Abstract
Background: Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS) are a group of hematologic malignancies of bone marrow characterized by morphologic and functional abnormalities in hematopoietic stem cells and with various degrees of cytopenias in peripheral blood. It is with one or more cytopenias depending on bone marrow dysfunction.
Chemokines are the cytokines that help the leukocytes and stem cells for chemotaxis in case of inflammation and homeostasis.
Aim: In this study we aimed to investigate the polymorphisms of MCP- 1A251G and CCR2V641 genes in MDS. These genes were related with solid tumors but have not been studied in MDS yet.
Study Design: We designed our to study to evaluate these 2 polymorphisms in 39 MDS patients, comparing them with 110 healthy volunteer subjects.
Methods: Thirty-nine MDS patients were included in this study and compared with 110 healthy volunteers.
Results: There was a significant difference between patient and healthy groups in regard of frequencies of MCP-1A251G genotypes and gene alleles (p:0.001 and p:0.0002). But there was no difference in CCR2V641 genotype (p>0.05).
Also the frequencies of MCP-1 AA genotype were higher in MDS patients versus healthy controls. The individuals with MCP-1 AA genotype have five-fold increased risk for the development of MDS (p:0,000; x2:13.60; OR:5.30; %95 CI:2.05-13.66).
The frequencies of MCP-1 AG and MCP-1 G+ genotypes were higher in healthy controls versus MDS patients (p:0.002; x2:9.39; OR:0.24; %95 CI:0.094- 0.62 and p:0.000; x2:13.60; OR:0.189; %95 CI:0.073-0.48).
Conclusion: The individuals who have genotypes of MCP-1AA have higher risk for MDS but MCP-1 AG and MCP-1 G+ were significantly higher in healthy population and may have a protective role versus the development of MDS.
Our study was the first study investigating the role of MCP-1A2581G and CCR2V641 gene polymorphism in MDS population. These effects should be further studied in larger group of patients for determining the exact role of these genes.
Keywords: Polymorphisms; Myelodysplastic syndrome; Chemokines
Introduction
Myelodysplastic syndromes are a group of clonal hematologic malignancies characterized as cytopenias in peripheral blood and morphologic and functional abnormalities in hematopoietic stem cells [1,2].
Chemokines are the cytokines that help both leukocytes and stem cells for chemotaxis. Chemokines are the molecules in protein structure with multiple domains. Until now more than 50 chemokines and 20 chemokine receptors had been identified. Some of the chemokines play role in the leukocyte migration and also has impact on degranulation of leukocytes and angiogenesis (e.g MCP-1- monocyte Chemoattractant protein) [3]. Chemokine receptors (e.g CCR2) are G-protein-coupled proteins and expressed on the surface of leukocytes. Chemokines binds the specific G-protein-coupled cell surface receptors on targeted cells and stimulates intracellular signal pathway and induces the cell migration and activation. Chemokines modulate the tumor growth and angiogenesis but also inhibit the stem cell proliferation [4].
The aim of this study is to clarify the role of MCP-1A2518G and CCR2V64I gene polymorphisms in MDS patients. These chemokines have been studied in solid tumors such as pancreatic adenocarcinoma, renal cell carcinoma and over carcinoma but not in MDS population earlier.
Materials and Methods
Study population
Our study population includes 39 patients who were diagnosed as MDS in our facility. Also 110 healthy volunteers without any malignancy history and normal laboratory examination were included as a control group. All individuals accepted the informed consent form due to local ethics committee.
Gene polymorphisms
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) is isolated from leukocytes via Miller et al method [5]. The variations of the genes were investigated with polymerase chain reaction/restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR/RFLP). The PCR products MCP-1A2318G and CCR2V64I were processed by the restriction enzymes PvuII and BsaBI. These PCR products examined over %2 agarose gel electrophoresis and compared with 50-1000 bp DNA molecular weight scale (Invitrogen, Grand Island, NY, USA). Two independent examiners had studied all the samples.
Statistics
All the analyses were run by SPSS software package (version 20.0 SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The results were published as mean +/- standard derivations. The MCP-1A2318G and CCR2V64I genes genotypes were compared between MDS and healthy population with Chi-square method.
Results
In our study group, median age was 69 years for healthy volunteers and 68.4 years for MDS population and there was no significant difference between 2 groups. The refractory cytopenias with multiline age dysplasia include %33 of the patients according to World Health Organization 2008 classification. Nearly %60 of the patient group had normal cytogenetic s (46XX/46XY). Also nearly half of the patient group was classified under 0.5 point according to International Prognostic System (IPSS) (Table 1).
Healthy(n=110)
MDS(n=39)
P-value
Median age, year
69.02±4.97
68.48±9.71
0.658
Female/Male
48/62
22/17
0.17
MDS subtypes(WHO)
(%)
MDS-U
2.6
RA
30.8
RAEB-1
10.3
RAEB-2
5.1
RA-IZOLEDELSQ
5.1
RARS
10.3
RCMD
33.3
RCUD
2.6
Cytogenetic Evaluation
11Q23(DEL)
2.6
46XX
33.3
46XY
5.1
46XX
7.7
46XY
30.8
47XY+8
2.6
ADD(1)P32-36(18)
2.6
DEL(11)(Q13Q23),DERS,DER1
2.6
DEL(20)(Q11,2)
2.6
DEL(5)(Q31Q35)+8,-18
2.6
DEL5(Q12Q33(16)
2.6
DELSQ
2.6
Not available
IPSS
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
34.8
47.8
8.7
4.3
4.3
Table 1: Baseline Characteristics.
There was a clinically significant difference between the control and MDS groups according to distribution of genotypes and alleles of MCP-1A2518G (p:0.001 and p:0.0002). But there was no difference in CCR2V61I genotype (p>0.05) (Table 2).
Polymorphism
Control
(n:110)
MDS
(n:39)
P-value
N
%
N
%
MCP-1A2518G
AA
56
50.9
33
84.6
0.001
GG
7
6.4
0
0
AG
47
42.7
6
15.4
A
159
72.27
72
92.3
0.0002
G
61
27.72
6
7.63
CCR2V64I
GG
85
77.3
32
82.1
0.330
AA
6
5.5
0
0
GA
19
17.3
7
17.9
A
189
85.9
71
91.02
0.24
G
31
14.09
7
8.97
Table 2: Distribution of genotype frequencies in control and MDS groups.
The frequencies of AA genotypes in MCP-1 genes were significantly higher in MDS patients versus control group. The risk of MDS is nearly five-fold increased in AA genotype carriers (Figure 1) (p:0.000; c2:13.60, OR:5.30, %95 CI: 2.05-13.66). Controversially, the frequencies of AG and G+ genotypes were significantly higher in healthy control group versus MDS group.
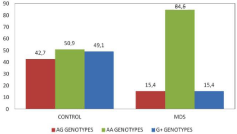
Figure 1: The frequencies of MCP-1A2518V genotypes.
We can interpret that AG and G+ genotypes have a protective effect on development of MDS (p:0.002; c2:9.39; OR:0.24, %95 CI: 0.094-0.62 and p:0.000; c2:13.60, OR:0.189, %95 CI: 0.073-0.48).
Discussion
Chemokines are a kind of cytokines that help both leukocytes and stem cells for chemotaxis. Also chemokines modulate the tumor growth and angiogenesis but inhibit the stem cell proliferation.
The aim of this study is to clarify the role of MCP-1A2518G and CCR2V64I gene polymorphisms in MDS patients. These chemokines have been studied in solid tumors such as pancreatic adenocarcinoma, renal cell carcinoma and over carcinoma but not in MDS population earlier.
Sica et al have studied the co-incidence of MCP-1 and CCR2 in ovary carcinoma. And they found out that the low levels of CCR2 are associated with the decrease in anti-inflammatory response and chemotaxis in advanced stage patients [6].
In another study, Yang et al also investigated the incidence of MCP-1 and CCR2 in non-small cell lung cancer patients. In this study 338 patients were compared with 200 healthy controls. MCP-1 AA genotype was significantly higher in patient group and may have a role in disease pathophysiology of disease, but there was no difference in CCR2 polymorphism [7].
Liu et al compared 416 renal cell carcinoma patients with 458 healthy controls. In the patients group, the incidence of MCP- 1 GG genotype was 1, 89 times higher than AA genotype. And also CCR2 AA genotype was 2.69 times higher than GG genotype. According to the results of this study, the MCP-1 A/G and CCR2 G/A polymorphisms can be a new risk factor and prognostic marker in renal cell carcinoma [8].
In hepatocellular carcinoma patients, Yeh et al investigated the role of MCP-1 and CCR2 polymorphism in predisposition and pathophysiology of disease. There was no difference in MCP-1 GA gene polymorphism in neither healthy nor patient group. But the incidence of CCR2 V641 gene polymorphism was higher in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Although incidence was higher there was no association between polymorphism and pathophysiology of disease [9].
Monti et al studied the role of MCP-1/CCL2 in patients with pancreatic carcinoma. The results were correlated with the incidence of CCL2 have a negative impact in disease progression [10].
In the time we applied this research, there was no study in the literature which investigated the role of these gene polymorphisms in MDS patients.
In our study we compared 39 patients previously diagnosed as MDS according to WHO criteria with 110 healthy controls. Both groups were investigated for gene polymorphisms in MCP-1A2518G and CCR2V64I.
There was a clinically significant difference in frequency of MCP 1A2518G genotypes and alleles when patients group compared with healthy controls (p:0.001; p:0.0002). But there was no difference in frequency of CCR2V64I genotype (p>0.05).
The frequency of MCP-1 AA genotype was higher in MDS group versus healthy controls and the risk of MDS development was nearly five-fold increased in this genotype carriers (p:0.000; x2:13.60; OR:5.30; %95 CI:2.05-13.66).
But the frequency of MCP-1 AG and G+ were significantly higher in healthy controls versus MDS patients (p:0.002; x2 :9.39; OR:0.24; %95 CI:0.094-0.62 and p:0.000; x2 :13.60; OR:0.189; %95 CI:0.073- 0.48 respectively).
Study Limitations
The main limiting factor of this study is the number of patients group. The results of further studies with higher number of patients will clarify the role of the gene polymorphisms in MDS patients, and maybe we can adopt these gene polymorphisms as a new risk factor and prognostic marker of MDS.
Conclusion
As a result, the MCP-1 AA genotype carriers are under higher risk in MDS development but MCP-1 AG and MCP-1 G+ gene polymorphism have a protective role in MDS development.
In this study we discovered the role of gene polymorphisms both augmenting the risk of disease development and also adding positive addition on protective effects.
References
- Pisani DF, Rainaldi A. Management of high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes. Clinical reviews in Oncology/Hematology. 2001; 40; 215-228.
- Gilliland GD, Dunbar EC. Myelodysplastic syndromes. In: Blood, Principles and Practice of Hemathology. Ed: Handin I R et al, second edition, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia. 2003; 355-377.
- Rossi D, Zlotnik A. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000; 18: 217-242.
- Bachelerie F, Ben-Baruch A, Burkhardt AM, Combadiere C, Farber JM, et al. International Union of Pharmacology. LXXXIX. Update on the extended family of chemokines receptors and introducing a new nomenclature for atypical chemokines receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2014; 66: 1-79.
- Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988; 16: 1215.
- Sica A, Saccani A, Bottazzi B, Bernasconi S, Allavena P, Gaetano B, et al. Defective expression of the monocyte chemotactic protein-1 receptor CCR2 in macrophages associated with human ovarian carcinoma. J Immunol. 2000; 164: 733-738.
- Yang L, Shi GL, Song CX, Xu SF. Relationship between genetic polymorphism of MCP-1 and non-small-cell lung cancer in the Han nationality of North China. Genet Mol Res. 2010; 9: 765-771.
- Liu GX, Zhang X, Li S, Koiiche RD, Sindsceii JH, Song H. Monocyte chemotactic protein-1 and CC chemokines receptor 2 polymorphisms and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2013; 34: 2741-2746.
- Yeh CB, Tsai HT, Chen YC, Kuo WH, Chen TY, Hsieh YH, et al. Genetic polymorphism of CCR2-64I increased the susceptibility of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 2010; 102: 264-270.
- Monti P, Leone BE, Marchesi F, Balzano G, Zerbi A, Scaltrini F, et al. The CC chemokines MCP-1/CCL2 in pancreatic cancer progression: regulation of expression and potential mechanisms of ant malignant activity. Cancer Res. 2003; 63: 7451-7461.
