
Research Article
Austin Chem Eng. 2020; 7(1): 1073.
Industrial Scale Kiln Problems and Their Solution with Controlling Different Operating Parameters
Fazeel Ahmad*
Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Wah, Wah Engineering College, Pakistan
*Corresponding author: Fazeel Ahmad, Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Wah, Wah Engineering College, Pakistan
Received: April 19, 2020; Accepted: May 12, 2020; Published: May 19, 2020
Abstract
The chemical composition homogeneity of kiln feed has an important relationship to fuel consumption, kiln operation, clinker formation and cement strength. Kiln operation can be made stable and smooth. The basis for this property is a well-burned clinker with consistent chemical composition and free lime. The main reason for the clinker free lime to change in situation with stable kiln operation is variation in the chemical composition of the kiln feed. This variation in chemical composition is related to raw mix control and the homogenization process. To ensure a constant quality of the product and maintain a stable and continuous operation of the kiln, the attention must be paid to storage and homogenization of raw materials and kiln feed. Due to variations in the kiln feed chemical compositions that affect its burn ability and the fuel consumption. The objective of this research paper is to provide solutions of the problems occurring in well burned clinker through stable kiln operation and efficient cooler heat transfer. The quality of cement is assessed typically from its compressive strength in concrete and mortland. The well-burned clinker and free lime with consistent composition is the basis for desired quality of the cement. To ensure product of constant quality ad kiln stable and continuous operation focus must be done on raw material hominization in the storage silos and kiln feed During the all reactions when all these parameters are altered then the chemistry of the reaction also changes and it effects on the Liter Weight (g/liter), Lime Saturation Factor, Degree of Calcination, Cement Blain, Silicate Module and Aluminum Moduli.
Keywords: Lime saturation factor; Free lime, Alumina ratio; Silicate ratio; Degree of calcination; Kiln speed; Residence time; Cement quality; Clinker burn ability Clinker; Limestone; Cement Quality; Portland cement
Introduction
Ordinary Portland cement is the most commonly used cement around the world. It has been reported that cement manufacturing process consist of three steps [1] including raw mixture preparation, clinker production and cement formation. Requirement for the demand of cement in the developing countries is increasing rapidly but in the developed countries it has reduced. (Pacheco-Torgal et al., 2014). Studied has been done about origin of raw material prepared for the kiln which are usually quarried in the local rocks whose composition varies from location to location, and sometimes to meet the desired composition addition of limestone, clay and recycled material is done [2-3]. These are passed through crusher to reduce their sizes less than 80 mm. These all material are passed through raw mill where material bed is maintained and grinded into smaller parts and there is a classifier after grinding fine material is passed through this due to suction of system fan.
According to literature [4] the energy utilized by the cement manufacturing process is nearly about 110 KWh/ton and approximately 40% of this energy is consumed in the grinding process which totally depends upon clinker with desired free lime content and alite and belite content along with specified liter weight (g/liter) amount. Therefore, major concern is on the energy reduction in this process.
Con G. Manias et al., has reported about pyro processing stage of clinker formation according to which raw material coming from homogenize silos passed through rotary kiln in which many reactions take place. There is series of sequence endothermic and exothermic reaction taking place in the kiln. Suggestion further have been reported about kiln aerodynamics, it is extremely surprising to know how a small difference in kiln hood, cooler bull nose, cooler throat, tertiary air off takes, secondary air temperature and velocity, and air leakage can have a huge effect on the pattern of air flow in the rotary kiln burning environment.
Pre-calciner is used to decompose raw material into its components after passing and preheating into the cyclones after that updraft causes the raw material to enter in the last level of cyclone for the solid gas separation. Due to sufficient inclination and various kiln speed, raw material continuous enters into the cooler grates section [7]. Wang et al., suggested to pre calcine the raw material calciner time is reduced and temperature dropped to about 150ºC. Many researchers have reported about maintain temperature in the burning zone which totally depends upon fuel burning to assist in chemical reactions to take place.
Therefore, many experts in the cement technology presented a trend of pre calcination at about 1300ºC with the raw material in the fluidized form and suspended form in which the heating, sintering and decomposing can be complete at the same time because time and the temperature in the precalciner is very high [2,7]. Suggestion has been made to reduce lime saturation factor in the clinker leads energy reduction this helps to decrease and increase in the alite phase content and belite amount [3,5]. Free lime content are directly measured by the burning of clinker inside the rotary kiln. It also has crucial effect on the grinding of clinker into fine cement which determine the strength of cement.
All these materials are transported into silo where homogeneous blending of material happens by roots blower of any type which are providing air perpetually into the silo (Pacheco-Torgal et al., 2014). Counter flow process happens in the rotary kilnin which endothermic and exothermic series of complex reactions takes place at different temperature starting from 800ºC to 1500ºC. Researcher have reported that for raw meal water evaporation to burning this highest temperature is required either in the cyclone pre heater section and in the kiln. Highest temperature is achieved in the burning zone of the kiln.
There is series of different individual reactions which takes place during the synthesis of clinker and its phases. Energy comes from the different sources which are the basic requirement in the kiln heating for decomposition of the many reactions. There are various kinds of fuels which can be used in the kiln consist of biomass, petroleum coke and mineral coal (Madlool et al., 2011). Due to global warming threat is posed which has created awareness in the public for the anthropogenic carbon emission and their great effect on the climate change in the global warming. The forthcoming level of CO2 emission in the atmosphere has reached 380 ppm (Sabine et al., 2004).
Including CO2 during the synthesis of clinker in the kiln many reactions also ejects NOx and SOx and other minor amount of toxin which covers range for local to global environmental impact.This toxic waste may damage to the nearby area through different disease including lungs and breathing problems. (Phair, 2006). There is eject point from where all these pollutants goes into the atmosphere. The most suitable tool for judging clinker synthesis and its supply chain impact on the environment is life cycle assessment (Boesch and Hellweg, 2009). Now a days, it is a big challenge to minimize CO2 emissions in the atmosphere by reducing component of clinker in the cement.
Due to some reasons mashing of clinker does not get complete and these small portion content goes inside the cement which reduces the strength of cement. When this cement is used in the building these particles get involved in the surrounding and evolves CO2. Many grinding aids which assist for complete clinker grinding such as fly ash and glycol, ash, slag and volcanic ashes which minimizes clinker content in final product of cement (Huntzinger and Eatmon, 2009). At the last Unit of clinker reforming there is also particulate matter which is in small size emissions in the atmosphere. There is also a huge challenge to reduce these losses into the atmosphere.
The main objective of this paper is to reduce the incomplete combustions during the reactions in the kiln so that toxic waste should be in very small amount in the all exhaust point of the clinker as well as cement synthesis process. Coal to air and fuel to air ratio place crucial role in the reactions which take place in the rotary kiln. By the alteration of these combustion product may vary from original products. These two important parameters are responsible for the temperature which is required during the different phases of the clinker in the kiln within different zones like calcination, burning and cooling zone.
There should be a fixed ratio of air and coal so that complete reactions should take place in the kiln and desired quality clinker should be produced. It has been studied that cement plant are large source of CO2 emissions in which its denseness goes high in the exhaust gases about 14-13 percent and in comparison, to cola fired plant which produces 12-13 percent. But there is a big issue of CO2 separation from the exhaust. Many technologies are available and have been studied to separate CO2 from flue gases. In this paper a complete review of amine scrubbing has been presented [2-3].Lime saturation factor and liter weight also plays important role in the cement grinding. When these parameters are in control manner then toxins emission are in control manners and can produce less environmental effects on the surrounding area. With the variation in the coal to air ratio both above parameter can be controlled which in terns will produce desired quality clinker.
Experimental Materials and Procedure
Sample preparation
Usually, the raw material sample is taken out from crusher outlet and after grinding mill but clinker sample is taken out from the last cyclone C5 as well as pre-calciner and cooler outlet. Liter weight (g/liter) test is done in the industrial scale laboratory. X- ray analysis is done to check all the compositions of the development of clinker formation studies on the basis of free lime contents mainly but other factors including liter weight, degree of calcination and alite and belite formation as well. Studies procedure is the most commonly used in all over the world. Initially, from the decomposition of calcium carbonate Cao is formed, which gradually consumed in the clinker phases. When amount of lime tends to be zero, complete clinker phases phenomenon take place.
Sample testing
Clinker formation and burning process in rotary kiln
Clinker formation : Well blended raw material enters into cyclones for efficient mass and heat transfer process through counter current contact with air. Pre-calcination and calcination process taking place into the pre-calciner as well as inside the kiln. For many years cement was synthesized by practical experience used by educated people experience which was gathering from the process plant physically checking samples of clinker and raw mill for kiln at different sections including cyclone 5 and cooler outlet There are many reactions taking place inside the kiln. Portland cement clinker includes higher values than 95% of CaO, SiO2 and Fe2O3. Figure 1 represent the clinker. It has been reported that transformation results initially with clinker phases [4].
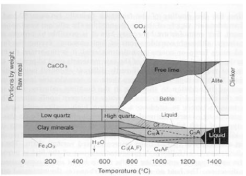
Figure 1: A schematic view of the clinker formation reactions [4].
Alite is the main constitute which consist of 50-70% of the Portland cement clinkers. It is also called as tricalcium silicate. Belite consist of 15-30% of the Portland cement. Most common name is called dicalcium silicate. Aluminate contains 5-10% of the ordinary Portland cement clinker. Modification in tricalcium aluminate is done due to variation in the structure of ionic substitutions. Ferrite includes 5-15% of Portland cement clinker. With the variation in the Fe/Al ratio tetra calcium aluminoferrate modified in its composition.
Series of reaction taking place inside the kiln are described in the Figure 1 at the start of the kiln inlet feed stock including limestone quartz (SiO2) and other clay minerals and iron oxide (Fe2O3) are introduced. Suggestions have shown that when the heating rate of raw material is above 600°C all the chemical as well as physical reactions happens simultaneously (Huanget al. 1999, Altun1999).
Therefore, limestone as well as clay will disintegrate into their constituent quickly and the newly formed SiO2, Al2O3 and CaO all have increase in their activity for mutual solid phase reactions. This phenomenon reduces the time of calcination about 150°C (Wang et al. 2003). At 700°C temperature, initially removal of free moisture and change in the metallic crystals structure occurs. Secondly, decomposition of CaCO3 happens at temperature range between 700-900°C and alumina ferric oxide and activated silica combined with lime. Belite formation takes place when temperature increase in the range of 900-1200°C. Scientist studies have shown that when temperature increases from 1250 or above 1300 Liquid phase occurs which increase the reaction between belite and free lime to form alite [5-7].
But with the variation of kiln speed as well as feed, decomposition of compounds and minerals show tremendous effect as the time passes out. With the change in flame position as well as kiln parameters (speed, feed, thermal load) also show huge effects on the phases formation including belite and alite formation. With variation of kiln speed, heat in terms of rise in temperature inside the all part of compounds (CaCo3) and minerals (Al2O3) and decomposition happens rapidly. Furthermore, active site of elements and constituent which forms belite and flux agents becomes more active and fastest reactions take place. By varying the fans flow rate , efficient heat transfer take place inside the cooler and deformation of Alite and Belite into clinker occurs simultaneously. Chemical reaction starts from decomposition of calcium carbonate and ends at Belite and Alite as given below.
Assume chemical reactions happening inside the kiln are:
CaCO3 → Cao + CO2 ................1
CaO + 2SiO2 → C2S ................2
CaO + C2S→ C3S ................3
3 Cao + Al2O3→C3A ................4
4Cao + Al2O3 + Fe2O3 →C4 AF ................5
Clinker burning process: In the modern clinker manufacturing process, the retention time for the kiln feed is about 30-40 minutes of which the major portion material passes inside the kiln is burning zone. The material temperature goes on higher side rapidly from 850°C to 1250°C to 1320°C at this temperature clinker melt phase occurs. Inside the burning zone, physical changes as well as chemical changes occurs simultaneously. This helps for clinkerlization reactions and agglomerations process in terms of clinker phases. It has been reported that the final temperature of melt phase totally depends upon chemical composition of the feed. When there is well blended and well mixed raw material then large surface will be available for the heat absorption and thus complete burning of the clinker take place.
Under specific conditions, when temperature drops below 1250 melt phase start to form. Scientist studies that burner flame is the main cause of maintain temperature inside the kiln. For some instant, addition of quartz grain in the feed of kiln give rise to the melt phase even at temperature 1200°C or 1180°C. The amount of CaO surrounding the burning zone, will increase the agglomeration phenomenon and crystal of belite start to form. In this way belite nest appears inside the clinker which can be identified at the hood section of kiln. Presence of alkali, sulphate and chlorides causes the formation of melt phase even at reduced temperature.
However, small temperature interval and short distance inside the rotary kiln, clinker melt phase is formed. Higher the coating on the bricks lining, lower will be the clinker melt phase formation. Soft and thin coating turns to dark in the start of burning zone or over the upper transition zone even within a half a meter. The temperature of the burning zone is the direct measure of calcination inside the kiln. Clinker mineral formation totally depends on the time as well as the temperature pretreatment and post treatment of the raw meal and on the entire chemical composition of the kiln feed [3-4].
But by using chemical analysis of clinker chemistry it was known that there exists a certain basic relationship between (feed raw material and cement clinker) burning, in which lime saturation factor, degree of calcination, free lime, Silicate module and Aluminum module varies with it. These modules are [7].
Chemical Composition Variation Influence of Kiln Feed
Effect of chemical composition of kiln feed on clinker burning
Chemical composition of the kiln feed directly determines the fuel consumption, clinker burnability, liter weight and cement performance. Researchers have reported that kiln feed composition depends upon efficient grinding and homogenization in storage silos. Kiln smooth and stable operation also depends upon raw material homogenization [11-12]. One of the most addition phenomenon is to optimize the fuel consumption and efficient burning process by kiln speed. Experienced operators can make kiln process stable as well as proper clinker burning by the variation of kiln speed.
Lime Saturation Factor (LSF) effect on clinker grinding and blain of cement
It is defined as ratio of actual amount of lime to the theoretical lime required by other major oxides in the raw mix or clinker. LSF employs a major role in the meshing of clinker into cement. When its values become high it influences on blain of cement which is the keyfinest of cement and its values are given in Table 1 and Table 2. But when its valuegets low, clinker becomes hard and difficulty comes in the grindability of clinker and cement becomes of low quality which is not required by customers. LSF value must achieve 90-95 percent for efficient grinding and highest blain (3200 cm²/g) in case of Ordinary Portline Cement (OPC).
When LSF >100% its shows ordinary clinker having free lime about 2 or more. If coal used in the kiln has some ash content (residue of burning of coal and wood) and glycol then clinker will produce having LSF greater than 100% which is undesired parameter for the clinker as well as cement strength. The addition of ash in the clinker reduces the value of LSF because of iron, silica and alumina component in the ash. The burning process is monitored by the amount of unconsumed free Cao in the clinker. Free Cao amount is directly involved in the reaction completion [3-5]. Lower amount will corresponds to complete reactions but too low amount free Cao make clinker hard and uneconomic burning. A target for free lime is 0.5 -1.5% free Cao.
Components
Limestone
Laterite
Clay
Sand
SiO2
8.32
8
53.75
60
Al2O3
2.76
6.31
14.4
3.2
Fe2O3
0.89
65.09
4.99
2.1
CaO
50.5
7.2
8.71
0.9
MgO
0.93
1.38
1.8
0.3
SO3
0
0.8
0.31
0.12
Na2O
0.31
0.51
1.99
3.1
K2O
0.03
0.71
0.62
2.1
LOI
36
6
13.37
20
Rest
0.26
4
0.06
8.18
Table 1: Chemical composition used to prepare kiln feed [5].
Kiln Speed (rpm)
Kiln residence time (H)
Degree of Calcination (%)
3
1
90.8
3.2
2.2
90
3.3
3
89
3.4
3.5
85
3.5
4
90
3.3
4.25
86
3.25
5
85
Table 1.1: Kiln Speed, Kiln residence time and LSF relation.
Classifier rpm
Residue
2.5
23
2.6
24
2.8
20
3
23
2.9
22
2.8
25
2.4
25
Table 1.2: Free lime, LSF and Cement blain relation.
Liter weight (g/liter)
Kiln Speed (rpm)
SR
Kiln residence time
(H)
1250
3.2
2.4
1
1230
3.3
2.35
2
1220
3.4
2.3
3
1230
3.4
2.2
3.5
1210
3.5
2.1
4
1190
3.5
2.3
4.5
1200
3
2
6
1200
2.9
1.9
7
Table 1.3: Effect of kiln speed and residence time on liter weight and SR.
Kiln Speed (rpm)
Kiln Residence time (H)
AR
3.4
1
1.3
3.3
1.5
1.1
3.2
2
1.2
3
2.5
1.28
3.2
3
1.3
3.4
3.6
1.2
3.3
4
1.25
Table 1.4: Effect of kiln Speed and residence time on AR.
A/R
Liter Weight (g/liter)
Free lime (g)
1.3
1250
1.9
1.1
1240
1.7
1.2
1235
1.5
1.28
1220
1.7
1.3
1240
1.5
1.2
1230
1.45
1.25
1250
1.4
1.24
1290
1.3
Table 1.5: Effect of AR on liter weight and free lime.
Kiln Speed (rpm)
Kiln residence time (H)
Degree of Calcination (%)
3
1
90.8
3.2
2.2
90
3.3
3
89
3.4
3.5
85
3.5
4
90
3.3
4.25
86
3.25
5
85
Table 1.6: Kiln Speed, Residence time and Degree of calcinations.
Classifier rpm
Residue
2.5
23
2.6
24
2.8
20
3
23
2.9
22
2.8
25
2.4
25
Table 1.7: Classifier rpm vs raw mill residue.
Silica Moduli (SM) effect on clinker liter weight and free lime
Silica Moduli acts crucial function in the quality of clinker. Silica moduli correlates to the melt phase formed in burning zone. Both are inversely related to each other by increasing SM melt phase goes on decrease and vice versa. When SM values becomes too high then nodules formation happens and chemical reactions occuring in the kiln becomes too slow and make it difficult to operate. Melt phase becomes too high when SM becomes too low and Sulphur coating becomes difficult to thick. Table 1.3 shows the effect of silica moduli on liter weight. With the increase in the silica ratio, cement hardening and slow setting becomes high. The lowest value of SM is 1.5 below which it is not in acceptable range. Normally its range lies between (1.9-3.2).
SM can be defined as
Alumina Ratio (AR) effect
AM is responsible for the temperature due which the melt phase occurs and it shows the composition of liquid phase available in the clinker. When kiln is charged with different feed then by variation in the speed will affect AR magnitude. When the AM value reaches 1.6 then temperature gets low and it is the optimum value of AM regarding clinker synthesis minerals and nodules. The colour of clinker as well as cement is also influenced by AM. The higher value will form bright colour of cement. When AM value becomes 1.5 then tetra calcium alumina ferrite appears in the clinker and there is no amount of tricalcium aluminate. This is called Ferrari-cement in which heat of hydration, settling and shrinking of clinker becomes slow. With the increase of high alumina ratio and low silica ratio results fast setting of cement.
AM is calculated by the formula as
Effect of coal burning on degree of calcination
It is also essential parameter in the clinker chemistry which represents how much limestone disintegrate into clinker and how much free lime is occurring into clinker. When coal burning becomes complete then decomposition of the raw material occurs. As the temperature goes on increase due to suitable amount of coal to air ratio then increase in the decomposition of the raw material into clinker becomes high. If there is no complete combustion then free lime appears in the clinker and reduces meshing of clinker into cement. Higher the value of degree of calcination lower will be free lime content in the clinker and vice versa. Coal percentage used inside kiln is 60% for the precalciner and 40% for the main flame of the kiln. For 2000 t/day kiln feed capacity, when coal amount is varied from (3.2 -3.5 t/h) on main flame and (13-15 t/h) on precalciner its value ranges from 80-90%.
Effect of coal burning on liter weight
It is defined as weight of clinker per unit volume (gram /Liter). It acts important function in the grindability as well as setting of clinker and cement blain. It also relates to the free lime content in the clinker. For the production capacity of 2000 tons /day kiln when coal amount is increased from 3.2 tons/ h to 3.5 tons /h on the main burner then there is large variation in the liter weight of the clinker. It changes from (1210-1270 g /L). It has been observed that there exists a basic relationship between free lime and liter weight of the clinker. Higher the value of liter weight lower will be the free lime and vice versa. Kiln speed as well as burning zone temperature both can reduce the liter weight in the clinker. High speed of kiln and lower temperature in the burning zone will reduce amount of liter weight in the clinker.
Process
Higher values of Liter weight, free lime, degree of calcination and all moduli are controlled by the two processes:
Raw millcomposition
Kiln behavior and feed
Raw mill process and rate of reaction
Raw material meshing and drying is done by raw mill. Rotating table having four rollers which are compressed by the hydraulic pressure and certain clearance present between rollers which helps for grinding. The finish product after meshing is called raw meal. Drying and grinding of raw mill is done in the raw mill. Finer the product from the mill higher will be the rate of reactions and smaller amount of coal will be consumed and complete combustion reactions will take place in the kiln. Material from the feeding area comes in the hopper from which it is transported into the constant feed weigh feeder. Belt conveyors are utilized to transport material from feeding area into the vertical roller mill. Small amount of water is sprinkled into the raw mill to make moist material to increase the grinding. Proper bed of material is maintained under table in this way grinding efficiency is increased. Final product is dried from the exhaust gases coming from the rotary kiln. Classifier present at the upper part of the mill, coarse and fine product. Higher the speed of classifier finer product will go outside the mill and higher will be residue. Air currents increases due to exhaust fan and gases coming from the kiln which lift material into the classifier.
Kiln process and coal burning
Raw material coming from the raw mill silo and also directly from the mill product goes into the preheater section by the assist of Elevator and conveyors where drying of material takes place. Single sting five stage preheater having cyclone from top to bottom section towards kiln. Temperature of raw material coming from the pre heater section is increased from 300-400ºC to the 1400ºC-1500ºC. Coal burning is key factor for increase of this temperature but when raw mill will be finer then complete combustion will occur and smaller amount of coal will be consumed. Inside the kiln temperature is maintained with the flame present at the outlet of kiln. Flame is generated from the coal and air which are coming from the burner having two separate coal burner and air burner. With the increase in the temperature of raw mill reactions starts and goes towards completion. Feed coming from the raw mill silo consist of limestone, clay, sand and laterite. When temperature reaches up to 700ºC, removal of water and crystal changes take place. CaCO3 disintegration take place at temperature about 700-900ºC along with ferric oxide , alumina, activated silica and sand at this stage more coal consumed.Bellite starts to form when temperature increases from 900-1200ºC. When temperature reaches 1300ºC liquid phase starts to appear and it increases reaction between free lime and Bellite to make Alite. During the cooling process if it is slow then tricalcium aluminate (C3A) crystals appear. Alkali sulphate separate out in condensed form after the cooling process [15].
Major steps involved in chemical operations
If the time for clinker production is given small interior the kiln then low-quality clinker will form. This will decrease capacity of grinding of clinker into cement and will cause more power requirement in the cement mill and it will require a lot of grinding aid inside the cement mill to grind the clinker in good manner. Sometime this will influence the temperature interior the kiln and due to which degree of calcination will increase inside the calcination zone.
If there is large fluctuation in the composition of raw material then there will be large variation of kiln feed chemical composition as well as clinker key parameters including liter weight free lime and degree of calcination.
If kiln is operated at constant temperature and constant residence time, it will cause change in composition of clinker and large of free lime in it. It has large significance because free lime is basic parameter to show how clinker is produced when raw mill is burned in the kiln with proper coal amount.
When the oxidation of clinker is hard then clinker will be produce having low porosity, Alite formation having large crystals and large dust in the hood section of the kiln. Cooling process will become slow, temperature is high side and low porosity clinker cannot be control easily.
When the clinker porosity mall then grinding of the clinker becomes difficult and higher cement mill power requirement causing low production of the mill [9].
Results and Discussion
Effect of raw mill changing composition on clinker formation
For the desired chemical composition required for clinker synthesis, raw mill composition is calculated to determine the quantitative components of raw material like limestone, laterite, clay and laterite. Raw mill composition acts important role in the synthesis of clinker . Maximum composition contains limestone which is major component and after that laterite, clay and sand. With the variation of all these components composition, clinker formation will be different composition and free lime. LSF must lie in the range of 92±1 but its minimum value should be 93.01 its average value comes 99.81 and its highest value reaches to 106.78 [10].
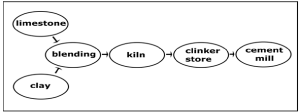
Figure 2: Simplified process schematic for mixing process of raw materials [3].
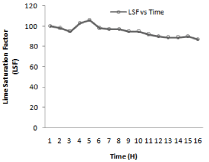
Figure 3: Lime saturation factor variation with kiln residence time.
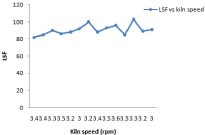
Figure 4: Effect of Kiln Speed on LSF.
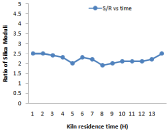
Figure 5: Effect of kiln residence time on silica moduli.
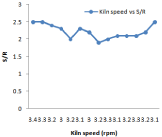
Figure 6: Effect of kiln speed on silica moduli.
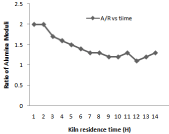
Figure 7: Effect of kiln residence time on AR.
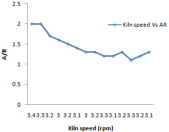
Figure 8: Effect of kiln speed on AR.
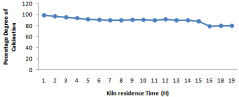
Figure 9: Effect of kiln temperature on degree of calcination.
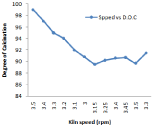
Figure 10: Effect of speed on degree of calcination.
Higher the value of LSF, lower will be the porosity of clinker and difficult will be its meshing. For different composition of raw mill components including limestone, laterite, clay and sand LSF vary with 24-hour time which is shown in Figure 3. Silica and Alumina ratio can be determine for the time period of 24 hours when the kiln is run at the capacity of 2000 tons /day it is shown in Figure 8. It has been observed from the fig. that S/R lowest value of 2.29, maximum value of 2.75, and average value of 2.47. Hence change in value from maximum to minimum in S/R is 0.17. In case of Aluminum ratio its maximum value reaches 1.36, minimum value 1.00 and average value comes in the range of 1.27. Hence variation in A/R value is observed as 0.07.It is very important to calculate these calculation to prepare kiln feed mixture having maximum calcium carbonate composition of (77-77.5) to avoid hard burning of clinker.
Effect of Kiln Feed and Coal heating on LSF
Large change in kiln feed chemical composition coming from preheater section through raw mill silo it affects coal consumption as well as burnability. Kiln thermal load, speedand feed variation affects A/R, S/R and LSF and little bit free lime due to residence time involvement. Figure 4 shows all these behavior in detail. In case of LSF highest value is 106.8 and lowest value 89 and average value is 92. It has been observed from Figure 7 that variation in S/R is 0.19 and maximum value is 2.25, minimum is 1.32 and average is 1.27.But in case of alumina ratio minimum ratio is 1.24 maximum is 1.33 and average value is 1.27 so there is variation of 0.03 This is because of large amount of fuel consumed for burning of 0.9% free lime [11].
Effect of Burning of Feed with Coal on Clinker
Effect of coal burning on kiln feed
Strength is the key property of the cement which is used in buildings and water dams. This property relays upon coal used for kiln feed burning and flame temperature. When burning of clinker is complete and coal is used in fine form so that reactions go in complete form. When kiln is running on stable side there are two main reasons to reduce and avoid further free lime: maximum size reduction in the kiln feed and variation in the composition of components used in raw meal. To obtain the clinker product having quality in continuous manner and to run kiln at stable operation depend upon ram mill product highest grinding as well as its homogenization within the silo. Coal consumption and burn abilitydepends upon raw meal homogenization and changes in kiln feed [12].
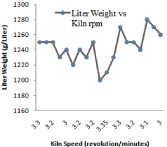
Figure 11: Effect of Kiln Speed on Liter Weight variation.
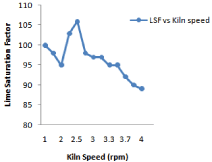
Figure 12: Effect of kiln speedon lime saturations factor.
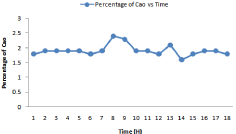
Figure 13: Formation of Cao (%) with respect to kiln residence time.
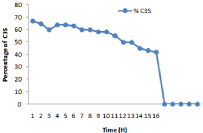
Figure 14: Initiation of C3S with respect to kiln residence time.
Cao and C3S Formation During Various Kiln Feed Proportion
There are four major phases which cement clinker contains: Tricalcium silicate (C3S) , tricalcium aluminate (C3A) , dicalcium sulphate and C4AF. Hydration reactions happens in complex way result hardening and setting of cement. One of the major phases of microstructure of cement includes Aluminates (AL), Portlandite and calcium silicate-hydrate. More information related to microstructure of cement are mentioned in [13]. In the homogenization methods basic requirement is to find the volume and its fraction of many constituents. Many volume fraction determine by using ratioof H2O / cement , chemical composition of the cement and hydration heat and its degree using the method of Bernard [14]. C3S should be in the range of 50-60%. The highest value of C3S should be 63, lowest value 45, average value of 54 and deviation of 5.58 respectively. Alite value corresponds to cement strength. With the increase of C3S content, strength of cement will increase.
Conclusion
Maximum grinding and homogenization of raw mill feed will correspond to efficient coal burning and kiln temperature as well as complete series of reactions taking place. If raw mill will be homogenous composition then there will be formation of clinker of good quality. High value of LSF as well as liter weight relates to hard burning of the clinker and higher power consumptions in the cement mill. Maximum preheating of feed for the kiln is required component for clinker production. With the fluctuation of kiln speed many important parameter which are producing inside the kiln can be controlled like liter weight, LSF, A/R, S/R and degree of calcination. The coal consumption basic rule is 40% inside kiln and 60% inside precalciner. Inside the kiln hood there should be maximum heat transfer between clinker and air coming from the fans of cooler. Complete reactions are the basic need to keep kiln hot side and to avoid free lime production inside clinker. Higher the value of free lime greater than 2.5, greater will be the difficulty to grind clinker and more power will be needed for grinding process. Variation of kiln feed also plays important role to vary degree of calcination and complete burning of the raw meal. Fine coal and moisture free coal will be major cause of complete reactions inside the kiln. Grindability increases the blain of cement and strength of cement.
References
- VC Johansen, LM Hills, FM Miller and RW Stevenson. "The Importance of Cement Raw Mix Homogeneity", International Cement, Chicago, USA, (2002), online on America's Cement .2003.
- G Frigionea, F Zenonea and MV Espositob. "The effect of chemical composition on Portland cement clinker grind ability", Cement and Concrete Research. 1983; 13: 483-92.
- G Frigionea, F Zenonea and MV Espositob. "The effect of chemical composition on Portland cement clinker grind ability", Cement and Concrete Research. 1983; 13: 483-92.
- PC Hewlett. "Lea's Chemistry of Cement and Concrete", 4th edition, Arnold Publishers, London, Great British. 1998.
- Operation datasheet of Al-Mergheb cement plant, Alahlia Cement Company, Al-Khoms city, Libya. 2010.
- J Bensted, GJ Audley, PN Aukett. Studies of early hydration with class g oil well cement using heat flow conduction calorimetry, Cement and Concrete Research. 1995; 25: 426-32.
- S Ghabezloo, J Sulem, S Gu´edon, F Martineau, J Saint-Marc. Poromechanical behaviour of hardened cement paste under isotropic loading, Cement and Concrete Research. 2008; 38: 1424-37.
- Saasen, PA Log. The effect of ilmenite plant dusts on rheological properties of class g oil well cement slurries, Cement and Concrete Research. 1996; 26: 707-15.
- P Yan, Y Zhou, Z Yang, J Qin. Microstructure formation and degradation mechanism of cementitious plugging agent slurries, Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Materials Science Edition. 2007; 22: 61-5.
- S Ghabezloo. Micromechanics analysis of thermal expansion and thermal pressurization of a hardened cement paste, Cement and Concrete Research. 2011; 41: 520-32.
- J Strigae, MT Palou, J Kristin, J Majling. Morphology and chemical composition on minerals inside the phase assemblage C–C2S–C4A3S?–C4AF–CS?, Ceram.-Silik. 2000; 44: 26-34.
- FM Miller. "Dusty Clinker and Grindability Problems: TheirRelationship to Clinker Formation", Rock Products, April. 1980; 152-7.
- C Moore. "Chemical Control of Portland Cement Clinker,” Ceramic Bulletin. 1982; 61: 511-5.
- WH Duda. "Cement data Book", Vol. 1, International Process Engineering in the Cement Industry, 3rd ed., Bauvelag GMBH, Berlin. 1985.