Case Report
Ann Surg Perioper Care. 2016; 1(1): 1005.
Choriostoma (Heterotopic Liver is it of Concern)
Yahya AI*, Ehteweish M and Endash S
Zliten University Hospital and Edwaw District Hospital, Zliten, Libya
*Corresponding author: Ali Ibrahim Yahya, Zliten University Hospital and Edwaw District Hospital, Zliten, Libya
Received: September 05, 2016; Accepted: October 07, 2016; Published: October 10, 2016
Abstract
Liver developed embryological as bud from gastrointestinal tube, by fifth week of intrauterine life the liver will be fully formed organ, because of unknown aberration in the growth of the liver, bud from liver may go missed anywhere in the abdominal or thoracic cavity and stay away from the mother liver, the common site where ectopic liver tissue found is on the gall bladder, four cases of ectopic liver tissue were reported over period of 26 years of general surgery practice at our institution, in all cases the ectopic liver were on the gall bladder, discovered during laparoscopic cholecystectomy and one case were discovered during diagnostic laparoscopy for trauma patient, in three cases ectopic liver were removed with the gall bladder and sent to the histopathology, none of the three were found with malignant change .in the forth case laparoscopy was done for trauma, and small ectopic liver tissue was seen attached to the gall bladder and was not causing symptom it was left alone.
Keywords: Choriostoma; Ectopic liver tissue; Gall bladder; Cholecystectomy
Introduction
The human being has only one liver, heterotpic liver were reported in literature since long time. 1904 was first noted by Albert and named as choristoma, ectopic liver was observed in different places in the abdomen, chest, on gall bladder, heptoumbilical ligament, omentum, spleen, pancreas diapharagm, esophagus and it was observed as mass, nodule and found as tissue on microscopic examination, Ectopic liver is hepatic tissue that histologically resembles the mother liver tissue but is located at site away from its usual location. A simple classification for anomalous liver tissues found on the wall of gallbladder is 1. Accessory liver lobe 2. Ectopic nodule 3. Aberrant microscopic tissue. Ectopic nodules of liver tissue attached to the gallbladder and completely detached from the liver and have been described by various names such as accessory lobe, ectopic liver, accessory liver, there are theories explain ectopic liver, it is atrophy of an accessory lobe of the liver or migration of liver tissue during embryological development of organ. Ectopic liver is associated with increased incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma, gall bladder stones and cholecystitis.
Case 1
35-year-old Libyan woman presented with symptoms and signs of cholecystitis, ultrasound showed there were gall bladder stones and no other pathology noted Patient underwent laparoscopic cholecystectomy. At the time of surgery nodule reddish in colour was observed attached to the fundus of the gall bladder resembling liver in colour and consistency and completely detached from the liver and attached to the gall bladder, measuring 6x2.5 cm (Figure 1). It has stalk consisting of vascular pedicle and duct, after careful dissection, the duct and the vascular pedicle were found draining directly to the liver, Both the duct and the vascular pedicle of ectopic liver lobule were clipped. And gall bladder removed laparoscopically. Histology confirmed normal hepatic architecture Figure 1. Ectopic liver located on gall bladder with its own pedicle.
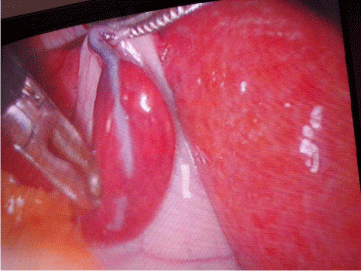
Figure 1: Ectopic liver located on gall bladder with its own pedicel.
Case 2
45 years Libyan female patient admitted to our hospital with symptoms and signs of biliary colic, ultrasound confirmed calcular cholecystitis, underwent laparoscopic cholecystectomy, operative finding, there was small liver segment attached to the surface of the gall bladder, separate from the mother liver, there were no clear duct or vascualr pedicle holding that liver segment to the mother liver, gall bladder was removed with the liver segment (Figure 2).
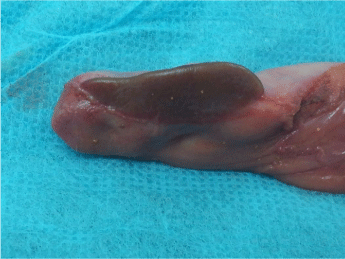
Figure 2: Ectopic liver located on gall bladder with its own pedicel.
Case 3
45 female patient underwent laparoscopic cholecystectomy for typical symptoms of gall bladder stones, during laparoscopy small liver nodule was noted laying on the gall bladder fundus with small pedicle attached this small baby liver to the mother liver, gall bladder and the ectopic liver tissue was removed as one piece (Figure 3).
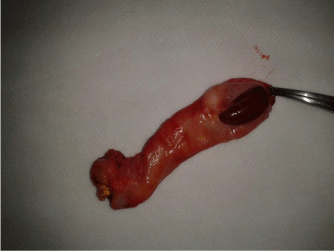
Figure 3: Ectopic liver nodule located on gall bladder with pedenculated stalk.
Case 4
20 years old male was admitted to surgery department with stab wound at right upper quadrant, vitally he was stable, the stab was bearching the peritoneum diagnostic laparoscopy was done, the wound was penetrating the abdomen with no intraperitoneal injury, reddish nodule was seen on the gall bladder fundus, it was small mass resembling the liver fixed and attached directly to the gall bladder, this mass is away from mother liver (ectopic liver tissue), laparoscopic picture is seen in (Figure 4).
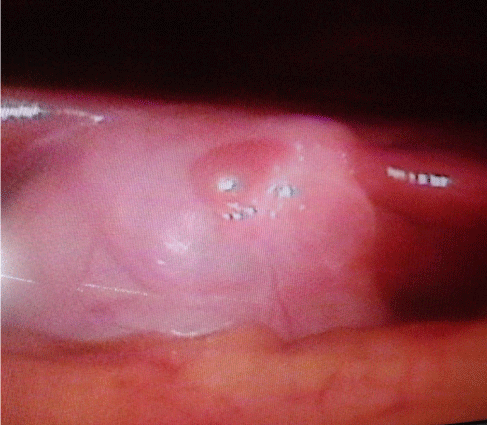
Figure 4: Small liver tissue is attached to gall bladder fundus discovered
during laparoscopy for 20 years boy for abdominal wall stab wound.
Discussion
Ectopic livers are rare and usually found incidentally, at the time of laparoscopy, laparotomy or autopsy. History of ectopic liver goes to long time since 1866 till to date only counted numbers were discovered, there are theories suggesting the aetiology of ectopic liver,
1. May follow traumatic implantation or seeding during surgery.
2. Displacement of part of the liver at the time of migration of pars hepatica in embryonic life; with subsequent atrophy of part of the liver connecting that tissue to the main liver with resultant separation of tissue.
Ectopic liver can be asymptomatic but rarely will cause symptoms like:
1. Abdominal pain may due to torsion of the organ [1].
2. Compression of adjacent viscera, like oesophagus portal vein, stomach, respiratory system [2-7].
3. Bleeding.
4. Ectopic liver may change to malignancy [8-11].
5. Ectopic livers have also been associated with cholelithiasis and acute or chronic cholecystitis [12-15].
Surgical excision of the symptomatic ectopic liver may be needed if causing abdominal pain because of torsion, bleeding due to rupture of the ectopic liver tissue .ectopic liver tissue located in relation to the gall bladder and associated with the gallbladder stone should be excised as part of the cholecystectomy.
Conclusion
Ectopic liver is an uncommon anomaly usually discovered accidentally, it can be asymptomatic, where does not need surgery, where it causes symptoms it will need surgery.
References
- Pujari BD, Deodhare SG. Symptomatic accessory lobe of the liver with review of the literature. Postgrad Med J. 1976; 52: 234–236.
- Jimenez AR, Hayward RH. Ectopic liver: A cause of esophageal obstruction. Ann Thorac Surg. 1971; 12: 300–304.
- Lasser A, Wilson GL. Ectopic liver tissue mass in the thoracic cavity. Cancer. 1975; 36: 1823–1826.
- El Haddad MJSS, Currie AB, Honeyman M. Pyloric obstruction by ectopic liver tissue. Br J Surg. 1985; 72: 917.
- Matley PJ, Rode H, Cywes S. Portal vein obstruction by ectopic liver tissue. J Pediatr Surg. 1989; 24: 1163–1164.
- Iber T, Rintala R. Intrapulmonary ectopic liver. J Pediatr Surg. 1999; 34: 1425-1426.
- Luoma R, Raboei E. An ectopic liver tissue causing severe respiratory insufficiency in a newborn. Duodecim. 2002; 118: 1269–1271.
- Arakawa M, Kimura Y, Sakata K, et al. Propensity of ectopic live to hepatocarcinogenesis: case reports and a review of the literature. Hepatology. 1999; 29: 57–61.
- Asselah T, Condat B, Cazals-Hatem D, et al. Ectopic hepatocellular carcinoma arising in the left chest wall: a long term follow-up. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001; 13: 873–875.
- Leone N, De Paolis P, Carrera M, et al. Ectopic liver and hepatocarcinogenesis: report of three cases with four years’ follow-up. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004; 16: 731–735.
- Caygill CP, Gatenby PA. Ectopic liver and hepatocarcinogenesis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004; 16: 727–729.
- Tejada E, Danielson C. Ectopic or heterotopic liver (choristoma) associated with the gallbladder. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1989; 113: 950–952.
- Sato S, Watanabe M, Nagasawa S, et al. Laparoscopic observations of congenital anomalies of the liver. Gastrointest Endosc. 1998; 47: 136–140.
- Orlando R, Lirussi F. Congenital anomalies of liver: laparoscopic Observations. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000; 51: 115–116.
- Sakarya A, Erhan Y, Aydede H, et al. Ectopic liver (choristoma) associated with the gallbladder encountered during laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a case report. Surg Endosc. 2002; 16: 1106.