Research Article
J Bacteriol Mycol. 2014;1(1): 1.
Pneumocystis Jiroveci Pneumonia
Xiangdong Mu
Department of Respiratory Medicine, Peking University First Hospital, China
*Corresponding author: Xiangdong Mu, Department of Respiratory Medicine, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China.
Received: July 15, 2014; Accepted: July 28, 2014; Published: July 29, 2014
Clinical Image
A 23-year-old man was admitted to hospital because of 10-day history of fever. Just before onset of fever he had taken prednisone 60 mg per day for 2 months because of nodular panniculitis. On admission, the patient began to feel a little breathless. Physical examination was normal except for mild tachypnea and tachycardia. Analysis of arterial gas on room air revealed severe hypoxemia. Chest CT scan (Figure 1) revealed diffuse ground glass opacities in both lungs. And what’s your diagnosis?
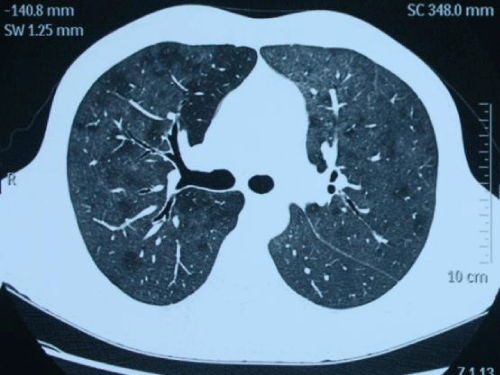
Figure 1: Revealed diffuse ground glass opacities in both lungs. And what’s your diagnosis?
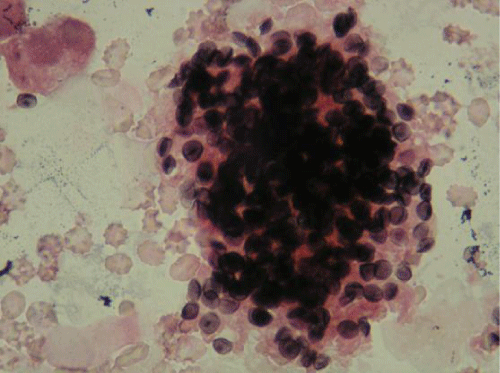
Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid examination (Figure 2) showed numerous cysts of Pneumocystis jirovecii were crowed in foamy alveolar casts (Gomori Methenamine Silver and eosin stains, ×400). The patient was diagnosed as Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP) and treated by trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX). Five days later his fever resolved and after 21-day therapy repeated chest CT scan became completely normal.