Abstract
The transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Device of the Solace Life-Sciences has been conceived to give a reduction or remission of a number of psychological disorders. However, it has been found by us that it has an output signal that is a multifractal. The pathophysiology of Heart Failure (HF) is characterized by hemodynamic abnormalities that result in neurohormonal activation and autonomic imbalance with increase in sympathetic activity and withdrawal of vagal activity. In normal subjects, in particular, a multifractal structure has been identified in heart rate dynamics and HRV. The pathology usually reduces or can disrupt this fractal or multifractal dynamics resulting in the alteration of its fractal properties. Atrial Fibrillation (AF) is a common cardiac arrhythmia. In previous experimental studies, the investigators found that Low-Level Vagus Nerve (VN) Stimulation (LLVNS), at voltages substantially below that which slowed the sinus rate, significantly suppressed AF inducibility and decreased AF duration. Since the above mentioned device produces a multifractal with an high multifractal strength, we encourage the researchers to experience it in their clinical cardiologic studies, and in particular, in atrial fibrillation.
Keywords: Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation; Heart rate variability; Multifractals; Atrial fibrillation; Autonomic imbalance; Heart failure
Introduction
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) is an high complex system that affects every physiological system with an highly complex anatomy, control, and physiological influence and Autonomic Neuroscience (AN) is becoming a new advanced discipline that studies function and dysfunction of the (ANS). Dysfunction of autonomic function leads to a variety of clinical problems that can be highly at risk for subjects. One basic feature is that the cardiac rhythm is modulated by the two limbs of the (ANS), the sympathetic and parasympathetic, which exert antagonistic effects. The Sympathetic (SNS) and Parasympathetic (PNS) branches of (ANS) are known to have strong influence on the pace maker cells of the heart. Heart Rate Variability (HRV) is used to quantify activity of the autonomic nervous system. The pathophysiology of Heart Failure (HF) is characterized by hemodynamic abnormalities that result in neurohormonal activation and autonomic imbalance with increase in sympathetic activity and withdrawal of vagal activity. While dominance of sympathetic modulation characterizes several pathophysiological conditions, the appropriate vagal modulation induces normal heart rate dynamics and the correct its intrinsic variability.
Presently, electrical Stimulation of the Vagus Nerve (VNS) is an FDA-approved treatment. The important tool is that (VNS) has emerged also as a promising therapeutic approach for cardiac diseases [1,2]. A new non-invasive stimulating procedure, called transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation (tVNS), has been developed [1]. Consequently, it becomes of fundamental importance to analyze in detail such innovating procedure under the technical as well as clinical profiles. In our studies we used the NuCalm device (https:// www.nucalm.com/). This device applies two gel electrode patches to the neck below the ear lobe (right and left) for transcutaneous stimulation of the afferent Auricular Branch of the Vagus Nerve (ABVN). The device received FDA approval, satisfying essential health and safety requirements. Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation (tVNS) targets the cutaneous receptive field of the ABVN at the outer ear [3]. Ear lobe vagal stimulation does not create adverse effects [4], but it does induce modulating effects on heart rate, blood pressure, or peripheral microcirculation during the stimulation procedure. The use of applied electrodes near both right and left ear lobes assures afferent and efferent induction since the right vagus nerve has efferent fibers to the heart. Of course, the use of the device is not recommended in the case of pregnancy, and is contraindicated for persons with metal in the body, such as pacemaker and ventricular assist devices or brain and cochlear implants. Actually, the whole Nu Calm arrangement has been designed as a combined system of components that work together in reducing psychological disorders as anxiety, depression and stress. First the subject applies a NuCalm topical cream that has been designed to induce relax by counteracting adrenaline. The treatment continues by applying tVNS by using an appropriate device and noise-dampening headphones with binaural beats used to bring brain to synchronize at proper frequency bands in the interval (12Hz-4Hz). The whole treatment uses lightblocking eye masks with the obvious meaning to reduce perceptive effects enhancing alpha and related relaxing bands. Initially, we performed our studies by using the tVNS NuCalm device on subjects affected from anxiety or depressions [5]. The study was performed on subjects having a serious ANS dysfunction as evidenced by our HRV analysis and examining the effect on the ANS of the Nu-Calm treatment for thirty minutes. All the considered subjects evidenced a net improvement in ANS as evidenced by HRV analysis. This encouraging result directed our subsequent research, and in particular we have been induced to analyze in detail the basic features of such tVNS device, inspecting not only its technical features but analizing in detail the features of its output signal. The aim is to delineate its basic features and the reasons because from a physiological as well as clinic profiles, such device induces the expected benefits. The reason of the study may be reassumed as it follows. The term fractal was first coined by the mathematician Benoît Mandelbrot in 1975 [6]. Fractal geometry mathematically characterizes systems that are basically irregular at all scales. A fractal structure has the property that if a small portion of the system is magnified, it shows the same complexity as the entire system. Fractals can be classified into two categories: monofractals and multifractals. Monofractal systems are those, whose scaling properties are the same in different scales. Multifractals are very complex self-similar systems consisting of differently weighted fractals with different non-integer dimensions. As a result a multifractal system is a generalization of a fractal system in which a single scaling exponent is not enough to describe its dynamics; really, a continuous spectrum of exponents (the so called singularity spectrum) is needed [7].
The salient feature that relates the finality of our paper is that in recent years multifractal analysis has been widely applied to diverse fields of biology and medicine [5,8,9] and in particular, a multifractal structure has been identified in heart rate dynamics and HRV [10- 17] that cover the basic interest of the present paper. The important concept is here that the pathology usually reduces or can disrupt this fractal or multifractal dynamics resulting in the alteration of its fractal properties. Atrial Fibrillation (AF) is a common cardiac arrhythmia. In previous experimental studies [18] the investigators found that Low-Level Vagus Nerve (VN) Stimulation (LLVNS), at voltages substantially below that which slowed the sinus rate, significantly suppressed AF inducibility and decreased AF duration.
Investigating the output tVNS Nu Calm device we have discovered that it is a multifractal. We retain that in tVNS it is the multifractal structure, given as stimulus, to induce cardio and neuromodulation and thus enabling to recover the physiological condition and the required multifractal dynamics. Since the NuCalm tVNS device has revealed such surprising feature to give a multifractal output, this result deserves consideration from a clinic view point. It seems important to experience it at cardiologic level as well as, to this regard, we are promptly arranging a detailed research project.
Materials and Methods
The first step was to evaluate the technical features of the instrument. It furnishes in output different currents at the electrodes with a minimum value of 0.1 mA that may be progressively increased. Our oscilloscope monitoring was performed for about twenty four hours of device running The NuCalm device output was also constantly monitored by a Welleman PCLAB 2000 SE computer interface with recording of the output values. In (Figure 1) we have the complete output signal given from the device.

Figure 1: Time behaviour of the output signal of the device.
The recorded time series data were analyzed by using the method of the Detrended Fluctuation Analysis (DFA) (MF-DFA-1D).
Results
The first step was to ascertain the stability of the output. The system resulted stable. We fixed a reasonable threshold value M and indicating the output signal by x(t), always we examined
|x(t)- x(t + Ti| ≤ M
being Ti the time periods of the signal.
The next step was to analyze the obtained output. We give here the obtained results. The first estimated variable was the Hurst exponent.
The results are given in (Figure 2).
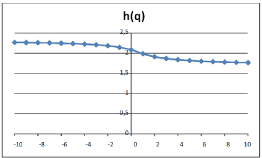
Figure 2: Estimated Hurst exponents.
h(q) shows monotonically decreasing values as function of q. The estimated Hurst exponents is H=1.9158. Soon after the function τ ≡ τ (q) was obtained.
(Figure 3) τ (q) evidences its typical non linear dependence upon q. Let us examine now α ≡ α (q).
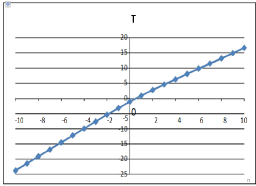
Figure 3: Estimated τ (q) function.
The results are given in (Figure 4)
Finally, we obtained the spectrum ƒ (α). The result is given in (Figure 5).
The results given from Figure 2 to Figure 5 indicate only one result.
The output signal of the NuCalm tVNS device is a multifractal. Its strength is given by
and result to be 0.5845 and 0.1931, respectively
Discussion
As previously said, multifractals are very complex self-similar systems consisting of differently weighted fractals with different noninteger dimensions. As a result a multifractal system is a generalization of a fractal system in which a single scaling exponent is not enough to describe its dynamics; really, a continuous spectrum of exponents (the so called singularity spectrum) is needed (Figure 5).
In the Introduction we outlined also that multifractals have been identified in heart rate dynamics and HRV. The emerging evident criterium is that the pathology usually reduces or disrupts the fractal or multifractal dynamics resulting in the alteration of its fractal properties. The MF-DFA-1D method that we have used was first conceived by [19] and as previously said, it enables to estimate If it exists a scaling in the fluctuation function Fq (s) ∝ sh(q) being q the order of the fluctuation.
In general the exponent h(q) depends on q. For stationary time series h(2) is identical with the Hurst exponent H. h(q) is said to be the generalized Hurst exponent. A mono fractal time series is characterized by unique h(q) for all values of q. In the multifractal case we obtain instead a distribution of values as in (Figure 4).
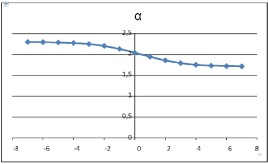
Figure 4: The estimated function α (q).
The generalized Hurst exponent h(q) is related to the classic scaling exponent τ (q) by the relation
τ (q) = qh(q)-1
A monofractal series with long range correlation is characterized by linearly dependent q order exponent τ (q) with a single Hurst exponent. Multifractal signal has multiple Hurst exponent and depends non-linearly on q as we obtain in (Figure 3).
The singularity spectrum ƒ (α) is related to h(q) by
α = h(q) + αh’(q)
and we obtain it in Figure 4 and the multifractal spectrum,
ƒ(α) = [α − h(q)]+1 is obtain in (Figure 5).
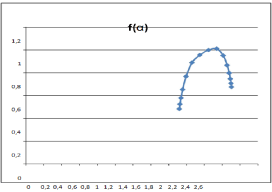
Figure 5: The singularity spectrum ƒ (α).
Conclusion
we have given demonstration that the output signal of the tVNS NuCalm device is a multifractal and it has high multifractal strength. A diminished fractal HRV was consistently reported in various heart disease processes. In addition, the sympathetic (SNS) and parasympathetic (PNS) branches of the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) are known to have strong influence on the pace maker cells of the heart. Atrial Fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia. In previous experimental studies [18], the investigators found that Low-Level Vagus Nerve (VN) Stimulation (LLVNS), at voltages substantially below that which slowed the sinus rate [20], significantly suppressed AF inducibility and decreased AF duration. Therefore the tVNS NuCalm device could be of interest in inducing a net improvement in AF or in general, in cardiac studies since its basic and fundamental property is just to stimulate the Vagus by a multifractal signal. Therefore this brief note has been devoted to encourage scientists to explore such possibility by using such device as well as we are arranging a detailed protocol of research in this direction.
References
- Schwartz PJ, De Ferrari GM, Sanzo A, Landolina M, Rordorf R, Raineri C, et al. Long-term vagal stimulation in patients with advanced heart failure: first experience in man. Eur J Heart Fail. 2008; 10: 884-891.
- De Ferrari GM, Crijns HJ, Borggrefe M, Milasinovic G, Smid J, Zabel M, et al. Chronic vagus nerve stimulation: a new and promising therapeutic approach for chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J. 2011; 32: 847-855.
- Ellrich J. Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation. Eur Neurol Rev. 2011; 6: 262-264.
- Kraus T, Hosl K, Kiess O, Schanze A, Kornhuber J, Forster C. BOLD fMRI deactivation of limbic and temporal brain structures and mood enhancing effect by transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation. J Neural Transm. 2007; 114: 1485-1493.
- Conte Sergio, Mendolicchio Leonardo, Kaleagasioglu Ferda, Norman Rich, Wang Fang, Losito Casciaro Francesco, et al. Rorschach ink blots are multifractals and a corresponding multifractal structure is realized in humans during their perception as measured by the GSR (Galvanic Skin Response) neurological and psycho-physiological signal. Chaos and Complexity Letters. 2017; 10: 187-210.
- Mandelbrot B. Fractal GeometryofNature. NewYork NY: Freeman. 1982.
- Hausdorff JM, Ashkenazy Y, Peng CK, Ivanov PC, Stanley HE, Goldberger AL. When human walking becomes random walking: fractal analysis and modeling of gait rhythm fluctuations. Physica A. 2001; 302: 138-147.
- Conte Elio, Norman Rich, Mordeniz Cengiz, Conte Sergio, Marvulli Riccardo, Ianieri Giancarlo, et al. A Multifractal Analysis of Neuron Locations and Calcium Activity in C-Elegans. Chaos and Complexity Letters. 2016; 10: 1-23.
- Conte Elio, Wang Fang, Norman Rich, Mordeniz Cengiz, Conte Sergio, Licata Ignazio. A Multifractal Analysis of Connectomics, Neuron Locations and Calcium Activity in C-Elegans. Chaos and Complexity Letters. 2016a; 10: 111-127.
- Ossadnik SM, Buldyrev SV, Goldberger AL, Havlin S, Mantegna RN, Peng CK, et al. Correlation approach to identify coding regions in DNA sequences. Biophys J. 1994; 67: 64-70.
- Peng CK, Buldyrev SV, Havlin S, Simons M, Stanley HE, Goldberger AL. Mosaic organization of DNA nucleotides. Phys Rev E. 1994; 49: 1685-1689.
- Buldyrev SV, Dokholyan NV, Goldberger AL, Havlin S, Peng CK, Stanley HE, et al. Analysis of DNA sequences using methods of statistical physics. Physica A. 1998; 249: 430-438.
- Blesic S, Milosevic S, Stratimirovic D, Ljubisavljevic M. Detrended fluctuation analysis of time series of afiring fusimotor neuron. Physica A. 1999; 268: 275-282.
- Liu Y, Gopikrishnan P, Cizeau P, Meyer M, Peng CK, Stanley HE. The statistical properties of the volatility of price fluctuations. Phys Rev E. 1999; 60: 1390-1400.
- Bunde A, Havlin S, Kantelhardt JW, Penzel T, Peter JH, Voigt K. Corrrelated and uncorrelated regions in heart-rate fluctuations duringsleep. Phys Rev Lett. 2000; 85: 3736-3739.
- Talkner P, and Weber RO. Power spectrum and detrended fluctuation analysis: application to daily temperatures. Phys Rev E. 2000; 62: 150-160.
- Ashkenazy Y, Baker DR, Gildor H, Havlin S. Nonlinearity and multifractality of climate change in the past 420000 years. Geophys Res Lett. 2003; 30: 2146-2149.
- Machada A, Gourine AV, Ackland GL. Vagal Modulation of Atrial Fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015; 66: 977-8.
- Kantelhardt JW, Zschiegner SA, Koscielny-Bunde E, Havlin S, Bunde A, Stanley HE. Multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis of non stationary time series. Physica A. 2002; 316: 87-114.
- Schachter SC, Saper CB. Vagus nerve stimulation. Epilepsia. 1998; 39: 677- 686.
Citation:Conte S, Sala N, Wang F, Serafini G, Kaleagasioglu F, Mendolicchio L, et al. The Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation Device of the Nu-Calm-Solace Lifesciences Gives an Output Signal that is a Multifractal: Is there a Support in the Treatment of the Atrial Fibrillation?. Austin Cardiol. 2017; 2(2): 1013.
