
Case Report
Austin J Anesthesia and Analgesia. 2016; 4(2): 1050.
Hypercarbia Induced Severe Bronchospasm and Unconsciousness Following Supraclavicular Block
Ajmal PM, Shahla Haleem*, Varun K Varshney, Abhishek Singh and Amrin Badar
Department of Anaesthesiology, Faculty of Medicine, J N Medical College, AMU, Aligarh, UP, India
*Corresponding author: Shahla Haleem, Department of Anesthesiology & Critical Care J N Medical College, AMU, Aligarh, UP, India
Received: November 29, 2016; Accepted: December 09, 2016; Published: December 12, 2016
Abstract
Though the popularity of brachial plexus block for upper limb surgery is well known fact, but, one must not forget the complications associated with it. Herein, we report a middle aged obese female with fracture olecranon and proximal end of radius was posted for tension band wiring of olecranon process under ultrasound guided supraclavicular brachial plexus block. She was a known case of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), with severe lung fibrosis and collapse, pleural thickening and mediastinal shift to the same side where she had to be operated. After repeated referral for optimization to tuberculosis and respiratory diseases she was posted for surgery after explaining the high risk involved to the patient. Following completion of procedure, she turned supine from lateral decubitus position, found unconscious and tachypnoeic. On auscultation, there was severe bronchospasm/silent chest; was immediately intubated and managed with difficulty.
Keywords: Supraclavicular brachial block; Unconsciousness following supraclavicular block; Severe Bronchospasm / silent chest
Introduction
Brachial plexus block under ultrasound guidance is considered as safe and dependable technique with high success rate and minimal or no complication. In spite the popularity of brachial plexus nerve blocks and its several advantages including providing effective analgesia, reducing narcotic requirements and facilitating ambulatory care surgery; one must not forget their impact on chest wall mechanics, tidal volume, PaO2 levels the unwanted effects of phrenic nerve palsy, if associated with central obesity.
Phrenic nerve paralysis/paresis is common and known complication associated with inter scalene brachial plexus block where the incidence is 90-100% [1-3]. In supraclavicular approach the incidence of phrenic nerve block is also reported as 40% to 60% [4,5], but often ignored, as the phrenic or cervical sympathetic nerve block (Horner’s syndrome) not create problem clinically and neuropathy usually requires reassurance only [4].
In the present case report successful supraclavicular brachial plexus block, was complicated by unconsciousness and respiratory distress at the end of procedure. On auscultation she had severe bronchospasm with minimal air entry/silent chest, was intubated and managed with difficulty.
Case Presentation
50 years old obese female (body mass index of 29.2kg/m²), with past history of tuberculosis was presented with injury to right elbow, chest and rib fracture, following fall in the bathroom. On General examination pulse: 72/min; B.P: 122/72mmHg; Respiratory rate: 22/ min. Trachea shifted to right side, bilateral rhonchi with additional fine crepitations were present on right side with decreased air entry on auscultation. Laboratory investigations showed leucocytosis and other investigations were within normal limits; Chest X Ray showed opacity in right upper and mid zones suggestive of granulomatous lesion with lung fibrosis with mediastinal shift to fracture side (Figure 1).
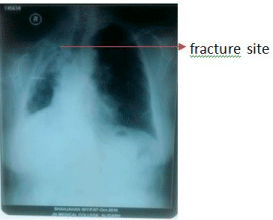
Figure 1: Pre-op x-ray chest.
Pulmonology reference was done for the same and advised that she is a known case of chronic obstructive airway disease, cannot be optimized further and operation can be done in high risk consent. She was posted for tension band wiring of olecranon process.
Before starting the case all monitors were attached to check the baseline vital parametrs. Her oxyhaemoglobin saturation (SpO2) was 99% on Hudson mask. USG guided supraclavicular brachial plexus (SCBB) block was planned considering her lung condition and for dependable block. Under all aseptic precuations sono ultrasonographic (USG) and peripheral nerve stimulator guided SCBB was given. Inj lignocaine 10ml (1.75%) with bupivacaine (0.5%) 15ml was injected after careful aspiration. Adequate analgesia achieved immediately and procedure started in lateral decubitus position, the healthy lung was on dependent side. Before completion of surgery she had one episode of hypertension for which inj. Labetolol 20mg was administered. Procedure lasted approximately one hour. After completion, she turned to supine position, was found unresponsive, sweating, pupils constricted and was in respiratory distress. On auscultation minimal air entry/silent chest was detected bilaterally. As the paient was unresponsive, was ventilated with 100% O2 by bag and mask, induced with Inj Propofol and relaxed with Inj Succinylcholine and intubated with cuffed ETT 7mm ID. Even after intubation, air entry was severely reduced bilaterally and rhonchi were heard all over the chest. Inj Deryphylline I.V. and salbutamol puffs were given through ETT. A low dose Adrenaline infusion was started to relieve severe unresponsive bronchospasm and patient was shifted to the ICU for mechanical ventilation. Chest X Ray was taken en route (Figure 2), showed increased lung collapse on right side. A blood sample was sent for ABG and it showed severe respiratory acidosis with a pH of 7.11 and pCO2 82mmHg; pO2: 126mmHg; HCO3 21mmol/L on 100% oxygen.
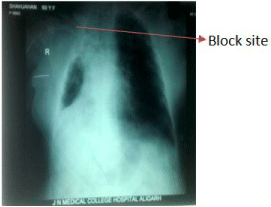
Figure 2: Post op x-ray chest.
In ICU she was kept on pressure control ventilation (PCV) mode for about 8 hours then converted to Synchronized Intermittent- Mandatory Ventilation (SIMV) mode. Repeat ABG was done, in which pH: 7.46; pCO2: 41 mm Hg; pO2: 119mm Hg; HCO3: 29mmol/L. Patient was extubated and shifted to HDU after 24 hours of ICU stay and was discharged from the ward after suture removal.
Discussion
Regional anesthesia has an expanding role in upper extremity surgery as it offers several advantages. However, the literature reports a strong association between regional anesthesia above the clavicle and phrenic nerve block, including a reported incidence of 60% for a single shot supraclavicular block [4].
Acute respiratory distress is a documented complication of inter scalene approach to brachial plexus block due to phrenic nerve involvement and palsy. Phrenic nerve arises from roots of C3, C4 and C5, and its involvement occurs because of its anatomical relation with brachial plexus and direct infiltration of local anesthetic on the nerve or cephalic spread of local anesthetic. As the sign of initiation of successful inter scalene block is the “Horner syndrome” which is sooner than the onset of a sensory blockade. However, few cases were reported symptomatic phrenic nerve palsy with supraclavicular route also [5,6]. Recently the ultrasound guided block has been practiced frequently for surgical anesthesia with more precise block of nerves with reduced doses of local anesthetic. However, complications do occur with USG guidance, in patients who are already compromised in respiratory functions [7]. In our case patient was obese and already a diagnosed case of COPD with lung collapse on the operating side, was taken under high risk consent as she cannot be optimized further, for USG guided supraclavicular brachial block.
The patient was positioned in lateral decubitus position for surgical ease with the normal lung was placed down in the dependant position and diseased lung was kept up. It might have aggravated the situation by compression of healthy lung by sandbags kept for positioning and sedation given during intra operative period for relief of anxiety. The compromised lung was not able to ventilate further due to phrenic nerve palsy and on the other side the healthy lung being dependant was compressed due to positioning was not able to compensate the ventilation compromise. Thus alteration in lung compliance curve; finally contributed to ventilation perfusion mismatch.
In spite, of patient having short neck and compact neck structures, we have given the total of 25ml of local anesthetic with stimuplex needle, to get more dependable block; which might have absorbed locally and produce phrenic nerve paralysis. The X-ray chest done postoperatively showed the increased lung collapse and further elevation of diaphragm on the affected side.
Furthermore, the sympathetic nerve supply to the bronchi arises from T1-T4 segments of the sympathetic chain. Blocking the sympathetic nerve supply to the bronchi might have cause bronchoconstriction due to unopposed vagal parasympathetic action. Local anesthetics, which we have injected through supraclavicular approach, might have spread to the lower down due to upper rib fracture on the affected side and the caudal spread of local anesthetic as far as T4. This might have been the added reason for severe bronchospasm complicating the situation further and critical. Hence, at the end of procedure patient became unconscious due to uncorrected CO2 retention secondary to phrenic nerve palsy/ bronchospasm, as well as positioning effect as evidenced by postoperative ABG findings.
Conclusion
Sequelaeconsciousness and severe bronchospasm (silent chest) is a rare complication of the ultrasound guided supraclavicular approach of the brachial plexus block. Anesthesiologists performing the block should have knowledge of possible complications of the brachial plexus block, specifically in vulnerable patients. Furthermore, obese and/or compromised lung patients with lateral position should also be monitored continuously for end tidal CO2 levels along with the oxygen saturation, diagnose the CO2 retention early. Thus, one can anticipate the problems, diagnose and plan the technique, do the appropriate timely intervention and treat the complications properly. In addition, to avoid further complications in patients of compromised respiratory functions, a continuous supraclavicular regional anesthesia could be provided through bent needle technique without phrenic nerve blockade [7].
References
- Urmey WF, Talts KH, Sharrock NE. One hundred percent incidence of hemi diaphragmatic paresis associated with inter scalene brachial plexus anaesthesia as diagnosed by ultrasonography. Anesth Analg. 1991; 72: 498–503.
- Ediale KR, Myung CR, Neuman GG. Prolonged hemidiaphragmatic paralysis following inter scalene brachial plexus block. J Clin Anesth. 2004; 16: 573– 575.
- Hood J, Knoblanche G. Respiratory failure following brachial plexus block. Anaesth Intensive Care. 1979; 7: 285–286.
- Pham-Dang C, Gunst J-P, Gouin F, et al. A novel supraclavicular approach to brachial plexus block. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1997; 85: 111–116.
- Bhat Pai RVB, Hegde V H, Santosh MCB and Roopa S. Bronchospasm following supraclavicular brachial plexus block. Anesth Essays Res. 2011; 5: 211–213.
- Chaudhuri S, Gopalkrishna M, Paul C, Kundu R. Can bilateral bronchospasm be a sign of unilateral phrenic nerve palsy after supraclavicular brachial plexus block? J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2012; 28: 249–251.
- Cornish PB, Leaper CJ, Nelson G, Anstis F, et al. Avoidance of phrenic nerve paresis during continuous supraclavicular regional anaesthesia. Anaesthesia. 2007; 62: 354-358.