
Research Article
Austin J Anesthesia and Analgesia. 2020; 8(2): 1091.
Propofol - In One-Day Surgery in Children
Nasibova EM*
Department of Anesthesia, Azerbaijan Medical University, Baku
*Corresponding author: Nasibova EM, Department of Anesthesia, Azerbaijan Medical University, Baku
Received: June 02, 2020; Accepted: July 01, 2020; Published: July 08, 2020
Abstract
Propofol (diprivan) is the drug of choice in one-day surgery in children. The use of the drug provides rapid awakening (due to rapid redistribution and short half-life) and a minimum incidence of postoperative complications. Total intravenous anesthesia with propofol infusion or bolus administration is an easily managed anesthesiologist, anesthesia comfortable for the patient (1, 2, 3, 4, 5,6, 7, 8, 9,10,11,12,13).
The aim of the study: Optimization of anesthetic benefits in one-day surgery by using propofol.
Keywords: Propofol; One-Day Surgery; Premedication
Material and Methods
The study included 58 patients operated on for inguinal and umbilical hernias, dropsy of testicular membranes, cryptorchidism, varicocele, hemangiomas of various localization, phimosis and paraphimosis. Depending on the age of the children, this group was divided into 3 subgroups: IA (n = 12) age 0-3 years, IB (n = 33) - 4-7 years old and IC (n = 13) - 8-16 years old. This study was carried out in five stages. For intravenous anesthesia in children, you must have access to a vein. To prevent a negative attitude of the child to this procedure, the local anesthetic drug EMLA was used. EMLA - eutectic mixture of local anesthetic, is an emulsion system in which the oil phase consists of an eutectic mixture of the bases of lidocaine and prilocaine in a 1: 1 ratio. The drug is available in the form of 5% cream and patch. One gram of cream or one patch contains 25 mg of prilocaine. EMLA cream was applied 2-3 g on a selected area, which was then tightly covered with a gauze cloth. After removing the wipes, the remaining cream was removed. 40 minutes after applying the cream with the introduction of the needle, a motor reaction to the manipulation was not observed. At the initial stage of the use of propofol in our clinic, we titrated the initial and maintenance doses of it. To date, we have experience with the use of propofol in various manipulations and surgical interventions in more than 3,000 children aged 0 to 16 years. The optimal, according to clinical data, induction dose of propofol in children older than 5 years was 3.5 ± 0.3 and 4.0 ± 0.4 mg/kg in children under 5 years of age [1]. Approximately 30- 40 seconds after the start of propofol administration, rapid breathing occurred in all patients, which then turned into apnea in the majority. During induction, a decrease in oxygen saturation to 92-94% was noted. Clinically, in 5 patients, motor sweeping movements were noted and in 6 patients - short-term hypoventilation. After oxygen hyperventilation, an increase in SpO2 of 98-99% was noted. Central analgesia was carried out with fentanyl at the rate of 1.5-2 μg/kg [2,3].
The Results of the Study
Changes in the indicators of central hemodynamics and external respiration relative to the first stage during intravenous total anesthesia (propofol + fentanyl) are presented in Table 1.
Indicators
Stage I (before sedation)
Stage II (after sedation)
Stage III (induction of anesthesia)
Stage IV (incision skin)
Stage V (traumatic moment)
Stage VI (awakening)
Heart rate (min)
109,9±0,7
106,8±1,0 *
96,5±1,7 ***
114,2±1,3 **
114,6±1,1 **
111,7±1,2
Mean arterial pressure (mmHg)
64,7±0,7
61,4±0,7 **
58,6±0,5 ***
68,7±0,8 **
71,4±0,9 ***
61,8±0,7 **
heart stroke volume (ml)
30,4±0,7
30,3±0,5
30,0±0,5
31,9±1,4
32,6±1,6
29,7±1,0
minute volume of blood circulation (l / min)
3,35±0,09
3,29±0,04
2,90±0,08 **
3,65±0,17
3,74±0,20
3,32±0,12
Total peripheral vascular resistance (dyn × sec × cm-5)
2242,4±66,8
2181,4±61,0
2313,2±69,5
2254,8±86,8
2317,3±99,5
2144,3±72,3
Respiratory rate (min)
26,7±0,2
23,7±0,4 ***
27,9±0,3 **
28,1±0,2 ***
28,3±0,2 ***
27,5±0,3 *
Tidal Volume (ml)
137,8±2,8
134,5±3,0
102,3±1,6 ***
114,7±2,1 ***
116,8±2,0 ***
137,4±2,7
PetCO2 (mm Hg)
37,0±1,3
39,1±0,3 ***
43,5±0,5 ***
44,1±0,3 ***
43,6±0,3 ***
37,2±0,3
SpO2
99,0±0,0
98,0±0,0
96,3±0,2 ***
95,3±0,3 ***
94,8±0,4 ***
96,0±0,2 ***
RPP
102,4±0,7
93,7±1,1 ***
80,2±1,4 ***
115,1±1,8 ***
121,1±2,4 ***
98.0±0,9 ***
Table 1: Hemodynamics and external respiration in patients with (propofol + fentanyl) in the age group 0-3 years.
Basically in all age groups, the performance of the cardiovascular system remained at the level of the initial values, however, certain hemodynamic changes characterizing the effect of propofol were revealed. During induction in anesthesia, Heart Rate (HR) decreased in the subgroup in patients aged 0-3 years (IA on average by 7.5% (p <0.001), and in patients aged 4-7 years (IB) by 4.8 (p <0.05), and in patients aged 7-16 years (IC) by 10.0% (p <0.01) compared with the initial stage of the study. The average Blood Pressure (SBP) decreased in patients aged 0-3 years by an average of 10.8% (p <0.001), and in children aged 4-8 years by 10.2% (p <0.001), and in children at the age of 8-16 years - by 13.1% (p <0.001). Changes in vascular tone were demonstrated in terms of total peripheral resistance, which decreased to a greater extent in patients of the IC subgroup (8-16 years) by 9.3% (p <0.01) during induction of anesthesia compared with the initial stage, in the IA subgroup (0-3 years) - 2.9% (p <0.01), and in the IB subgroup (4-7 years) - 3.8% (p <0.01). An increase in stroke volume of the heart (CCS) was noted by the IA subgroup by 3.3% (p <0.01), in the IB subgroup by 4.2% (p <0.01) and in patients with the IC subgroup by 0.5% (p <0.01) compared with the initial stage was noted before the skin incision [4-6].
The minute volume of blood circulation (IOC) at the induction stage mainly remained almost at the level of indicators of the previous stage in all groups. As can be seen from the reaction directly to the induction of anesthesia, the reaction of the blood circulation to an operative trauma fully corresponded to the picture of transitional inactivity. Since the IOC has not changed almost, a change in the main components (a decrease in heart rate and an increase in stroke volume of the heart (UO) against a background of a decrease in mean arterial pressure (SBP) and total peripheral resistance (OPSS) allows us to conclude that the hemodynamic regime has reached a more intense regulation mechanism that accompanies increased cardiac performance to maintain overall cardiovascular system performance in the form of physical inactivity at baseline [7]. This type of hemodynamic regime cannot be considered useful, since it can lead to the depletion of compensatory mechanisms. The characteristic imbalances of the main parameters of the volumetric blood flow indicate hemodynamic stress that occurred against the background of the action of propofol in all groups during the induction of anesthesia. All this clearly and objectively characterizes the vasodilating properties of propofol, as a factor that causes the most typical changes in central hemodynamics. By the time of the skin incision after administration of fentanyl at the rate of 3 μg/kg, an unexpected increase in heart rate was observed by 8.7% (p <0.001) in patients of the IA subgroup, by 8.2% (p <0.001) in patients of the IV subgroup and by 15, 8% (p <0.001) in patients with IC subgroups compared with the previous stage (Figure 1).

Figure 1: The dynamics of changes in heart rate in children of group I.
An increase in mean arterial pressure was also observed in patients of the I A subgroup by 4.8%, in patients of the IB in the subgroups by 4.6% and the I C subgroups by 4.2%. These changes indicated a lack of analgesia and forced us to an additional administration of fentanyl at a dose of 1.5 μg/kg. At stage V (the traumatic moment of the operation), the studies, despite the additional administration of fentanyl, did not improve hemodynamic parameters. So, in patients with IA subgroups, heart rate and mean blood pressure increased by 10.3% (p <0.001) and 7.2% (p <0.001), respectively, compared with the initial stage, in group I B subgroups by 4.2% ( p <0.001) and 5.8% (p <0.001), and in patients with IC, the subgroups were 18.8% (p <0.001) and 8.1% (p <0.001), respectively (Figure 1). A significant increase in RPP was also detected by 21.3% (p <0.001) in patients of the IA subgroup, by 19.5% (p <0.001) in the IB subgroup, by 29.3% (p <0.001) in patients of the IC subgroup compared to the previous step. And this testified to the inadequacy of anesthesia and prompted us to additional administration of fentanyl. Moreover, the total amount of fentanyl introduced during the entire operation was 5-6 μg/kg (Figure 2) [8,9].
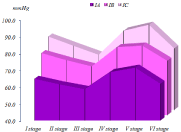
Figure 2: Dynamics of changes in blood pressure in children of group I.
Indices of external respiration after premedication at the induction stage tended to decrease and indicated moderate hypoventilation. At the traumatic stage of the study, an increase in BH was observed, which was associated with the appearance of pain. At this stage, a decrease in SpO2 was also observed. In 5 patients hypoventilation was observed and required manual ventilation of the lungs with a bag and spontaneous breathing was quickly restored. In the period of awakening, the indicators of external respiration tended to increase and approached the initial values. Starting from the 15th minute from the last injection of propofol, more than 50% of children could follow the command “open their eyes “, “cough”. In some children, hypersalivation was noted. At the 20th minute, 90% of the children could answer simple questions and were oriented in time and space. At the 25th minute from the last bolus of propofol and fentanyl, all patients could answer complex (commensurate with age) questions, were oriented in time and space, and could even share their impressions. Some patients even expressed a desire to stand up, move independently, although they felt muscle weakness. After 40-60 minutes, patients were allowed to walk in the ward, although many noted moving freely and comfortably much earlier.
Thus, propofol induction proceeded with a hypodynamic type of blood circulation. At the most traumatic time of the operation, despite an increase in the dose of fentanyl, hemodynamic parameters were hyperdynamic type of blood circulation, associated with insufficient relief of the pain component. And an increase in the dose of fentanyl led to the development of hypoventilation with subsequent apnea, which required mechanical ventilation. After mask ventilation, respiratory failure was easily corrected and SpO2 rose to 97-99%. The total time of induction into anesthesia with propofol and fentanyl was 30-60 seconds, and a complete exit from anesthesia in patients of group I was noted at the 20th minute. Clinically, in 4 patients, erratic epileptiform movements were noted and in 5 patients - an attack of short-term apnea. None of the patients in the postoperative period had apnea [10]. During induction in anesthesia in patients of group I (propofol + fentanyl), the circulatory reaction fully corresponded to the picture of transitional physical inactivity. Since the IOC has not changed almost, a change in the main components (decrease in heart rate and increase in stroke volume of the heart) with a decrease in mean arterial pressure and general peripheral vascular resistance allow us to conclude that the hemodynamic regime has entered a more intense regulation mechanism that accompanies an increase in heart function to maintain overall productivity of the cardiovascular system in the mode of physical inactivity at the level of the initial values. This type of hemodynamic regime cannot be considered useful, since it can lead to the depletion of compensatory mechanisms [12]. The characteristic imbalances of the main parameters of the volumetric blood flow indicate hemodynamic stress, which occurred against the background of the action of propofol and inadequate pain relief in all groups in the most traumatic stage of the operation (Figure 3) [11-13].

Figure 3: The dynamics of changes in OPSS in children of group I.
Conclusion
Analyzing the results obtained, it should be noted that anesthesia during “small” surgical interventions with propofol and fentanyl is not an optimal method. Since at the most traumatic time of the operation, it is necessary to increase the dose of fentanyl, and this leads to hypoventilation with the subsequent development of apnea, which requires correction.
References
- Michel Foehn ER. Adult and pediatric anesthesia/sedation for gastrointestinal procedures outside of the operating room. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2015; 28: 469-477.
- Youn AM, Ko YK, Kim YH. Anesthesia and sedation outside of the operating room. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2015; 68: 323-331.
- Hinkelbein J, Lamperti M, Akeson J, Santos J, Costa J, De Robertis E, et al. European Society of Anaesthesiology and European Board of Anaesthesiology guidelines for procedural sedation and analgesia in adults. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2018; 35: 6-24.
- American Society of Anesthesiologists. Continuum of depth of sedation: definition of general anesthesia and levels of sedation/analgesia.
- Butterworth JF, Mackey DC, Wasnick JD. Clinical anesthesiology. 6th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education. 2018; 187-197.
- Butterworth JF, Mackey DC, Wasnick JD. Clinical anesthesiology. 6th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education. Intravenous anesthetics. 2018; 171-185.
- Morgan JF, Mackey DC, Wasnick JD. Morgan & Mikhail’s clinical anesthesiology. 6th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education. Intravenous anesthetics. 2018; 324-362.
- Machata AM, Willschke H, Kabon B, Kettner SC, Marhofer P. Propofol-based sedation regimen for infants and children undergoing ambulatory magnetic resonance imaging. Br J Anaesth. 2008; 101: 239-243.
- Brechmann T, Maier C, Kaisler M, Vollert J, Schmiegel W, Pak S, et al. Propofol sedation during gastrointestinal endoscopy arouses euphoria in a large subset of patients. United European Gastroenterol J. 2018; 6: 536-546.
- APP Pharmaceuticals. Diprivan (propofol) injectable emulsion for IV administration prescribing information.
- Michel-Macías C, Morales-Barquet DA, Reyes-Palomino AM, Machuca- Vaca JA, Orozco-Guillén A. Single dose of propofol causing propofol infusion syndrome in a newborn. Oxf Med Case Reports. 2018; 2018: 23.
- Furniss SS, Sneyd JR. Safe sedation in modern cardiological practice. Heart. 2015; 101: 1526-1530.
- Wheeler DS, Vaux KK, Ponaman ML, Poss BW. The safe and effective use of propofol sedation in children undergoing diagnostic and therapeutic procedures: experience in a pediatric ICU and a review of the literature. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2003; 19: 385-92.