Research Article
Austin J Bioorg & Org Chem. 2014;1(1): 6.
Virtual Screening and its Experimental Validation Reveal Novel Compounds with Promising Anticancer Activity Among 4-Thiazolidinone- Pyrazoline- and Isatin-Based Conjugates
Devinyak OT1,2, Havrylyuk DYa1, Avdieiev SS3, Chumak VV4, Panchuk RR4, Stoika RS4, Kavsan VM3 and Lesyk RB1*
1Department of Pharmaceutical, Organic and Bioorganic Chemistry, Danylo Halytsky Lviv National University, Ukraine
2Department of Pharmaceutical Disciplines, Uzhgorod National University, Ukraine
3Department of Biosynthesis of Nucleic Acids, Institute of Molecular Biology NAS of Ukraine, Ukraine
4Institute of Cell Biology NAS of Ukraine, Ukraine
*Corresponding author: Lesyk RB, Department of Pharmaceutical, Organic and Bioorganic Chemistry, Danylo Halystky Lviv National Medical University, 69 Pekarska St, Lviv, 79010, Ukraine.
*Corresponding author: Chung-Hang Leung, State Key Laboratory of Quality Research in Chinese Medicine, Institute of Chinese Medical Sciences, University of Macau, China
Received: July 31, 2014; Accepted: September 01, 2014; Published: September 02, 2014
Abstract
In silico screening of virtual 4-thiazolidinones library has been carried out with several self-developed QSAR and pharmacophore models of anticancer activity. Such approach has allowed us to choose 14 the most probable anticancer hits - conjugates of 4-thiazolidinone, pyrazoline and isatin, which in turn have been synthesized. Half of these compounds were subjected to anticancer activity evaluation and biological experiments confirmed our predictions, although in a qualitative manner. The most sensitive to tested compounds cancer cell line is Mino (the lowest IC50 reached 0.17 μM), which represents mantle cell lymphoma– a rare but very aggressive tumor. That identifies the further direction of biological studies of the novel anticancer hit compounds.
Keywords: 4-thiazolidinones; Virtual screening; Pharmacophore; Anticancer activity
Introduction
The identification of novel biologically active compounds among 4-thiazolidinone derivatives is a successful trend since molecules with this scaffold demonstrate high affinity for various biotargets. The most popular 4-thiazolidinones activities cover anti-inflammatory [1]; antibacterial, antifungal and antitubercular [2]; antiviral (anti-HIV predominantly [3]); antidiabetic [4] and anticancer [5,6] activity. The last topic has been granted with strong interest over the last few years [7-18]. Antitumor mechanisms of 4-thiazolidinones can be associated with their affinity for tumor necrosis factor TNFα [19], anti-apoptotic biocomplex Bcl-XL-BH3 [20], JNK-stimulating phosphatase-1 (JSP- 1) [21], integrin αvβ3 receptor [22], non membrane protein tyrosine phosphatase (SHP-2) [23], inhibition of necroptosis [24], etc. Several structure-anticancer activity studies of 4-thiazolidinones were carried out and resulted in predictive QSAR models [25]. The purpose of these models is to perform virtual screening and thus to raise hits ratio in the search for new anticancer agents significantly. Continuing our efforts in the search of new 4-thiazolidinones with antitumor properties, we are reporting the application of the mathematical models to the virtual database of new 4-thiazolidinone derivatives and purposeful synthesis based on virtual screening results. In order to confirm the prognosis, the synthesized compounds were evaluated for anticancer activity in vitro.
Materials and Methods
Virtual database
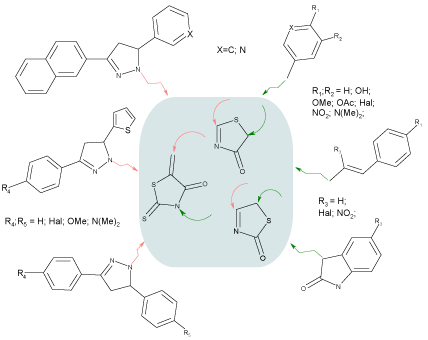
Varying the substituents in 2,4 and 5 positions of 4(2)-thiazolidinone, the library of 690 compounds has been created (Scheme 1). The choice of substituents has been based on previously identified priorities and structure-activity relationships [4,5,7,26-28].
Scheme 1 : Virtual database for in silico screening.
Predictive models
To perform virtual screening three previously developed models have been utilized. The in home library which has been used to derive these models contained about 700 compounds which were synthesized and checked for anticancer activity in vitro under the Developmental Therapeutics Program of National Cancer Institute (USA) [29,30]. The dependent variable in all models was presented with the tumor cells growth percent or activity class based on this indicator.
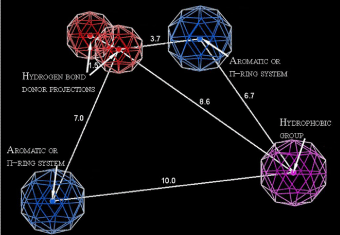
The first model used in screening is pharmacophore model, which has been developed combining clustering of 4-thiazolidinone derivatives into different activity mechanisms and making subsequent pharmacophore search [31]. The pharmacophore (Figure 1) consists of two aromatic or p-ring system centers, the hydrophobic group and the two projections of the hydrogen bond donors (electron pair acceptors). Using presented in the paper confusion matrix, the statistical parameters of model were obtained. The error rate of this model is 0.8% with accuracy = 87.5% and precision = 99.5%. In order to conduct virtual screening, the conformational search of virtual database has been carried out and then each conformer was aligned with the pharmacophore. The conformers were obtained using systematic bonds rotations (with 30° step) and further energy minimization with the aim to select only energetically favorable geometries. Conformers which have energy more than 7kcal/ mol above the minimum for a given compound were treated as energetically unfavorable and were removed from the database.
Figure 1: Probable pharmacophore model of 4-thiazolidinones anticancer activity. The distances are presented in angstroms.
The second is Random Forest classification model, reported by Zimenkovsky et al. [32]. The model incorporates the ensemble of 100 decision trees and is capable to recognize compounds into “active” or “non-active” classes. The decision is based on a vast number of molecular descriptors, all of which can be obtained through E-DRAGON online service [33] (the model’s input is molecular descriptor matrix). The error rate of Random Forest model has been estimated at 2.08%, with sensitivity = 56% and specificity = 99.64%. These values indicate that the model can miss up to 50% of active compounds (making false negative error), but true positive error is highly unlike. So a compound which is predicted to be active by this model has strong chances to show anticancer activity in vitro. To check whether predicted compounds fall into applicability domain of Random Forest model, the distance to model has been evaluated for each compound [34,35]. The threshold distance value, above which the compound is recognized as outlier, was found using analysis of the distribution of training compounds distances. This empirical distribution was fitted with lognormal distribution model. The threshold distance was presented with the 0.999 quantile of fitted lognormal distribution.
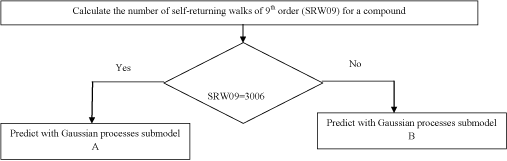
The third model is the Gaussian processes QSAR model disclosed in Devinyak et al. [25]. The model acts as follows (Scheme 2).
Scheme 2 : The scheme of anticancer activity predicting with the Gaussian processes QSAR model.
The prespecified SRW09 value of 3006 represents the structurally similar group of compounds, the majority of which have shown high levels of antitumor activity. In such a way submodel A primarily indicates less active compounds among those having SRW09=3006, while submodel B tries to define few remaining active compounds in the dataset. Submodels A and B are based on the eigenvalue molecular descriptors EEig10x (Eigenvalue 10 from edge adjacency matrix weighted by edge degrees) descriptor and EEig02d (Eigenvalue 02 from edge adjacency matrix weighted by dipole moments) respectively and are presented with corresponding covariate functions (Figure 2). Though the statistical parameters of overall model are moderate (R2=0.656, R2ext =0.602), it predicts the anticancer activity in a quantitative manner, returning cancer cells growth percent. The verification of falling into applicability domain has been carried out with quantile-quantile plot, using chi-squared distribution as a theoretical and Mahalonobis distance distribution as an observed component [36].
Figure 2: Covariate functions of the Gaussian processes regression submodels.
Biological experiments
C6 cells were kindly provided by Dr. V. Baklaushev (State Research Center of Forensic and Social Psychiatry, Moscow, Russian Federation), Mino cell line by Dr. V. Ribrag (Department of Medicine, Institute Gustave Roussy, Villejuif, France). C6 and L1210 cells were grown in DMEM (Hyclone, USA), Mino and Jurkat cells in RPMI (Gibco, USA). All culture mediums were supplemented with FBS at 10%, penicillin at 100 units/ml, and streptomycin at 100 μg/ml final concentration. Cells were cultivated in the environment of 95% air/5% CO2. C6 and Mino cells were seeded in triplicates (Jurkat and L1210– in duplicates) into 96-well plate at density 3× 103 cells/ well. Compounds were applied at final concentration 0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, and 100 μM, which were reached by serial dilution. 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) (Sigma), which is converted to dark blue, water insoluble MTT formazan by mitochondrial dehydrogenases, was used to determine viable cells according to manufacturer’s protocol (Sigma). Dose-response curves have been fitted with 4-parameter log-logistic function in R [37,38]. IC50 have been determined using fitted models.
Results and Discussion
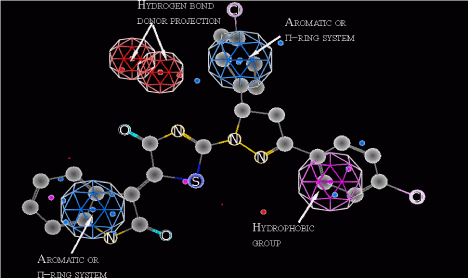
The conformational search of virtual database results in a 12787 energetically favorable conformers. Each conformer has been aligned with the pharmacophore and these way 101 compounds have passed the screening. It is interesting, that among those structures which have good alignment with pharmacophore model, 92 are conjugates of 4-thiazolidinone, pyrazoline and isatin. In these structures nitrogen and oxygen atoms of 4-thiazolidinone core provide necessary hydrogen bond donor projections, while isatin and diarylpyrazoline fragments act as aromatic and hydrophobic constituents (Figure 3).
Figure 3: Alignment of compound 1 with pharmacophore model.
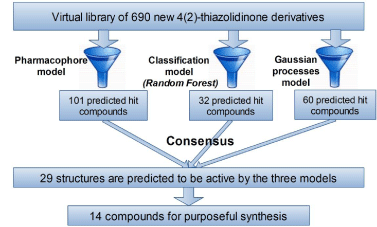
Random Forest model predicted as active 32 compounds from virtual library. Analysis of distances to model have showed that all compounds predicted as active fall into applicability domain, while there are 47 out-of-domain compounds among those predicted as inactive. Gaussian processes model predicted cytotoxic effect on tumor cells (GP<0) for 60 structures. All compounds from virtual library were located inside the applicability domain. The choice of virtual screening hits has been based on the consensus between all predictions (Scheme 3). These way 29 compounds are predicted as active by all three used screening models. Among them, 14 structures have been selected for synthesis (Scheme 4). The preference has been granted to the structures with common starting compounds and known synthetic methods. The idea was to vary halogen substituents in isatin and in para-position of phenyl ring in the 3rd position of pyrazoline core.
Scheme 3: Virtual screening scheme.
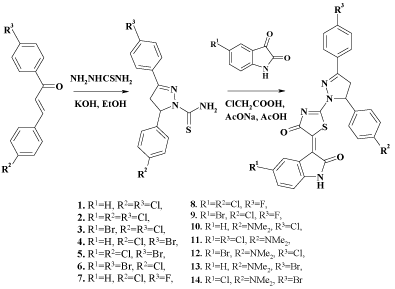
The synthesis has been conducted in two stages, with the initial obtaining of 3,5-diaryl-1-thiocarbamoyl-2-pyrazolines through the interaction of thiosemicarbazide with corresponding chalcones in ethanol in the presence of potassium hydroxide. Following one-pot methodology resulting compounds were subjected to the condensation with chloroacetic acid and appropriate isatins in the presence of fused sodium acetate in refluxing acetic acid (Scheme 4) [7]. Compounds 1-6 and 12 have been already reported in [18], so only 7-11, 13 and 14 are presented in chemistry section. The characteristic patterns of AMX system (CH2-CH protons of pyrazoline fragment) have been found in 1H NMR spectra of 1-14. The chemical shifts of HA, HM and HX are in the ranges δ=3.46-3.52; 4.12-4.20 and 5.82-6.03 respectively with corresponding coupling constants JAM = 17.5-18.6, JAX = 10.6-11.5, and JMX = 3.0-4.4. Besides that, the displacement of CH proton in the 4th position of 2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-2-one fragment into the weak field (δ=8.90-9.14) indicates Z-configuration of double bond between thiazolidine and indoline systems, which is consistent with X-ray crystallographic analysis of similar compounds in [7]. NH group of indoline shows signal at δ=10.80-11.22 and spectra of compounds 10-14 have intense singlet in strong field (δ=2.86-2.95) due to dimethylamino group in para-position of phenyl ring.
Scheme 4 : Sunthesis of 4-thiazolidinone, pyrazoline and isatin conjugates.
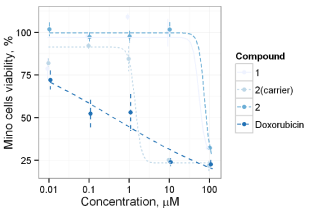
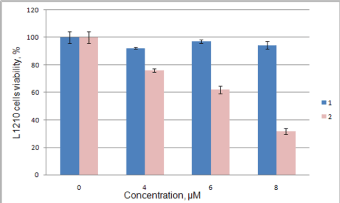
Anticancer effect of synthesized compounds has been studied using C6, Mino, Jurkat and L1210 cell lines. The results of anticancer activity evaluation for compounds 1-6 and 12 on C6 and Mino cells have been already reported by Avdieiev et al. [18]. It has been found that compound 2 has significant cytotoxic activity in C6 cells (IC50=1.22 μM), which can be enhanced through immobilization on the polymeric carrier (IC50=0.13 μM). The advantage of immobilization has been also observed in Mino cells viability inhibition experiment. While soluted in DMSO pure compounds 1 and 2 show IC50=68.2 and 80.7 μM respectively, the immobilized version of 2 yields IC50=1.58 μM (Figure 4). Another series of biological experiments on Mino cells using weaker concentrations of treatment compounds (from 0.001 to 10 μM) has identified significant antitumor potential of compounds 3, 6 and 12 with IC50=0.73, 0.27 and 0.16 μM respectively [18]. Compound 5 showed weaker cytotoxicity with IC50=7.4 μM, and IC50 of 4 lays out of studied concentration range (IC50 > 10 μM). Since ranges of concentration in Jurkat cells inhibition study were limited, exact IC50 values could not be determined. The obtained data allows saying, that IC50 of 2, 3, 5 and 6 do not exceed 10 μM, which is argument for their significant anticancer activity (Figure 5). IC50 of compound 1 exceeds 10 μM, while compound 4 did not show even weak effect. These results are in good correlation with Mino cells inhibition assay. Studying the anticancer effect of 1 and 2 on the L1210 cells growth it has been observed that this cell line is resistant to treatment with 1, but sensitive to compound 2 (IC50≈ 7 μM, Figure 6).
Figure 4: Cytotoxicity of compounds 1 and 2 in Mino cells.
Figure 5: Inhibition of Jurkat cells viability by 4-thiazolidinone derivatives.
Figure 6: Inhibition of L1210 cells viability by compounds 1 and 2.
Conclusion
Using previously obtained QSAR and pharmacophore models, the virtual screening of 4(2)-thiazolidinone derivatives library has been carried out, and 14 novel 3-[2-(3,5-diaryl-4,5-dihydropyrazol-1- yl)-4-oxo-4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazol-5-ylidene]-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol- 2-ones were selected and synthesized. The success of the purposeful synthesis strategy has been confirmed by biological assays, according to which the synthesized compounds can inhibit cancer cells growth even being applied in micromolar concentrations. Since QSAR and pharmacophore models have been trained using NCI-60 cell panel results, but other cell lines have been used for activity evaluation of synthesized compounds, we may claim just qualitative confirmation of the prediction. The four most potent synthesized compounds 3, 5, 6 and 12 show IC50 values between 0.16-10μM under MTT assays of rat glioma cells C6, Mino cells, Jurkat and L1210 cells viability inhibition. Additionally, it has been discovered that the immobilization of compounds on the oligo electrolyte polymeric carrier significantly increases the activity. The most sensitive cancer cell line is Mino, which represents mantle cell lymphoma– a rare but very aggressive tumor. That identifies the further direction of biological studies of the novel anticancer hit compounds.
Chemistry
The starting 3,5-diaryl-1-thiocarbamoyl-2-pyrazolines were obtained according to the method described previously [27,39]. Melting points were measured in open capillary tubes on a BUCHI B-545 melting point apparatus and are uncorrected. The elemental analyses (C, H, N) were performed using the Perkin–Elmer 2400 CHN analyzer. Analyses indicated by the symbols of the elements or functions were within ±0.4% of the theoretical values. The 1H NMR spectra were recorded on Varian Gemini 400 MHz in DMSO-d6 using tetramethylsilane (TMS) as an internal standard. Chemical shifts are reported in ppm units with use of δ scale.
General procedure for synthesis of 3-{2-[3,5-bis-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,5-dihydropyrazol-1-yl]-4-oxo-4H-thiazol-5-ylidene}-1,3-dihydroindol-2-ones [7]
A mixture of 3,5-diaryl-1-thiocarbamoyl-2-pyrazoline (10 mmol), chloroacetic acid (10 mmol), appropriate isatin (12 mmol), and anhydrous sodium acetate (20 mmol) was refluxed for 5 h in glacial acetic acid (10 mL). Precipitate obtained upon cooling was filtered off, washed with water and methanol and recrystallized with DMF/ethanol mixtures (1:2 vol). Compounds 1-6 and 12 have been reported in [18].
3-{2-[3-(4-Fluorophenyl)-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,5-dihydropyrazol-1-yl]-4-oxo-4H-thiazol-5-ylidene}-1,3- dihydroindol-2-one (7). Yield 77%, mp 292–293 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6+CCl4): 11.14 (s, 1H), 8.90 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 7.87– 7.89 (m, 2H), 7.45 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 7.29–7.34 (m, 4H), 7.28 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 6.95 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 6.87 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 5.95 (dd, J = 11.0, 3.6 Hz, 1H), 4.09 (dd, J = 18.0, 11.0 Hz, 1H), 3.51 (dd, J = 18.0, 3.6 Hz, 1H). Calcd for C26H16ClFN4O2S: C, 62.09; H, 3.21; N, 11.14; Found: C, 61.38; H, 3.25; N, 11.29.
5-Chloro-3-{2-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,5-dihydropyrazol-1-yl]-4-oxo-4H-thiazol-5-ylidene}-1,3- dihydroindol-2-one (8). Yield 73%, mp 294–295 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6+CCl4): 11.22 (s, 1H), 8.92 (br s, 1H), 7.87–7.89 (m, 2H), 7.45 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 7.31–7.38 (m, 4H), 7.01 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.91 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H), 5.95 (dd, J = 11.1, 3.6 Hz, 1H), 4.12 (dd, J = 18.0, 11.1 Hz, 1H), 3.52 (dd, J = 18.0, 3.6 Hz, 1H). Calcd for C26H15Cl2FN4O2S: C, 58.11; H, 2.81; N, 10.43; Found: C, 57.97; H, 2.84; N, 10.37.
5-Bromo-3-{2-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,5-dihydropyrazol-1-yl]-4-oxo-4H-thiazol-5-ylidene}-1,3- dihydroindol-2-one (9). Yield 68%, mp >300°C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6+CCl4): 11.18 (s, 1H), 9.04 (br s, 1H), 7.81–7.84 (m, 2H), 7.28-7.51(m, 6H), 6.96 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 6.85 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 1H), 5.92-5.95 (m, 1H), 4.08-4.12 (m, 1H), 3.51 (dd, J = 17.9, 3.5 Hz, 1H). Calcd for C26H15BrClFN4O2S: C, 53.67; H, 2.60; N, 9.63; Found: C, 53.91; H, 2.66; N, 9.44.
3-{2-[3-(4-Chlorophenyl)-5-(4-dimethylaminophenyl)-4,5-dihydropyrazol-1-yl]-4-oxo-4H-thiazol-5-ylidene}-1,3- dihydroindol-2-one (10). Yield 77%, mp 290–291 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6+CCl4): 11.17 (s, 1H), 8.90 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.76- 7.78 (m, 2H), 7.61 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.34 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 7.25 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 7.00-7.04 (m, 2H), 6.92 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 5.90 (dd, J = 10.9, 3.5 Hz, 1H), 4.13 (dd, J = 18.3, 10.9 Hz, 1H), 3.50 (dd, J = 18.3, 3.5 Hz, 1H), 2.95 (s, 6H). Calcd for C28H22ClN5O2S: C, 63.69; H, 4.20; N, 13.26; Found: C, 63.80; H, 4.25; N, 13.34.
5 - C h l o r o - 3 - { 2 - [ 3 - ( 4 - c h l o r o p h e n y l ) - 5 - ( 4 - dimethylaminophenyl)-4,5-dihydropyrazol-1-yl]-4-oxo-4H-thiazol-5-ylidene}-1,3-dihydroindol-2-one (11). Yield 74%, mp >300°C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6+CCl4): 11.17 (s, 1H), 8.94 (br s, 1H), 7.91 (d, J=7.9 Hz, 2H), 7.58 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.35 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.12 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 6.90 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.68 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 5.83 (dd, J = 10.8, 3.3 Hz, 1H), 4.10 (dd, J = 18.5, 10.8 Hz, 1H), 3.50 (dd, J = 18.5, 3.3 Hz, 1H), 2.86 (s, 6H). Calcd for C28H21Cl2N5O2S: C, 59.79; H, 3.76; N, 12.45; Found: C, 60.05; H, 3.78; N, 12.13.
3-{2-[3-(4-Bromophenyl)-5-(4-dimethylaminophenyl)-4,5-dihydropyrazol-1-yl]-4-oxo-4H-thiazol-5-ylidene}-1,3- dihydroindol-2-one (13). Yield 71%, mp 298-299°C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6+CCl4): 11.15 (s, 1H), 8.90 (d, J=8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.86 (d, J=8.6 Hz, 2H), 7.75 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 7.34 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 7.11 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 7.04 (t, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 6.91 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 6.69 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 5.83 (dd, J = 10.7, 3.6 Hz, 1H), 4.10 (dd, J = 18.5, 10.7 Hz, 1H), 3.48 (dd, J = 18.5, 3.6 Hz, 1H), 2.86 (s, 6H). Calcd for C28H22BrN5O2S: C, 58.75; H, 3.87; N, 12.23; Found: C, 60.01; H, 3.91; N, 12.12.
5 - C h l o r o - 3 - { 2 - [ 3 - ( 4 - B r o m o p h e n y l ) - 5 - ( 4 - dimethylaminophenyl)-4,5-dihydropyrazol-1-yl]-4-oxo-4H-thiazol-5-ylidene}-1,3-dihydroindol-2-one (14). Yield 69%, mp 299-300 °C. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6+CCl4): 11.20 (s, 1H), 8.93 (d, J=8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.82 (d, J=8.2 Hz, 2H), 7.70 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.35 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.12 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 6.90 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 6.69 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 5.82 (dd, J = 11.0, 3.5 Hz, 1H), 4.10 (dd, J = 18.2, 11.0 Hz, 1H), 3.50 (dd, J = 18.2, 3.5 Hz, 1H), 2.87 (s, 6H). Calcd for C28H21BrClN5O2S: C, 55.41; H, 3.49; N, 11.54; Found: C, 55.80; H, 3.52; N, 11.38.
Acknowledgement
The authors support all people of good will currently struggling for sovereign and unified Ukraine.
References
- Ottanà R, Maccari R, Barreca ML, Bruno G, Rotondo A, Rossi A, et al. 5-Arylidene-2-imino-4-thiazolidinones: design and synthesis of novel anti-inflammatory agents. Bioorg Med Chem. 2005; 13: 4243-4252.
- Desai NC, Rajpara KM, Joshi VV, Vaghani HV, Satodiya HM. Synthesis and characterization of some new thiazole based thiazolidinone derivatives as potent antimicrobial and antimycobacterial agents. Anti-Infective Agents. 2012; 10: 75-86.
- Tian Y, Zhan P, Rai D, Zhang J, De Clercq E, Liu X, et al. Recent advances in the research of 2,3-diaryl-1,3-thiazolidin-4-one derivatives as potent HIV-1 non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Curr Med Chem. 2012; 19: 2026-2037.
- Lesyk RB, Zimenkovsky BS. 4-Thiazolidones: centenarian history, current status and perspectives for modern organic and medicinal chemistry. Curr Org Chem. 2004; 8: 1547-1577.
- Havrylyuk D, Zimenkovsky B, Lesyk R. Synthesis and anticancer activity of novel nonfused bicyclic thiazolidinone derivatives. Phosphorus, Sulfur Silicon Relat Elem. 2009; 184: 638-650.
- Havrylyuk D, Mosula L, Zimenkovsky B, Vasylenko O, Gzella A, Lesyk R. Synthesis and anticancer activity evaluation of 4-thiazolidinones containing benzothiazole moiety. Eur J Med Chem. 2010; 45: 5012-5021.
- Havrylyuk D, Zimenkovsky B, Vasylenko O, Gzella A, Lesyk R. Synthesis of new 4-thiazolidinone-, pyrazoline-, and isatin-based conjugates with promising antitumor activity. J Med Chem. 2012; 55: 8630-8641.
- Kaminskyy D, Bednarczyk-Cwynar B, Vasylenko O, Kazakova O, Zimenkovsky B, Zaprutko L, et al. Synthesis of new potential anticancer agents based on 4-thiazolidinone and oleanane scaffolds. Med Chem Res. 2012; 21: 3568-3580.
- Panchuk R, Chumak V, Fil M, Havrylyuk DY, Zimenkovsky B, Lesyk R, et al. Study of molecular mechanisms of proapoptotic action of novel heterocyclic 4-thiazolidone derivatives. Biopolymers and Cell. 2012; 28: 121-128.
- Havrylyuk D, Zimenkovsky B, Vasylenko O, Day CW, Smee DF, Grellier P, et al. Synthesis and biological activity evaluation of 5-pyrazoline substituted 4-thiazolidinones. Eur J Med Chem. 2013; 66: 228-237.
- Romagnoli R, Baraldi PG, Salvador MK, Camacho ME, Balzarini J, Bermejo J, et al. Anticancer activity of novel hybrid molecules containing 5-benzylidene thiazolidine-2,4-dione. Eur J Med Chem. 2013; 63: 544-557.
- Zhang Q, Liu X, Li X, Li C, Zhou H, Yan B. Antitumor activity of (2E, 5Z)-5-(2-hydroxybenzylidene)-2-((4-phenoxyphenyl)imino)thiazolidin-4-one, a novel microtubule-depolymerizing agent, in U87MG human glioblastoma cells and corresponding mouse xenograft model. Journal of pharmacological sciences. 2013; 122: 223-231.
- Joseph A, Shah CS, Kumar SS, Alex AT, Maliyakkal N, Moorkoth S, et al. Synthesis, in vitro anticancer and antioxidant activity of thiadiazole substituted thiazolidin-4-ones. Acta Pharm. 2013; 63: 397-408.
- Deep A, Narasimhan B, Ramasamy K, Mani V, Mishra RK, Majeed AB, et al. Synthesis, antimicrobial, anticancer evaluation and QSAR studies of thiazolidin-4-ones clubbed with quinazolinone. Curr Top Med Chem. 2013; 13: 2034-2046.
- Devinyak O, Havrylyuk D, Zimekovsky B, Lesyk R. Computational search for possible mechanisms of 4-thiazolidinones anticancer activity: the power of visualization. Mol Inf. 2014; 33: 216-229.
- Wu J, Yu L, Yang F, Li J, Wang P, Zhou W. Optimization of 2-(3-(arylalkyl amino carbonyl) phenyl)-3-(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-thiazolidinone derivatives as potent antitumor growth and metastasis agents. Eur J Med Chem. 2014; 80: 340-351.
- Sharath Kumar KS, Hanumappa A, Hegde M, Narasimhamurthy KH, Raghavan SC, Rangappa KS, et al. Synthesis and antiproliferative effect of novel 4-thiazolidinone-, pyridine- and piperazine-based conjugates on human leukemic cells. Eur J Med Chem. 2014; 81: 341-349.
- Avdieiev S, Gera L, Havrylyuk D, Hodges RS, Lesyk R, Ribrag V, et al. Bradykinin antagonists and thiazolidinone derivatives as new potential anti-cancer compounds. Bioorg Med Chem. 2014; 22: 3815-3823.
- Carter PH, Scherle PA, Muckelbauer JK, Voss ME, Liu RQ, Thompson LA. Photochemically enhanced binding of small molecules to the tumor necrosis factor receptor-1 inhibits the binding of TNF-alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001; 98: 11879-11884.
- Degterev A, Lugovskoy A, Cardone M, Mulley B, Wagner G, Mitchison T, et al. Identification of small-molecule inhibitors of interaction between the BH3 domain and Bcl-xL. Nat Cell Biol. 2001; 3: 173-182.
- Cutshall NS, O'Day C, Prezhdo M. Rhodanine derivatives as inhibitors of JSP-1. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005; 15: 3374-3379.
- Dayam R, Aiello F, Deng J, Wu Y, Garofalo A, Chen X. Discovery of small molecule integrin alphavbeta3 antagonists as novel anticancer agents. J Med Chem. 2006; 49: 4526-4534.
- Geronikaki A, Eleftheriou P, Vicini P, Alam I, Dixit A, Saxena AK, et al. 2-Thiazolylimino/heteroarylimino-5-arylidene-4-thiazolidinones as new agents with SHP-2 inhibitory action. J Med Chem. 2008; 51: 5221-5228.
- Zheng W, Degterev A, Hsu E, Yuan J, Yuan C. Structure-activity relationship study of a novel necroptosis inhibitor, necrostatin-7. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008; 18: 4932-4935.
- Devinyak O, Zimenkovsky B, Lesyk R. Biologically active 4-thiazolidinones: a review of QSAR studies and QSAR modeling of antitumor activity. Curr Top Med Chem. 2012; 12: 2763-2784.
- Lesyk R, Zimenkovsky B, Kaminskyy D, Kryshchyshyn A, Havrylyuk D, Atamanyuk D, et al. Thiazolidinone motif in anticancer drug discovery. Experience of DH LNMU medicinal chemistry scientific group. Biopolymers and Cell. 2011; 27: 107-117.
- Havrylyuk D, Zimenkovsky B, Vasylenko O, Zaprutko L, Gzella A, Lesyk R, et al. Synthesis of novel thiazolone-based compounds containing pyrazoline moiety and evaluation of their anticancer activity. Eur J Med Chem. 2009; 44: 1396-1404.
- Havrylyuk D, Kovach N, Zimenkovsky B, Vasylenko O, Lesyk R. Synthesis and anticancer activity of isatin-based pyrazolines and thiazolidines conjugates. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2011; 344: 514-522.
- Boyd MR, Paull KD. Some practical considerations and applications of the national cancer institute in vitro anticancer drug discovery screen. Drug Dev Res. 1995; 34: 91-109.
- Shoemaker RH. The NCI60 human tumour cell line anticancer drug screen. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006; 6: 813-823.
- Zimenkovsky BS, Devinyak, Lesyk RB. Modeling of possible pharmacophore group for 4-thiazolidinones with anticancer activity (in Ukrainian). Journal of Organic and Pharmaceutical Chemistry (Ukraine). 2012; 10: 76-82.
- Zimenkovsky BS, Devinyak, Lesyk RB. QSAR Study of 4-Thiazolidinones as Anticancer Agents Using Regression Analysis and Classification Modeling (in Ukrainian). Journal of Organic and Pharmaceutical Chemistry (Ukraine). 2012; 10: 43-49.
- Tetko IV, Gasteiger J, Todeschini R, Mauri A, Livingstone D, Ertl P, et al. Virtual computational chemistry laboratory--design and description. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2005; 19: 453-463.
- Steffens M, Lamina C, Illig T, Bettecken T, Vogler R, Entz P, et al. SNP-based analysis of genetic substructure in the German population. Hum Hered. 2006; 62: 20-29.
- Liaw A, Wiener M. Classification and regression by random Forest. R news. 2002; 2: 18-22.
- Filzmoser P, Hron K, Reimann C. Interpretation of multivariate outliers for compositional data. Computers & Geosciences. 2012; 39: 77-85.
- Dean CB, Nielsen JD. Generalized linear mixed models: a review and some extensions. Lifetime Data Anal. 2007; 13: 497-512.
- Knezevic SZ, Streibig JC, Ritz C. Utilizing R software package for dose-response studies: the concept and data analysis. Weed Technology. 2007; 21: 840-848.
- Ozdemir A, Turan-Zitouni G, Kaplancikli ZA, Chevallet P. Synthesis of some 4-arylidenamino-4H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thiols and their antituberculosis activity. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2007; 22: 511-516.