Keywords
Atrial fibrillation; Spontaneous echo contrast
Clinical Image
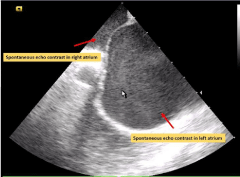
A 55-year-old man with symptomatic drug-refractory paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation (AF) was arranged to receive catheter ablation of AF. The CHA2DS2-VASc score is zero and no anticoagulant was prescribed before ablation. Computed tomography of the heart revealed normal size of the left atrium and no thrombus in the left atrial appendage. AF attacked one day before ablation and spontaneously terminated at the start of general anesthesia for ablation. The intracardiac echocardiography revealed spontaneous echo contrast, “smoke”, in the both right and left atria in sinus rhythm (Figure 1). Although electricity was converted spontaneously to sinus rhythm, the mechanical function of atria did not completely recover. Ablation procedure was terminated due to high risk of stroke. Although with a CHA2DS2-VASc score of zero, the paroxysmal AF patient has high risk of stroke. The anticoagulant was prescribed to this patient for stroke prevention after discharge.