Abstract
Background: Periodontal plastic surgeries aim to cover the exposed root surfaces thereby improving esthetics, relieving hypersensitivity which are the most common reasons why patients seek treatment. Auto grafts are the gold standard treatment option but owing to the involvement of a second surgical site and increased patient morbidity, research has led to various allograft options. One such novel allograft is the amniotic membrane. It is a rich source of various growth factors, and helps in maintaining the structural integrity and anatomical configuration of the regenerated tissues.
Objectives: To evaluate the regenerative potential of gingiva and its esthetic outcome using dehydrated amniotic membrane.
Methods: 10 patients with Millers class I and II gingival recession were chosen. Recession Depth (RD), Recession Width (RW), Pocket Probing Depth (PPD), Clinical Attachment Loss (CAL) and Width of Keratinized Gingiva (WKG) were recorded at baseline,3 months and 6 months. Pain was assessed using Visual Analog Scale (VAS) at the time of surgery and 1 week post operatively. Root esthetic score was recorded at 6 months to evaluate the esthetic outcome of procedure.
Results: Six months following root coverage procedure, the clinical parameters showed improvement and there was a reduction in pain too.
Conclusion: Amniotic membrane is an effective alternative to autografts in the management of gingival recession defects.
Keywords: Dehydrated Amniotic Membrane; Gingival Recession; Percentage Root Coverage; Visual Analog Scale; Root Coverage Esthetic Score (RES).
Introduction
Gingival recession mostly occurs due to plaque accumulation resulting in inflammation of gingival tissues. Many other risk factors also cause recession such as developmental defect, chronic trauma due to impaction of foreign bodies, frictional injury to the gingiva, abnormal tooth brushing, malpositioning of teeth, gingival ablation, abnormal frenal attachment etc. The exposure of the root surface may lead to problems such as root caries, dentinal hypersensitivity and esthetic problem [1]. Many treatment modalities such as pedicle grafts, free gingival grafts and subepithelial connective tissue graft requires an adjacent donor site with adequate attached gingiva, and is associated with disadvantages of pain, discomfort, unsatisfactory esthetics and gingival recession at the donor site [2]. To overcome all these short comings, research has led to the finding of an alternative treatment which can provide promising results and patient comfort.
Recently, allografts have been introduced in the form of dermis tissue products eg. (Alloderm®, LifeCell Corporation, Branchburg, NJ, USA). Though it has various advantages, the unavailability of these materials and cost factor has further made the researchers to look for newer materials [3]. Amnion the inner most portion of the amniotic sac consists of a single layer of epithelium cells, thin reticular fibers, a thick compact layer, and a fibroblast layer. The amniotic basement membrane closely mimics the basement membrane of human oral mucosa. Amnion also contains growth factors that may aid in the formation of granulation tissue by stimulating fibroblast growth and neovascularization [4]. As only sparse literature is available regarding amniotic membrane in the field of reconstructive periodontal surgery, the current study was aimed to evaluate the clinical efficacy of dehydrated amniotic membrane (Amnio-guard®) in the treatment of gingival recession.
Methodology
By purposive sampling 10 patients with millers’ class I and class II gingival recession were selected from the outpatient department of Periodontology, JSS Dental College and Hospital, Mysuru, India. This was an interventional study with a duration of 6 months.
Ethical Clearance and Informed Consent
A prior written informed consent was taken based on Declaration of Helsinki (1964) and ethical clearance was obtained from Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the JSS Dental College and Hospital, Mysuru, Karnataka, India.
The inclusion criteria comprised of Systemically healthy patients, in the age range of 18-50 years, Miller’s class I or II gingival recessions with a recession depth of =3mm but less than 5mm., well aligned teeth, patients who were able to and willing to follow study procedures and instructions.
The exclusion criteria comprised of patients who did not provide consent for the study, gingival recession (class III and IV), thin gingival biotype, teeth with restored cervical abrasions, pregnant/lactating women, smokers, root caries, patients with any immunologic disease and who are currently receiving or have received within two months prior to study entry, systemic corticosteroids, immunosuppressive agents, radiation therapy, and/or chemotherapy which would compromise wound healing.
Methodology
Pre-Surgical Procedure
The patients fulfilling the inclusion criteria were sent for routine haematological investigations after Phase I therapy. They were recalled after 2 months to check the oral hygiene and gingival status. Patients with adequate oral hygiene maintenance (PI, GI and SBI <1) were considered for the surgery.
Clinical parameters like plaque index [5], gingival index [6] and sulcus bleeding index [7], Recession depth, Recession width, Probing depth, Width of keratinized gingiva, Clinical attachment level [7,8] were recorded at baseline, 3 months and 6 months postoperatively. All the parameters were made using a UNC-15 Periodontal Probe.
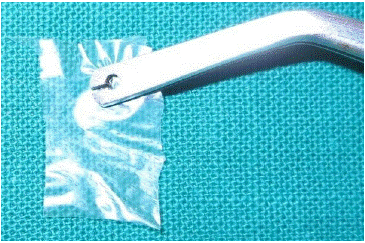
Figure 1: Dehydrated amniotic membrane (Amnio-guard) ®.
Post-operative pain was assessed using VAS scale (0-10) [8] (Figure 2) just after surgery also at 24hrs, 2nd day, 3rd day, 4th day, 5th day, 6th day and at 1-week post-surgery. In addition to the other clinical parameters (Root coverage, Percentage root coverage, Root coverage esthetic outcome [8]) were also assessed at 3 and 6 months.
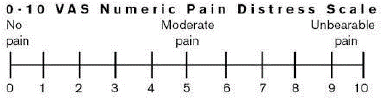
Figure 2: Visual Analog Scale.
Surgical Protocol
Preparation of Recipient Site (Figure 3-7)
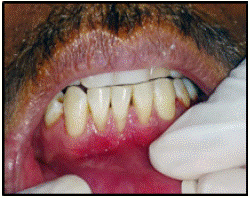
Figure 3: Pre-operative view.
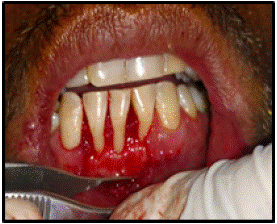
Figure 4: Full thickness flap.
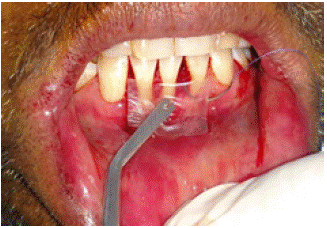
Figure 5: Placement of Dehydrated.
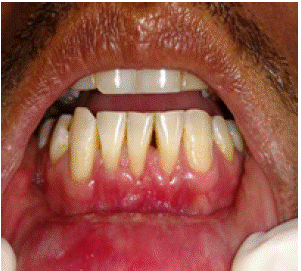
Figure 6: 3 months postoperatively Amniotic Membrane.
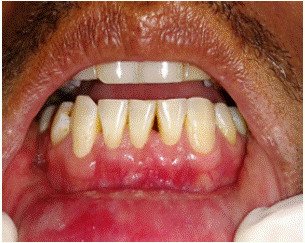
Figure 7: 6 months postoperatively.
The surgical area was prepared with adequate anesthesia using 2% Lignocaine HCl containing 1:80,000 adrenaline. A trapezoidal flap was designed [9]. A full-partial thickness flap was extended beyond the mucobuccal fold so that it exhibited no tension when pulled coronally beyond the cementoenamel junction. The root was thoroughly planed. The intact papilla mesial and distal to the recession were de-epithelialized. A measurement of the approximate length and width of the material required was obtained with the use of a periodontal probe. Only in cases with inadequate width of attached gingiva the surgical procedure included the bridge flap technique as introduced by Margraff and Romanos [10].
The sterile dehydrated Amniotic membrane, commercially available and purchased from Biocover Laboratories, Karnal (Figure 1) was trimmed and contoured to cover the recipient site, Firm pressure was applied over the membrane with sterile moist gauze for 5 minutes to adapt and adhere to the recipient site.
The pedicle was coronally repositioned over the membrane to completely cover it, and secured in position with double sling sutures using 4-0 vicryl. Coe-pack was applied on the operative area. Post-operative antibiotics and analgesics were prescribed ((Amoxicillin 500 mg thrice daily for 5 days and ibuprofen 400mg twice daily for 3 days).
Postoperative instructions were given to the patients and they were prescribed. Patient was recalled 1 week after surgery for pack removal. Patient was asked to report of any adverse effect too.
Post-Operative Pain Evaluation
Patients were asked to maintain a diary to evaluate post-operative pain and discomfort. Just after surgery, 24hrs, 2nd day, 3rd day, 4th day, 5th day, 6th day, and at 1 week postoperatively pain assessment was done using Visual Analog Scale (0-10) [8] (Figure 2). Any additional analgesics if taken were noted by the patients.
• Root coverage (in mm): [preoperative recession] – [post-operative recession] mm
• Percentage of root coverage = [preoperative gingival recession depth-post-operative recession depth] / [preoperative recession depth] ×100 %
Esthetic outcome was assessed at the end of 6 months using:
Root coverage esthetic outcome (RES) [6] was calculated according to Gingival Margin (GM), Marginal Tissue Contour (MTC), Soft Tissue Texture (STT), Marginal Gingival Junction alignment (MGJ), Gingival Colour (GC).
Statistical Analysis
Data was entered in Microsoft excel and analyzed using SPSS 10.0.5). The results were averaged (mean + standard deviation) for continuous data. Normalaity was tested using Shaipro-Wilks test. Parametric test was used to compare between the groups. One-way analyses of variance were used to test the difference between groups. The student test was used to determine statistical difference between groups.
Results
The study included a total of 10 patients showing at least one localized Miller’s Class I and Class II gingival recession. 8 were treated with coronally advanced flap and 2 patients with bridge flap technique. All patients were followed for 6 months postoperatively. Clinical parameters were recorded at baseline,3 months and 6 months postoperatively. Visual Analog scale was used to record the pain experienced immediately after surgery, 24 hrs, 2nd day, 3rd day, 4th day, 5th day, 6th day and 1 week post-operatively. Percentage root coverage was also recorded at 3 and 6 months post-operatively. Root coverage Esthetic Score (RES) was recorded at 6 months.
The mean plaque, gingival and bleeding indices shows significant improvement from baseline through 6 months postoperatively(p<0.001) (Table 1).
N
P value
Pre
10
<0.001
Day of Surgery
10
Month 3
10
Month 6
10
Table 1: Intra-group comparison of plaque, gingival and bleeding indices at various time intervals using one way ANOVA.
The difference in recession depth between baseline and 6 months was 1.8±0.67 mm and the result of one-way ANOVA test showed significant improvement (p<0.001). The mean recession width reduced at 6 months which was significant (p<0.001) (Table 2)
N
P value
Day of Surgery
10
<0.001
Month 3
10
Month 6
10
Table 2: Comparison of mean recession depth and width at various time intervals using one way ANOVA.
The mean clinical attachment level was 3.7±0.85 mm at baseline which increased by1.7±0.94 at 3 months and 1.75±0.92 mm which showed significant improvement at 6 months(p<0.001) (Table 3).
N
Mean
SD
P value
Day of Surgery
10
3.7
0.856
<0.001
Month 3
10
2
0.943
Month 6
10
1.95
0.926
Table 3: Comparison of mean clinical attachment level at various time intervals using one way ANOVA.
The mean probing depth was 0.95±0.49 mm at baseline which reduced to 0.88±.45mm at 3 months and 0.85±47 mm at the end of 6 months (Table 4).
N
Mean
SD
P value
Day of Surgery
10
0.95
0.497
0.891
Month 3
10
0.88
0.459
Month 6
10
0.85
0.474
Table 4: Comparison of mean pocket probing depth at various time intervals using one way ANOVA test.
The mean keratinized gingiva width was 2.2±0.91mm which increased to 3.5±0.94 mm (p=0.004) (Table 5).
N
Mean
SD
P value
Day of Surgery
10
2.2
0.919
0.008
Month 3
10
3.38
0.948
Month 6
10
3.5
0.943
Table 5: Comparison of mean width of keratinized gingiva at various time intervals using one way ANOVA test.
The mean percentage root coverage was analyzed using student t test. The mean percentage root coverage at 3 months was 61.5±27% and 65±21.04% at 6 months (Table 6).
N
Mean
SD
P value
Month 3
10
61.5
27.2
0.16
Month 6
10
65
21.04
Table 6: Comparison of mean percentage root coverage at various time intervals using one way student t test.
The mean root coverage esthetic score obtained by scoring the outcome on the basis of percentage root coverage, soft tissue texture, marginal gingival contour, gingival color and alignment of the MGJ of was good score of 7.1.
The visual analog scale showed statistical significance over time (Table 7).
N
Mean
SD
P value
Month 3
10
5.8
1.317
<0.001
Month 6
10
0.9
0.568
Table 7: Comparison of mean Visual analog scale for pain at various time intervals using one way student t test.
Discussion
This study was carried out to evaluate dehydrated amniotic membrane (Amnioguard®) for root coverage in mandibular anterior. Many autogenic grafts have been used of which SCTG has been found to be the gold standard The only limitation was that a donor site is required.
To overcome this, various allografts such as Acellular dermal matrix, and Placental derived membranes (Amniotic membrane and chorionic membrane) have been developed. The placental derived membranes have the advantages of the barrier membrane and in addition are found to contain mesenchymal stem cells, growth factors which help in the regeneration. As most of the research published in the literature regarding the amniotic membrane are case reports this study using the novel membrane was conducted with more number of patients.
The amniotic membrane used in the study facilitates epithelialization, preserves normal phenotype of the epithelium, suppresses inflammation, promotes angiogenesis and reduces the formation of scar tissue [11].
The patients were asked to use a 10 cm scale and mark the severity of pain at the time of surgery, 24 hrs, 2nd to 6th day and 1 week post-operatively. The number of analgesics taken was also recorded. The results revealed a significant decrease between the time of surgery to the 3rd day and 1 week postoperatively.
This could be due to the improved antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties of amniotic membrane which include elastase-inhibiting factor and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. The explanation for the reduced inflammation and pain observed in our study could also be due to the unique property of the amniotic membrane where it provides better hydration and soothes the wound bed to promote faster healing [12].
In this study a significant reduction in the recession depth occurred by the end of 3 months through 6 months. The mean width of keratinized gingiva increased significantly from baseline to 6 months, similar results were observed by Gahroudi et al and Chakraborthy [13] et al. Some studies have concluded that the presence of keratinocyte growth factor present in the amniotic membrane, can promote keratinization of the epithelial cells and helping the mucogingival junction to maintain its position by inducing keratinization [13].
By the end of 6 months there was no presence of scarring and this could be due to the anti-scarring property of the Amniotic Membrane (AM) as it secretes various growth
factors such as Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) and Hepatocytes Growth Factor (HGF) that maintains a balance between Transforming Growth Factor (TGF)-1 and TGF-3 to prevent scarring. AM has also proven to down- regulate TGF-beta and its receptor expression by fibroblast that causes a reduction in fibrosis at the wound site [4].
The mean percentage root coverage obtained was 61.5 % and 65% respectively at 3 months and 6 months. It was in accordance to a study conducted by Ghahroudi et al who compared the amnion allograft with connective tissue graft procedure. They had found 67 % coverage in areas of recession treated with the amniotic membrane [12].
Further a significant decrease in Recession Depth (RD) was observed during the 3 to 6month interval. The decrease in Recession Depth (RD) seen after 3 months in the study might be attributed to the improved capacity of AM to induce creeping attachment. Any root coverage that is achieved after a month of procedure is attributed to creeping attachment [14].
Fibroblast proliferation and vascular growth factors in the amniotic membrane accelerates angiogenesis and tissue maturation which may be responsible for the prevention of necrosis of the coronal portion of the flap, resulting in better wound healing and creeping attachment. In a histological study in rabbits Rinastiti [15] et al had found induction of fibroblasts and formation of numerous new blood vessels in the areas treated with the amniotic membrane.
The CAL gain was significant and decrease in PD was seen but it was not significant at 6 months after surgery. This might be contributed to the beneficial properties of the amniotic membrane as it resembles the oral mucosa basement membrane and contains different aminins, especially laminin-5, which plays a role in the adhesion of gingival cells [16,17].
The antimicrobial agents in amniotic membrane, especially secretory leukocyte proteinase inhibitor I, lactoferrin, defensin and elafin might have also contributed to wound healing. The mean width of keratinized gingiva increased significantly from baseline to 6 months and the results are similar to those observed by Gahroudi et al and Chakraborthy et al. [12,13].
In this study, the Root coverage Esthetic Score system (RES) was used to assess the treatment outcome. The mean RES score obtained was 7.1 and this is accordance to a study done by Pini-Prato et al. [18] RES score gives more importance to CRC (6 points) when the CEJ is completely undetectable; even a minimal visual exposure of the CEJ is not considered CRC [18]. Evaluation of the cases in this study was accomplished taking this presupposition into account. Furthermore, gingival color was good and almost indistinguishable from the neighboring teeth [6]. Results may also be attributed to the fact that the amniotic membrane has the property of prevention of keloid formation. Thus, this treatment could be indicated in the esthetic treatment of recessions.
Every subject in the study showed good oral hygiene and a healthy clinical gingiva throughout the study. This was the result of repeated oral hygiene instructions given to the patients throughout the study period. The decrease in PI, GI and Sulcus bleeding index at the end of 6 months, is in accordance with the findings of Cortellini et al [18].
The limitations of the study include small sample size. A stent should have been used to standardize the positioning of the probe. Patient centered evaluation of the esthetics was not done. Further longitudinal studies are required to determine the stability of the results.
Conclusion
Coronally advanced flap with dehydrated amniotic membrane is effective in treating gingival recession. The self-adherent nature of amnion significantly reduced the surgical time and made the procedure easier to perform. It can therefore be considered as a futuristic periodontal regenerative material.
Author Statements
Future Considerations
Further long- term clinical trials investigating the full potential of the material in tissue regeneration is needed to strengthen the beneficial properties of amniotic membrane.
References
- The natural history of periodontal disease in man: prevalence, severity, and extent of gingival recession. J Periodontol. 1992; 63:489-495
- Chambrone L, Sukekava F. Root-Coverage Procedures for the Treatment of Localized Recession-Type Defects: A Cochrane Systematic Review. J Periodontol. 2010; 81:452-478.
- Zucchelli G, Mounssif I. Periodontal plastic surgery. Periodontology. 2015; 68: 333–368.
- Chopra A, Thomas BS. Amniotic Membrane: A Novel Material for Regeneration and Repair. J Biomim Biomater Tissue Eng. 2013; 18: 106-113.
- Silness J, Löe H. Periodontal disease in pregnancy. II. Correlation between oral hygiene and perio- dontal condition. Acta Odont Scand. 1964; 22: 112-135.
- Löe H, Silness J. Periodontal disease in pregnancy. I. Prevalence and severity. Acta Odont Scand. 1963; 21: 533-551.
- Muhlemann HR, Son S. Gingival Bleeding-A Leading Symptom In Initial Gingivits. Helvetica Odontologica Acta. 1971; 15: 107- 113.
- Cairo F, Rotundo R, Miller Jr, Pini Prato. Root Coverage Esthetic Score: A System to evaluate the Esthetic Outcome of the Treatment of Gingival Recession Through Evaluation of Clinical Cases. J Periodontol. 2009; 80: 705-710.
- De Sanctis M, Zucchelli G. Coronally advanced flap: A modified surgical approach for isolated recession-type defects: Three-year results. J Clin Periodontol. 2007; 34: 262-268.
- Marggraf E. A direct technique with a double lateral bridging flap for coverage of denuded root surface and gingival extension. Clinical evaluation after 2 years. J Clin Periodontol. 1985; 12: 69-76.
- Gomes JA, Romano A, Santos MS, Dua HS. Amniotic Membrane Use in Ophthalmology. Current Opinions in Ophthalmology. 2005; 16: 233-240.
- Ghahroudi RA, Khorsand A, Reza A, Seyedzadeh. Comparison of Amnion Allograft with Connective Tissue Graft for Root Coverage Procedures: A Double- Blind, randomized, Controlled Clinical Trial. Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology. 2013; 154: 101-12.
- Chakraborthy S, Sambashivaiah S, Kulal R, Bilchodmath S. Amnion and Chorion Allografts in Combination with Coronally Advanced Flap in the Treatment of Gingival Recession: A Clinical Study. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research. 2015; 9: ZC98-ZC101.
- Borghetti A, Gardella JP. Thick Gingival Autograft for the Coverage of Gingival Recession: A Clinical Evaluation. International Journal of Periodontics and Restorative Dentistry. 1990; 10: 216-29.
- Rinastiti M, Harijadi, Santoso AL, Sosroseno W. Histological Evaluation of Rabbit Gingival Wound Healing Transplanted with Human Amniotic Membrane. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. 2006; 35: 247-251.
- Gurinsky B. A novel dehydrated amnion allograft for use in the treatment of gingival recession: an observational case series. The Journal of Implant & Advanced Clinical Dentistry. 2009; 1: 65–73.
- Arya SK, Bhala S, Malik A, Sood S. Role of Amniotic Membrane Transplantation in Ocular Surface Disorders. Nepalese Journal of Ophthalmology. 2010; 2: 145-153.
- Cortellini P, Pini-Prato G, Tonetti M. Periodontal regeneration of intrabony defects. Effect of oral hygiene on long term stability. Journal of Clinical Periodontology. 2005; 21: 571-642.
