
Case Report
Austin J Clin Case Rep. 2024; 11(4): 1328.
Artificial Hip Replacement Combined with Proximal Femoral Locking Plate in The Treatment of Intertrochanteric Femur Fracture with Peritrochanteric Fracture
Pengjuan Zhao¹; Wendong Xie²; Chao Zhang¹*
¹Orthopedics Department, Gansu Provincial Hospital, PR China
²Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, PR China
*Corresponding author: Chao Zhang Orthopedics Department, Gansu Provincial Hospital, No.204, Donggang WestRoad, Lanzhou, 730000, Gansu Province, PR China. Email: zc-315@163.com
Received: July 08, 2024 Accepted: July 18, 2024 Published: July 25, 2024
Abstract
Intertrochanteric femoral fracture with peritrochanteric fracture is a common osteoporotic fracture that is difficult to treat and has a high complication rate. Intertrochanteric femoral fracture is a fracture between the base of the femoral neck and the level of the lesser trochanter. Intertrochanteric fractures can be divided into internal and external types, with the external type of fracture being more common. Peri-rotor fractures, on the other hand, are fractures in the area around the femur’s rotor, including fractures of the greater and lesser trochanter and intertrochanteric line of the femur. Traditional treatments often cannot effectively restore hip function and are prone to complications such as fracture non-union and hip dysfunction. Artificial hip replacement combined with proximal femoral locking plate has the following advantages in treating intertrochanteric fracture with peritrochanteric fracture: femoral head replacement can effectively restore the function of the hip joint and reduce the occurrence of hip complications, which is especially suitable for elderly patients. Proximal femoral locking plate has good biomechanical stability, which can effectively fix the fracture end and promote fracture healing.
Keywords: Intertrochanteric fracture; Perirotrochanteric fracture; Artificial hip replacement; Proximal femoral locking plate
Introduction
Intertrochanteric femoral fracture is one of the common types of fracture in the elderly, and the incidence of osteoporosis increases with age, leading to a corresponding increase in the incidence of intertrochanteric femoral fracture [1]. Intertrochanteric fractures of the femur are accompanied by perirotrochanteric fractures, which are challenging to treat. Currently, there are various treatment methods, including conservative treatment and surgical treatment. Conservative treatment mainly includes plaster immobilisation and traction, but prolonged bed rest may lead to complications [2]. Surgical treatment mainly includes artificial hip replacement, proximal femoral locking plate fixation, etc.
Case Report
The patient was a 64-year-old male who had been hospitalized for 15 days due to pain, swelling and limited movement in his right hip. He reported that 6 hours before admission, he was hit by a car resulting in a right hip injury, and his family sent him to our hospital after the pain was relieved by oral painkillers. Physical examination showed that the right hip was swollen with obvious tenderness, the right lower limb showed flexion, shortening and external rotation deformity, the sensation of the right lower limb was normal, and the dorsalis pedis artery of the right side had good pulsation. X-ray examination and CT scan showed that there were comminuted fracture of the right intertrochanteric femur, fracture of the greater as well as the lesser trochanter of femur, and the surrounding soft tissues were swollen (Figure 1 a-l).
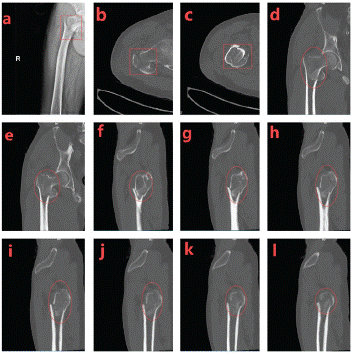
Figure 1: X-ray examination and CT scan showed a comminuted intertrochanteric fracture of the right femur, a fracture of the greater as well as the lesser trochanter of the femur, and swelling of the surrounding soft tissues.
After admission, right hip examination, right femoral head replacement and right greater trochanter fixation were performed under general anesthesia. Intraoperative fractures of the right intertrochanteric femur, right greater and lesser trochanter were seen. The fractured femoral head and the surrounding blood clot were removed and the marrow cavity was expanded to the appropriate size. The marrow cavity was further dilated using a femoral stem test mould, and then the marrow cavity was repeatedly flushed with saline to prevent infection. Finally, the appropriate femoral stem was selected according to the size of the femoral marrow cavity, and the femoral stem was slowly implanted (Figure 2 a-i). To further stabilise the fracture, the already fractured greater trochanter was next fixed with a proximal femoral locking plate. After repositioning the fracture breaks, the fracture breaks were fixed with Kirschner's pins and pliers, then the appropriate locking plate was selected for fixation, and finally the screws were implanted, and the fracture was examined and found to be in good alignment (Figure 3 a-d). Three days after the operation, the patient could gradually walk on the ground. Postoperative X-ray examination showed that the internal fixation device was in good position (Figure 4 A-C). Continue to follow up the patient's recovery.
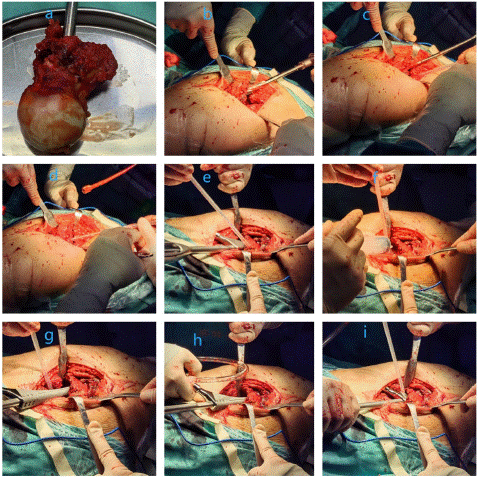
Figure 2: First, the bone marrow cavity was further expanded with a femoral stem test mound, and then the bone marrow cavity was repeatedly flushed with saline to prevent infection. Finally, a suitable femoral stalk was selected according to the size of the femoral marrow cavity and slowly implanted.
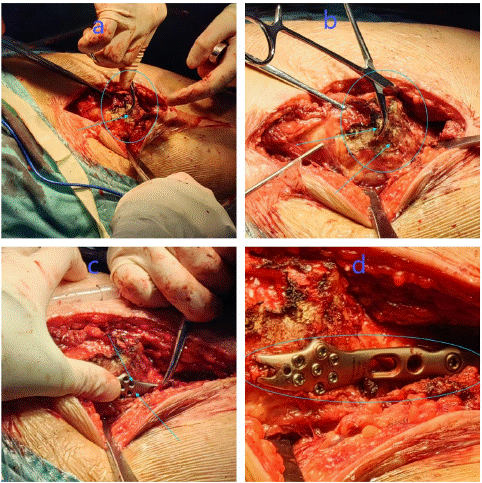
Figure 3: After fixing the already fractured greater trochanter with a locking plate of the proximal femur, the fractured broken end was reset. The fractured broken end was fixed with Kirschner’s pin and pliers first, then the appropriate locking plate was selected for fixation, and finally screws were implanted.
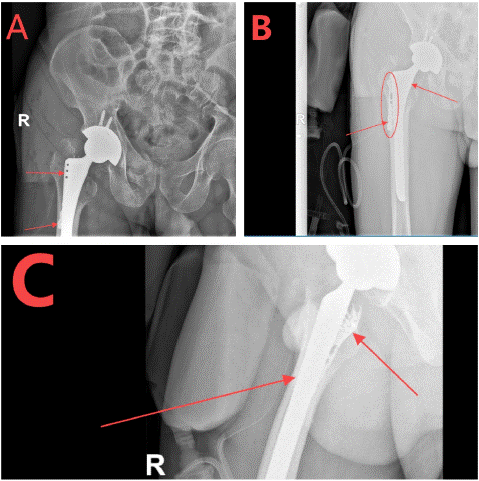
Figure 4: Internal fixation device well positioned.
Discussion
Treatment of intertrochanteric femur fracture with perirotrochanteric fracture is challenging. Conservative treatment may lead to complications and affect the patient's quality of life. Surgical treatment aims to restore hip function and reduce complications. Artificial hip replacement combined with proximal femoral locking plate fixation has the following advantages: 1) Artificial hip replacement can effectively restore hip joint function, reduce postoperative pain, and improve patients' quality of life [3]. 2) Proximal femoral locking plate fixation can effectively control the fracture end, promote fracture healing, and reduce complications [4]. 3) Intraoperative exposure is sufficient, which is conducive to anatomical reduction of the fracture and reduction of postoperative complications. 4) Convenient postoperative functional exercise is conducive to the recovery of hip joint function.
In conclusion, artificial hip replacement combined with proximal femoral locking plate is an effective treatment for intertrochanteric fracture with peritrochanteric fracture. During the treatment process, the indications and contraindications for surgery should be strictly grasped, and perioperative management should be strengthened to reduce the occurrence of complications and promote the recovery of patients' hip joint function.
Author Statements
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no financial disclosures or other conflicts of interest to report related to the content of this article.
References
- Zhang WP, Li XG, Wang LW. Advances in the treatment of intertrochanteric femoral fractures. China Orthopaedic Injury. 2015; 28: 1085-1088.
- Liu KL, Liu BQ, Wu HT, et al. Clinical efficacy analysis of femoral head replacement combined with proximal femoral locking plate in the treatment of intertrochanteric femur fracture. China Orthopaedic Injury. 2019; 32: 615-618.
- Zhang Hongtao, Wang Mingliang, Li Jian, et al. Clinical study of femoral head replacement combined with proximal femoral locking plate in the treatment of intertrochanteric femur fracture. Chinese Journal of Trauma. 2018; 34: 512-515.
- Cui GQ, Wang ZT, Li XG, et al. Clinical analysis of femoral head replacement combined with proximal femoral locking plate in the treatment of intertrochanteric femur fracture. Chinese Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery. 2017; 25: 421-424.