
Review Article
Austin J Bus Adm Manage. 2022; 6(1): 1050.
The New Application of Global Positioning for Truck in RTT Logistic at Cameron Highlands
Vijayakumar Y*
Open University Malaysia (OUM), Sri Rampai, Malaysia
*Corresponding author: Yogesh Vijayakumar, Open University Malaysia (OUM), Sri Rampai, Malaysia
Received: February 14, 2022; Accepted: March 09, 2022; Published: March 16, 2022
Abstract
This research sought to determine how Ringlet Trading Transport Logistics in Cameron Highlands used a new application known as a Global Positioning System for truck to improve on-time delivery performance in order to fulfil customers’ expectations and satisfaction through on-time delivery. This research, on the other hand, contributes to the enhancement of RTT Logistics procurement and production by giving an effective application for businesses to save expenses (cost minimizations) by calculating the most direct route to their destination. In order to properly achieve the study’s goal, data was also collected through a survey and an interview session. In addition, 30 truck drivers in Cameron Highlands responded to the survey. The truck drivers were between the ages of 18 and 55. The drivers were asked to determine if they agreed that on-time delivery has increased their capacity to meet the expectations of their clients. In this study, the Global Positioning System (GPS) was found to make truck drivers’ everyday work trips easier. Aside from that, RTT Logistics’ owner believed that implementing a new application would assist the company in achieving its goals and objectives.
Keywords: Global Positioning System; Ringlet Trading Transport Logistics
Introduction
This study intends to improve on-time delivery performance, procurement, and production in order to satisfy customers’ expectations and satisfaction through delivery, time, and determining an efficient route for truck drivers. The study also aims to verify the route time length estimated by the Global Positioning System (GPS) in the absence of traffic, as well as the real-time required by truck drivers to get at their destination without delay. The background of the study, the problem description, the research theory, the research objectives, the research questions, the importance of research, the research limitation, the definition of terminology, and the chapter summary are all covered in this chapter.
background and context
Globalization is a prominent trend in logistics because the global marketplace and procurement operations are a reality in today’s business environment. It provides businesses with numerous options to operate in the global market by expanding prospective market locations and clients, as well as expanding the potential supply network. Similarly, globalization imposes other pressures, such as the contemporary global economy’s desire for the finest quality items at the lowest cost, regardless of where they are created. In order to build cost-effective and customer supply chains, multinational enterprises necessitate worldwide logistics networks.
Logistics centers are essential nodes in the global logistics system that can boost the value of logistics services in the logistics value chain and, in particular, provide efficient terminal operations, boosting supply chain competitiveness. In a global logistics network, logistics hubs may play a role. These can be focused on certain markets or specialized in the needs of specific products or business segments. The network of logistics service providers can also be utilized to focus on the location and service level of logistics facilities. When assessing the significance of these types of logistics structures in the global network, the location of the logistics centre in the customer’s supply chain is the most important factor to consider.
Global positioning system (GPS)
The Global Positioning System (GPS) offers vital and long-awaited features that are beneficial to businesses. Through the use of more effective logistics, these features will assist businesses in increasing their growth and creating a better profit margin. Companies will be able to give better customer care to their customers through real-time tracking attributable to global positioning systems. Companies will be able to execute work more efficiently and pursue new projects that were previously unattainable, effectively passing the savings on to the client.
The Global Positioning System is still currently in the growing phase of its lifecycle. The price of this technology is decreasing because of increasing adopting by consumers. With the prices lowering, more companies are able to adopt GPS. In addition, companies are adapting the technology and developing new ways to use the product. They are also discovering a multitude of purposes in addition to its well-known mapping capabilities.
Radio frequency identification (RFID)
Radio Frequency Identifying (RFID) is a type of identification that allows products to be tracked and traced throughout supply chains. Operational efficiency, precision, visibility, and security are the four benefits of Radio Frequency Identification technology. Radio Frequency Identification tags provide several benefits for supply chain management, according to Kapoor, Dwivedi, Piercy, Lal and Weerakkody [1], including improved asset management, improved inventory control, shrinkage reduction, increased product availability and fulfillment rates, labour cost reduction, decreased operational time, material handling efficiency, improved process throughput, and improved customer service, including returns and recall management. According to Hu et al. [2], using Radio Frequency Identification in a terminal can reduce queuing and the number of gates required in a gatehouse, lowering infrastructure costs and improving operational efficiency.
In the not-too-distant future, radio frequency identification tags are likely to displace barcodes [1]. When compared to barcodes, the advantages of Radio Frequency Identification tags include the fact that they do not require line of sight between tags and readers, that multiple items can be read at the same time, that tags can be read through non-metallic materials, and that they are resistant to temperature and other external factors such as moisture. RFID tags can be read and reprogrammed multiple times as well. Furthermore, battery-powered Radio Frequency Identification tags can track environmental factors such as temperature and bacteria levels [3].
The research proposal’s main focus is on identifying the characteristics that influence vehicle operation in RTT logistics (rtt. co, 2017). The maximum speed limit for a truck with a Gross Vehicle Mass (GVM) of more than 4.5 tonnes is 100km/h. For trucks, street preparations, and transports, special speed point of confinement signs may be put depending on the street conditions. The drivers should not drive at a higher speed than the speed shown on the clue. The Global Positioning System (GPS) is the application that determines how far a vehicle may travel at its maximum speed. If a truck collides with one of the accompanying groups, its speed must be limited to 100km/h.
As a result, new applications with global positioning have had a significant impact on truck driver performance. The truck’s global positioning application at RTT Logistics in Cameron Highlands will improve the short course by maintaining a strategic distance from the roadways, which have been made into systematic parking spaces. This research is critical for the exploration to improve the time of the executives by opposing the outcomes sought by the lorry driver, especially during events and when driving to a different destination. The ‘Global Positioning System,’ or GPS, is a satellite route structure that determines an item’s ground position. The ability to track in order to establish the position of a given component is at the heart of global positioning principles. It helps to determine the exact location and the position of the subject by Hwang S & Yu D [4].
The problem statement
Fuel costs are still a major concern in the logistics industry. Higher fuel prices will almost certainly increase transportation expenses for most transportation service providers. Rising diesel fuel costs are causing additional charges to be applied to cargo rates, reversing a two-year pattern in which rising fuel costs cut into truckers’ income and profit. The logistics industry has found it more difficult to keep up with new improvements in business processes due to business process improvement and the requirement for new technologies.
While taking advantage of these new options may sound appealing, adoption and onboarding can be challenging. Aside from that, customer service is a major concern in the logistics sector, since most consumers want complete transparency about where their deliveries are at all times. In today’s world, a bundle’s region is as interwoven as an informal organization. Truth be told, as customer demands have grown, their willingness to pay for expedited shipping has decreased, since most purchasers are unwilling to pay anything extra for shipping that takes longer than two days. Specific issues include the following:
Fuel costs: Fuel expenses are perhaps the most startling expenditure contributing to the ‘reducing transportation costs’ worry. Higher gasoline rates will almost certainly increase transportation expenses for Malaysian shippers this year as fuel extra charges rise. Increasing Malaysia diesel fuel costs are increasing additional charges imposed to cargo rates, reversing a two-year pattern that has cut into trucker’s fuel costs, business process, client administration income and profit.
Customer service: Clients require complete transparency on the status of their transfer. Nowadays, a bundle’s region is as interrelated as your interpersonal network (social network). In fact, as customer expectations have grown, so has their willingness to pay for expedited shipment, with over 64% of buyers unwilling to pay anything more for shipping that takes longer than two days.
The Objectives (s)
• To improvise on-time delivery performance of RTT Logistic by 15% - 20% in orders to meet customer’s expectation and satisfaction, through delivery, time and identifying an effective route for the truck drivers and simplify the application with the compilation of obstacles of the route.
• To validate the route time duration estimated by the Global Positioning system without traffic data, a route planned by considering 18% - 20% traffic data and the real-time needed by the truck to reach the destination.
• To improvise the procurement and production of RTT Logistic by 19% - 20% by getting an effective application for companies to reduce the cost minimizations by getting the easiest route to reach a destination.
The Questions (s):
• What is the role of Global Positioning Systems in facilitating RTT Logistic firm performance?
• Is there any difference in RTT Logistic firm performance on the implementation of Global Positioning Systems?
• What are the key issues faced by RTT Logistic firm in adopting Global Positioning System into operations?
Literature Review
Benefits of global positioning system (GPS)
Google Map is a web mapping administration built by Google, according to Jethani, Jain, Thomas, Pechetti, Pareek, Gupta, and Singal [5]. It provides satellite photos, guides, 360-degree Celsius wide-angle views of highways, constant development circumstances, and course planning for passing by foot, vehicle, bicycle, and truck. Google Maps provides the most basic information about geographical locations and objectives around the world. In addition to typical tools, Google Maps provides ethereal and satellite views of certain locations. Google Maps includes road views using photographs collected from vehicles in select urban areas. For truck drivers that use the Global Positioning System Framework (GPS) area of cell phones, Google Map for Mobile provides an area benefit that can be accessed alongside information from remote and cell systems. In management activities, GPS tracking systems can provide a variety of major advantages. The majority of the advantages are efficiencyrelated, supporting organizations in lowering costs and increasing profits. The following are four advantages of using a GPS for a truck:
Global Positioning System provides route optimization
The Global Positioning System (GPS) was introduced for truck drivers to improve continuous information on the area of each truck, allowing the driver to send the perfect course for the truck to take in order to maintain a strategic distance from deferrals due to development, roads that have been turned into parking lots, or accidents (mishaps).
Decrease response times for improving customer service
The Global Positioning System (GPS) will increase your response times when dealing with clients by allowing the truck driver to choose alternate routes to arrive to their destination within the allotted time, allowing you to provide rapid, responsive service.
Reduce fuel costs
Fuel expenditures are one of the most significant expenses for a business, particularly for truck drivers, but the Global Positioning System (GPS) can assist decrease these costs and save businesses money. The Global Positioning System (GPS) application allows truck drivers to reduce the amount of time they spend sitting in traffic or not in use by showing them the most effective route to follow when stuck in traffic.
Improve the safety of truck drivers and trucks
Another significant advantage of the Global Positioning System (GPS) is that it improves the overall safety of the truck. The Global Positioning System (GPS) enables owners to detect a problem with a driver before incurring a costly repair charge as a result of poor driving habits. When drivers are aware that their driving behaviours are being observed, they are less likely to take needless risks and cause unnecessary wear and tear on their vehicles.
Longitude and latitude co-ordinate system
The location of each point on a planar surface can be adequately defined by both a horizontal and a vertical co-ordinate, according to research by Taylor, E.G.R., and The Haven-finding Art: A History of Navigation from Odysseus to Captain Cook, Hollis & Carter, London [6]. A simple evenly spaced grid system might be utilized to depict any location on the world if the earth was genuinely flat and rectangular as it had been perceived in the past. The earth, on the other hand, is neither flat nor rectangular. It’s far from being a perfect spherical. The earth is an oblate ellipsoid, a spherical with a slightly egg-shaped shape. To describe accurate places on Earth, a grid-like system of latitudes and longitudes was established. Both latitude and longitude are measured in terms of degrees, (°).
Advantages of global positioning system (GPS)
According to Paul Bartee and Dooley [7], the Global Positioning System (GPS) has a number of advantages over older methods and technologies for improving on-time delivery and customer satisfaction (Figure 1 and Table 1).
Traffic and Weather alerts
One positive aspect of GPS is that it is constantly occurring. This means you'll be warned if there's a traffic jam or other delay ahead, or if the truck drivers are approaching an area where a severe weather event is taking place. Not only would this reduce their travel time, but it will also improve their safety.
Updated and maintained
The US Department of Defense pays for, updates, and maintains the GPS system to ensure that it is always accurate. Most GPS-enabled software programmes, and devices are also updated on a regular basis, usually for free. As a result, unlike a traditional printed map that becomes outdated after a time, GPS and related technology are usually quite accurate.
Flexible Navigation
GPS provides real-time route options, allowing for greater flexibility. Drivers can select a route based on their specific needs or wants. If they make a wrong turn, GPS can be used to compute a new route. If their path is obstructed due to an occurrence, GPS can be utilised to generate an alternative route.
Simple to utilize
When compared to traditional approaches and advancements, such as map-reading, taking a route using GPS is frequently extremely straightforward and needs little experience or effort. Most of the time, the user only needs to enter the destination and the gadget will handle the rest. GPS is also a less complicated and increasingly effective technology.
Minimal cost
The US Department of Defense pays for, maintains, and updates the GPS satellites. That implies the system is fundamentally free, however users may be required to pay for a device and software in order to use it. GPS-enabled cell phone applications, such as Google Maps, are usually free.
Navigation
The most well known application of GPS is in route planning. It becomes an incredible tool for street cars and vessels when combined with guiding innovation. GPS can precisely locate a device's location, and by looking at directions, the information may be used to compute a device's heading and speed. This data can be used to create detailed instructions from point A to point B in real-time.
Safety
The owners of the vehicle can utilise GPS to keep track on its drivers. Workers and others can utilise GPS tracking for personal safety and to ensure that their location is known in the event of an emergency.
Table 1: Technologies to improve on-time delivery to meet customer’s satisfactions Paul Goodman [7].
Methodology
Research methodology
This study used a survey method as part of a quantitative research strategy. The truck driver’s hurdles in reaching their location were observed using this research method. After using the new system to increase on-time delivery performance and minimize the company’s cost minimization, the strategies for how the system works were recognised. Furthermore, it advocates for the elimination of confounding variables that could distort the study’s results and impede the discovery of an underlying association. The data from the polls were analyses using descriptive statistics to determine how truck drivers viewed GPS technology in terms of improving on-time delivery and customer satisfaction.
Participants and setting
A random sampling approach is used to select the study’s sample. The term “random sampling method” refers to sampling strategies in which each sample has an equal chance of being chosen. For this study, 30 truck drivers aged 18 to 55 from Ringlet Trading Transports (RTT) Logistics in Cameron Highlands were chosen.
Results and Findings
Business performances
When it comes to logistic, business execution is critical in order to have a smooth advantages and conveyance procedure that dazzles the client with exceptional and on-time delivery. The business execution before and after the use of GPS in RTT Logistic is depicted in Figure 1 and 3.
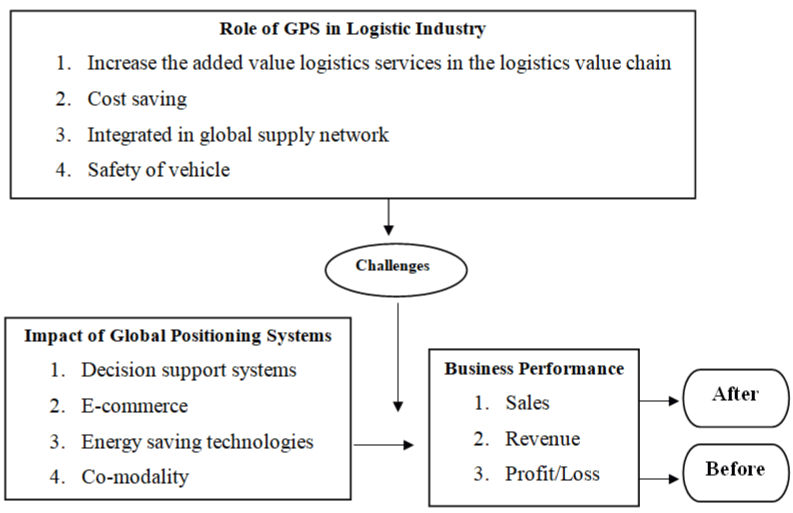
Figure 1: The challenges for logistic industry to sustain the business performance.
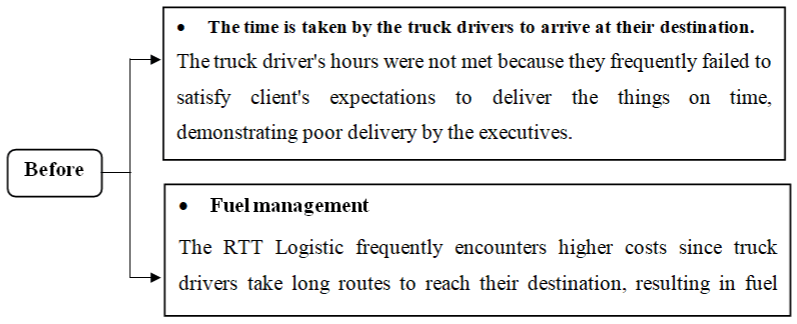
Figure 2: Demonstrates the business execution before the usage of GPS in
RTT Logistic.
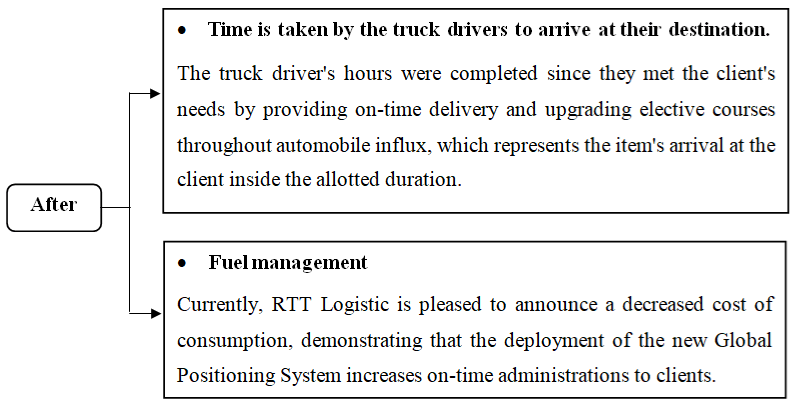
Figure 3: Demonstrates the business execution after the usage of GPS in
RTT Logistic.
The implementation of new application global positioning system (GPS)
Mr. Yogesh Vijayakumar is the founder of Ringlet Trading Company, a vital transportation company that was founded in 1992. As a result, RTT Logistics identifies ‘Curl Trading Transports (RTT) Logistic’ as the alternative transportation developed in 2014. RTT Logistic is primarily focused on cargo transportation in Malaysia. RTT Logistics offers a cutting-edge stockroom the board structure for managing client stock across many states. RTT Logistics finetunes its strategy by gaining a better grasp of the client’s needs and reworking administrations to answer their concerns. The analyst preferred to continue the investigation with RTT Logistic to ensure that the investigation’s purpose and points were met without difficulty. Furthermore, RTT Logistic was chosen as the analyst to address many concerns such as consumer loyalty in transportation, high cost consumption, transportation support, and time duration to reach their destination.
The study focuses on a single strategic, Cameron Highlandsbased RTT Logistics. The investigation was enlisted to carry out a new application among RTT Logistics in order to resolve the concerns that had been identified. The researcher chooses the auxiliary RTT Logistic because transportation has a number of challenges, including driver dissatisfaction, a long wait for drivers to reach at their destination, and client satisfaction. The scientist is well-prepared and wisely chooses the RTT Logistic to implement the novel use of concentrate to address the calculated problems.
The owner of RTT Logistics ensures that the truck drivers are still taking the long route because they aren’t used to taking alternative routes to get to their destinations. The proprietor requests that the long course be used to increase consumption, gasoline, and time to reach their objectives, as well as the driver’s safety. Based on the information received, the owner stated that the drivers are exceeding the truck’s speed limit in order to arrive at their destination within the allotted time, resulting in occasional mishaps during the transportation. This demonstrates that the proprietor is sincerely concerned about the new application’s security and cost reductions.
Survey questionnaire
The use of the new Global Positioning System (GPS) is a fantastic application. When a truck driver’s regular life is integrated into the application, the driver is better prepared to use the Global Positioning application in their everyday travel in order to make their voyage smoother and happier while meeting the exceptional conveyance among consumers.
According to Table 2, 76.7 percent of truck drivers strongly agreed that the new application allows them to meet their clients’ desires and fulfil their obligations through on-time delivery. These shows the drivers figuring out how to gather traffic data and alternative routes to reach at their planned destination and offer the client’s stuff without any hassles. As a result, 90.0% of truck drivers stated that using a global positioning system helps them arrives at their destination on time and that they have consistently figured out how to deliver things on time to satisfy customers.
No
Statements
Strongly Disagree
Disagree
Neutral
Agree
Strongly Agree
N
%
N
%
N
%
N
%
N
%
1
This application helps me to meet my customer’s expectations and satisfaction through delivery.
0
0
0
0
7
23.3
11
36.7
12
40
2
I think GPS is beneficial to reach the destination within the stipulated period.
0
0
0
0
3
10
13
43.3
14
46.7
3
Using the new Global Positioning System application cause to alter my behaviours through meeting the customer’s satisfaction.
0
0
0
0
9
30
6
20
15
50
4
The new Global Positioning System application helps me to improvise on-time delivery performance.
0
0
0
0
11
36.7
7
23.3
12
40
5
The new application often ensures the traffic data and shows the real-time. Needs to reach the planned destination.
0
0
0
0
4
13.3
12
40
14
46.7
Table 2: The implementation of GPS to ease the truck drivers’ routine.
On the other hand, a large number of truck drivers stated that GPS assisted them in changing their practices, which clearly clarifies that the drivers changed practices such as burning through the time it took to transport the item, using less fuel, spending less money on truck maintenance, and other related issues. Besides, 63.3% believed that GPS applications expedite on-time delivery and help the firm achieve its goals and objectives. It illustrates that truck drivers have found out how to obtain alternative routes and traffic data in order to improve company execution.
Last but not least, 86.7 percent of drivers noted that the new programme provides them with accurate congested road information and allows them to evaluate the continuous needs to reach at their chosen destination. As it outlines how drivers acquire precise traffic information and data and interacts, the programme ensures traffic information and illustrates the continual needs to arrive at the predetermined destination.
According to Table 3, 86.7% of truck drivers believe they can reduce their company’s expenses, including fuel costs and lorry maintenance costs. In addition, 90.0% of them agreed that they could determine the exact time they would arrive at their location. For example, they can exactly obtain the exact duration of hours and minutes in order to determine the whereabouts of their consumers.
No
Statements
Strongly Disagree
Disagree
Neutral
Agree
Strongly Agree
N
%
N
%
N
%
N
%
N
%
1
I can reach the planned destination in advance with no wastage of time.
0
0
0
0
4
13.3
12
40
14
46.7
2
I can estimate the traffic data and the real-time needed to reach my destination with no stress.
0
0
0
0
3
10
13
43.3
14
46.7
3
With alternative ways, I can reduce the company’s cost minimizations by getting the easiest route to reach my destination.
0
0
0
0
9
30
6
20
15
50
4
I can drive very peacefully with no stress as I can estimate my reaching time to the destination with low cost of diesel.
0
0
0
0
7
23.3
11
36.7
12
40
Table 3: The improvement in business performance.
70.0% of them agreed that finding the shortest route to my goal would help them save money for the company. As a result, it claims that they will be able to reduce the company’s expenses, as well as the cost of gasoline and the cost of lorry maintenance. Lastly, 76.7% of the drivers also felt that given low diesel prices, they could estimate their arrival time at their destination.” This implies that members can work without stress and arrive at their client’s location without a hitch, as they consistently affirmed that the Global Positioning application assisted them in various ways, particularly by suggesting alternate routes to their destinations during periods of heavy traffic.
Comparison of performances before and after the use of GPS
Before the use of GPS: Workers at RTT logistic come from a variety of ethnic backgrounds and bring a variety of skills to the table. Despite the presence of a speed trap, drivers frequently encountered mishaps as a result of excessive speed, and were frequently late in delivering the client’s things, disappointed in on-time delivery, and unsatisfactory in fulfilling customer satisfaction and demands. These are the common problems that arise among employees. If things are being delivered from Cameron Highlands to Kuala Lumpur, for example, the minimum time to reach at my customer’s location is 3-4 hours. Workers, on the other hand, used to work for 5-6 hours, clearly demonstrating that oil is being wasted and that consumption is at an all-time high. As a result of this problem, transportation bargains have arisen from the separate clients, who have complained about the drivers consistently failing to deliver the things on time.
After the use of GPS: The new Global Positioning System application ensures that the driver’s everyday travel is stress-free. Previously, I had to listen to rumours from my drivers about delays, but now I can anticipate the exact time it will take them to reach at their destination, demonstrating on-time delivery of goods to customers. As a result, the Global Positioning System (GPS) has aided me in a variety of ways, particularly in providing a smooth and easy travel experience for my drivers, as well as a friendlier workplace in comparison to the previous working zone, where speed trap messages would regularly cause them to slow down. To summarize, the GPS system I chose is beneficial to my business, and I am on track to fulfil my goals. The drivers, on the other hand, achieved RTT Logistics’ company’s objectives and goals after using GPS. The main goal is to ensure that the client’s needs are met and that they are delivered on time. Finally, during weekends and public holidays, they were able to estimate the precise time to arrive at the destination and collect traffic statistics from the Global Positioning application. This is a fantastic application that makes a significant contribution to the overall improvement of the firm. Finally, the company agreed that they worked together to achieve RTT Logistics’ goals. Therefore, setting goals and staying on pace to achieve them while growing RTT Logistics business is the ultimate goal.
Discussion
Getting the company’s aims and objectives accomplished might be difficult, especially for inexperienced drivers with less than a year of service experience. For these types of drivers, the Global Positioning application can play an important role, not only in assisting them in looking up information provided through the application, but also in inspiring them to complete the company’s goals and objectives by filling in route and traffic data from the application, which they may lack motivation when given different objectives to achieve. The Global Positioning System (GPS) application is essentially just a tool that allows you to organize and track data in a way that connects with the application to fulfil the customer’s satisfaction and expectations. There are varieties of common concerns that need to be resolved among the RTT Logistic. Truck drivers may notice the new Global Positioning application, which includes route information, speed trap notifications, and travel time to a destination.
Furthermore, some people believe that advanced drivers, such as those with more than 20 to 30 years of driving experience, will find the Global Positioning application unchallenging. However, what they do not realise is that the Global Positioning application is not only for filling up information for traffic data. They can be used to improve information such as projected travel time to a location, speed trap cameras, and other related information about route obstructions. For example, this new application might be offered to all drivers to increase their driving passion in order to fulfil the company’s goals and ensure the drivers’ safety. There are varieties of challenges that the RTT Logistic owner should look for so that they may use them to help their drivers overcome those issues and problems and earn more money.
We have witnessed a considerable difference in the impacts of the drivers after using the Global Positioning application, according to the conclusions of this study. Although the truck drivers had some difficulties using the programme, their results were considerably better, as they demonstrated that the Global Positioning System influenced their driving and made their voyage enjoyable and stressfree, with no health issues. This proves that the app is one of the most effective tools for boosting driver performance. As a result, the Global Positioning application can be extremely beneficial to all types of truck drivers that are under a lot of pressure to meet customer expectations and deliver things to them. Truck drivers of all ages can use Global Positioning applications, but it is critical for the company owner to understand which types of Global Positioning are appropriate for various job reasons.
Recommendation
The new Global Positioning application should take no more than three to four months to complete. This is due to the fact that, given the time constraints, it is impossible to identify the implementation’s aftereffects among the Logistic. The truck drivers’ interest could not be gauged in the small time frame of four weeks; therefore, a longer time frame would be beneficial. Logistic should be introduced with numerous types of studies rather than merely the use of Global Positioning application study for further research. The researcher only collected data on the use of the new application in this study. In RTT Logistic, there are numerous types of difficulties that can be studied repeatedly until the problems and issues are resolved.
Global Positioning appears to be an effective application intervention for troublesome Logistics’ individuals aiming for ontime conveyance and achieving the company’s aims and goals, based on the findings of this study. Investigating solutions to improve various types of difficulties in Logistics is justified, and it is necessary to advance for their instructive success. Further research could focus on a bigger sample size to analyze the use of the Global Positioning application in enhancing the company’s aims and objectives to fulfil customer satisfaction and expectations, because the larger the sample size, the more accurate the study’s conclusions. Further study may enable respondents to set their own goals for getting to their destination, delivering things on time, and updating the daily report to the owner, rather than waiting for the owner to call and collect the daily report. Truck drivers should be allowed to take alternate routes to get to their destination within the time limit so that they are not overly reliant on the owner.
References
- Kapoor K, Dwivedi Y, Piercy NC, Lal B, Weerakkody V. RFID integrated systems in libraries: extending TAM model for empirically examining the use. Journal of Enterprise Information Management. 2014.
- Chen H, Zhu Y, Hu K, Ku T. RFID network planning using a multi-swarm optimizer. Journal of Network and Computer Applications. 2011; 34: 888-901.
- Michael K, McCathie L. The pros and cons of RFID in supply chain management. In International Conference on Mobile Business (ICMB’05). 2005: 623-629.
- Hwang S, Yu D. Remote monitoring and controlling system based on ZigBee networks. International Journal of Software Engineering and Its Applications. 2012; 6: 35-42.
- Jethani S, Jain E, Thomas IS, Pechetti H, Pareek B, Gupta P, et al. Surveillance system for monitoring social distance. In International Advanced Computing Conference. Springer, Singapore. 2020: 100-112.
- Taylor EGR. The heaven-finding art, a history of navigation from Odysseus to Captain Cook. The heaven-finding arts. 1971.
- Bartee RL & Dooley L. African American veterans career transition using the transition Goals, Plans, Success (GPS) Program as a Model for Success. Journal of Veterans Studies. 2019; 5.