Systematic Review
Ann Surg Perioper Care. 2022; 7(1): 1050.
Similar to Crohn’s Disease, but Diagnosed with Stenotic Ischemic Enteritis or Ischemic Colitis: Case Series and a Systematic Review
Xiang B¹, Zhang Q¹, Wang C², Lou X², Zhang M², Huang Y² and Zhi M¹*
¹Department of Gastroenterology, Sun Yat-sen University, China
²Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-sen University, China
*Corresponding author: Min Zhi, Department of Gastroenterology, The Sixth Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yatsen University, 26 Yuancun Erheng Road, Guangzhou, Guangdong 510655, China
Received: July 19, 2022; Accepted: August 22, 2022; Published: August 29, 2022
Abstract
Background and Study Aims: Stenotic ischemic enteritis or ischemic colitis, along with transmural inflammation, ulcers and strictures, is extremely similar to Crohn’s disease. We aimed to report relevant cases and perform a systematic review to help distinguish two diseases.
Patients and Methods: We reviewed our institutional experience with stenotic ischemic enteritis or ischemic colitis. Besides, we performed a comprehensive literature review using Medline (OvidSP), Web of Science, PubMed, Cochrane Library, and Embase from inception to March 2022. Demographic parameters, serological indexes, imaging markers, histological features and treatment were abstracted from our cases and included literatures.
Results: We reported four cases of stenotic ischemic enteritis and one stenotic is chemic colitis in our centre, and they were all male, aging 22-65 years old. Characteristics of the five patients were presented and histological examination played an essential role in discriminating them from CD. Besides, 35 patients of stenotic IE from 17 publications were included in the systematic review and the characteristics of included patients were also presented.
Conclusions: The treatment to stenotic ischemic enteritis or ischemic colitis and CD was different. Although they are very similar, but they can be distinguished from each other according to demographic features, radiographic and endoscopic imaging, especially histological evaluation.
Keywords: Ischemic enteritis; Crohn’s disease; Stricture; Stenosis
Introduction
Ischemic Enteritis (IE) is a small intestinal disease caused by inadequate blood flow due to anatomic occlusion or pathophysiologic vasospasm of mesenteric vessels [1]. Ischemic Colitis (IC) is more common than IE, because small intestinal is characterized by rich lateral circulation [2]. Thus, the diagnostic criteria of IE are not sufficiently established due to its rarity. IE could be classified into transient and stenotic IE [2]. Transient IE is characterized by an acute onset, while stenotic IE develops after chronic inflammation [2]. Stenotic IE patients often suffer from recurrent obstruction and require surgical treatment or balloon dilation [3].
Crohn’s Disease (CD), a subtype of inflammatory bowel disease, is a chronic relapsing inflammatory disease. CD may occur in any segment of the gastrointestinal tract and about 30% of CD patients have small bowel involvement [4]. Small bowel CD usually present with ulcer, stricture or fistula in small intestine, while these appearances also occur in IE patients. Approximately 20% of CD patients present with strictures at diagnosis and over 50% develop apparent strictures in their lifetime. Stenosis is also a marked feature of stenotic IE. Besides, both of IE and CD can involve in whole layers of intestinal wall [5]. Thus, it’s difficult to discriminate these two diseases, sometimes even for physicians specialized in inflammatory bowel disease. The most frequently used medications among CD were 5-aminosalicylic acid, glucocorticoids, immunomodulatory medications and biological agents [6]. Especially, biological agents reach a significant effect [6]. However, these medications have very limited effect on IE. Besides, they may not only bring a great financial stress to some patients and their families but also cause some side effects [6,7]. Thus, it’s important to discriminate stenotic IE from CD.
Here, we reported fives cases very similar to CD and performed a systematic review to share our experiences and help further discriminating stenotic IE from CD. Owing to ischemic colitis has been reviewed a lot, this systematic review mainly focused on stenotic IE.
Materials and Methods
Case Series
The study was performed at the Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University in China, a tertiary referral centre for IBD. We retrospectively reviewed Electronic Medical Records (EMR) of patients initially suspected as CD, but eventually diagnosed as stenotic IE or IC between March 2019 and March 2022. IE was diagnosed according to new diagnostic criteria in previous report [2].
Literature Review of Published Cases
We comprehensively and systematically searched the databases including Medline (OvidSP), Web of Science, PubMed, Cochrane Library, and Embase for eligible studies from inception to March 2022. Search term used was ischemic enteritis, and the search was performed without limitations. Studies that met the following inclusion criteria were included: stenotic IE was diagnosed according to clinical manifestation, radiographic, endoscopic and histological imaging and biochemical examinations. Besides, IE caused by other diseases such as paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, hepatitis C virus-associated polyarteritis nodosa, sickle cell disease and longterm dialysis were excluded.
Data Extraction
Demographic and clinical parameters including sex, age, disease duration, Body Mass Index (BMI), clinical presentation, serological indexes, imaging markers, histological features and treatment of the patients were abstracted and reviewed.
Results
Case Series
A total of five patients, initially considered as CD but finally diagnosed with ischemic colitis, were enrolled. The clinical characteristics of the included studies were listed in (Table 1).
Case1
Case2
Case3
Case4
Case5
Age (y)
42
41
42
65
22
Gender
Male
Male
Male
Male
Male
BMI (kg/m2)
13.6
17.5
15.4
23.7
20.8
Underlying disease
No
No
No
No
No
Surgical history
Lysis of adhesions and decompressive longitudinal incision of small intestine ten years ago
Appendectomy and partial small bowel resection ten years ago
Appendectomy
and perforation repair three years agoPartial small intestinal resection
Appendectomy ten years ago,
anal fistula operation one year agoMain symptoms
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain
Diarrhea
Course
10 years
10 years
10 years
10 years
4 years
Lesion location
Ileum,cecum, rectum
Ileum, cecum, colon and anal
Ileum, sigmoid colon and rectum
Ileum
Descending colon, sigmoid colon and rectum
Stricture
Ileum, 0.5cm
Ascending colon ,2.5cm; sigmoid-descending colon junction,2.2cm
Ileum
Ileum
Sigmoid colon
Ulcer
No ulcer in colon
Irregular ulcers and annular ulcer around the anastomosis
Unknown
Ulcers in ileum
Ulcers in colon
Intestinal fistula
No
No
Small intestinal fistula in 2018, small intestinal fistula in 2020
No
Colon fistula and rectal abscess in 2019
Anal fistula
No
No
Yes
No
Yes
WBC (10^9/L)
7.9-12.5
5.34-17.76
3.28-6.38
3.61-9.6
5.32-9.80
HB (g/L)
40-131
79-126
49-127
29-93
29-127
PLT (10^9/L)
267-443
247-700
134-313
256-667
275-376
ALB (g/L)
31.29-40.28
29.24-43.01
28.49-34.29
22.39-36.73
21.93-33
CRP (mg/L)
1.18-9.11
0.94-195.73
16.44-32.84
0.79-16.1
6.2-119.28
ESR (mm/h)
5-20
3-100
44-55
5.53
16-18
Triglycerides (mmol/L)
0.95-1.30
0.92-2.06
1.14-2.79
1.22-1.45
1.38-2.48
Total cholesterol
2.12-3.34
2.17-2.99
3.54-4.51
4.4-4.7
3.11-3.59
Treatment
Endoscopic balloon dilation, intestinal resection
Anorectal stricture dilation, partial small intestinal resection and multi-segment colectomy after enteral nutrition, infliximab
Small intestinal fistula surgery, partial small intestinal resection
Partial small intestinal resection, glucocorticoids and azathioprine, thalidomide, infliximab, vedolizumab
Intestinal fistula and abscess resection
WBC white blood cells, RBC red blood cells, Hb hemoglobin, PLT platelets, ALB albumin. Normal value: WBC 4-10Í10^9, HB 120-160g/L, PLT 100-300Í10^9, ALB 44-55 g/L, CRP 0-10mg/L, ESR 0-15mm/h, Triglycerides 0.23-1.81 mmol/L, Total cholesterol 2.9-5.68 mmol/L.
Table 1: Demographics and clinical characteristics of stenotic IE patients: current series.
Case 1: A 42-year-old man underwent lysis of adhesions and decompressive longitudinal incision of small intestine eleven years ago in the other hospital due to abdominal pain and eventually diagnosed as adhesive intestinal obstruction. Then, the patient was admitted to our hospital with more frequent abdominal pain again for three years, accompanied by anemia even as low as 40g/L. Computed Tomographic Enterography (CTE) showed multiple thickening of the wall in small intestine and ascending colon, accompanied by stenoses in jejunum and ileum, and also showed narrowing of the superior mesenteric vein and its branches (Figure 1A). Barium radiography showed no remarkable changes (Figure 1B). Colonoscopy showed hyperemia and edema on rectal mucosa. Then, the patient received endoscopic incision and endoscopic balloon dilation (Figure 1C and 1D) and the abdominal pain relieved. However, obstruction was recurred after one month. Then the patient received partial small intestinal resection and the histological examination suggested stenotic IE (Figure 1E).

Figure 1: Case 1. A, CTE showed thickening of the wall and stricture
(red arrow) in ileum. B, No remarkable changes in barium radiography. C,
Double-balloon endoscopy showed a stricture in ileum. D, The stricture
after endoscopic incision and endoscopic balloon dilation. E, Histological
examination showed lymphocytes and plasma cells infiltrated in the lamina
propria (E1), mucosal necrosis only with continuing injury progressively
involves most of the crypts and lined by an attenuated epithelium (E2),
and fibrin deposition in the submucosal (E3) and serosal (E4) layers
with pachyvessels.
Case 2: A 41-year-old man underwent appendectomy ten years ago in the other hospital due to abdominal pain. The multiple small intestinal stenoses were discovered during the operation, subsequently the partial small intestinal resection was carried out. The patient was admitted to our hospital with abdominal pain again with anemia for two months. CTE showed multiple thickening of the wall in ileum, colon and rectum, accompanied by multiple stenoses in cecum, sigmoid-descending colon junction to the upper rectum (Figure 2A). Barium radiography showed strictures in ascending colon and sigmoid-descending colon junction (Figure 2B). Colonoscopy showed anal stenosis. Barium enema examination showed stenoses in ascending colon, sigmoid-descending colon junction. Then, the patient received anorectal stricture dilation, partial small intestinal resection and multi-segment colectomy after enteral nutrition. Double-balloon endoscopy was performed after four months of the surgery and revealed multiple irregular ulcers and annular ulcer around the small intestinal anastomosis (Figure 2C) and ileocolonic anastomosis (Figure 2D). Initially, CD was suspected. The patient received Infliximab (IFX) as induction treatment, but developed many new onset ulcers. Thus, gastroenterologist communicated with pathologist again. Eventually, the patient was diagnosed as stenotic and the histological pictures were presented in Figure 2E.
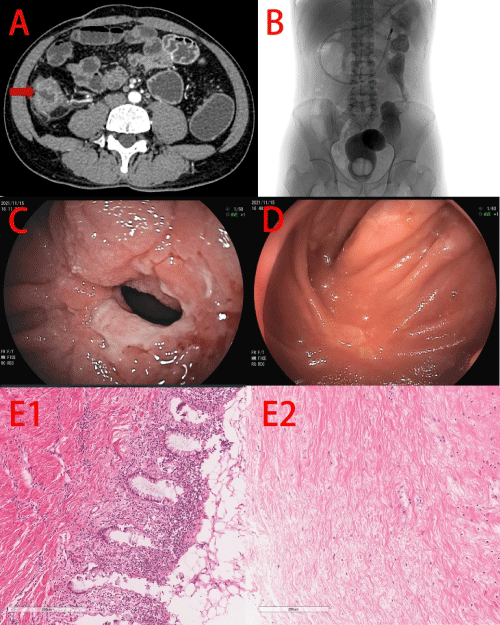
Figure 2: Case 2. A, CTE showed thickening of the wall and stricture (red
arrow) in cecum. B, Barium radiography showed strictures in ascending
colon and sigmoid-descending colon junction. C, Double-balloon endoscopy
showed annular ulcer around the small intestinal anastomosis. D, Doubleballoon
endoscopy showed irregular ulcer around the ileocolonic anastomosis.
E, Histological examination showed mucosal necrosis only with continuing
injury progressively involves most of the crypts, eventually reaching the base
and the crypts appear to be bursting, dilated, and lined by an attenuated
epithelium (E1). Besides, fibrous tissue proliferated in whole layers (E1, E2).
Case 3: A 42-year-old man was admitted to our hospital with recurrent abdominal pain for ten years and aggravated with diarrhea and hematochezia for two weeks, accompanied with anemia even as low as 49g/L. The patient underwent appendectomy in the other hospital due to right lower quadrant abdominal pain three years ago. However, the patient developed obstruction and small intestinal perforation one week after operation and received the repair surgery subsequently. In our hospital, CTE showed thickening of the wall in ileum, sigmoid colon and rectum, accompanied by stenoses, dilation and fistula in ileum (Figure 3A). Barium radiography showed fistula between sigmoid colon and small intestine (Figure 3B). Colonoscopy showed distortions in recto sigmoid junction, which could not be passable by endoscope, mucosal hyperemia in rectum. Then, the patient received small intestinal fistula surgery after enteral nutrition. Postoperative histological examination showed inflammatory cell infiltration in whole layers with abscess formation. The patient still presented with symptoms of intestinal obstruction and received partial small intestinal resection after five months of intestinal fistula surgery. Postoperative histological examination suggested stenotic IE (Figure 3C).

Figure 3: Case 3. A, CTE showed thickening of the wall, stricture (red arrow)
and fistula in ileum. B, Barium radiography showed fistula between sigmoid
colon and small intestine. C, Histological examination showed inflammatory
cell infiltration in mucosal layer, continuing injury progressively involves
most of the crypts, eventually reaching the base and the crypts appear to be
bursting, dilated, and lined by an attenuated epithelium (C1), fibrous tissue
proliferated in submucosal (C2) and serosal layer (C3) with dilatation and
congestion of capillary vessels, no granuloma.
Case 4: A 65-year-old man was admitted to our hospital with recurrent abdominal pain for ten years and aggravated for two years, accompanied with anemia even as low as 29g/L. The patient underwent partial small intestinal resection due to small intestinal inflammation and obstruction three years ago. Initially, CD was suspected. However, glucocorticoids, azathioprine, thalidomide and IFX were not effective. CTE revealed thickening of the wall in the anastomosis (Figure 4A). Barium radiography showed no remarkable changes. Double-balloon endoscopy showed stenosis with ulcers in ileum (Figure 4B). Postoperative histological examination suggested stenotic IE (Figure 4C).
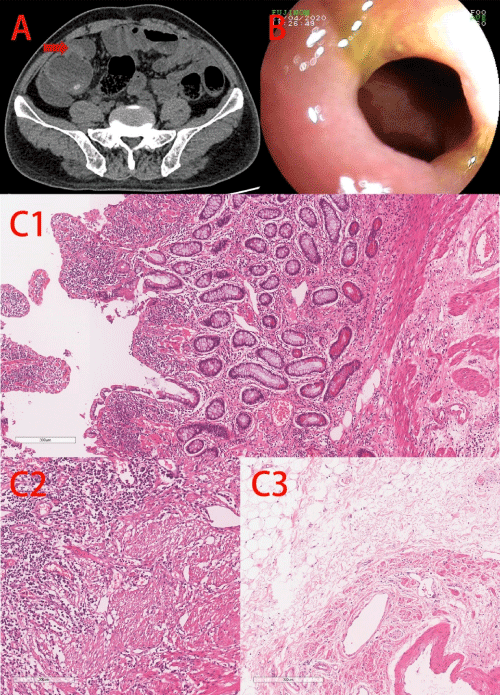
Figure 4: Case 4. A, CTE revealed thickening of the wall in the anastomosis
(red arrow). B, Double-balloon endoscopy showed stenosis with ulcers in
ileum. C, Histological examination showed inflammatory cell infiltration,
erosion, inflammatory exudation and necrosis in mucosal layer only with
continuing injury progressively involves most of the crypts, eventually
reaching the base (C1), fibrin deposition in submucosal (C2) and serosal
layer (C3).
Case 5: The patient was admitted to our hospital with recurrent diarrhea, mild abdominal pain and perianal pain for four years, accompanied with anemia even as low as 29g/L. The patient was diagnosed with CD in other hospital and received IFX as induction treatment after an anal fistula operation. However, IFX were not effective. In our hospital, CTE showed thickening of the wall in descending colon, sigmoid colon and rectum accompanied with remarkable colonic distension, and abscess was formed around the sigmoid colon (Figure 5A). Then, intestinal fistula and abscess resection was performed. Postoperative histological examination suggested stenotic IC (Figure 5B).
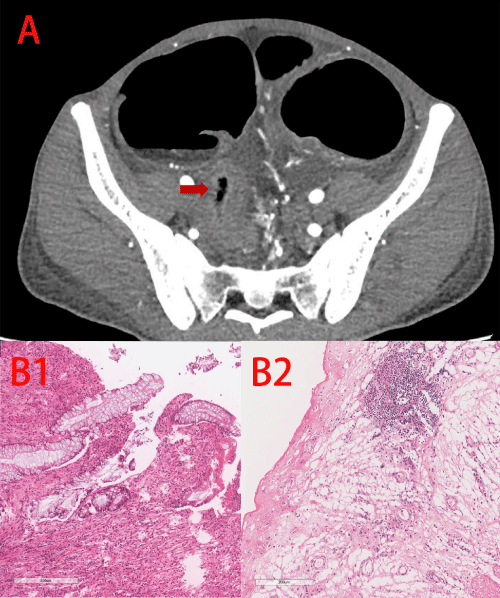
Figure 5: Case 5. A, CTE revealed significant thickening of the wall in the
sigmoid colon (red arrow). B, Histological examination showed inflammatory
cell infiltration in whole layers, erosion, inflammatory exudation and necrosis
in mucosal layer only with continuing injury progressively involves most of
the crypts, eventually reaching the base (B1). Fibrous tissue proliferated in
serosal layer (B2) with dilatation and congestion of capillary vessels.
Literature Review
1197 studies were captured from the initial search, 17 publications including 35 patients of chronic stenotic IE were included in the final systematic review (Figure 6). Among the included literatures, 14 studies were from Japan [2,3,8-19], 1 from Italy [20], 1 from USA [21] and 1 from China [22]. As for gender, there were more male patients (n=27) than female patients (n=8). Age ranged from 34 to 89 years old, and most were over 60 years old as shown in (Table 2). BMI were around 20 kg/m2. 11 patients had no history of previous abdominal surgery [3,12,14-22], while 7 patients had a history of previous abdominal surgery [2,9,13]. One patient had a history of anal fistula operation [17]. About 15 patients had underlying disease histories, mainly diabetes (n=4) [2,14], hypertension (n=9) [2,8,9,14,16,18], dyslipidemia (n=3) [2,8], cerebrovascular and cardiovascular disease (n=13) [2,3,12,14,16]. Symptoms consisted mostly intestinal obstruction symptoms, such as abdominal pain (n=24) [2,3,8-10,15-21], nausea, vomiting and abdominal distension (n=10) [2,3,9,11,12,16,18,19], and also bloody diarrhea (n=1) [10] or melena (n=3) [2,8]. Besides, two patients presented with intestinal fistula [13,21]. Radiographic imaging showed vascular issues in 6 patients including arteriovenous malformation in the inferior mesenteric artery region [8], hepatic portal venous gas [9,11,15], significant narrowing of the ileal artery branch [16] and a dense blood vessel image [19]. As for stricture location, 10 patients had stricture in jejunum [2,9,10,14,19], 18 patients had stricture in ileum [2,3,12,14- 18], 1 patient had stricture in ileocecum [21] and 1 patient had stricture in colon [8]. Stricture length ranged from 2-40cm. Lesions of two patients involved colon [8,12]. All patients had strictures with or without ulcers, including circumferential ulcer (n=9-10), longitudinal ulcer (n=3), banding ulcer (n=2), geographic ulcer (n=6), annular scar (n=3-5), longitudinal scar (n=1-2). Ulcers involved in mucosal layer, sub mucosal layer or whole mucosal layers. Besides, granular structure at the base of ulcer were observed in 10 patients. Generally, histopathological examination showed congestion, hemorrhage, necrosis or loss of crypt structure with inflammatory cell infiltration in the mucosal layer. Fibrosis was described, especially in the submucosal layer in 9 patients. Hemosiderin- and iron-positive cells were observed in 5 patients. Abnormal blood vessels including dilatation of capillary vessels, venous dilatation, or blood blots were observed in 4 patients. Most patient received intestinal resection (n=24), 8 patients received balloon dilation, 1 patient received side-to-side isoperistaltic strictureplasty and 1 patient treated with observation.
Author
Year
Country
No.
Type
Age, y
Gender (M,F)
BMI
Surgical history
Underlying disease
Chemical examination
Shiraishi, T
2022
Japan
1
IC
70
Male
N/A
N/A
Hypertension and Dyslipidemia
N/A
Pradhan, U
2021
USA
1
IE
34
Male
N/A
No
No
N/A
Nakamura, M
2021
Japan
15
IE
68 (45–86)
13,2
20.1 ± 3.2
5 patients had abdominal surgical history
Cerebrovascular and cardiovascular disease:8;
Hypertension:3; Diabetes:3;
Dyslipidemia:2;
No:3N/A
Iwai, N
2018
Japan
1
IE
69
Male
19.1
Laparotomy to treat rectal carcinoma
Hypertension
Hb 11.7 g/dL, WBC 3,500/mm3, PLT 297,000/mm3, ALB 3.8 g/L, CRP 0.08 mg/dL
Koshikawa, Y
2016
Japan
1
IE
75
Male
N/A
No
Arrhythmia
ALB 2.2 g/L, CRP 1.9 mg/dL
Kawakami, K
2015
Japan
1
IE
68
Male
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Fukita, Y
2015
Japan
1
IE
82
Male
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
Takeuchi, N
2013
Japan
1
IE
69
Male
18.5
No
Congestive heart failure
Hb 9.2g/dL, WBC 7000/ul, PLT 27.2Í 104/ul, ALB 2.4 g/L, CRP 4.8 mg/dL
Hotokezaka, M
2012
Japan
1
IE
67
Male
19.9
Ileocecal resection, total gastrectomy
N/A
Hb 12.5g/dl, WBC 6800/ul, PLT 22.8Í 104/ul, ALB 3.5 g/L
Nishimura, N
2011
Japan
5
IE
68,75,42,49,89
4,1
N/A
No
Ischemic heart disease and hypertension:1; Diabetes+hypertension+ischemic cerebrovascular disease:1; No:3.
N/A
Yang, X. Y
2009
China
1
IE
67
Female
N/A
No
N/A
N/A
Kashizuka, H
2006
Japan
1
IE
84
Female
22.8
No
No
Hb 12.5g/dl, WBC 9600/ul, PLT 23.1Í 104/ul, ALB 3.9 g/L
Spada, C
2005
Italy
1
IE
83
Female
N/A
No
N/A
N/A
Watanabe, T
2000
Japan
1
IE
68
Male
22.9
No
Hypertension, Cerebral infarction, Atrial fibrillation
Hb 13.6g/dl, WBC 8300/ul, PLT 44.1Í 104/ul, ALB 2.9 g/L, CRP 12.4 mg/dL
Hada, T
2000
Japan
1
IE
52
Male
20.1
Anal fistula operation
No
N/A
Hagimoto T
1999
Japan
1
IE
74
Female
21.1
No
Hypertension
Hb 11.2g/dl, WBC 6000/ul, PLT 37.5Í 104/ul, ALB 2.9 g/L, CRP 4.1 mg/dL
Hidaka H
1997
Japan
1
IE
49
Female
21.9
No
No
Hb 12.5g/dl, WBC 4840/ul, PLT 10.0Í 104/ul, ALB 3.76 g/L
Table 2-1: Characteristics of included studies.
Author
Year
Main symptoms
Course
Ulcer
Stricture(n,length)
Vascular issues
Histopathological features
Treatment
Shiraishi, T
2022
Abdominal pain, Melena
2 years
No
Sigmoid-descending colon junction to the upper rectum
Arteriovenous malformation in the inferior mesenteric artery region
Abnormal blood vessels and blood clots
Conventional laparoscopic low anterior resection
Pradhan, U
2021
Abdominal pain, Urinary tract infections
N/A
No
Ileocecal stricture
N/A
Congestion, hemorrhage, and necrosis extending up to the mucosal layer; Loss of villi; Inflammatory cells infiltration
Limited resection of the ileocecal junction with ileo-ascending anastomosis and repair of the urinary bladder
Nakamura, M
2021
Abdominal pain:13, Melena:2
Nausea and vomiting:5157(72–651) days
Circumferential ulcer:2-3, Longitudinal ulcer:2, Banding ulcer:2, Geographic ulcer:6; Circumferential ulcer scar:2-4, Longitudinal scar:1-2; Granular structure at the base of ulcer:8
Jejunum: 6, ileum:9; 6 (2–10)cm
N/A
N/A
Intestinal resection (n=11), endoscopic balloon dilation (n=3), and observation (n=1)
Iwai, N
2018
Abdominal pain
1 year
Circumferential ulcer
Jeunum, 6cm
Hepatic portal venous gas
Loss of the mucosal layer, an edematous submucosa, and chronic inflammation with lymphocytic and plasma cell infiltration; Fibrosis in the submucosal layer; No granuloma or sideroferous cells
Intestinal resection
Koshikawa, Y
2016
Abdominal pain
N/A
Circumferential ulcer
Ileum, 6cm
N/A
Transmural ulceration with marked fibrosis; Disappearance of crypt and marked inflammatory cell infiltration in the mucosal layer; Sideroferous cells
Intestinal resection
Kawakami, K
2015
Abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea
N/A
Ulcer: +
Jejunum
N/A
Submucosal ulcer; Fibrosis in the submucosal layer; Hemosiderin- and iron-positive macrophages
Intestinal resection
Fukita, Y
2015
Severe vomiting
5 months
Circumferential ulcer
Small intestine
Hepatic portal venous gas
N/A
Intestinal resection
Takeuchi, N
2013
Vomiting and abdominal distension
N/A
Circumferential and Longitudinal ulcer; Granular structure at the base of ulcer
Ileum
No
Fibrosis; Inflammatory cell infiltration; Dilatation and congestion of the submucosal capillary vessels; Sideroferous cells
Intestinal resection
Hotokezaka, M
2012
Symptoms of intestinal obstruction
9 months
No
Small intestine, 30-40cm
N/A
Atrophic blunt villi, edematous submucosa, and venous dilatation
Side-to-side isoperistaltic strictureplasty
Nishimura, N
2011
N/A
5-34 weeks
N/A
Jejunum:2,ileum:3
No
N/A
Balloon dilation Effective(n=4) Ineffective(n=1)
Yang, X. Y
2009
Symptoms of intestinal obstruction
N/A
N/A
Small intestine
N/A
N/A
Intestinal resection
Kashizuka, H
2006
Abdominal pain
N/A
Circumferential ulcer
Ileum,20cm
hepatic portal venous gas
Fibrosis from the submucosal layer to the intrinsic muscle layer
Intestinal resection
Spada, C
2005
Abdominal pain
N/A
N/A
Small intestine, 7cm
N/A
N/A
N/A
Watanabe, T
2000
Abdominal pain, nausea or vomiting
N/A
N/A
Ileum
Significant narrowing of the ileal artery branch was observed
Fibrosis; Strong inflammatory cell infiltration
Intestinal resection
Hada, T
2000
Abdominal pain
N/A
Circumferential ulcer, Circumferential ulcer scar
Ileum,10cm
N/A
Fibrosis in the submucosal layer; Inflammatory cell infiltration
Intestinal resection
Hagimoto T
1999
Abdominal pain, nausea or vomiting
N/A
Circumferential ulcer; granular structure at the base of ulcer
Ileum, 16.5cm
No
Inflammatory cell infiltration; Fibrosis in the submucosal layer; Sideroferous cells
Intestinal resection
Hidaka H
1997
Abdominal pain, vomiting
2 months
N/A
Jejunum, 5cm
A dense blood vessel in the narrowed part of the jejunum
Vascular stenosis and blood clots; Granulation tissue; Sideroferous cells; Inflammatory cell infiltration
Intestinal resection
Table 2-2: Characteristics of included studies.
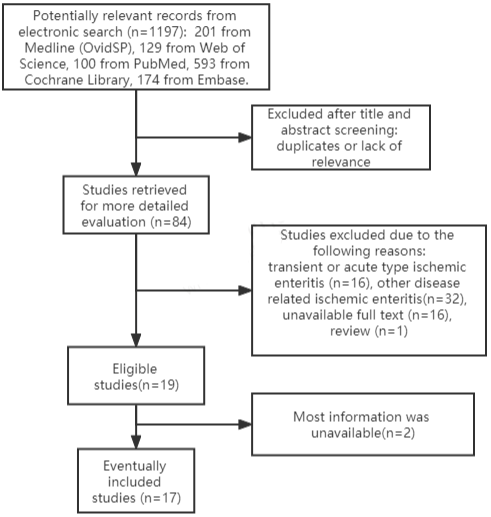
Figure 6: Flow diagram of the articles retrieved and inclusion progress
through the systematic review stages.
Discussion
All patients reported here were male which was in agreement with literature data, 77% included patients was male. In our cases, three patients (Case 1-3) were between 41 and 42 years old, one (Case 4) was sixty-five years old and one (Case 5) was twenty-two years old, while most patients in literatures were over 60 years old. BMI was lower in most current cases than that in literatures. All the patients in our cases had no underlying diseases, while about 43% patients in included literatures had underlying diseases. 4 patients in our cases had severe anemia, which was more evident than that from literatures. Intestinal and anal fistula was present in our cases and included literatures, but the frequencies were low. Recurrent abdominal pain and intestinal obstruction were common presenting features in current cases and literatures. CTE usually revealed lesions in bowel, but limited in vascular issues in stenotic IE. In our cases and included literatures, only Case 1 and another one previous case [8] were reported with vascular issues by CTE, while histological examination revealed vascular issues in Case 1, 3 and another 3 previous cases [12,13,19]. The small intestine was considered as the most difficult part to be visualized in traditional ways. The Double Balloon Endoscopy (DBE) and Capsule Endoscopy (CE) made it possible to observe small intestine intuitively. DBE and CE have been used to diagnose IE in some studies [2,22]. DBE was also carried out in Case 1, 2 and 4. Circumferential ulcer was more common in IE, while CD was usually featured with longitudinal ulcer andfissure-like ulcer [23]. However, CE should be performed with caution because CE retention may occur in stenotic IE [22]. Some patients were not suitable for DBE or CE such as Case 3 and 5 due to intestinal fistula. Therefore, histological examination of endoscopic biopsy specimen or resected bowel segment was important to diagnose IE. Apart from intestinal fistula, anal fistula also presented in stenotic IE such as Case 3, 5 and one previous case [17]. Thus, intestinal fistula and anal fistula could be the evidence to identify stenotic IE or CD. The data from included literatures revealed most stenotic IE required surgery treatment (71%) or balloon dilation (23%) and all of our cases also underwent surgery treatment. According to our cases, medications for CD such as glucocorticoids and azathioprine, thalidomide, infliximab and vedolizumab were ineffective for stenotic IE.
Here, we shared experience in diagnosing stenotic IE, and reviewed the previous cases of stenotic IE. However, there are several limitations. Firstly, the number of our cases was small. Secondly, most included studies were from Japan.
In conclusion, stenotic IE was similar to CD, but the mindlines of treatment were not the same. Thus, it’s important to discriminate stenotic IE from CD according to clinical, radiographic, endoscopic and histological features.
References
- Nakase H. [Ischemic enteritis]. Nihon rinsho. Japanese journal of clinical medicine. 2008; 66: 412-415.
- Nakamura M, Yamamura T, Maeda K, Sawada T, Mizutani Y, Ishikawa E, et al. Clinical Features of Ischemic Enteritis Diagnosed by Double-Balloon Endoscopy. Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology. 2021; 2021: 1-9.
- Koshikawa Y, Nakase H, Matsuura M, Yoshino T, Honzawa Y, Minami N, et al. Ischemic enteritis with intestinal stenosis. Intestinal Research. 2016; 14: 89.
- Steinhardt HJ, Loeschke K, Kasper H, Holtermüller KH, Schäfer H. European Cooperative Crohn’s Disease Study (ECCDS): clinical features and natural history. Digestion. 1985; 31: 97-108.
- Ahmed M. Ischemic bowel disease in 2021. World Journal of Gastroenterology. 2021; 27: 4746-4762.
- Lamb CA, Kennedy NA, Raine T, Hendy PA, Smith PJ, Limdi JK, et al. British Society of Gastroenterology consensus guidelines on the management of inflammatory bowel disease in adults. Gut. 2019; 68: s1-s106.
- Lichtenstein GR, Shahabi A, Seabury SA, Lakdawalla DN, Espinosa OD, Green S, et al. Lifetime Economic Burden of Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis by Age at Diagnosis. Clinical gastroenterology and hepatology: the official clinical practice journal of the American Gastroenterological Association. 2019; 18: 889-897.e10.
- Shiraishi T, Kunizaki M, Takaki H, Horikami K, Yonemitsu N, Ikari H. A case of arteriovenous malformation in the inferior mesenteric artery region resected surgically under intraoperative indocyanine green fluorescence imaging. International Journal of Surgery Case Reports. 2022; 92: 106831.
- Iwai N, Handa O, Naito Y, Dohi O, Okayama T, Yoshida N, et al. Stenotic Ischemic Enteritis with Concomitant Hepatic Portal Venous Gas and Pneumatosis Cystoides Intestinalis. Internal Medicine. 2018; 57: 1995-1999.
- Kawakami K, Ishida K, Inoue T, Higuchi K. Endoscopic Findings of Ischemic Enteritis. Internal medicine. 2015; 54: 1943-1944.
- Fukita Y, Adachi S, Nozawa S, et al. A case of stricture-type ischemic enteritis presenting with hepatic portal venous gas and pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis at onset. Gastroenterological Endoscopy 2015; 57: 2455-2462.
- Takeuchi N, Naba K. Small intestinal obstruction resulting from ischemic enteritis: a case report. Clinical Journal of Gastroenterology. 2013; 6: 281- 286.
- Hotokezaka M, Mibu R, Maehara R, Tanaka M, Chijiiwa K, Fujino M, et al. Side-to-side isoperistaltic strictureplasty for chronic ischemic enteritis: report of a case. Surgery Today. 2011; 42: 80-83.
- Nishimura N, Yamamoto H, Yano T, Hayashi Y, Sato H, Miura Y, et al. Balloon dilation when using double-balloon enteroscopy for small-bowel strictures associated with ischemic enteritis. Gastrointestinal endoscopy. 2011; 74: 1157-1161.
- Kashizuka H, Yamamoto M, Nishiwaki H, et al. A case of stenotic type ischemic enteritis with hepatic portal venous gas. Japanese Journal of Gastroenterological Surgery. 2006; 39: 1850-1855.
- Steinhardt HJ, Loeschke K, Kasper H, Holtermüller KH, Schäfer H. European Cooperative Crohn’s Disease Study (ECCDS): clinical features and natural history. Digestion. 1985; 31: 97-108.
- Hada T, Kohno S, Oda Y, et al. Resection and stricturoplasty for ischemic enteritis: A case report. Japanese Journal of Gastroenterological Surgery. 2000; 33: 1831-1834.
- Hagimoto T OK, Nakata K, Seo M, Okada M, Tomita A, Yamada Y, Iwashita A. Serial radiographic change of ischemic enteritis —Report of a case—. 1999.
- Hidaka H, Kobayashi K, Kokubu S, Igarashi M, Katsumata T, Saigenji K, et al. [An operated case of ischemic stricture of the small intestine complicated with extra-hepatic portal occlusion]. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai zasshi = The Japanese journal of gastro-enterology. 1997; 94: 839-44.
- Spada C, Spera G, Riccioni M, Biancone L, Petruzziello L, Tringali A, et al. A novel diagnostic tool for detecting functional patency of the small bowel: the Given patency capsule. Endoscopy. 2005; 37: 793-800.
- Pradhan U, Kumar R, Agarwal PN, Singh G, Puri P. First Case of Enterovesical Fistula Caused by Ischaemic Enteritis. Cureus. 2021; 13.
- Yang X, Chen C, Zhang B, Yang L, Su H, Teng L, et al. Diagnostic effect of capsule endoscopy in 31 cases of subacute small bowel obstruction. World journal of gastroenterology. 2009; 15: 2401.
- Camí MM, Serracarbasa A, D’Haens G, Löwenberg M. Characterization of Mucosal Lesions in Crohn’s Disease Scored With Capsule Endoscopy: A Systematic Review. Frontiers in Medicine. 2020; 7.