
Research Article
J Bacteriol Mycol. 2024; 11(3): 1224.
Antimicrobial Potential of Tinospora Cordfolia (Willd.) Miers (Menispermaceae) Against Disease-Causing Clinical Bacterial Pathogens
Pinky Gupta*; Sushma Dubey
Department of Biotechnology, Kalinga University, India
*Corresponding author: Pinky Gupta,Department of Biotechnology, Kalinga University, Naya Raipur, Chhattisgarh, India. Email: gpinky324@gmail.com
Received: November 12, 2024; Accepted: December 04, 2024; Published: December 05, 2024
Abstract
Tinospora cordifolia is an important plant growth herb belonging to the family Menispermaceae. It is a climbing deciduous and succulent shrub considered traditional medicine in Ayurveda. It has various sources of bioactive compounds and medicinal properties that produce great varieties of secondary metabolites with a broad spectrum of biological activities. It is well known for its nutraceutical food that provides health benefits mainly due to the phytochemicals present in the plant such as alkaloids, flavonoids, proteins, and carbohydrates. It has a wide application in pharmacological research such as antitumor, antiinflammatory, Cerebro-protective, cardio-protective, immunoregulatory, Vasorelaxation, and anxiolytic. Tinospora cordifolia showed antimicrobial activity against a few pathogenic bacteria and pathogenic fungi but not many clinical bacterial pathogens and hospital-acquired infections. In this study, the author focused on the antimicrobial activity of Tinospora cordifolia against eight clinical pathogenic bacteria (Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, MRSA, Proteus mirabilis, Salmonella typhi, Shigella sonnei, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumanii) isolated mainly from patient’s sample. T. cordifolia was extracted from two different solvents, methanol and water. The antimicrobial activity was determined using an agar well diffusion assay. T. cordifolia extract has antibacterial activity against all tested clinical bacterial pathogens and has the highest antibacterial activity against Salmonella typhi in all ratios of methanol concentrations (47.5μg/ml). The Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of Tinospora cordifolia methanol extract was found at 100μg/ml. Methanol solvent concentration with the most active antibacterial activity of the extract was of different concentrations as 300μg/ml followed by 450μg/ml and 500μg/ml.
Keywords: Antibacterial activity; Tinospora cordifolia; Clinical bacterial pathogens; Plant extracts; Salmonella typhi; Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MIC)
Introduction
Herbal preparations are medicines that contain one or more plants in precise amounts to provide benefits for treating, diagnosing, and preventing illness in humans and animals [20]. It is also known as botanical medicine or phytomedicine [16]. It also belongs to the ancient culture called “Amrit”. Earlier in the twentieth century, herbal medicine was the prime medication system as antibiotics or analgesics were not available. The increasing use of allopathic system of medicine due to its fast therapeutic action and herbal medicine gradually lost their popularity among the people. For example, Curcuma has been used in Traditional Chinese Medicine for more than two thousand years to treat anti-inflammatory and robust antioxidants [12]. About 70-80% of people are still using it for their primary health because of the fewer side effects and better compatibility with the human body [28]. Herbal medicine has been rapidly gaining popularity due to its effectiveness, surpassing that of synthetic drugs.
T. cordifolia (synonym: Tinospora sinesis (Lour.) Merr.) is also known as Guduchi/Amrita and its name in Latin: is Tinospora cordifolia (Wild) Hook. f. & Thomson, English: Tinospora Gulancha/Indian Tinospora, Hindi: Giloya. It belongs to the family of Menispermaceae and is found in Myanmar, Sri Lanka, India, and China [28]. The plant is commonly used in traditional Ayurvedic medicine and has several therapeutic properties [4,25] such as jaundice, rheumatism, urinary disorder, skin diseases, diabetes, anemia, inflammation, allergic condition, anti-periodic, radioprotective properties, etc [9,35]. The T. cordifolia root is a powerful emetic for treating bowel obstruction. The plant’s starch serves as an effective remedy for chronic fever, providing relief from burning sensations, and boosting energy and appetite.
Giloya is useful in the treatment of helminthiasis, heart diseases, leprosy, and rheumatoid arthritis, supports the immune system, and the body’s resistance to infections, and supports standard white blood cell structure, function, and levels [13]. It also helps with digestive ailments such as high peracidity, colitis, worm infestations, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, excessive thirst, and vomiting, and even liver disorders like hepatitis [14,24]. These pharmacological activities of the plant are due to its chemical constituents like diterpenoid lactones, glycosides, steroids, sesquiterpenoid, phenolics, aliphatic compounds, essential oils, a mixture of fatty acids, and polysaccharides and are present in different parts of the plant body, including root, stem and whole part [17]. In this study, eight strains of microbial species including Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA), Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Salmonella typhi, Shigella sonnei, Acinetobacter baumanii, and Proteus mirabilis were used for the antimicrobial activity screening. The whole plant of Tinospora cordifolia is isolated using different extraction methods with the help of different solvents and tested against all eight bacterial clinical pathogens isolated from the hospital from patient samples.
Materials and Methods
Isolation, Culture, and Identification of Bacterial Clinical Pathogens
A clinical cross-sectional study was conducted in the Department of Microbiology, Anugrah Narayan Magadh Medical College and Hospital, Gaya, Bihar for 2 years. Eight clinical bacterial pathogens from the patient's sample were isolated from ANMMCH (Anugrah Narayan Magadh Medical College and Hospital), Gaya, and IGIMS (Indira Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences), Patna. A total of 501 samples have been collected, and out of 501, 398 showed positive specimens having different sites of infection such as Urine infection-216 (54.2%), Pus infection-46 (11.56%), Swab or Sputum infection-16 (4%), CSF-5 (2.1%), SSI-120 (30.1%) [6,7]. Growth on culture plates was identified by its colony morphology and characteristics and its standard biochemical tests (Akanmu AO et al.,2021). After confirmatory biochemical tests, the bacterial clinical pathogens were identified [6,7].
Maintenance of Culture
Isolated Clinical bacterial pathogens were maintained on Nutrient Agar (Hi-Media), MacConkey Agar (Hi-Media), XLD, and DCA Agar and Cetrimide Agar. All the cultures were kept at 37°C for 24 hours in the Incubation. The strains that were used in this study are Acinetobacter baumanii, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, MRSA, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Shigella sonnei, and Salmonella typhi [6,7].
Plant Collection
Fresh stems of Tinospora cordifolia were collected from various Dist-Gaya (Bihar) localities in March 2023 (Figure 1). Plant authenticated by a taxonomist from the Department of Botany Magadh University, Bodhgaya [6]. Processing of the sample fresh stem of plants was washed well using tap water and twice using g distilled water and it was dried in shade for 12-15 days, at an ambient temperature of 32°C [6]. After drying plant stems were cut into small pieces [6]. The dried samples were grind properly using a mortar pestle and later using a grinder, to obtain the powdered form and stored at room temperature till their use in the experiment [6].

Figure 1: Stem.
Extract Preparation with Different Solvents
Dried powdered material (Figure 2) (10 gm) of the sample was extracted with methanol in 200ml and distilled water in 200ml separately in soxhlet apparatus. The temperature of the heating mantle was adjusted to 65°C for methanol extract and 100°C for aqueous extract. The extracts were concentrated by gradually evaporating the respective solvent in the hot water bath. The concentrated extract was collected in sterile bottles and refrigerated until use (Sharma et al., 2013) [6]. The extraction yield (%) was calculated as follows:

Figure 2: Plant Powder.
100 mg of methanol extract and 100 mg of aqueous extract further dissolved in 10 ml of methanol and distilled water for further expermimentations. 6420mg/ml of methanol extract stock solution was made and 7000 mg/ml of aqueous extract stock solution was made. 300μg/ml, 450μg/ml, and 500μg/ml of methanol and aqueous extract concentrations were taken for experimentation.
Determination of Antimicrobial activity
Well diffusion assay (Rautenbach et al., 2000)
The susceptibility of all the isolated organisms to the selected Tinospora cordifolia plant stem was tested using the Agar well diffusion method. Sterile Mueller-Hinton agar plates were prepared. Identified pathogens were inoculated in nutrient broth tubes separately and incubated at 37°C for 24 hours. Test organisms were inoculated 0.1 ml to the surface of MHA plates, spreading to create a lawn. The cultures were allowed to dry on the plates for 5-10 minutes at room temperature. A cork borer made about 5mm of diameter wells in each plate. 300μg/ml, 450μg/ml, 500μg/ml methanol, and aqueous extract combinations were added to the well by using a sterile pipette in a sterile MHA plate [6]. The well added with the solvent acted as a control and incubated for 24 hours at 37°C and the zone of inhibition around the well was measured (including the well) n nearest mm [6]. Tinospora cordifolia showed antimicrobial activity against tested clinical bacterial pathogens. Methanol was found to be the best solvent for extracting and retention of the antimicrobial activity of this plant herb.
Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of Plant Extracts
The overnight cultures were prepared by inoculating the bacterial pathogens in respective broth-like nutrient broth (Bacteria) grow at 37°C for 24 hours. The overnight grown cultures (10 μl) were added to the respective broth (500 μl) and redissolved plant extract (300 μg/ ml) was added to this mixture. This setup was incubated at 37°C for 24 hours and the OD values are measured at 640 nm in colorimeter. The minimum concentration at which there was a drop in OD value was considered the MIC [6].
Bacterial Clinical Pathogens were Isolated from Different Samples and Characterized by Morphological, Microscopic, and Biochemical Tests
The different pathogenic bacteria samples were collected and isolated aseptically using sterile plastic container, syringe, and cotton swabs from each patient having infections in a specific area in Anugrah Narayan Magadh Medical College and Hospital, Gaya. Out of 501, 398 show positive specimens having different sites of infection. Urine infection - 216 (54.2%) samples, Pus infection - 46 (11.56%) samples, Swab or sputum infection - 16 (4.0%) samples, CSF - 5 (2.1%) samples and SSI – 120 (30.1%) samples and confirmed by colony morphology and staining. The bacterial cultures were confirmed by gram staining and biochemical tests such as indole test, MR-VP test, Citrate test, Motility test, Catalase test, Oxidase test, Urease test, Coagulase test, Nitrate reduction test, and sugar fermentation test. The results are tabulated (Table 1) [6].
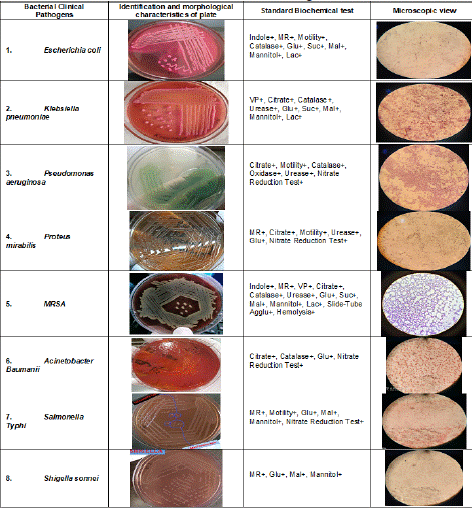
Table 1: Overall survival, autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) versus no ASCT (p=0.12).
Tinospora Cordifolia was Extracted using Different Solvents
The plant was collected from various localities of Gaya District, dried and powdered, and extracted by using methanol and distilled water after overnight incubation. The plant extract showed effective antimicrobial activity against bacterial clinical pathogens.
Tinospora Cordifolia showed Antimicrobial Activity against the Tested Bacterial Clinical Pathogens
Antimicrobial activity was analyzed using the well-diffusion method (Figure 3). The extracted plant was dissolved in the respective solvent (300μg/ml, 450μg/ml, 500μg/ml,) and 300μl was added to the well. The control wells were added with respective solvents. The plant extract showed effective antagonistic activity by producing a clear zone of inhibition compared to that of the solvent. The antimicrobial activity of the selected plant herb Tinospora cordifolia (extracted with two different solvents like methanol and distilled water against eight pathogenic bacteria is tabulated in (Table 2). The highest activity of 47.5 mm based on the highest concentration (5000 μg/ml) was recorded in Tinospora cordifolia extracted by methanol against Salmonella typhi and the lowest activity of 16 mm against Pseudomonas aeruginosa by methanol extract and all pathogens showed complete inhibition (C.I.) by water extract.
Name of the Bacterial Pathogens
Concentration μg/ml
Diameter zone of inhibition in (mm)
Methanol
Distilled Water
Escherichia coli
300
C.I.
C.I.
450
C.I.
C.I.
500
C.I.
C.I.
Klebsiella pneumoniae
300
40
C.I.
450
42
C.I.
500
26.5
C.I.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
300
16
C.I.
450
39
C.I.
500
42.5
C.I.
Proteus mirabilis
300
21.6
C.I.
450
C.I.
C.I.
500
C.I.
C.I.
MRSA
300
38.5
C.I.
450
44
C.I.
500
39
C.I.
Acinetobacter baumanii
300
21.3
C.I.
450
19
C.I.
500
36.5
C.I.
Salmonella typhi
300
41
C.I.
450
42.5
C.I.
500
47.5
C.I.
Shigella sonnei
300
30
C.I.
450
41
C.I.
500
42.5
C.I.
Table 2: Antimicrobial activity was determined by the diameter of the zone of inhibition for different solvent extracts of Tinospora cordifolia against the respective bacterial pathogens. The values represent the difference in the diameters of the test (solvent extract of the plant) and solvent-only control wells. * The values that are bolded indicate the maximum inhibition. C.I.: Complete Inhibition in both control and test.
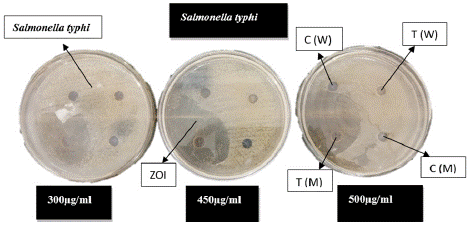
Figure 3: Representative plate showing the well-diffusion method used.
Here, Salmonella typhi is showing a zone of inhibition in the methanol extract
of Tinospora cordifolia. The difference between test (plant powder dissolved
in solvent) and control (only solvent) wells has been evaluated.
Methanol extract of T. cordifolia exhibited effective antibacterial activity against Shigella sonnei in all three tested concentrations (300 μg/ml 450 μg/ml 500 μg/ml) as 30mm, 41mm, and 42.5 mm respectively. Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumonia, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumanii, Salmonella typhi, and Shigella sonnei, MRSA, and Proteus mirabilis were completely inhibited in all three concentrations by aqueous solvent plant extract, this indicates that water itself has effective inhibition against these organisms. These results clearly show that Tinospora cordifolia exhibits antimicrobial activity against the tested clinical bacterial pathogens in one or more extract solvents (Figure 3). Aqueous extract results could not be analyzed effectively in this study because there was inhibition of growth in both test and control wells for all the tested organisms. This could be due to the inherent antimicrobial activity of aqueous extract (Romani et al., 2023). The Graphs showed antimicrobial activity expressed as a zone of inhibition, of the indicated solvent extracts of Tinospora cordifolia against the indicated clinical bacterial pathogens. T. cordifolia showed the highest antimicrobial activity against Salmonella typhi and the lowest against Proteus mirabilis (Figure 4,5).
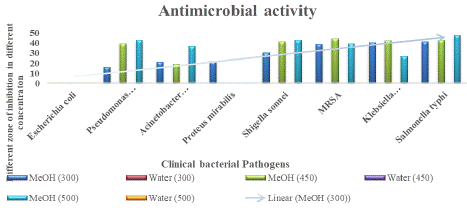
Figure 4: Graph showing antimicrobial activity, expressed as a zone of
inhibition, of the indicated solvent extracts of Tinospora cordifolia against the
indicated clinical bacterial pathogens. Numbers in parentheses indicate the
plant concentration of the solvents.
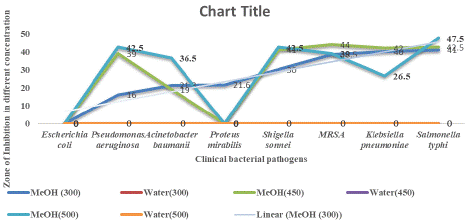
Figure 5: Graph showing antimicrobial activity, expressed as a zone of
inhibition, of the indicated solvent extracts of Tinospora cordifolia against
the indicated clinical bacterial pathogens. T. cordifolia showed the highest
antimicrobial activity against Salmonella typhi..
The Methanol Extracts of Tinospora Cordifolia were Found to be the Most Effective of the Tested Solvents
In this study, it was observed that T. cordifolia extracted by methanol was found to be significantly effective against all organisms. This shows the efficiency of methanol to extract the antimicrobial substance from the plant. The difference between the inhibition zone of control and the test shows that the antimicrobial activity of this plant is more than the solvent.
Water also exhibited inhibition against organisms’ shows Complete Inhibition (CI). The MIC of the methanol extract of Blumea lacera against E.coli, Klebsiella pneumonia, MRSA, Proteus mirabilis, Salmonella typhi, Shigella sonnei, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Acinetobacter baumanii was determined to be 80 μg/ml, 50 μg/ ml, 70 μg/ml, 70 μg/ml, 100 μg/ml, 80 μg/ml, 80 μg/ml, and 50 μg/ ml, respectively. Thus, if one solvent has to be chosen for universal application against bacterial clinical pathogens, from this study author can determine this to be methanol. Methanol, also safe to be consumed or be present in the pharmaceutical field or Medicinal field in trace amounts, can be safely used for bacterial clinical pathogen treatment in Hospitals.
Conclusion
The author started this study with the expectation of determining whether the antimicrobial activity of the herb T. cordifolia could be effectively used against bacterial clinical pathogens, which could then serve as an alternative for chemical treatments in the medical field in the future. In this present study, the results confirmed that the plant herb Tinospora cordifolia has a significant potential to counter the growth of bacterial clinical pathogens in hospitals under tested laboratory conditions. So, further research on the identification of the particular antimicrobial substance and its purification is needed. Also, the dosage and methods of application need to be evaluated in future studies. Thus, this study paves the way for further improvements in chemical-free medical practices.
Author Statements
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the Kalinga Education Foundation and the Department of Biotechnology, Kalinga University, Raipur. This research project was done under the Research and Ethical Committee and Department of Microbiology, Anugrah Narayan Magadh Medical College and Hospital. We thank the department and the college for their support. We thank Dr. Sanjay Nag (Associate. Professor), Dr. Ramesh (Asst. Professor), and the Department of Microbiology. We thank my Guide Dr. Sushma Dubey, the Department of Biotechnology, Kalinga University, Raipur. We thank the department and the college for their support. We are highly grateful to the gardener in Gaya (Dist.), Bihar, for providing the plant samples. We are also thankful to the Dean and Head of the Department of Magadh Medical College, Gaya, Bihar who provided us with a well-equipped lab to work on my plant extracts.
Declaration Statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Funding
This is non-funding research work.
References
- Uren AG, O’Rourke K, Aravind LA, Pisabarro MT, Seshagiri S, Koonin EV, et al. Identification of paracaspases and metacaspases: two ancient families of caspase-like proteins, one of which plays a key role in MALT lymphoma. Mo Cell. 2000; 6: 961–967.
- Agarwal P, Nagesh L, Murlikrishnan. Evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of various concentrations of tulsi (Ocimum sanctum) extracts against Streptococcus mutans: an in-vitro study. Indian J Dent Res. 2010; 21: 357– 359.
- Kapil A, Sharma S. Immunopotentiation compounds from Tinospora cordfolia. Ethnopharmacology. 1997; 58: 89–95.
- Meena AK, Singh A, Panda P, Mishra S, Rao MM. Tinospora cordifolia: its bioactivities & evaluation of physicochemical properties, IJPPR. 2010; 2: 50–55.
- Rajan VK, A Soman D, Kundagol MC, Chacko J. Ayurvedic management of gouty arthritis: a case report. J Ayur Herb Med. 2018; 4: 154–157.
- Gupta P, Dubey S. Antimicrobial Potential of Blumea Lacera Against Disease- Causing Clinical Bacterial Pathogens. Lat Am J Pharm. 2023; 42: 11.
- Gupta P, Dubey S. A clinical study of bacterial pathogens from hospitalacquired infections in ANM Magadh Medical College and Hospital. Gaya. 2022.
- Birla H, Rai SN, Singh SS, Zahra W, Rawat A, Tiwari N, et al, Tinospora cordifolia suppresses neuroinflammation in Parkinsonian mouse model. Neuro Molecular Med. 2019; 21: 42–53.
- Goel HC, Prasad J, Singh S, Sagar RK, Agrawal PK, Bala M, et al. Radioprotective potential of an herbal extract of Tinospora cordifolia. J Radiat Res. 2004; 45: 61–68.
- Asthana JG, Jain S, Mishra A, VijayKant MS. Evaluation of antileprotic herbal drug combinations and their combination with Dapsone, Indian Drugs. 2001; 38: 82–86.
- Antul P, Amandeep S, Gurwinder C. Anuj, Review on pharmacological profile of medicinal vine: Tinospora cordifolia, CJAST. 2019; 35: 1–11.
- Singletary K. Turmeric: an overview of potential health benefits. Nutr Today. 2010; 45: 216–225.
- Sinha K, Mishra NP, Singh J, Khanuja SPS. Tinospora cordifolia (Guduchi) a reservoir plant for therapeutic applications. Indian J Tradit Knowle. 2004; 3: 257–270.
- Salkar K, Chotalia C, Salvi R. Tinospora cordifolia: an antimicrobial and immunity enhancer plant. Int J Sci Res. 2017; 6: 1603–1607.
- Gao L, Cai G, Shi X. Beta-ecdysterone induces osteogenic differentiation in mouse mesenchymal stem cells and relieves osteoporosis, Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008; 31: 2245-9.
- Sharma P, Dwivedee BP, Bisht D, Dash AK, Kumar D. The chemical constituents and diverse pharmacological importance of Tinospora cordifolia. Heliyon. 2019; 5: e02437.
- Khan MM, dul Haque MS, Chowdhury MSI. Medicinal use of the unique plant Tinospora cordifolia: evidence from the traditional medicine and recent research. Asian J Med Biol Res. 2016; 2: 508–512.
- Shamsuzzaman M, Hasan MR. A review of anticancer potential medicinal plants. J Sci Facts. 2019; 5: 1–4.
- Narayana DA. The Ayurvedic Pharmacopoeia of India: Part II. A Good Beginning. (Formulations). 2008.
- Olabiyi AS, Nkemehule FE, Odukoya OA, Samuel TA, Ogbonnia SO. Inhibition of glycosylation as an index of activity in plants with antidiabetic Potentials. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013; 2: 181.
- Kapur P, Wuttke W, Jarry H, Seidlova DW. Beneficial effects of beta-ecdysone on the joint, epiphyseal cartilage tissue and trabecular bone in ovariectomized rats. Phytomedicine. 2010; 17: 350-5.
- Khanal P, Mandar BK, Patil BM, Hullatti KK. In silico antidiabetic screening of borapetoside C, cordifolioside A and magnoflorine. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2019; 81: 550–555.
- Nagaraja PK, Kammar KF, Devi S. Modulation of morphology and some gluconeogenic enzymes activity by Tinospora cordifolia (Willd.) in diabetic rat kidney. Biomed Res. 2019; 5: e024378.
- Upreti P, Chauhan RS. Effect of leaf powder of Giloya (Tinospora cordifolia) in fish feed on survival and growth of post-larvae of Catla catla. J Appl Nat Sci. 2018; 10: 144–148.
- Rana V, Thakur K, Sood R, Sharma V, Sharma TR. Genetic diversity analysis of Tinospora cordifolia germplasm collected from the northwestern Himalayan region of India. Journal of Genetics. 2012; 91: 99.
- Royani A, Hanafi M, Julistiono H, Dinoto A, Lotulung PDN, Manaf A. The potential of Tinospora cordifolia extracts as antibacterial material against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Trends in Sciences. 2023; 20: 3884-3884.
- Wilken R, Veena MS, Wang MB, Srivatsan ES. Curcumin: a review of anticancer properties and therapeutic activity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, Mol. Cancer. 2011; 10: 1–19.
- Saha S, Ghosh S. Tinospora cordifolia: One plant, with many roles. Ancient science of life. 2012; 31: 151–159.
- Saha S, Ghosh S. Tinospora cordifolia: one plant, many roles. Ancient Sci Life. 2012; 31: 151–159.
- Sharma P, Dwivedee BP, Bisht D, Dash AK, Kumar D. The chemical constituents and diverse pharmacological importance of Tinospora cordifolia. Heliyon. 2019; 5: e02437.
- Vedavathy S, Rao KN. Antipyretic activity of six indigenous medicinal plants, J. Ethnopharmacology. 1991; 33: 193–196.
- Sharma U, Bala M, Kumar N, Singh B, Munshi RK, Bhalerao S. Immunomodulatory active compounds from Tinospora cordifolia, J. Ethnopharmacology. 2012; 141: 918–926.
- Spandana U, Ali SL, Nirmala T, Santhi M, Babu SDS. A review on Tinospora cordifolia. Int J Curr Pharm Res. 2013; 4: 61–68.
- Kumar V, Singh S, Singh A, Dixit AK, Srivastava B, Sidhu GK, et al. Phytochemical, antioxidant, antimicrobial, and protein binding qualities of hydro-ethanolic extract of Tinospora cordifolia. JBAPN. 2018; 8: 192–200.
- Sonkamble VV, Kamble LH. Antidiabetic potential and identification of phytochemicals from Tinospora cordifolia. Am J Phyto Med Clin Ther. 2015; 3: 97–110.