Abstract
It is proposed here that a deficiency in Bradykinin (BK) might be a significant factor in the pathophysiology of hypertension. In this regard, it is suggested that the role of renal BK is to excrete the excess of sodium. Therefore, a reduction in the generation of renal BK may be the cause in the development of hypertension as a result of the accumulation of sodium in the body. Thus, the development of a compound having renal kallikrein-like activity may serve the purpose of excreting excessive sodium from the kidney in the treatment of hypertension. Also it has been demonstrated that transgenic mice over-expressing renal tissue kallikrein were hypotensive and that administration of aprotinin, a tissue kallikrein inhibitor, restored the BP of the transgenic mice. Recently, it has been proposed that tissue kallikrein gene delivery into various hypertensive models exhibits protection, such as reduction in high blood pressure, attenuation of cardiac hypertrophy, inhibition of renal damage and stenosis. This may indicate the future therapeutics aspect of kallikrein gene therapy for cardiovascular and renal pathology.
Keywords: Bradykinin system; Hypertension
Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases are the most common cause of mortality worldwide. Hypertension and diabetes are the two major risk factors in the development of cardiac hypertrophy, ischemic heart disease and cardiac failure. In Kuwait, high rate of prevalence of hypertension and diabetes has been described. Previous studies have indicated altered activities of the Bradykinin (BK)-generating components in hypertension and diabetes [1]. Bradykinin is pharmacologically active polypeptide that can promote both cardiovascular and renal function, for example, vasodilation, natriuresis, diuresis and release of Nitric Oxide (NO) [2,3]. In addition, B2 kinin receptors are present in the cardiac endothelial cells which may enhance the biosynthesis and release of NO [4]. Demonstrated that reduced tissue kallikrein levels may be associated with the development of high blood pressure in Spontaneously Hypertensive and Diabetic Rats (SHR). The BK may produce their pharmacological effects via NO and cyclic GMP release [5] (Figure 1).
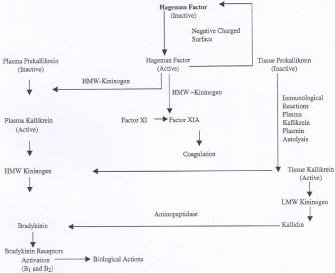
Figure 1: Shows the kinin formation and its inactivation.
Hypertension and Bradykinin system
Hypertension is a major risk factor in the development of cardiovascular diseases, such as coronary heart disease, congestive heart failure and peripheral vascular & renal diseases. There is ample evidence documenting the role of BK in the pathogenesis of hypertension [6,2]. The pharmacological actions of BK in regulation of systemic BP are vasodilation in most areas of circulation, reduction in total peripheral vascular resistance and regulation of sodium excretion from the kidney [7]. The role of KKS in hypertension was established by Margolius and co-investigators [8] with the observations that urinary kallikrein excretion is significantly reduced in hypertensive patients.
In addition, transgenic mice over-expressing renal tissue kallikrein were hypotensive and that administration of aprotinin, a tissue kallikrein inhibitor, restored the BP of the transgenic mice [9]. We have shown the suppression of hypotensive responses of ACEIs by aprotinin in SHR [10]. These findings highlight a role of tissue kallikrein in the regulation of BP. Recently; it has been proposed that tissue kallikrein gene delivery into various hypertensive models exhibits protection, such as reduction in high BP, attenuation of cardiac hypertrophy, inhibition of renal damage and stenosis [11-13]. This may indicate the future therapeutics prospect of kallikrein gene therapy for cardiovascular and renal pathology.
ACEIs are currently used in the treatment of both clinical and experimental hypertension [14,15]. Kininase II inhibitors could lower BP by inhibiting the biodegradation of kinin as well as blocking the formation of angiotensin II (AgII). Previous study has demonstrated that urinary kallikrein excretion was found to be diminished in family members at risk for hereditary hypertension and that urinary kallikrein may be one of the major genetic markers associated with family history of hypertension [16].
Left ventricular hypertrophy is regarded as an independent risk factor in hypertensive patients in inducing cardiac abnormalities. BK can counter the development of LVH in rats with hypertension produced by aortic banding [17,18]. This anti-hypertrophic effect of BK was abolished by the B2 receptor antagonist treatment as well as by NO synthetase inhibitor. Thus, the BK has a role in protecting the heart against developing LVH by releasing NO in this model of hypertension induced by aortic banding. In this regard, we have for the first time demonstrated that the lack of the cardiac KKS could be responsible for the induction of LVH in SHR and SHR with diabetes [4]. It is suggested that the reduced cardiac tissue kallikrein and cardiac kininogen may be responsible for reduced BK generation in the heart. Therefore deficient components of the BK in the heart may be responsible for inducing excessive hypertrophy and myocardial dysfunction in cases of hypertension. It is highly desirable to develop stable compounds of BK to evaluate their efficacy and potency in cases of cardiac failure, cardiac ischemia and hypertension.
We have recently observed the reduction in plasma prekallikrein prekallikrein levels in Kuwaiti patients with hypertension those they did not receive the treatment. This might be serving as early marker in the development of renal and cardiovascular abnormalities [19,20] (Figure 2).
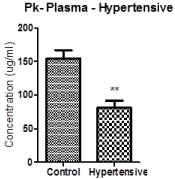
Figure 2: Plasma prekallikrein levels in healthy subjects and hypertensive
patients. Data are presented as mean and SEM. There is a **(p<0.001)
significance between control and hypertensive. Number=4 (unpublished
observation by Sharma et al. 2017).
References
- Leeb-Lundberg LM, Marceau F, Müller-Ester W, Pettibone DJ, Zuraw BL. International Union of Pharmacology. XLV. Classification of the kinin receptor family: From Molecular mechanisms to Pathophysiological consequences. Pharmacol Rev. 2005; 57: 27-77.
- Katori M, Majima M. A missing link between a high salt intake and blood pressure increase. J Pharmacol Sci. 2006; 100: 370-390.
- Linz W, Wiemer G, Scholkens BA. Cardioprotective actions of bradykinin in myocardial ischemia and left ventricular hypertrophy. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1994; 8: 1949-1954.
- Sharma JN, Uma K, Yusof APM. Altered cardiac tissue and plasma kininogen levels in hypertensive and diabetic rats. Immunopharmacol. 1999; 43: 129-132.
- Carretero OA. Vascular remodeling and the kallikrein-kinin system. J Clin Invest. 2005; 115: 588-591.
- Sharma JN. Hypertension and bradykinin system. Curr Hypertens Reports. 2009; 11: 178-181.
- de Freitas FM, Farraco EZ, De Azevedo DF. General circulatory alterations induced by intravenous infusion of synthetic bradykinin in man. Circulation. 1964; 29: 66-70.
- Margolius HS, Geller R, Pisano JJ. Altered urinary kallikrein excretion in human hypertension. Lancet. 1971; 2: 1063-1065.
- Wang C, Chao L, Chao J. Human tissue kallikrein induces hypotension in transgenic mice. Hypertension. 1994; 23: 236-243.
- Sharma JN, Amrah SS, Noor AR. Suppression of hypotensive responses of captopril and enalapril by kallikrein inhibitor aprotinin in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Pharmacology. 1990; 50: 363-369.
- Chao J, Chao L. Kallikrein gene therapy in hypertension, cardiovascular and renal diseases. Pharmacol Res. 1997; 35: 517-522.
- Chao J, Chao L. Kallikrein-kinin in stroke, cardiovascular and renal disease. Exp Physiol. 2005; 90: 291-298.
- Chao J, Bledsoe G, Yin H, Chao L. The tissue kallikrein-kinin system protects against cardiovascular and renal diseases and ischemic stroke independently of blood pressure reduction. Biol Chem. 2006; 387: 665-675.
- Antonacci M. Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1982; 22: 57-87.
- Sharma JN, Fernandez PG, Kim BK. Cardiac regression and blood pressure control in Dahl rats treated with enalapril maleate (MK 421), an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor. J Hypertension. 1983; 1: 251-256.
- Kailasam MT, Martinez JA, Cervenka JH, Yen SSC, O’Connor DT, Parmer RJ. Racial differences in renal kallikrein excretion: Effect of the ovulatory cycle. Kidney Int. 1998; 54: 1652-1658.
- Linz W, Wiemer G, Scholkens BA. Bradykinin prevents left ventricular hypertrophy in rats. J Hypertension. 1993; 11: 96-97.
- Madeddu p, Emanueeli C, El-Dahr S. Mechanisms of disease; tiss kallikrein-kinin system in hypetension and vascular remodeling. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol. 2007; 3: 208-221.
- Webster ME, Gilmore JP. Influence of kallidin-10 on renal function. Amer J Physiol. 1964; 206: 714-718.
- Woolly-Miller C, Chao J, Chao L. Restriction fragment length polymorphism’s mapped in spontaneously hypertensive rats using kallikrein probs. J Hypertension. 1989; 7: 865-871.
