
Research Article
Austin Pathol. 2016; 1(1): 1003.
Evaluation of Immunological Reactivity in Patients with Cataract Who Received Low Doses of Ionizing Radiation
Yeltokova M*
JSC- Astana Medical University, Institute of Radiobiological Research, Kazakhstan
*Corresponding author: Yeltokova M, Institute of Radiobiological Research, JSC Astana Medical University, Kazakhstan
Received: May 23, 2016; Accepted: July 25, 2016; Published: July 29, 2016
Abstract
Mathematical calculation of the six integral hematological indices of the leukogram showed the decrease of functional metabolic and phagocytic activity of micro and macrophages in cataracts of Liquidators of the Accident Consequences (LAC) on Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant (CNPP), who live in Kazakhstan (Astana city) and in workers of the atomic industry of the Stepnogorsk Mining And Chemical Combine (SMCC), RK on the extraction and processing of concentrates of enriched uranium. The specificity of the process of autosensibilization leukocyte antigens of the lens, among these people was estimated in the reaction of the leukergy stimulated by lens antigens in vitro. Leukergy significantly manifested in LPA exposed to ionizing radiation at a dose of 3.3 to 18.2 cGy, and ranged from 5.7% to 8.0% and 9.0% of the workers «SMCC» at a total effective dose of 61,16±21,64 mSv, with 1.0% in the control group. Thus, the proposed method of leukergy in the presence of lens antigens in vitro is quite informative and resource useful for the empowerment of the differential diagnosis of cataract of radiation genesis.
Keywords: Integrated Hematology Index; Stimulated Leukocyte Agglomeration; Radiation Cataract; Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant (CNPP); Stepnogorsk Mining and Chemical Combine (SMCC)
Introduction
The increasing role of atomic energy in the world and particularly in Kazakhstan requires a special attention to the problem of investigating the deterministic effects initiated by the ionizing radiation with low Linear Energy Transfer (LET) in visual organ and especially in one of its most radiosensitive structures-lens.
In latest reports of the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) about the unpredicted high incidence of lens pathology and probability of lens effects with lower (or probably lower) threshold doses [1,2,3]. Therefore, in the process of optimization of radiobiological response of the lens, as the result of low dose radiation exposure, it is important to study the process of self-tolerance, autoimmune reaction of lens on radiation exposure, taking into account its immunological privilege and architectonics [4,5]. The study aim is to evaluate the immunological reactivity with cataract under of short-term and prolonged exposure to low doses of ionizing radiation.
Materials and Methods
The study of immune diagnostics cataract genesis of radiation as a result of the randomization of the total population by random selection of the exposed group-I was formed and consisted of 62 patients, males, liquidators of the accident consequences on Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant (CNPP), who live in Kazakhstan (Astana city), at the age of 42 to 60 years old, with the early and immature stage of a Posterior Capsular Cataract (PSC). Depending on the year of entering the zone of contingency operations, and the obtained average dose of radiation exposure, according to the Russian state medical radiation-measuring registry [6] patients were divided into 3 subgroups: The I subgroup was composed of 32 men, with the average age of 34 years at the time of the accident, and the obtained dose of radiation exposure in 1986 was 18.2±0.6 cGy; the II subgroup-consisted of 18 men, at the age of 37-45 years, and with radiation exposure dose in 1987 of 8.4±0.6 cGy; and the III subgroup included 12 men, with the age of 40-52 year at the time of the accident, and radiation exposure dose in 1988-1989 of 3.3±0.3 cGy. The duration of stay in the zone of heightened radiological emergency constituted 5-30 days [7]. The exposed group-II was represented by 39 men, workers of the atomic industry, by the extraction unit of the Stepnogorsk Mining and Chemical Combine (SMCC), RK on the extraction and processing of concentrates of enriched uranium with the early and immature stage of a Posterior Capsular Cataract (PSC). Mean age is 51.1±11.1 years old. The average professional experience of the subjects of this group was 19.2±12.8 years. The total effective dose in average was 61.2±21.7 ms, Screening-a study of the exposed group-II conducted the 2013-2014 as part of a research project of Ministry of Health of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
The unexposed groups included (196 men, without exposure to ionizing radiation in history) of them comparison group (SG)-97 patients, at the age of 45-58 years with different stages of development of a cataract A control group constituted of 99 patients, of the similar age without lens pathology. Risk factors of a cataract were examined in the both above described groups. Follow-up period of the study group and the comparison group is about 10 years. A diagnostic examination of the lens of patients was conducted through a direct focal illumination of slit lamp with a narrow angle of the microscope (10-20 degrees) and maximally narrow lighting gap. The use of mathematical integral indices, part of which are changed already in the pre-morbid period or on the earliest stages of the disease, allows to assess the status of various chains of immune system without referring to special diagnostic methods [8,9]. Based on the results of the peripheral blood analysis, we have conducted mathematical calculation of the six integral indices, and thus we were able to assess indirectly the status of various chains of immune system in patients with cataract: Leucocytal Index (LI), Leucocytal Index of Intoxication (LII), Leucocytes and ESR Ratio Index (LESRRI), Lymphocytic Granulocytic Index (LGI), Neutrophil and Lymphocyte Ratio Index (NLRI), Neutrophil and Monocyte Ratio Index (NMRI). Further, in the immunological aspect we have examined the reaction of leukergy stimulated by lens antigens in vitro by the method of Wexler (1977) which allows assessing the peculiarity of the process of autosensibilization of leucocytes in peripheral blood to lens antigens.
We used the lens extract as an antigen, which was obtained by standard technology: Extracapsular extraction of cataract. “Lens antigen” diagnosticum was obtained by biochemical method [10,11,12]. The test was considered as positive, if under in the exposed group the agglomeration index in the presence of lens antigen stimulator was for 1/3 higher than in control [7].
Statistical analyses were carried out using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences of Windows version 15.0 (SPSS, Chicago, III, USA). Data were expressed as Mean±SD with a significance level of p<0.001. Intergroup comparisons were evaluated by one-way ANOVA. In cases of significant differences among measurements the Bonferroni-adjusted Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used as a post hoc analysis. In all analyses, a p-value less than 0.05 were accepted as statistically significant.
Results
The study of the clinical features of cataract in individuals exposed groups-I and -II was characterized mostly as complicated, the initial stage, regardless of the exposure ratio. The data from (Table 1) shows that leukocyte index (LI) reflecting the relationship of humoral and cellular parts of the immune system, as a result of the calculation in time (2003-2013) in persons of comparison group was within the control limits. The liquidators of the accident consequences on CNPP (Table 2) affected by short-term radiation, this indicator in the I-subgroup exceeded the level of healthy individuals by 66.4% (p<0.001) 2002-2003 and 69.2% (p<0.001) in 2012-2013, in the -II -. 25.9% (p<0.001) in 2002-2003 and 75.0% (p<0.001) in 2012-2013., 23.2% (p<0.05) 2002-2003 and by 70.4% (p<0.05) in 2012-2013 in subgroup-III (Table 3). At the same time among workers of «SMCC» who have received the total effective dose of ionizing radiation accounted to be consistent with the level of LAC subgroup-I - 66.7% (p<0.001) (Table 4). When calculating the Leucocytal Index of Intoxication (LII) in all groups except the control group an increase was noticed. So, there was an increase of this indicator by 1.3 times in the comparison group (p<0.02). In LAC the first and second subgroups LII exceeds reference limits 1.8 times (p<0.001) and in the third group 1.6 times (p<0.001), which is probably due to higher levels of endogenous intoxication in 2002-2003. At the time there was an increase LII index by 22.9% (p<0.05) in the SG, by 79% (p<0.001) in the subgroup of LAC in I- and 78% (p<0.001) in the II- and IIIsubgroups. Do staff «SMCC» LII was 71% (p<0.001).The leucocytes and ESR ratio index (LESRRI) of persons with cataract (SG) was higher for 42% (р<0.001) in 2003-2006 and by 33.3% in 2011-2013 than the results of a control group. As for cataract patients exposed subgroup-I, the highest rates were registered LESRRI in subgroup 1 and 2, the data of which exceeded the standard values by 59% in 2003- 2006 (p<0.001) and 58.1% (p<0.001). And in 2011-2013 the highest LESRRI we noted in these subgroups by 99.2% (p<0.001) and 99.4% (p<0.001) correspondingly. Patients in subgroup-III 2003-2006, also showed an increase of this indicator by 49.4% (p<0.05) relative to the control data Rupp. In Exposed group-II the workers «SMCC»- LESRRI was 99.7% (р<0.001) However, when calculating the Lymphocyte Granulocyte-Index (LGI), which allows to differentiate autointoxication, only decrease has been found in the comparison group by 36.4% (p<0.001), in 2003-2006 and, conversely, an increase in SG by 39.3% (p<0.05) and from 84.7 to 87.8% (p<0.001) in the exposed group-I in 2012-2013 on the results of the control groups. In the exposed group-I in 2002-2003, regardless of the dose of ionizing radiation LGI index was in the normal range. The LGI index of the staff of the «SMCC» amounted to 87.9% (p<0.001).
Hematological Indices
The Unexposed Groups
2003-2006
2011-2013
Control Group
(N=99)
Comparison Group
(N=97)
Control Group
(N=99)
Comparison Group
(N=97)
LI
0.43±0.02
0.51±0.09
0.16±0.01
0.27±1.67
LII
0.83±0.07
1.13±0.11*
1.88±2.02
2.44±1.67
LESRRI
1.65±0.24
2.84±0.21*
0.02±0.00
0.03±0.00
LGI
4.01±0.18
2.55±0.12*
0.54±0.03
0.89±0.03
NLRI
2.54±0.11
1.98±0.38
24.04±1.58
13.91±1.82
NMRI
17.3±3.42
45.08±3.14*
1.06±0.08
1.02±0.11
Note: *Р˂0.05
Table 1: Entropy of integral hematological indices the unexposed groups (М±m) for the period of 2003-2013 years.
Hematological
Indices
Control Group
(n=99)
Exposed Group I
I subgroup
(n=36)
II subgroup
(n=12)
III subgroup
(n=12)
LI
0.43±0.02
1.28±0.09*
0.58±0.04*
0.56±0.06*
LII
0.83±0.07
1.49±0.09*
1.47±0.11*
1.34±0.08*
LESRRI
1.65±0.24
4.28±0.05*
3.94±0.21*
3.26±0.76*
LGI
4.01±0.18
4.03±0.06
4.19±0.12
3.97±0.22
NLRI
2.54±0.11
1.99±0.77
1.74±0.35
1.83±0.41
NMRI
17.3±3.42
47.95±2.1*
49.53±3.15*
48.84±2.18*
Note:*р˂0.05
Table 2: Entropy of integral hematological indices the LPA on CNPP whis cataract who received a short-term dose of ionizing radiation (M±m) from 2002-2003.
Hematological
Indices
Control Group
(N=99)
Exposed Group I (N-75)
I Subgroup
(N=36)
II Subgroup
(N=12)
III Subgroup
(N=12)
LI
0.16±0.01
0.52±0.02*
0.64±0.03
0.54±0.05
LII
1.88±2.02
8.86±0.47*
8.69±063
8.69±0.63
LESRRI
0.02±0.00
2.77±0.25*
2.52±0.18
3.24±0.32
LGI
0.54±0.03
4.44±0.17
5.27±0.25
4.38±0.38
NLRI
24.04±1.58
2.19±0.09
1.92±0.21
2.45±0.39
NMRI
1.06±0.08
2.63±0.15
4.57±0.27
3.55±0.27
Note: * Р˂0.05.
Table 3: Entropy of integral hematological indices the LPA on CNPP with cataract who received a short-term dose of ionizing radiation (M±m) from 2012-2013.
Hematological
Indices
Control Group
(N=99)
Exposed Group II
(N-99)
«SMCC» (N-37)
LI
0.16±0.01
0.48±0.02*
LII
1.88±2.02
6.41±0.40*
LESRRI
0.02±0.00
1.61±0.14*
LGI
0.54±0.03
4.48±0.00
NLRI
24.04±1.58
2.34±0.08
NMRI
1.06±0.08
5.73±0.36
Note: * Р˂0.05.
Table 4: Entropy of integral hematological indices the staff of the Stepnogorsk mining and chemical industry with prolonged exposure to ionizing radiation (M±m) for the period of 2013-2014.
The index of the ratio of Neutrophils and Lymphocytes (NLRI) over time in patients with cataracts in the SG and in both the exposed groups-I and -II, regardless of the multiplicity of radiation tended to decrease. This fact is confirmed by the excellent results of calculating the index ratio of Lymphocytes and Monocytes (LMRI). So patients SG LMRI exceed reference limits by 61.6% (p<0.001) in 2002-2003 in contrast to 2011-2013 for which there was a decrease of 3.8% compared with the control group. Increasing LMRI in LAC on CNPP by 63.9% (p <0.001) in group-I, 65.1% (p<0.001) - in the second and 64.6% (p<0.001) in the third, respectively, in 2002- 2003, and subsequently a further increase in the subgroups I-59.7% (p<0,001), II-75.7% (p<0.001) and III-70.1 (p<0.001). The highest indexes were the subjects of the «SMCC», 81.5% (p<0.001). Results improved method of stimulated leukergy by the lens extract in vitro with cataract. In the study of stimulated leukergy by lens extract the level of leukergy in the control group was 1.03±0.05%, which was determined as a referent limit in the study. Among patients with cataract and no radiation genesis was an increase of leukocytes agglomeration index up to 3.2±0.3% in 2002-2003 which exceeded the reference value of 68%. A similar trend was observed at the time of the study (10 years ago), when the degree of intensity of lymphocytes agglomeration cataract was 3.3±0.2%, exceeding the level of control by 69%. At the same time, LAC on CNPP of cataract who underwent brief exposure to ionizing radiation at a dose of 18.2±0.58 cGy, observed maximum values of leukocytes agglomeration level was 5.8±0.7%. Research conducted in 2012-2013 showed further growth of the index up to 8.2±0.7%, which exceeded both controls of 87% and the value of the comparison group by 60%.
In the II- subgroup, where the ionizing radiation dose was 8.43±0.60 cGy, the sensitivity of peripheral blood leukocytes to radiomodifying agent-antigen lens exceeded the set reference value by 79% and the amount of agglomerates was 4.6±0.5%. After 10 years of study the dynamics of the degree of agglomeration of leukocytes intensity remained at the same level 4.5±0.5% [7].
A similar trend was observed in patients exposed to ionizing radiation at a dose of 3.3±0.31 cGy results agglomeration in 2013 remained on par with 2006 and amounted to 4.0±0.5% and 4.0±0.4%, respectively.
The exposed group-II of extraction unit of the «SMCC» noted an increase in leukocyte agglomeration index to 9.0±0.1% (p<0.001) in 2012-2013 that the control values greater than 88% and in the SG- 69%. From the data in (Figure 1) correlation with sufficient statistical significance is observed (p<0.05), obtained correlation coefficients between the total dose of radiation and index leukergy cataract among workers of the «SMCC».
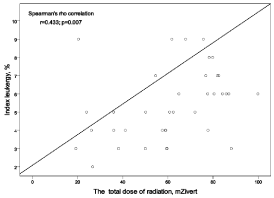
Figure 1: The relationship between the total radiation dose and the index of
leukergy.
Discussion
Radiobiological effects of lens opacities exposed to groups-I and -II regardless of the multiplicity of irradiation is not specific, but at the same time has clinical features that allow them to predict, as the radiation-induced. It should be noted that the study resonates with the research scientists involved in a similar problem in the countries of near and far abroad. Formation of immune dysfunction, decrease in functional and metabolic and phagocytic activity of micro-and macrophages, cataract continuing and worsening over time both in the short-term and with prolonged exposure to small doses of radiation has been reflected in the calculation of the integral 6 hematological parameters So, the calculation of the Leukocyte Index (LI), evidencing the relationship between cellular and humoral immune system, it has shown a direct correlation increase of this indicator on the dose of ionizing radiation. At the same time significant changes were observed in LAC-1986 y., in which whether the results in contrast to the unexposed groups intensified over time (2003-2013) from 66.4% to 69.2% (p<0.001). Despite of the reduction in the dose of radiation exposure in the period from 1987 to 1988 if the index has been significantly increased over time compared to the referent outside by 25.9% (p<0.001) to 75.0% (p<0.001) and 23.2% (p<0.05) to 70.4% (p<0.001), respectively. Endogenous intoxication in the form of increased leucocyte index of intoxication was found in all subjects with cataracts, but more pronounced, and increasing the time 79% (p<0.001)-from the LAC in 1986 control year. LESRRI sharp increase in time from 58% (p<0.001) to 99.4% (p<0,001) were observed in LPA in 1986 and 1987. Ascertaining high to 99.7% (p<0.001) LESRRI the staff «SMCC» suggests that regardless of exposure multiplicity observed the presence of an autoimmune component in the formation of cataracts as a result of exposure to low doses of radiation. On strengthening autointoxication and reducing nonspecific resistance of the body in time to the study groups suggest indicators: lymphocyte-granulocyte index, the ratio of neutrophils and lymphocytes and phagocytic activity of micro and macrophage system. This fact is confirmed by the growth of the index ratio of lymphocytes and monocytes in time in participants of the Chernobyl nuclear power plant in the period from 1986 to 1988 an average of 64.5% (p<0.001) to 75.7% (p<0.001). The fact that the high index of 81.5% (p<0.001) to 92.4% (p<0.001) in subjects «SMCC».
Thus, a comprehensive, adequate mathematical model of integral hematologic indices is more informative than a simple study of the hemogram. It allows evaluating the development of, for eye pathology, homeostasis study groups summarize the data in a single index, to evaluate the effectiveness of the therapy and to determine the future strategy to achieve maximum (safe) therapeutic effect.
Given the high radio sensitivity of privilege and antigenic properties of the lens, leukergy studied in vitro in the presence of the lens reaction to the antigen. It is important that the immunological methods of research (carried out in vitro) as compared to in vivo methods make it possible to establish the diagnosis of cataracts even in clinically expressed little manifestations of the disease, as well as in identifying sensitization to a specific substance in the late period of the disease and any exposure ratio. In addition, in vitro reaction does not cause aggravation of the disease, often observed in a study using Allergic reactions in vivo. Method for determining the adhesive properties of the cells easy to carry out in a routine clinical laboratory in contrast to the similar reactions - inhibition of leukocyte migration (RTML) Reactions Specific Agglomeration of Leukocytes (RSAL), the specific damage response of basophils (RSPB), specific degranulation of basophilic leukocytes [7].
The advantage of the method, unlike the method spontaneous leukergy is that this particular method due to the presence of the lens antigen of the reaction increases leukocyte sensitivity for delayed type reactions, especially to low molecular weight allergens, identifying intensification of oxidative metabolism in the sensitized leukocytes in contact with the allergen, determining its descriptiveness in the specific diagnosis of radiation cataract genesis [13,14].
For the first time the authors set the reference limit of 1.03±0.05% stimulated leukergy a control group. This fact is a direct indication of auto sensibility of a body, in particular, leukocyte antigens as a lens to enhance its adhesive properties. Signs of autoimmune component and qualitative changes of leucocytes, particularly to enhance their adhesive properties with cataract in time (2002-2013), it was observed in the exposed group-I and -II. Thus, subjects of the Exposed group-I, with cataracts, a strong correlation was observed growth of agglomeration time leukocytes dose of ionizing radiation. When dose 18.2±0.58 cGy, the highest rates were observed stimulated leukergyfrom 5.7±0.7% to 8.2±0.7%, exceeding the reference limits 5.4 times (p< 0.001). At LAC 1987 at a dose of radiation of 8.43±0.60 cGy, leukergy index remained at the same level 4.6±0.5% and was higher than in control subjects was 4.8 times (p<0.001). A similar situation in 1988-1989, when LAC beam load 3.27±0.31 cGy the number of leukocytes agglomeration ranged from 4.9±0.5% higher than the data to healthy subjects was 4.7 times (p<0.001). A High leukergy index equal to 9.0±0.1%, ascertained in subjects exposed group 2, extraction unit of the Stepnogorsk Mining and Chemical Combine when the total effective dose of 61.2±21.7 mSv. Thus, the reaction of leukergy direct relationship determined dose of ionizing radiation and the extent of auto sensibility: The higher the dose, the higher the degree of sensitization to leukocyte antigens lens.
Conclusion
In the formation of the pathology of the lens in terms of radiation exposure, the leading role belongs to reduce immunological protection factors, at the same time: Analysis of integral hematological parameters showed that inhibition of functional metabolic and phagocytic activity of micro- and macrophages exhibited in groups -I and -II. Activation of the index from 5.7 to 8.05% (p<0.001), with short-term exposure to low doses of radiation, the persons who participated in the liquidation of the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant and 9.0±0.1% (p<0.001), the staff «SMCC» mining and processing of enriched uranium concentrates at 1.0 % in the control group, evidence of autoimmune aggression to the lens antigens. Thus, the proposed method of leukergy in the presence of lens antigens in vitro is quite informative and resource useful for the empowerment of the differential diagnosis of cataract of radiation genesis.
References
- ICRP. Radio Pathology of skin and eye and radiation risk. ICRP Publication on 85. Ann. ICRP. 2000; 30.
- ICRP (2007). Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. ICRP Publication 103. Ann. ICRP. 2007: 37; 2-4.
- ICRP. Publication 118. Ann. ICRP. 2012; 41:1-2.
- McKenna K, Kapp J. Ocular immune privilege and CTL tolerance. Immunol. 2004; 29: 103-112.
- Niederkorn J. Immune privilege in the anterior chamber of the eye. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2002; 22: 13-46.
- Ivanov V, Tsyb A, Ivanov S, Maksyutov M, et al. The liquidators of the Chernobyl disaster: Radiation-epidemiological analysis of the medical consequences. Monograph. Moscow. Galanis press. 1999.
- Yeltokova M, Zharliganova D, Shaidarov M, Bakhtin M, Kazymbet P, Tel L, et al. Deterministic effect of lens at leukergy of patients who received low doses of ionizing radiation. Oxsford jormal Radiation Protection Dosimetry. 2015; 166: 324-327.
- Kalf-Caliph Y. About leukocyte index of intoxication and its practical value. Physician deal. 1941; 1: 31-35.
- Mustafina J, Kramarenko Y, Kobtseva V. Integral haematological parameters in the assessment of immunological reactivity in patients with ophthalmopathology. Wedge. Lab. Diagnostics. 1999; 5: 47-48.
- Wexler H. Questions of general reactivity. Coll. scientific work of doctors. Tallinn. 1977; 277-285.
- Osterman L. Chromatography of proteins and nucleic acids. Moscow press. 1985.
- Williams B, Wilson K. Methods of practical biochemistry. Moscow: Mir press. 1978.
- Vassilyev H, Kazankova L. The collection of Moscow City Scientific and Practical Conference. Moscow press. 1991.
- Mogilenkova L, Rembovsky V. Phenomena of leukergy in the pathogenesis of hemodynamic disorders in professional intoxication. Toxicological Bulletin. 2006; 5: 8-13.