
Research Article
Austin Chem Eng. 2023; 10(1): 1093.
Ultrasonic Extraction of Java Ginseng Leaves (Talinum Triangulare (Jacq.) Willd) with Variables of Ethanol Solution Ratio and Extraction Time
Adhika B1, Hendrawati TY1*, Ismiyati1, Hasyim UH2 and Nugrahani RA5
¹Department of Master Chemical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Universitas Muhammadiyah Jakarta, Indonesia
²Department of Chemical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Universitas Muhammadiyah Jakarta, Indonesia
*Corresponding author: Hendrawati TYDepartment of Chemical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Universitas Muhammadiyah Jakarta, Indonesia
Received: January 26, 2023; Accepted: March 07, 2023; Published: March 14, 2023
Abstract
Indonesia has abundant biodiversity for types of plants that are thought to have efficacy as herbal medicines. Javanese Ginseng (Talinum Triangulare (Jacq.) Willd) is one of them, so it is necessary to conduct research to utilize it. The purpose of this study was to determine the process conditions to obtain the highest extraction yield and to determine what components of flavonoid bioactive compounds contained in the Javanese Ginseng extract. As part of the ultrasonic extraction method, the variables tested were, among others, various ratios between ethanol-dried Javanese Ginseng powder and sonication time. Javanese ginseng was dried in an oven at 60°C for 4 days to a moisture content of less than 4%, then ground and filtered using a 40-mesh filter. The first phase of this study was to test the various ratios of solutions between dried Javanese Ginseng powder and 96% ethanol (m/v), which were 1:1, 1:2, 1:3, 1:4, and 1:5 at constant concentration for 30 minutes. The second phase is to vary the sonication time, namely 10, 15, 20, 25 and 30 minutes at a constant solution ratio, namely the ratio with the highest extract yield obtained from extraction with various solution ratios between dried Java Ginseng powder and 96% ethanol (m/v). Through this research, the ultrasonic wavelength used was 40kHz and the temperature of the water bath to concentrate the Javanese Ginseng was set at a temperature of 50 – 60oC. The best yield of both phases was 10.14% for the parameter ratio 1:5 (m/v) and the sonication time was 30 minutes with an extract pH of 4.36, a density of 1.0415 g/cm³, and a greenish-brown color.
Keywords: Gingseng Jawa (Talinum Triangulare (Jacq.) Willd); Ultrasonic; Yield; Flavanoid
Introduction
Indonesia has abundant biodiversity, including the wealth of various types of plants that have properties as a source of active substances. The use of natural materials as a source of bioactive substances has become an issue that is widely discussed as a research topic and tends to be an option for the people of Indonesia. In addition, the prolonged health crisis due to the outbreak of the Corona COVID-19 virus has encouraged people to turn to the use of natural ingredients as a source of active substances to prevent outbreaks, which are expected to increase stamina and immunity.
One of the natural ingredients that have potential as a source of bioactive substances is Javanese Ginseng Leaf (Talinum Triangulare (Jacq.) Willd). Javanese ginseng leaves are known to contain active substances in the form of flavonoids [1,2]. In plants there are small molecular chemical compounds whose distribution is limited and are often referred to as secondary metabolites. The number of secondary metabolites in plants is less than the primary metabolites (carbohydrates, fats, proteins). Phytochemical tests were carried out to determine secondary metabolites from plants. Secondary metabolites in plants include saponins, flavonoids, phenols, alkaloids, steroids, terpenoids and tannins [3]. The following is a description of the phytochemical properties of Javanese ginseng leaves [4].
Utilization of natural materials as a source of bioactive substances requires proper handling. In general, the extraction of active substances in natural ingredients uses a method that has been widely used, namely extraction. The extraction method that is mostly used for the process of taking active compounds from plants is maceration extraction (soaking). However, this method is known to be a conventional method and is considered to take quite a long time so it is considered less effective [5,3].
Ultrasonic is a modified maceration method using ultrasound (high frequency signal). This is done to apply mechanical pressure to the cell to produce a cavity in the sample. Cell damage can cause an increase in the solubility of the compound in the solvent and increase the extraction yield [6].
The purpose of this study was to determine the best extraction time by ultrasonic method and the optimum ethanol solvent ratio to obtain the best yield and to analyze qualitatively the types of flavonoid bioactive compounds contained in the extract of Javanese Ginseng (Talinum Triangulare (Jacq.) Willd).
Phytochemicals are bioactive compounds found in plants and can have health effects on humans. In plants there are a small molecular chemical compound whose distribution is limited and are often referred to as secondary metabolites (Sirait, 2007). The number of secondary metabolites in plants is less than the primary metabolites (carbohydrates, fats, proteins). Phytochemical tests were carried out to determine secondary metabolites from plants. Secondary metabolites in plants include saponins, flavonoids, phenols, alkaloids, steroids, terpenoids and tannins.
Flavonoids are found in large amounts in plants and cannot be synthesized by humans and animals. Because of their activity as free radical scavengers, flavonoids are very important for human health to protect tissues from oxidation processes. As a component of food ingredients, flavonoids act as a color, flavor, and prevent fat oxidation so that they can protect vitamins from enzymes in food [7].
Javanese ginseng leaves are known to contain various kinds of active substances, one of which is flavonoids which have functions as antioxidants, anti-radical activity [8], anti-mutagenesis and anti-promotion [9]. Undulatoside A with molecular formula C16 H18 O9 as Anti-inflammatory [10] Anti-Adipogenic. In addition, this plant also contains compounds 3-O-[β-D-Glucopyra-nosyl-(1→2)]-β-D-glucopyranosyl-kaempferol and Kaempferol-3-O-(2G-a-L-rhamnosyl) -rutinoside with molecular formulas C27 H30 O16 and C33 H40 O19 which has anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial, anti-free radical [11] and anti-hyperglycemic activities.
Extraction is a method of separating one substance from another mixture using a suitable solvent. This method is a method that has been widely used with several types of extraction. The choice of extraction method depends on the nature of the material and the compound to be isolated. Before selecting a method, the extraction target needs to be determined.
Ratio (m/v)
Java Ginseng Powder Weigth (g)
Volume Ethanol (ml)
Java Ginseng Extract Weight (g)
Yield(%)
1:1
50
50
1.018
2.04
1:2
50
100
1.867
3.73
1:3
50
150
2.643
5.29
1:4
50
200
3.839
7.68
1:5
50
250
5.070
10.14
Table 1: Results of Ultrasonic Extraction of Javanese Ginseng.
In this study, the extraction method with the help of ultrasonic waves is used, or commonly called ultrasonic extraction (ultrasonic-assisted extraction). Ultrasonic extraction method is an extraction process that utilizes ultrasonic waves or acoustic waves with a frequency greater than 16-20 kHz to obtain extract [12]. This type of extraction was chosen because it has several advantages, including speeding up the extraction process (compared to thermal extraction or extraction conventional methods, such as maceration), is safer, more time efficient, and can increase the crude yield of extracts. In addition, ultrasonic extraction can also be used in the extraction of heat-resistant materials [5,12].
The working principle of ultrasonic extraction is that with local high temperatures and mechanically increasing the movement of the solid and liquid interface movements, it is useful in the form of acoustic streaming and acoustic cavitation (Iersel, 2008). Acoustic streaming is sound waves that are transferred into a liquid forming a fluid motion in the direction of longitudinal wave propagation
Ethanol is a compound that does not occur freely in nature. This substance is a class of ordinary alcohol or primary alcohol which is made from glucose or other types of sugar by fermentation. Ethanol can be produced both petrochemically by hydration of ethylene and biologically by fermentation of sugars with yeast.
Methods
The research was conducted at the Chemical Engineering Laboratory, University of Muhammadiyah Jakarta and Saraswanti Indo Genentech from May to October 2021. The tools used included a 500 ml glass beaker, 1 L glass beaker, digital scale, oven, thermometer, grinder, 40 mesh siever, airtight container. 1 L air, 4 L airtight container, 500 ml aluminum foil container, Ultrasonic sonicator, whatman filter paper No.1, 250 ml erlenmeyer, 500 ml erlenmeyer, measuring cup, plastic sample bottle, rotary vacuum evaporator, 250 ml glass sample bottle, 1000 ml glass sample bottle. The ingredients used include dried Javanese Ginseng which is made into a powder. With the composition of dry Javanese Ginseng stem powder: dry Javanese Ginseng leaf powder is 1:1 (m/m), 96% ethanol.
The first research stage was to reduce the size of the Javanese ginseng, then it was dried in an oven at 60oC for 4 days. After 4 days, then the dried Javanese ginseng was ground and sieved at 40 mesh to get the same surface area. The first phase in this study was to vary the dried Javanese Ginseng powder with ethanol (m/v) in a ratio of 1:1, 1:2, 1:3, 1:4, and 1:5 with a time (t) of 30 minutes. The first phase of this research was carried out to determine the best ratio of solvent and powder of Javanese ginseng leaves with a sonicator wavelength of 40 kHz.
The next stage is the filtration process to separate Javanese Ginseng powder solids and solvents. Extract concentration was carried out using a rotary vacuum evaporator at a temperature (T) of 50-60°C. From the results of concentration using a rotary vacuum evaporator, the yield of Javanese ginseng extract was obtained, the yield calculation was based on the weight of the Javanese ginseng extract compared to the Javanese ginseng powder before it was extracted [3].
The Javanese ginseng extract was then analyzed by parameters of pH, density and color. The flow chart of the research procedure is presented in (Figure 1).
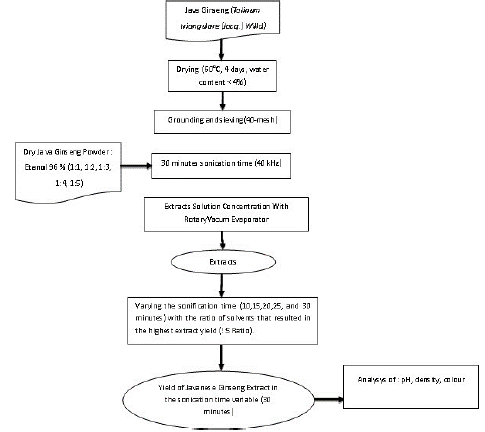
Figure 1: Research Flow Chart.
Result and Discussion
The leaves and stems of Javanese Ginseng were dried in an oven at 60oC for 4 days until the moisture content was less than 4%, then ground and filtered using a 40-mesh filter. As much as 50 g was taken for ultrasonic extraction with a wavelength of 40 kHz with a variation of ethanol solvent (m/v) namely 1:1, 1:2, 1:3, 1:4, and 1:5 at a constant length of time for 30 minutes, the ethanol solvent was separated using a rotary vacuum evaporator at a temperature of 50-60oC. Then the extract was weighed to calculate the yield.
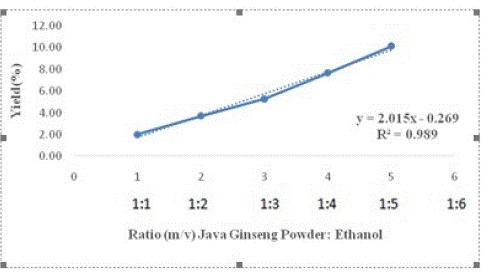
Figure 2: The Effect of the Ratio of Dry Java Ginseng Powder and Ethanol Solvent on the Yield of Javanese Ginseng Extract.
Based on Figure 3, the ratio of Javanese ginseng powder affects the yield following the linear regression equation y=2.015 x–0.269, where the value of y is the yield and x is the ratio of powder and solvent. The R2 value is 0.989, this shows a close correlation between y and x, where the greater the ratio of powder and solvent used, the greater the yield. The yield of Javanese ginseng extract with a time of 30 minutes, through the ultrasonication process the best was obtained at a ratio of 1:5, which was 10.14%.
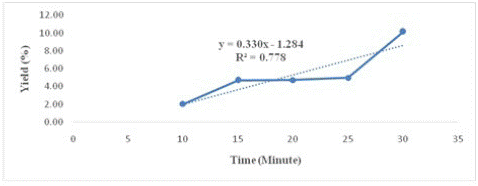
Figure 3: The Effect of Sonication Time on the Yield of Javanese Ginseng Extract.
The best ratio results are used for the next variable, namely the sonication time with variations of 10, 15, 20, 25, 30 minutes. The results of sonication time on the yield of Javanese ginseng extract are presented in (Figure 3).
Based on (Figure 3), the sonication time affects the yield following the linear regression equation y=0.330 x=1.284, where the value of y is the yield and x is the sonication time. The value of R2 is 0.778, this shows a close correlation between y and x, where the longer the sonication time, the greater the yield. The yield of Javanese ginseng extract with a ratio of 1:5, through the ultrasonication process the best was obtained at 30 minutes, which was 10.14%.
According to research by Lestario et al., 2009 the extraction of Javanese ginseng leaves using a solvent ratio of 1:5 (w/v), and then shaking for 16 hours. The filtrate was filtered and the residue was extracted again with the same solvent for 2 x 4 hours. yielded 18.40% yield. The yields obtained based on the research of Lestario et al are greater, but the time required is longer. This proves that the sonication method is better than the maceration method, because cavitation when treated with ultrasonic waves can break down the cell walls of the material [13,14].
Then an analysis of the pH value, density and color was carried out. The pH value of the Javanese ginseng extract which had the best yield (1:5 ratio and 30 minutes of sonication time) was 4.36. The Javanese Ginseng Extract also has a density of 1.0415 (gr/ml) and is greenish-brown in color.
Conclusions
The best extraction results using the ultrasonic method of Javanese Ginseng (Talinum Triangulare (Jacq.) Willd) with 96% ethanol solvent were obtained at a ratio of 1:5 (m/v) and a sonication time of 30 minutes. The yield of the extract was 10.14%, pH 4.36, density 1.0415 gr/cm³, and the color of the extract was greenish brown.
References
- J Swarna, TS Lokeswari, M Smita, R Ravindhran. Characterisation and determination of in vitro antioxidant potential of betalains from Talinum triangulare (Jacq.) Willd. Food Chem. 2013; 141: 4382–4390.
- JM Calderón-Montaño, E Burgos-Morón, C Pérez-Guerrero, M López-Lázaro. A Review on the Dietary Flavonoid Kaempferol. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2011; 11: 298–344.
- TY Hendrawati, A Nuraini, RJ Hakim, NH Fithriyah. Characterization and properties of gedi (Abelmoschus manihot l.) leaf extract with liquid chromatography mass spectrometry using quadrupole time-of-flight technology (lcms-qtof). Food Sci Technol (United States). 2020; 8: 79-86.
- Aja PM, Okaka ANC, Onu PN, Ibiam U, Urako AJ. Phytochemical Composition of Talinum Triangulare (Water Leafe) Leaves. J Pakistan Journal of Nutrition. 2010; 9: 527-530.
- X Lin, L Wu, X Wang, L Yao, L Wang. Ultrasonic-assisted extraction for flavonoid compounds content and antioxidant activities of India Moringa oleifera L. leaves: Simultaneous optimization, HPLC characterization and comparison with other methods. J Appl Res Med Aromat Plants. 2021; 20: 100284.
- FM Dalla Nora, CD Borges. Pré-tratamento por ultrassom como alternativa para melhoria da extração de óleos essenciais. Cienc. Rural. 2017; 47: 1–9.
- N Andarwulan, D Kurniasih, RA Apriady, H Rahmat, AV Roto, et al. Polyphenols, carotenoids, and ascorbic acid in underutilized medicinal vegetables. J Funct Foods. 2012; 4: 339–347.
- S Chaudhuri, B Pahari, B Sengupta, PK Sengupta. Binding of the bioflavonoid robinetin with model membranes and hemoglobin: Inhibition of lipid peroxidation and protein glycosylation. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol. 2010; 98: 12–19.
- DF Birt, B Walker, MG Tibbels, E Bresnick. Anti-mutagenesis and anti-promotion by apigenin, robinectin and indole-3-carbinol. Carcinogenesis. 1986; 7: 1617-1619.
- B Peng, Bai RF, Li P, Han HY, Wang H, et al. Two new glycosides from Dryopteris fragrans with anti-inflammatory activities. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2016; 18: 59–64.
- T Julianti, Mieri MD, Zimmermann S, Ebrahimi SN, Kaiser M, et al. HPLC-based activity profiling for antiplasmodial compounds in the traditional Indonesian medicinal plant Carica papaya L. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014; 155: 426-434.
- PK Patial, A Sharma, I Kaur, DS Cannoo. Correlation study among the extraction techniques, phytochemicals, and antioxidant activity of Nepeta spicata aerial part. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol. 2019; 20: 101275.
- Sani RN, Nisa FC, Andriani RD, Maligan JM. View of ANALISIS RENDEMEN DAN SKRINING FITOKIMIA EKSTRAK ETANOL MIKROALGA LAUT Tetraselmis chuii. 2014; 2: 121-126.
- S Ayu Anggraini, T Yuni Hendrawati. The Influence of Operation Conditions of Gedi Leaf Drying Process (Abelmoschus Manihot. L) On Antioxidant Activity. J Appl Sci Adv Technol J Homepage. 2020.