Editorial
To 12th World Conference Bioethics, Medical Ethics & Health Law, March 21-23, 2017, from Limassol, Cyprus, the conference president, Prof. Amnon Carmi showed that for the first fifty years of bioethics was discussed the construction and development of its bioethic concept and that we are now facing a second stage, a new task, that seems to be even more important, complex and difficult, namely the delivering of our message to society, by planting the ethical values into the soul of the people and into their daily life and behavior.
In bioethics are very important two different tools: educational tool that consist of the use of novel methods and a legal tool by translated and adopted of theory and language of bioethics by the legislator and the judiciary, e.g. the Universal Declaration of Bioethics and Human Rights of United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO).
In actual society are many bioethical controversial issues, including: stem cell research, “in vitro” fertilization, human cloning, euthanasia, genetically modified crops, bioethics in food security, production of GMO (Genetically Modified Organisms), beyond species barriers, and their commercialization.
Bioethics addresses a wide array of issues and the controversies which may arise and must be tackled in academic education. For example, the ethical principles of stem cell research, embryonic cell type that can grow into highly specialized cells found in various organs, are debated upon in various states, like United States of America, Great Britain, and Japan. The main controversy is focused on whether human embryos should be obtained to be used in scientific research since they will be destroyed; also, if stem cells are used to produce organs, the embryo from which the cells are collected will be destroyed and, therefore, a life will be terminated, what is immoral. The human cloning - a multiplication without fertilization - is a bioethic problem. Current human society is not yet ready to accept the process of cloning as a method of assisted reproduction medical, there is a real danger to enable amoral evolution and even destructive actions. “Bioethics -so there is no science and no new ethics (…), but a multidisciplinary focus, the border with current ideologies, philosophy, theology and law. The fact that in this way attracts other disciplines and civil society exceeds ethics. Contribution of other disciplines gives an identity that exceeds bioethics controversies and instability” [1].
For overcoming these problems, it needs education, so bioethical education
The road opener in the bioethics science was the American biochemist Van Rensselaer Potter in 1970 that sought to integrate biology, ecology, medicine, and human values and points out that “Bioethics has emerged as a new discipline which unites biological knowledge with knowledge Bioethical education of human value systems. I chose bio - to represent biological knowledge, the science of living systems, I chose ethics - to represent human value systems” [2].
According to the scientist Denis Buican, geneticist, agronomist, historian and philosopher of sciences, bioethics represents the “ethics governing fundamental biological, medical and agronomic research on all living creatures” [3].
A study showed that “Bioethics aims to identify an ethical framework by means of a multidisciplinary debate open to the scientific community, in order to allow support to scientists involved in biomedical research [4].
In our efforts of reconceptualization, point out that Bioethics is a multidisciplinary area that studies the application of ethics laws, juridic laws to complex of Sciences, involving various branches of human knowledge: Biology, medicine and healthcare, socialcare, zootechny, philosophy, psychology, sociology, cultorology, etc.
The bioethical education aims to educate young people so as to apply moral laws in close correlation with the laws of biology in scientific research and scientific advances in biology, human medicine, veterinary medicine, agriculture, zootechny, and also in everyday aspects of their social, professional and family life and life in general on Earth.
Bioethical education, as a component and as a cornerstone of moral education, looks at the education of young people, so as they will be able to apply both moral laws and Biology laws in their subsequent scientific research and endeavours. Bioethical education it is of the utmost importance in higher education in the profile of Biology, of Food faculties, of Medicine, Environmental, Agricultural faculties etc. encompassing heuristic strategies, interactive teaching methods, active traditional teaching methods and new, modern methods resorting to multi-media and electronic platforms.
Bioethics education is the result of interference of many sciences (Figure 1), such as: Biological Sciences; Natural Sciences; Human Medical Science; Veterinary Medical Science; Agricultural Science; Zoo technical Science; Educational Sciences and Psychology; and so on.
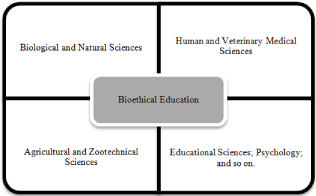
Figure 1: The mainly sciences underlying bioethical education.
In framework of Biological Sciences and in its Border Sciences, the bioethics issues and bioethical education can be approach in following scientific branches (Figure 2): Principles of Genetics and GMO, Genetic engineering, General Microbiology, Molecular Biology, Cells Biology, Biochemistry, Ecology and so on.
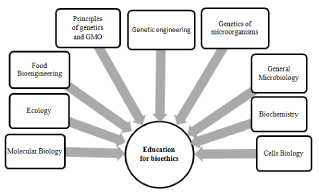
Figure 2: Main scientific branches in framework of Biological Sciences and in
its Border Sciences that contribute to bioethical education.
Through bioethical education, young people must understand that throughout their lives they have to act responsibly towards science and humanity, regardless of their professional goals and career objectives in the future.
Bioethical education requires the use of d interactive methods in the teaching process, that on the one hand, these methods will boost analytical thinking, analogic reasoning, synthetic and flexible approaches and, on the other hand, they will encourage personal responses, opinions backed by scientific arguments, scientific demonstrations and interactions in groups and teams. Such methods can mentioned: lectures with opponents, lecture-debate-discussion, Socratic dialogues, discussion, brainstorming, but mainly modern methods, as fishbowl, clustering, cooperation, cube method, mosaic methods, Philips 6/6 method and so on. Also, some experiments, as traditional methods can contribute to bioethical education, but mainly if these are modernized, for example by simulation with help of computer.
The atmosphere emerging in this teaching environment will be similar to that characteristic of scientists and decision-makers who can impact the humankind in a positive and non-intrusive manner.
For example, fishbowl is based on educational interaction as the students are divided into two groups (8-10) and will take turns getting involved in the discussion, being observed / not involved in discussion, acting as observers in order to come up with solutions to controversial issues and to develop good relationships in their group, to increase their observation skills and others. “Through its interventions, the teacher-moderator will try to bring new ideas, new viewpoints and arguments to the overall task completion” [5].
Some controversial issues that can be addressed for discussion to students in fishbowl are following:
• Does Modified Genetics Crops have any advantages or disadvantages? Argue the answer!
• GMOs are useful or harmful to human life? Argue the answer!
Multimedia techniques can be applied in organizing a stimulus demonstration to provoke discussion.
Through discussion, students determine that the GMO or transgenic organisms are organisms created artificially in the laboratory only, crops or animals apparently normal, which, by means of genetic engineering techniques were transferred genes from other species: viruses, bacteria, plants, animals and even human genes to confer new characteristics, they may be toxic, extremely dangerous to human health and can cause many diseases. “The best known plants until now as GMO are maize, potatoes and soybeans” [6,7].
Since 2007, it has been demonstrated that Monsanto’s genetically modified MON863 corn, approved for human consumption on the European Union market, causes serious changes in the liver and kidney of humans, with research being done on guinea pigs. Genetically modified plants can have negative effects on the environment, be they test or commercial, they cannot be controlled because they interact freely with the whole ecosystem, and the surrounding conventional or organic crops can be polluted, due to wind or insects, the entire biodiversity suffered from insect and herbicide-resistant genetically modified crops.
When it comes to academic education, for example interactive lectures on General Microbiology, which focus on microorganisms, may promote the bioethical education by tackling the artificial manipulation of genes found in microorganisms. Thus, microorganisms with a new genetic architecture can be created and they may feature peculiar infectious properties and unpredictable ecological effects.
Students must be provided with the kind of theoretical and practical training which can be later turned into the ethical foundation of their career. They should become able to internalize the humanistic values of their future profession. Bioethics displays crosscurricular attributes, which is why to discussing on and resolving the issues raised ought to stem should realizated by contributions of professionals in all life-related scientific domains.
“Man becomes moral when complying with applicable laws and morals both in everyday life and in scientific research biological, medical, agricultural, business, in all its scientific enterprises. This is the direction in which it is recommended bioethical education of young people as a means of moral education and also as a component of moral education”.
So, Bioethics and bioethical education, whereto? Towards development of these fields, to new ways of education on live long, for the respect and protection of living creatures, of biological, of entire live world.
References
- Scripcaru G. Bioethics between life sciences and human rights. Romanian Journal of Bioethics. 2005; 3: 15-25.
- Potter VR. Bioethics the Science of Survival. Perspectives in Biology and Medicine. 1970; 14: 120-153.
- Buican D. Biognoseology. Evolution and revolution knowledge. Paris: Kimé. 1993.
- Guidoni L. [Bioethics: problems and prospects within a research institute]. Ann Ist Super Sanita. 2004; 40: 309-315.
- Cerghit I. Educational methods. Iasi: Polirom Publishing House. 2006.
- Mencinicopschi G. About genetically modified organisms, shortly before it’s too late - Ghe. Mencinicopschi. Formula AS. 2008; 807: 91-92.
- Iancu M. Bioethical education-component and cornerstone of the moral education of the youth. European Journal of Science and Theology. 2014; 10: 95-102.
