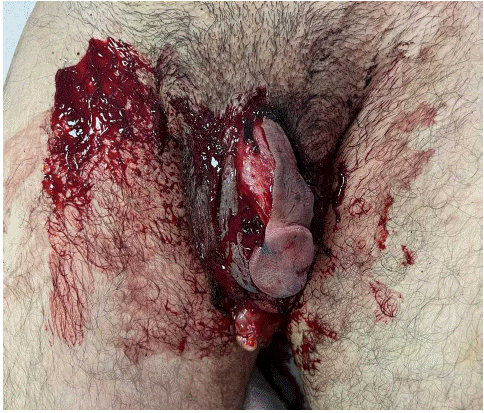
Figure 1:
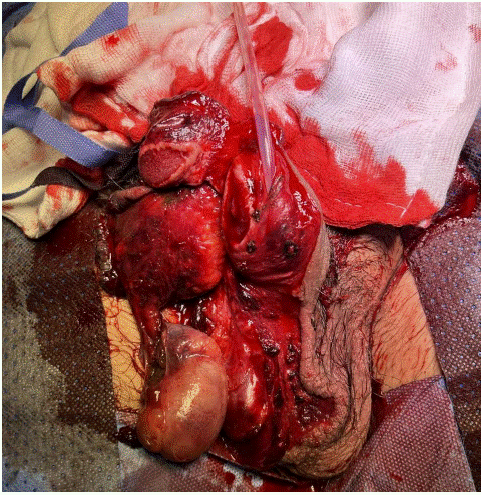
Figure 2:
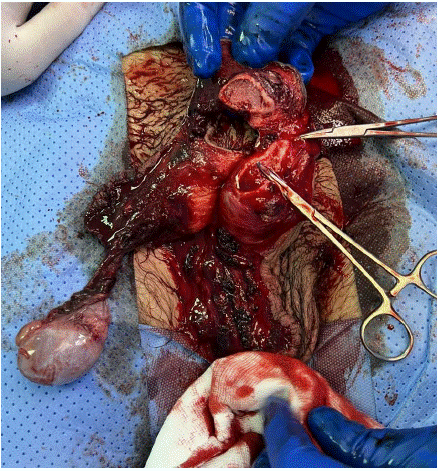
Figure 3:
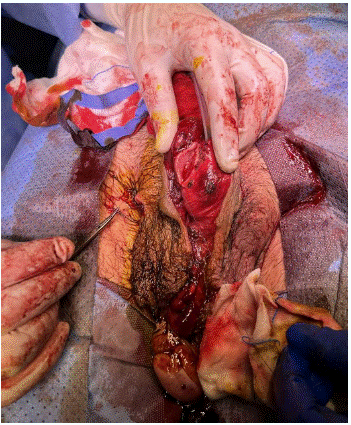
Figure 4:
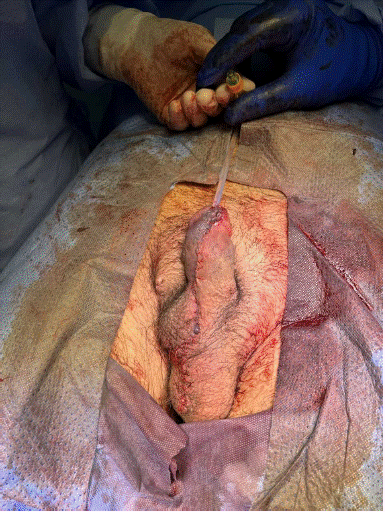
Figure 5:
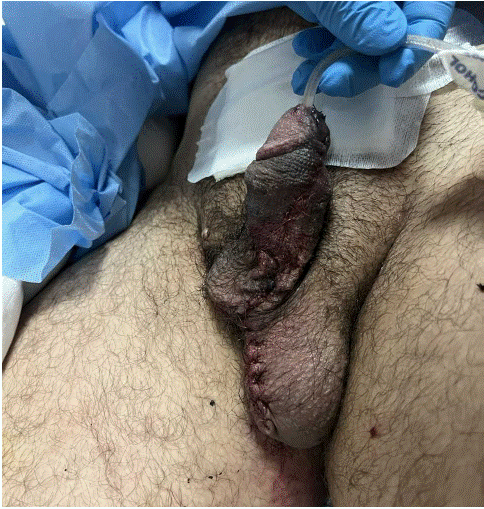
Figure 6:
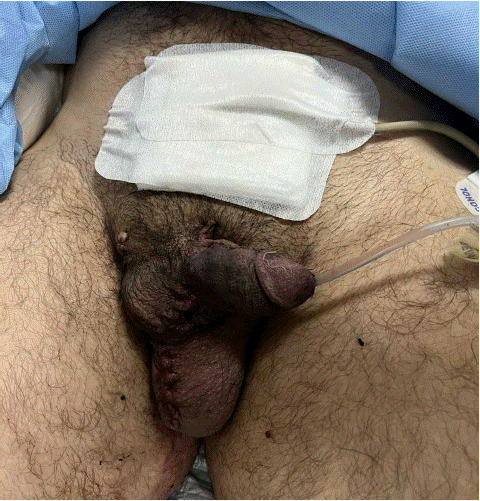
Figure 7:
At the initial inspection under anaesthesia the following injuries were noted.
1) Rupture of the glans penis on the ventral aspect with near complete detachment of the glans from the cavernosal body on the right side.
2) Degloving of penis ventrally with split in skin exposing corpora and urethra
3) Right testis near avulsion from spermatic cord and epididymis separated from body of testis.
4) Urethral injury just inside the meatus on the ventral aspect
5) Superficial lacerated wound in the inner thigh extending upto the muscle.
After thorough cleaning with antiseptic solution
The urethra was cannulated with 16 fr catheter and clear urine was drained.10 ml was placed in the balloon. There after any bleeders were diathermised.
The corpora was sutured with continuous 3/0 vicryl and approximated.
The dorsal skin split was closed with tacking interrupted skin sutures.
As the right testis had no tenable blood supply, right orchidectomy was performed.
A mummy wrap dressing was done for the penis to reduce penile edema.
A suprapubic catheter was placed along with the urethral catheter for healing of the urethral injury.
Inspection of the wound on post operative day 1 showed reduced edema of the penile swelling with both urethal and suprapubic catheter in place.
The urethral catheter was spigotted and placed for 3 weeks. After 3 weeks patients underwent a trial removal of urethral catheter with the suprapubic catheter in place.
At 4 weeks the Suprapubic catheter was also removed with the patient voiding spontaneously.
Patient reported normal erections at 6 weeks.
Discussion
Blast injuries to the groin area can result in severe injuries which can be mutilating and life threatening.Primary blast injury relates to the overpressure generated by forcibly expanding gasses and is sometimes called the blast wave. The most important factor in salvaging functional capacity is early intervention and clear identification of the injured areas which need meticulous repair.
It is interesting to note in this case that a part of the Glans penis was almost decapitated but healed well with direct apposition underlying the importance of early careful repair.
As with any trauma injured patient the Advanced Trauma Life support guidelines need to be followed. Thereafter a prompt repair of the injured genitalia can result in better functional outcome.
Conclusion
Traumatic blast injuries to external genitalia can cause life changing injuries. These injuries need managed urgently as earlier intervention leads to better functional outcome.
References
- Moga HK, Parmar AP, Gohil ND. An autopsy case of death due to ac compressor blast - a rare case illustrating primary, secondary, tertiary & quaternary blast injuries. J Forensic Leg Med. 2021; 80: 102173.
- Serafetinidis E, Campos-juanatey F, Hallscheidt P, Mahmud H, Mayer E, Schouten N, et al. Summary paper of the updated 2023 european association of urology guidelines on urological trauma. Eur urol focus. 2023: s2405-4569(23)00196-7.
- Mydlo JH, Hayyeri M, Macchia RJ. Urethrography and cavernosography imaging in a small series of penile fractures: a comparison with surgical findings. Urology. 1998; 51: 616-9.
