Abstract
Alteration in size of gingiva is one of the clinical features of periodontal disease. Increase in size of gingiva, which is termed as gingival enlargement or gingival over growth is a common clinical sign of gingival disease and a matter of great clinical concern. Increase in size alters the physiologic contour of gingiva, creates areas of plaque accumulation, intereferes with regular oral hygiene procedures, and creates aesthetic problems. In severe cases, it interefere with mastication and phonation. Enlargement may involve one or more components of gingiva. Depending on the involvement of components of gingiva and distribution, gingival enlargement can be Localized, genaralized and marginal, papillary, diffuse and discrete. Depending on etiology and pathogenesis, it can be classified as inflammatory enlargement, fibrotic enlargement, combined enlargement, enlargement associated with systemic conditions, neoplastic enlargement and false enlargements.
Keywords: Generalized; Papillary; Gingival Over Growth
Introduction
Inflammatory gingival enlargement is most common type of over growth, which manifest because of increase in volume of gingival tissue in response to local microbial irritation. Inflammatory enlargement may be acute or chronic. Fibrotic gingival enlargement or non-inflammatory fibrous gingival over growth is believed to be the result of genetic predispostion or adverse effect of drug. Large number of drugs and genetic disorders are associated with occurrence of gingival over growth in susceptible individuals. They may be [1].
• Drug induced gingival enlargement
• Idiopathic gingival enlargement
Drug Induced Gingival Enlargement
The drugs that are reported to be associated with gingival over growth are anti-convulsants, immune suppresents and calcium channel blockers (Table 1). Despite their pharmacological diversity, all these drugs have similar mechanism of action at cellular level. They are known to inhibit intracellular calcium ion induced influx. Therefore, the clinical features of gingival over growth (Figure 1) by these agents and even the histologic appearance are reported to have common characteristics such as increase in extra cellular ground substance, number of fibroblast and acanthosis of epithelium.
Category
Generic Name
Trade Name
Anti-convulsants
Phenytoin
Valproic acid
Carbamazepine
VigabatrinDilantin
Depakene
Tegretol
SabrilCalcium channel blockers
Amlodipine
Diltiazem
Felodipine
Isradipine
Nicardipine
Nifedipine
Nisoldipine
VerapamilNorvasc
Cardizem
Plendil
Dyanacirc
Cardene
Nifedical
Sular
CalanImmunosuppresants
Cyclosporine A
Tacrolimus
Mycophenolate mophetil
serolimusNeoral
Prograf
Cellcept
Rapamunel
Table 1: List of drugs causes gingival enlargement.
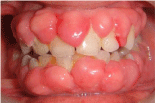
Figure 1: Generalized enlargement of marginal gingiva, attached gingiva and
interdental papillae.
Anticonvulsants
These are the drugs, which are used to control epileptic seizures. Clinically it may manifest as generalized hyperplasia in mouth, but it is most severe in maxillary and mandibular anterior region. The 1st change noted is a painless bead like enlargement of gingiva, starting with one or two interdental papillae. The surface of gingival shows an increase in stippling and finally a cauliflower, warty or pebbled surface. Hyperplasia may develop massively covering a considerable portion of the crown. They may interfere with occlusion, increase plaque accumulation, resulting in secondary inflammatory process [2].
Laborotary studies on phenytoin-induced enlargement have observed fibroblast like cell proliferation, proliferation of epithelium, increased synthesis of Glycosoaminoglycans sulfate and reduced degeneration of collagen. Phenytoin induced reduction of folic acid leads degerative chanes in epithelium exacerbated in presence of inflammatory factors. The increased synthesis of testosterone metabolite by fibroblast can causes gingival enlargement [2].
Some studies have found that pre threshold serum phenytoin was directly aenlargement, while no association was found post threshold phenytoin and gingival enlergment. Girgis et al., found a direct relationship between gingival enlargement in 50% of patients, while no relationship and even an inverse relationship was found in rest 50% [2].
Studies have demonstrated that oral hygiene procedures may limit the severity of the lesion but are unable alone to lead to the reversal of the condition [2].
Immunosuppressants
Cyclosporine is apotent immunosuppressive agent used to prevent organ transplant rejection and to treat several disease of autoimmune origin. Clinically it is similar to that induced by dilantin. Mechanism of action of cyclosporine is not fully understood; however, blood and cellular immunity response seems to be influenced by selective and reversible inhibition of T helper cells. There is disagreement between severity of gingival enelrgement in blood and saliva. Some studies have reported that development of gingival enlargement requires a threshold of drug concentration. In blood plasma, while its severity is not associated with the dose. The dosage 500mg is considred as threshold [3].
Calcium Channel Blockers
Calium channel blockers induces direct dilation of coronary arteries and arterioles, improving the oxygen supply to the heart muscles. It is used in the treatment of acute and chronic coronary insufficiency. Gingival over growth occurs in 20% of cases. The stratified squamous epithelium covering the gingival is thick and has a keratinized layer. The rete pegs are extremely long sometimes called “test pegs” with considerable confluence seen [4]. Calcium channel blockers affect the Ca metabolism by reducing the intra cellular Ca flow and limiting the production of active collagenase. Gingival enlargement occurs by taking 30-100mg Nefedipine per day [4].
Idiopathic Gingival Enlargement
It is also termed as gingivostomatitis, elephantiasis, idiopathic fibromatosis, hereditary gingival hyperplasia and congenitally familial fibromatosis. It is a proliferative fibrous lesion that causes aesthetic and functional problems. Both genetically and pharmacologically induced forms of gingival enlargement exists. Clinically it is seen on attached gingiva, gingival margina and interdental papilla. It appears as pink, firm and leathery with pebbled surface. Teeth are completely covered. In severe cases, jaw appears distorted due bulbous enlargement [5].
Pregnancy Induced Gingival Enlargement
The prevalence of pregnancy gingivitis changes from 35- 100%. The gingiva shows increased level of inflammation often characterized by edema, colour and contour change and propensity to bleed on gentle stimulation (Figure 2). The marginal gingival tends to be more prominent than facial and lingual surfaces. And inflammatory reaction to the local irritants that occurs after 3rd month of pregnancy is called pregnancy tumour. This lesion appears as discrete, mushroom, flattened spherical masses, that protrude from gingival margin, more frequently interproximal space and are attached by sessile or pedanculated base [6].
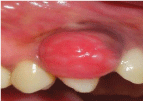
Figure 2: Discrete flattened spherical mass protruding from gingival margin.
Puberty Induced Gingival Enlargement
It is inflammatory type of gingival enlargement, which occurs in both male and females in pubertal age groups. it involves mainly marginal and interdental gingiva (Figure 3). It is characterised by prominent bulbous interproximal papilla. After puberty the enlargement undergoes spontaneous reduction but does not disappear until local irritants are removed [7].
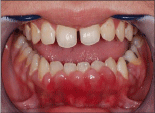
Figure 3: Bulbous enlargement seen in the interproximal area.
Management
Treatment for drug-induced hyperplasia includes substitution with another drug. Sodium valproate has been used as alternative to dilantin sodium in management of epilepsy. Anti-hypertensives other than calcium channel blockers may be considered for replacement of Nifedipine. Tacrolimus has been used successfully as calcium channel blocker. Most of the gingival enlargement during pregnancy can be prevented by removal of local irritants and institution of fastidious oral hygiene. Hyperplasia at puberty can be managed by removal of lesions along with elimination of irritating factors [8].
Conclusion
Gingival enlargement has varied presentations, hence diagnosis of these entities become challenging for the clinician. Detailed investigation is necessary. So prompt diagnosis and removal of the etiologic factors is the main treatment objectives.
References
- Amit Arvind Agrawal. Gingival enlargements: Differential diagnosis and review of literature. World J Clin Cases. 2015; 3: 779-788.
- Bharti V, Bansal C. Drug-induced gingival overgrowth: The nemesis of gingiva unraveled. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2013; 17: 182-187.
- Greenberg KV, Armitage GC, Shiboski CH. Gingival enlargement among renal transplant recipients in the era of new-generation immunosuppressants. J Periodontol. 2008; 79: 453-460.
- Quach H, Ray-Chaudhuri A. Calcium channel blocker induced gingival enlargement following implant placement in a fibula free flap reconstruction of the mandible: a case report. Int J Implant Dent. 2020; 6: 47.
- Shah K, Khan K, Pandilwar PK, Anoop Unnikrishnan KS, Sanap M, Nikalje T. Long standing Idiopathic gingival hyperplasia of oral cavity with invasion of maxillary sinus: A rare case report. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2020; 77: 62-66.
- Chauhan SS, Pandey A, Raj A, Raj A. A classical case of pregnancy induced gingival enlargement: a case Report. Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences. 2014; 3: 11104-11108.
- Siddharth T. Puberty Induced Gingival Enlargement. Biomed J Sci & Tech Res. 2017.
- Taylor BA. Management of drug-induced gingival enlargement. Aust Prescr. 2003; 26: 11-13.
